概念
双向绑定概念其实很简单,就是视图(View)的变化能实时让数据模型(Model)发生变化,而数据的变化也能实时更新到视图层。我们所说的单向数据绑定就是从数据到视图这一方向的关系。
分析
1、响应式数据
使用Object.defineProperty、Proxy对数据进行监听拦截。
//obj:必需。目标对象
//prop:必需。需定义或修改的属性的名字
//descriptor:必需。目标属性所拥有的特性
Object.defineProperty(obj, prop, descriptor)
vue3.0 开始 Proxy代替Object.defineProperty
let p = new Proxy(target, handler);
2、input事件监听
绑定事件处理函数,实时修改数据。
3、相关dom操作
将数据与相关dom节点绑定在一起,修改数据的时候对应的dom节点也应一起改变。
实现
1、html页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>v-model</title>
</head>
<body>
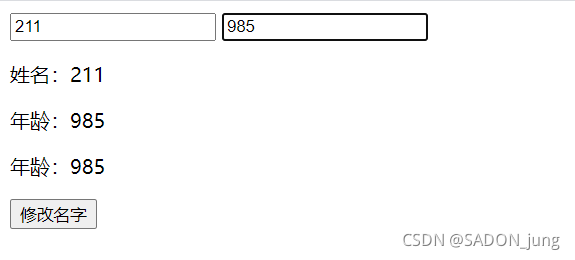
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="name" placeholder="姓名"/>
<input type="text" v-model="age" placeholder="年龄"/>
<div>
<p>
姓名:<span>{{name}}</span>
</p>
<p>
年龄:<span>{{age}}</span>
</p>
<p>
<p>
年龄:<span>{{age}}</span>
</p>
</p>
</div>
<button id="btn">修改名字</button>
</div>
</body>
<script src="./VModel.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new VModel('#app',{
name:'',
age:''
});
document.getElementById('btn').addEventListener('click',function() {
app.setData('name','名字改变了');
})
</script>
</html>
2、VModel.js
(1)构造VModel
class VModel {
constructor(el,data) {
this.el = document.querySelector(el);
//存放数据对象
this._data = data;
//存放绑定数据的dom节点
this.domPoll = {};
this.init();
}
}
(2)初始化数据对象
使用Object.defineProperty
initData () {
const _this = this;
this.data = {};
for(let key in this._data){
Object.defineProperty(this.data,key,{
get(){
console.log("获取数据",key,_this._data[key]);
return _this._data[key];
},
set(newVal){
console.log("设置数据",key,newVal);
_this.domPoll[key].innerText = newVal;
_this._data[key] = newVal;
}
});
}
}
使用Proxy
initData () {
const _this = this;
this.data = {};
this.data = new Proxy(this.data,{
get(target,key){
return Reflect.get(target,key);
},
set(target,key,value){
// _this.domPoll[key].innerText = value;
_this.domPoll[key].forEach(item => {
item.innerText = value;
})
return Reflect.set(target,key,value);
}
})
}
(3)绑定dom节点
bindDom(el){
const childNodes = el.childNodes;
childNodes.forEach(item => {
//nodeType为3时该dom节点为文本节点
if(item.nodeType === 3){
const _value = item.nodeValue;
if(_value.trim().length){
//匹配是否有两个花括号包裹的数据
let _isValid = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/.test(_value);
if(_isValid){
const _key = _value.match(/\{\{(.+?)\}\}/)[1].trim();
// this.domPoll[_key] = item.parentNode;
//一个数据可以被多个dom节点绑定,所以应该用数组来进行保存
//未定义时先初始化
if(!this.domPoll[_key]) this.domPoll[_key] = [];
this.domPoll[_key].push(item.parentNode);
//替换绑定的值
item.parentNode.innerText = this.data[_key] || undefined;
}
}
}
//递归遍历子节点
item.childNodes && this.bindDom(item);
})
}
####(4)输入框数据绑定
bindInput(el){
//获取input所有元素节点
const _allInput = el.querySelectorAll('input');
_allInput.forEach(input => {
const _vModel = input.getAttribute('v-model');
//判断是否有v-model属性
if(_vModel){
//监听输入事件 input.addEventListener('keyup',this.handleInput.bind(this,_vModel,input),false);
}
})
}
handleInput(key,input){
const _value = input.value;
//数据变化的时候会同步修改dom节点绑定的数据。
this.data[key] = _value;
}
(4)完整代码
class VModel {
constructor(el,data) {
this.el = document.querySelector(el);
this._data = data;
this.domPoll = {};
this.init();
}
init(){
this.initData();
this.initDom();
}
initDom(){
this.bindDom(this.el);
this.bindInput(this.el);
console.log('domPoll',this.domPoll);
}
initData () {
const _this = this;
this.data = {};
// for(let key in this._data){
// Object.defineProperty(this.data,key,{
// get(){
// console.log("获取数据",key,_this._data[key]);
// return _this._data[key];
// },
// set(newVal){
// console.log("设置数据",key,newVal);
// _this.domPoll[key].innerText = newVal;
// _this._data[key] = newVal;
// }
// });
// }
this.data = new Proxy(this.data,{
get(target,key){
return Reflect.get(target,key);
},
set(target,key,value){
// _this.domPoll[key].innerText = value;
_this.domPoll[key].forEach(item => {
item.innerText = value;
})
return Reflect.set(target,key,value);
}
})
}
bindDom(el){
const childNodes = el.childNodes;
childNodes.forEach(item => {
if(item.nodeType === 3){
const _value = item.nodeValue;
if(_value.trim().length){
let _isValid = /\{\{(.+?)\}\}/.test(_value);
if(_isValid){
const _key = _value.match(/\{\{(.+?)\}\}/)[1].trim();
// this.domPoll[_key] = item.parentNode;
if(!this.domPoll[_key]) this.domPoll[_key] = [];
this.domPoll[_key].push(item.parentNode);
item.parentNode.innerText = this.data[_key] || undefined;
}
}
}
item.childNodes && this.bindDom(item);
})
}
bindInput(el){
const _allInput = el.querySelectorAll('input');
_allInput.forEach(input => {
const _vModel = input.getAttribute('v-model');
if(_vModel){
input.addEventListener('keyup',this.handleInput.bind(this,_vModel,input),false);
}
})
}
handleInput(key,input){
const _value = input.value;
this.data[key] = _value;
// console.log(this.data);
}
setData(key,value){
this.data[key] = value;
}
}
