1、formatter两种使用形式
可以通过函数和字符串模板来自定义formatter
①通过函数动态创建节点
通过循环param的长度,不写死节点,这样有一个好处就是当点击了某一个legend取消了数据的展示的时候,tooltip提示框不至于报错。
formatter: function (params) {
? var result = "<div>" + params[0].axisValue + "</div>";
? ? ? ? ? ? ? params.forEach(item=>{
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? if(item.data!==null){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? let item1 =
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? "<span style='display:inline-block;margin-right:5px;margin-bottom:2px;border-radius:10px;width:9px;height:9px;background-color:"+
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? item.color +
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ";'></span>"
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? item1 +=item.seriesName+":"+ __numFmt3(item.data,2)+'万元' + "<br/>"
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? result+=item1}
? ? ? ? ? ? ? })
? ? ? ? ? ? ? return result;
},②字符串模板的简易写法
formatter: `{a|${curValue}%}`
//设置的富文本
rich: {
? ? a: {
? ? color:curColor,
? ? fontSize: 11,
? ? padding: [5,0,0,0]
? ? },
}当然也可以写成下面这种的echarts自带的形式
//a(系列名称),b(数据项名称),c(数值), d(百分比)
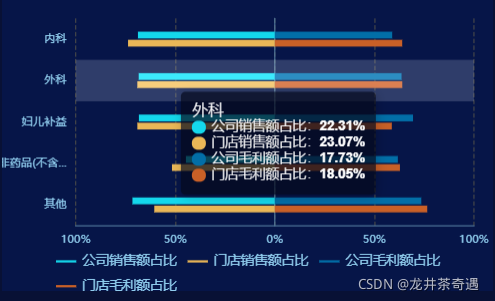
formatter: '{a}{b}:{d}%'2、蝴蝶图的绘制
蝴蝶图绘制,即在y轴两端对齐的图表,通过设置series.stack为同一个,即可在同一个起点绘制。tooltip也是通过动态的方法设置的。y轴左侧的数据是通过将真实数据取反,然后通过将坐标轴及数据的取绝对值实现的。
第一次绘制这类的图形,还是比较特殊的,也并不算常见。
?由于图表的数据是通过异步请求获取到的,所以需要对传入的props通过setTimeout宏任务来进行控制,否则没有数据的情况下echarts会控制台报错。
watch:{
typePer:{
handler(){
setTimeout(()=>{
this.showBar()
},1000)
},
immediate:true
}
},
选项设置
series.push({
type: "bar",
name: '公司销售额占比',
barWidth: 6,
color: color[0],
data: company_amt_rate,
stack: 'company'
})
series.push({
type: "bar",
name: '门店销售额占比',
barWidth: 6,
color: color[1],
data: store_amt_rate,
stack: 'store'
})
series.push({
type: "bar",
name: '公司毛利额占比',
barWidth: 6,
color: color[2],
data: company_pro_rate,
stack: 'company'
})
series.push({
type: "bar",
name: '门店毛利额占比',
barWidth: 6,
color: color[3],
data: store_pro_rate,
stack: 'store'
})
//调用方法
showBar(){
const dChart = this.$echarts.init(document.getElementById('leftBar'));
//清除上一次的图像
dChart.clear()
//动态传入的legData,yData,series值
let typePer=this.typePer
const option = {
legend: {
bottom: -6,
icon: 'rect',
itemWidth: 18,
itemHeight: 2,
textStyle: {
fontSize: 12,
color: '#90CDEE'
},
data: typePer.legData
},
grid: {
left: '15%',
right: '4%',
bottom: '23%',
top:'5%'
},
tooltip:{
trigger: 'axis',
axisPointer: {
type: 'shadow'
},
formatter: function (params, ticket, callback) {
let s = ''
params.forEach(item => {
s += `<li class="item">
<span class="point" style="background:${item.color};"></span>
<span class="txt">${item.seriesName}:<span class="val" style="min-width:unset;">${item.data.real_tt_ || '0%'}</span></span>
</li>`
})
return `<ul class="tooltip-20210730">
<li class="tit">${params[0].name}</li>
${s}
</ul>`
},
borderWidth:'0',
// 设置提示框背景
backgroundColor: 'rgb(4,9,27,0.7)',
textStyle: {
fontSize: 10,
fontWeight: 300,
color: '#FFFFFF',
lineHeight: 14
},
},
xAxis: [
{
type: 'value',
nameTextStyle: {
color: '#90CDEE',
fontSize: 10
},
splitLine: {
lineStyle: {
color: 'rgb(72,72,72)',
type:'dashed'
}
},
axisLine: {
show: true,
lineStyle: {
color: 'rgb(84,124,159)',
width: 1,
}
},
axisLabel: {
color: '#90CDEE',
fontSize: 10,
formatter: (val) => {
return Math.abs(val) / 2 * 100 + '%';
}
},
max: 2,
min: -2
}
],
yAxis: [
{
type: 'category',
axisTick: {
show: false
},
nameLocation: 'end',
nameTextStyle: {
color: '#90CDEE',
fontSize: 10
},
splitLine: {
lineStyle: {
color: 'rgb(72,72,72)',
type:'dashed'
}
},
axisLine: {
show: true,
lineStyle: {
color: 'rgb(84,124,159)',
width: 1,
}
},
axisLabel: {
color: '#90CDEE',
fontSize: 10,
width: 62,
overflow: 'truncate'
},
data: typePer.yData
}
],
series: typePer.series
};
dChart && dChart.setOption(option)
}