1.根据下面代码,.subbox盒子距.box盒子顶部距离多大?(C)
.box{ float: left; width: 300px; height: 200px; }
.subbox { margin-top:50%;}
<div class=”box”>
<div class=”subbox”></div>
</div>?A、50px B、100px C、150px D、200px
解析:如果父元素中有内容的时候,子元素的外边距是相对父元素内容,如果没有内容则一直向上追溯寻找如果都没有找到(案例四中可以看到),最终以浏览器视口为参考点。所以说margin-top:50%值是相对于父元素的宽度的一半的意思,所以此题选择C。(*关于margin-top中 %?是以父元素的宽度为基准进行计算)
2、说说你对语义化的理解?列举5个语义化的标签?
解析:
一、语义化标签是什么?
常用的语义化标签包括
头部?导航栏 区块(有语义化的div) 主要区域 主要内容 侧边栏 底部
nav header footer aside article
二、为什么会用语义化标签?
平时,我们都会采用DIV+CSS布局我们的页面。但是这样的布局方式不仅使我们的文档结构不够清晰,而且不利于浏览器对页面的读取。所以HTML5新增了很多新的语义化标签。并且,在我们未给页面添加css样式时,用户体验并不好。语义化标签也能让浏览器更好的读取页面结构。再就是便于团队开发和维护,语义化更具可读性,遵循W3C标准的团队都遵循这个标准,可以减少差异化。
1、页面布局
如下图,如果我们用div来实现此图的布局,那么就要涉及到加类名或者选择符的问题,还有起名字,很多时候就会弄混。直接用语义化标签就会标记出每个区域的作用并且更好是实现页面布局。
前端初学者对html语义化标签的理解
2、在移动端布局方面应用
学习一阶段的最后我们会学习到移动端的布局与书写,那么此时选择使用语义化标签往往要比div书写更简单优化。比如移动端布局中我们要采用百分比布局或者rem布局方式,就会涉及到弹性盒中的固比固。比如在我们移动端页面中,拿QQ举例。
前端初学者对html语义化标签的理解
QQ的页面中就可以划分状态栏,header,main,footer。三个区域。在我们的消息区域,有很多消息时,要想查看最底部消息就要下拉,但与此同时header与footer是不动的。那么我们就用到了语义化标签。用到了弹性盒中的固比固(固定高:flex:1:固定高);
三、总结
其实总结起来也就是一句话,没有没有用的东西,div等无语义化的标签有他们的好处,语义化标签也有语义化标签的好处,不可一概而论。但是语义化标签也不是乱用的,视我们页面需求与情况而定。
3、编程题
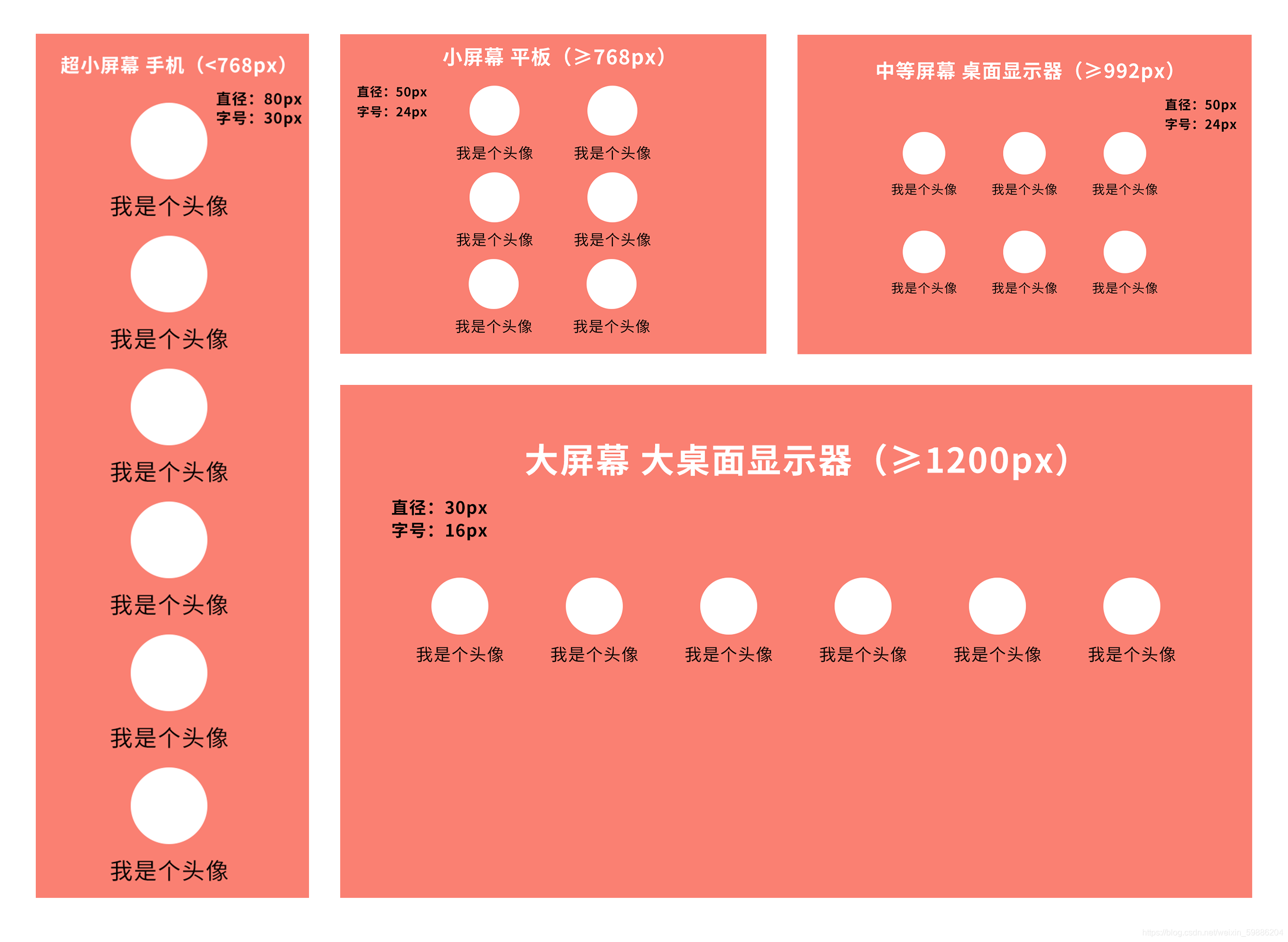
(1)、实现适配(@media + rem)
?
?解析:
CSS3的媒体查询,在第一段代码上面我用的是小于960px的尺寸的写法,那现在我们来实现等于960px尺寸的代码,以下代码需要写在style标签或者css文件中:
@media screen and (max-device-width:960px){
body{background:red;}
}然后就是当浏览器尺寸大于960px时候的代码了:
@media screen and (min-width:960px){
body{background:orange;}
}?我们还可以混合使用上面的用法:
@media screen and (min-width:960px) and (max-width:1200px){
body{background:yellow;}
}?*上面的这段代码的意思是当页面宽度大于960px小于1200px的时候执行下面的CSS。
一、Media所有参数汇总
以上就是我们最常需要用到的媒体查询器的三个特性,大于,等于,小于的写法。媒体查询器的全部功能肯定不止这三个功能,下面是我总结的它的一些参数用法解释:
width:浏览器可视宽度。
height:浏览器可视高度。
device-width:设备屏幕的宽度。
device-height:设备屏幕的高度。
orientation:检测设备目前处于横向还是纵向状态。
aspect-ratio:检测浏览器可视宽度和高度的比例。(例如:aspect-ratio:16/9)
device-aspect-ratio:检测设备的宽度和高度的比例。
color:检测颜色的位数。(例如:min-color:32就会检测设备是否拥有32位颜色)
color-index:检查设备颜色索引表中的颜色,他的值不能是负数。
monochrome:检测单色楨缓冲区域中的每个像素的位数。(这个太高级,估计咱很少会用的到)
resolution:检测屏幕或打印机的分辨率。(例如:min-resolution:300dpi或min-resolution:118dpcm)。
grid:检测输出的设备是网格的还是位图设备。
(max-width:599px)
(min-width:600px)
(orientation:portrait) 竖屏
(orientation:landscape) 横屏
(-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 2) 像素比?
二、关键字
1.and
2.not not关键字是用来排除某种制定的媒体类型
3.only only用来定某种特定的媒体类型
-很多时候是用来对那些不支持媒体特性但却支持媒体类型的设备
三、常用的几种屏幕宽度设定:
@media screen and (min-width: 1200px) {
css-code;
}
@media screen and(min-width: 960px) and (max-width: 1199px) {
css-code;
}
@media screen and(min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 959px) {
css-code;
}
@media screen and(min-width: 480px) and (max-width: 767px) {
css-code;
}
@media screen and (max-width: 479px) {
css-code;
}rem是什么?
rem(font size of the root element)是指相对于根元素的字体大小的单位。简单的说它就是一个相对单位。看到rem大家一定会想起em单位,em(font size of the element)是指相对于父元素的字体大小的单位(rem可以控制整个页面所有元素有关PX类,只要是你设置数值的地方都可以实现控制。在rem里面1rem=HTML的font-size的大小)。它们之间其实很相似,只不过一个计算的规则是依赖根元素一个是依赖父元素计算。
这题的解题代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
@media screen and (max-width:768px) {
body,
html {
font-size: 30px;
}
.mbox div {
width: 2.66666667rem;
height: 2.66666667rem;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.fox {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: space-around;
flex-wrap: wrap;
width: 9rem;
}
}
@media screen and (min-width:768px) {
body,
html {
font-size: 24px;
}
.mbox div {
width: 2.0833333rem;
height: 2.0833333rem;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.fox {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: space-around;
flex-wrap: wrap;
width: 14rem;
}
}
@media screen and (min-width:922px) {
body,
html {
font-size: 24px;
}
.mbox div {
width: 2.0833333rem;
height: 2.0833333rem;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.fox {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: space-around;
flex-wrap: wrap;
width: 19rem;
}
}
@media screen and (min-width:1200px) {
body,
html {
font-size: 16px;
}
.mbox div {
width: 1.875rem;
height: 1.875rem;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.fox {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: space-around;
width: 100%;
}
}
.mbox {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
}
.fox {
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="fox">
<div class="mbox">
<div></div>
<p>我是个头像</p>
</div>
<div class="mbox">
<div></div>
<p>我是个头像</p>
</div>
<div class="mbox">
<div></div>
<p>我是个头像</p>
</div>
<div class="mbox">
<div></div>
<p>我是个头像</p>
</div>
<div class="mbox">
<div></div>
<p>我是个头像</p>
</div>
<div class="mbox">
<div></div>
<p>我是个头像</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>(2)根据以下效果图,任选两种效果,实现代码
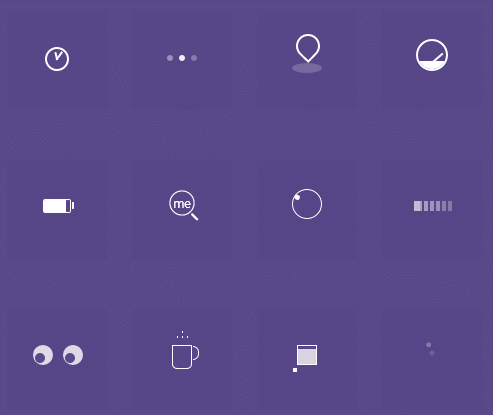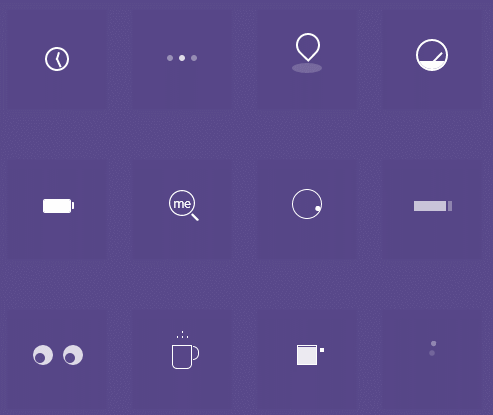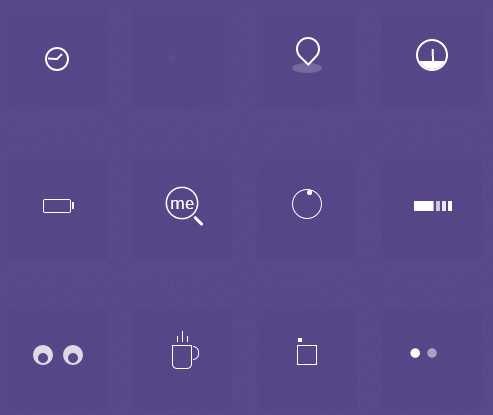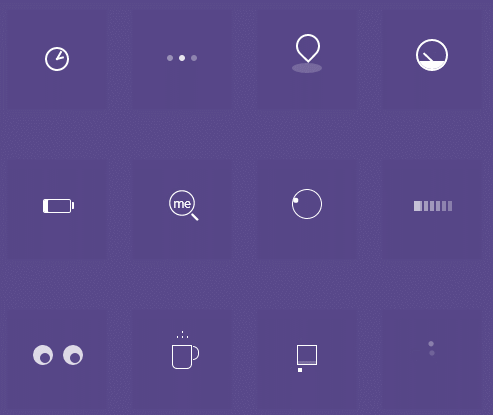
解析:?
这是对css的综合使用 ,运用各种css的语句来实现出该效果
?相关知识点:
例举两个:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: rgb(11, 0, 73);
}
.fbox {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border-radius: 50%;
border: 1px solid white;
position: relative;
}
.shi {
width: 3px;
height: 20px;
background-color: white;
transform-origin: 0px 20px;
left: 50%;
top: 3px;
border-radius: 0 0 25% 25%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
position: absolute;
animation: run 3s;
}
.fen {
width: 1px;
height: 23px;
background-color: white;
left: 50%;
top: 0px;
transform: translateX(-50%);
position: absolute;
transform-origin: 0px 23px;
animation: run1 3s;
border-radius: 0 0 25% 25%;
}
.dian {
width: 5px;
height: 5px;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 50%;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%) translateY(-50%);
position: absolute;
}
@keyframes run {
0% {
transform: rotateZ(0deg);
}
100% {
transform: rotateZ(50deg);
}
}
@keyframes run1 {
0% {
transform: rotateZ(0deg);
}
100% {
transform: rotateZ(360deg);
}
}
.dianchi {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.qita {
background-color: white;
width: 30px;
height: 60px;
}
.bian {
width: 130px;
height: 120px;
border: 1px solid white;
}
.jindu{
width: 0px;
height: 120px;
animation: identifier 3s;
background-color: white;
}
@keyframes identifier {
0%{}
100%{
width: 100%;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="fbox">
<div class="shi"></div>
<!-- <div class="dian"></div> -->
<div class="fen"></div>
</div>
<div class="dianchi">
<div class="bian">
<div class="jindu"></div>
</div>
<div class="qita"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行结果:
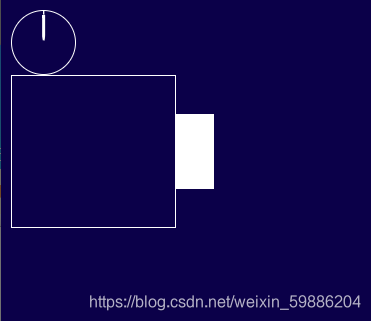
?