文章目录
树
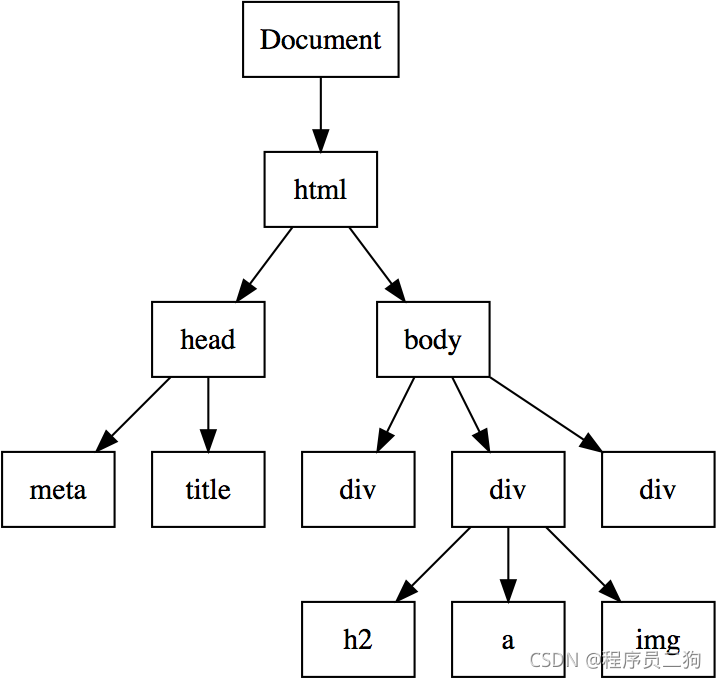
树是一种抽象的分层数据模型,例如前端常见的DOM树:
JavaScript中没有树,但是可以用数组和对象来模拟树。
以虚拟DOM为例:vdom就是JS用数组和对象来模拟的树。
vdom = {
type: 'div',
props: {
'id': 'content'
},
children: [
{
type: 'ul',
props: {
'class': 'list'
},
children: {
{
type: 'li',
props: '',
children: ['选项一']
}
}
}
]
}
树的常用操作
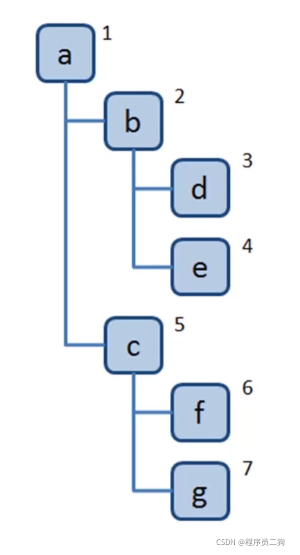
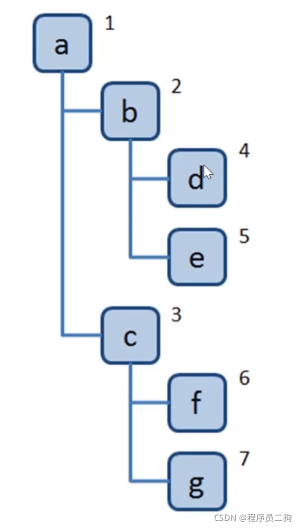
定义树
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children:[
{
val: 'b',
children:[
{
val: 'c',
children:[
{
val: 'd',
children:[]
}
]
},
{
val: 'e',
children:[]
}
]
},
{
val: 'f',
children:[
{
val: 'g',
children:[]
}
]
}
]
}
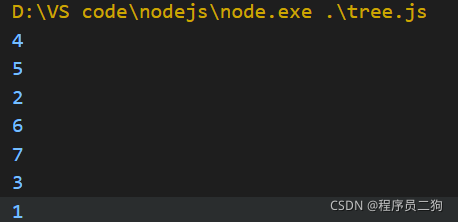
深度优先遍历
深度优先遍历就是尽可能深的搜索树的分支。
深度优先遍历就像我们看书一样,一页一页的往后翻看。
深度优先遍历过程
- 访问根节点;
- 再把每个子节点当作根节点进行深度遍历;
代码实现
//深度优先遍历
const dfs = (root) => {
//console.log(root.val);
root.children.forEach(dfs);
}
//调用深度优先遍历
dfs(tree);
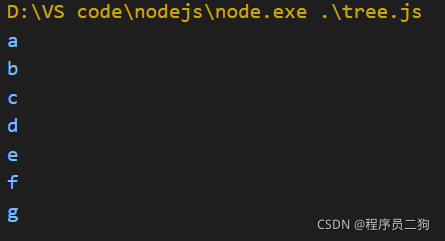
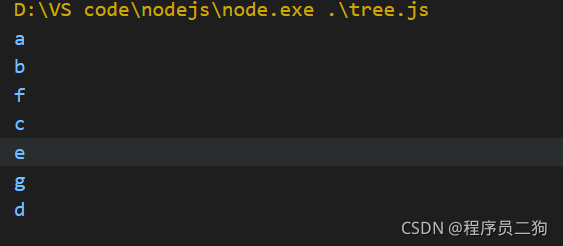
广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历就是尽可能访问离根节点(树最顶端的节点)近的节点。
广度优先遍历也像我们看书一样,不过他先看目录和各个章节是什么内容,然后再一页一页的翻看。
广度优先遍历过程
- 新建队列,把根节点入队;
- 把对头出队并访问;
- 把对头的子节点挨个入队;
- 重复前两步;
代码实现
// 广度优先遍历
const bfs = (root) => {
const q = [root];
while(q.length > 0){
const n = q.shift();
//console.log(n.val);
n.children.forEach( child => {
q.push(child);
} )
}
}
bfs(tree);
二叉树
每个节点最多有两个子节点的树叫二叉树。
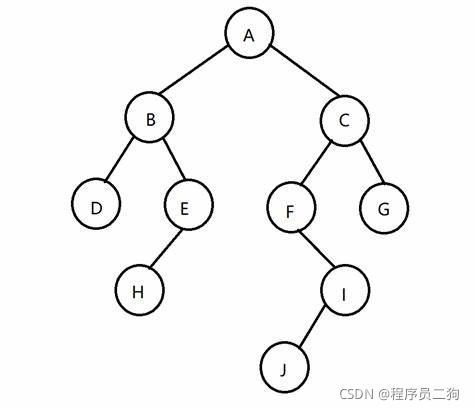
二叉树的常用操作
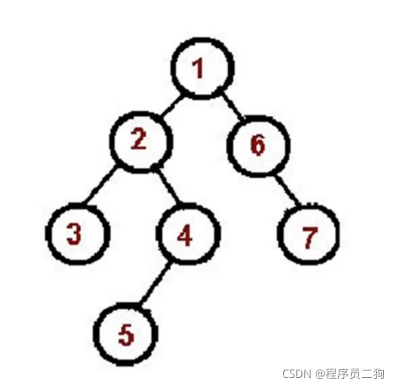
定义二叉树
//定义二叉树
const bt = {
val: 1,
left:{
val: 2,
left:{
val: 4,
left:null,
right:null
},
right:{
val: 5,
left:null,
right:null
}
},
right:{
val: 3,
left:{
val: 6,
left:null,
right:null
},
right:{
val: 7,
left:null,
right:null
}
}
}
前序遍历
前序遍历过程
根 => 左 => 右
- 访问根节点;
- 对根节点的左子树进行前序遍历;
- 对根节点的右子树进行前序遍历;
代码实现
用递归实现前序遍历:
//前序遍历
const preorder = (root) => {
if(!root){
return ;
}
console.log(root.val);
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
}
preorder(bt);
用栈实现前序遍历:
const preorder = (root) => {
if(!root)return ;
const stack = [root];
while(stack.length){
const n = stack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
if(n.right)stack.push(n.right);
if(n.left)stack.push(n.left);
}
}
preorder(bt);
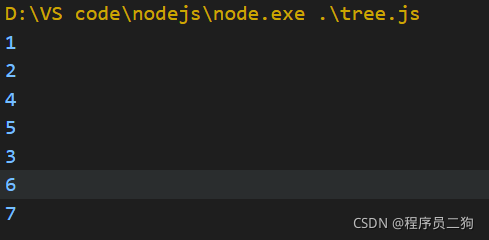
中序遍历
中序遍历过程
左 =>根 => 右
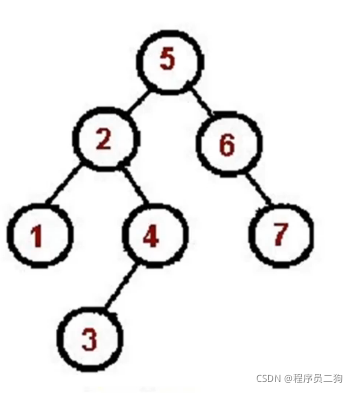
- 对根节点的左子树进行前序遍历;
- 访问根节点;
- 对根节点的右子树进行前序遍历;
代码实现
用递归实现中序遍历:
const inorder = (root) => {
if(!root){
return ;
}
inorder(root.left);
console.log(root.val);
inorder(root.right);
}
inorder(bt);
用栈实现中序遍历:
const inorder = (root) => {
if(!root){
return ;
}
const stack = [];
let p = root;
while(stack.length || p){
while(p){
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
const n = stack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
p = n.right;
}
}
inorder(bt);
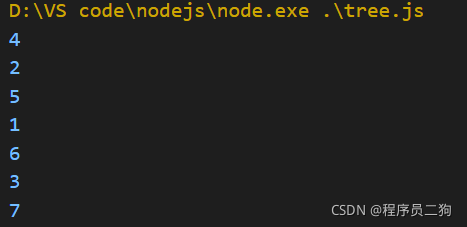
后序遍历
后序遍历过程
左 => 右 => 根
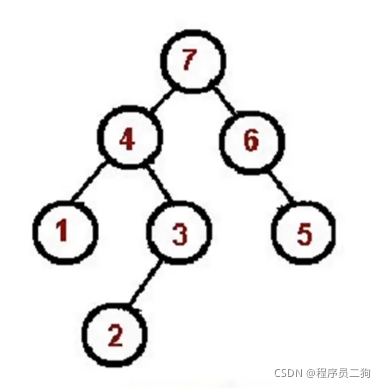
-
对根节点的左子树进行前序遍历;
-
对根节点的右子树进行前序遍历;
-
访问根节点;
代码实现
用递归实现后序遍历:
const postorder = (root) => {
if(!root){
return ;
}
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
console.log(root.val);
}
postorder(bt);
用栈实现后序遍历:
const postorder = (root) => {
if(!root){
return ;
}
const outputstack = [];
const stack = [root];
while(stack.length){
const n = stack.pop();
outputstack.push(n);
if(n.left) stack.push(n.left);
if(n.right) stack.push(n.right);
}
while(outputstack.length){
const n = outputstack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
}
}
postorder(bt);