| |
|
|
开发:
C++知识库
Java知识库
JavaScript
Python
PHP知识库
人工智能
区块链
大数据
移动开发
嵌入式
开发工具
数据结构与算法
开发测试
游戏开发
网络协议
系统运维
教程: HTML教程 CSS教程 JavaScript教程 Go语言教程 JQuery教程 VUE教程 VUE3教程 Bootstrap教程 SQL数据库教程 C语言教程 C++教程 Java教程 Python教程 Python3教程 C#教程 数码: 电脑 笔记本 显卡 显示器 固态硬盘 硬盘 耳机 手机 iphone vivo oppo 小米 华为 单反 装机 图拉丁 |
| -> JavaScript知识库 -> 尤大都推荐的组件库是如何开发出来的? -> 正文阅读 |
|
|
[JavaScript知识库]尤大都推荐的组件库是如何开发出来的? |
|
> 注意:为了让篇幅尽可能简洁一丢丢,在有些地方贴源码时,我尽可能贴最能反映要讲解内容的源码,其他重复性的代码就略去了,所以如果你自己尝试去阅读源码时,可能会发现和文章里的代码有出入。文章跑通 Naive UI 所用到的源码仓库为:[https://github.com/pftom/naive-app](https://github.com/pftom/naive-app "https://github.com/pftom/naive-app") # 简洁的抽象 前端开发者现在几乎已经离不开 UI 组件库了,典型的如 Ant Design、Material Design、以及最近 Vue 生态兴起的 Naive UI 等,组件库提供了简单、灵活、易用的使用形式,如一个页面中最常见的 Button 的使用如下: ``` ? <n-button>Default</n-button> ? <n-button type="primary">Default</n-button> ? <n-button type="info" dashed>Default</n-button> ? <n-button type="success" dashed size="small">Default</n-button> ? <n-button text>Default</n-button> ? <n-button text tag="a" href="https://anyway.fm/news.php" type="warning" ? ? >安妮薇时报</n-button ? > ? <n-button disabled> 不许点 </n-button> </template> 上述几行简单的代码就可以完成如下有意思的效果:  甚至是,可以一键切换皮肤,如 Dark Mode: 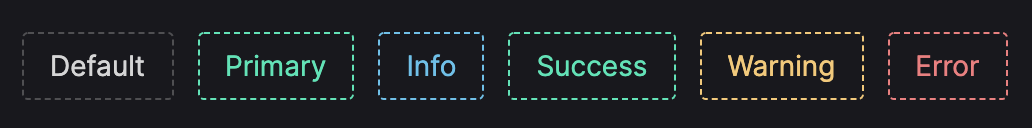 当然还可以处理事件、添加 Icon、处理 Loading 等,通过简单给定一些 Props,我们就可以拥有一个好看、实用的 Button,相比原始的 HTML 标签来说,实在是不可同日而语... ?  # 冰山理论  组件库在带来灵活、方便的同时,其内部的原理却并非如它使用般简单,就像上述的冰山图一样引人深思。 让我们翻一翻最近的 Vue 组件库新秀 Naive UI 的 CHANGELOG,就可以窥见编写一个入门的组件库大致需要多少时间: 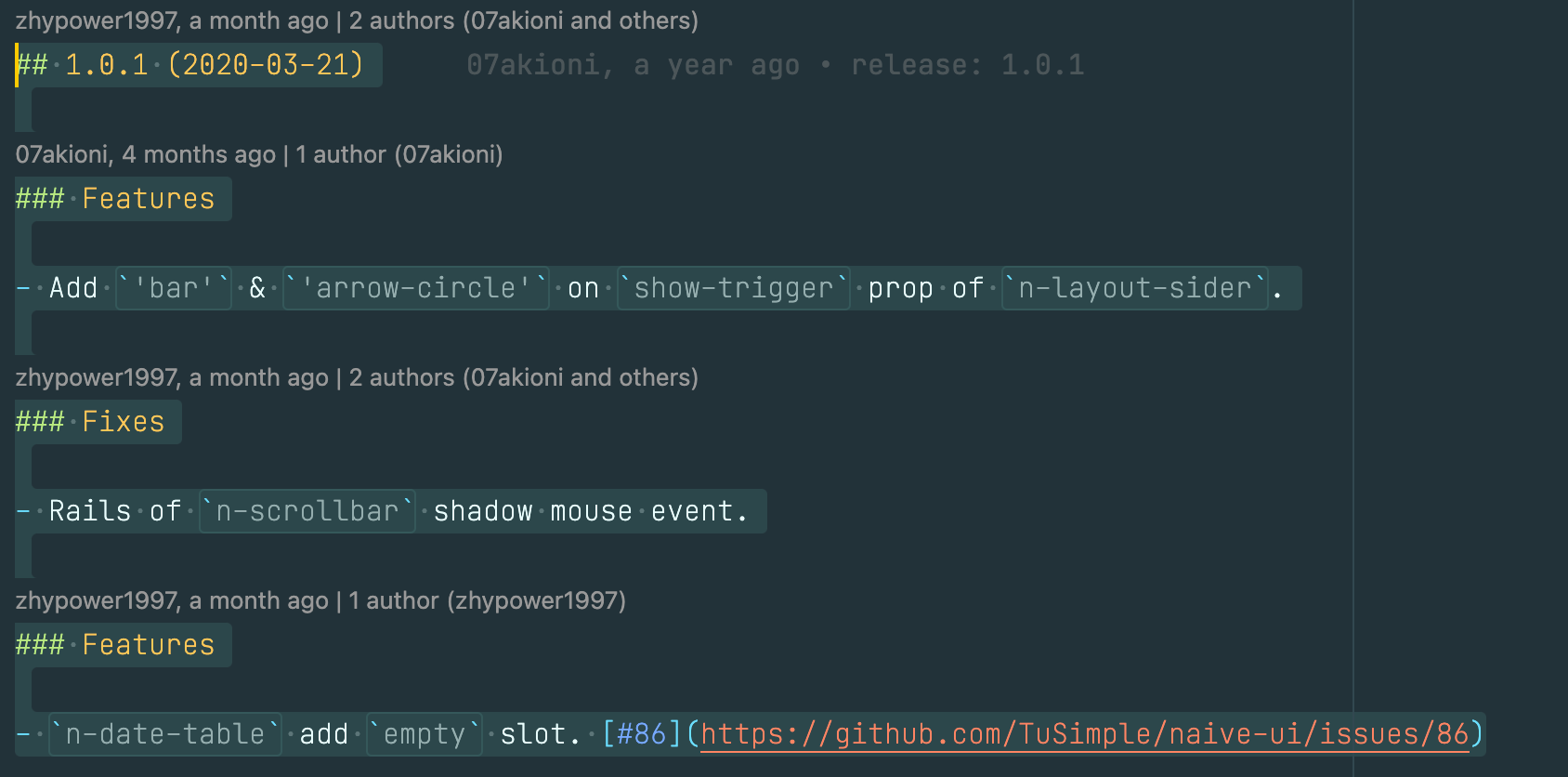 可以看到,2020-03-21 就发布了 `1.x` 版本,而在 `1.x` 之前又是漫长的思考、设计与开发,至今应该差不多两年有余。 而为了跑通一个 Naive UI 的 Button,大致需要如下的文件或代码: ``` |_____utils | |____color | | |____index.js | |____vue | | |____index.js | | |____flatten.js | | |____call.js | | |____get-slot.js | |____index.js | |____naive | | |____warn.js | | |____index.js | |____cssr | | |____create-key.js | | |____index.js |_____internal | |____loading | | |____index.js | | |____src | | | |____Loading.jsx | | | |____styles | | | | |____index.cssr.js | |____index.js | |____icon-switch-transition | | |____index.js | | |____src | | | |____IconSwitchTransition.jsx | |____fade-in-expand-transition | | |____index.js | | |____src | | | |____FadeInExpandTransition.jsx | |____wave | | |____index.js | | |____src | | | |____Wave.jsx | | | |____styles | | | | |____index.cssr.js | |____icon | | |____index.js | | |____src | | | |____Icon.jsx | | | |____styles | | | | |____index.cssr.js |_____styles | |____common | | |_____common.js | | |____light.js | | |____index.js | |____transitions | | |____fade-in-width-expand.cssr.js | | |____icon-switch.cssr.js | |____global | | |____index.cssr.js |____config-provider | |____src | | |____ConfigProvider.js |____button | |____styles | | |_____common.js | | |____light.js | | |____index.js | |____src | | |____Button.jsx | | |____styles | | | |____button.cssr.js |____assets | |____logo.png |_____mixins | |____use-style.js | |____use-theme.js | |____index.js | |____use-form-item.js | |____use-config.js # 看似困难的背后 虽然跑通一个看似简单的 `<Button />` 背后需要大量的工作,涉及到几十个文件的依赖,但对于一个组件库来说,复杂度是量级近似的,即从一个简单的 `<Button />` 到一个复杂的 `<Form />` ,其实在组件库的领域内,90% 的内容是相似的,所以如果搞懂了 `<Button />` 的运行流程,那么基本可以说搞懂了组件库近 90% 的内容,剩下的 10% 则是具体组件的具体实现。 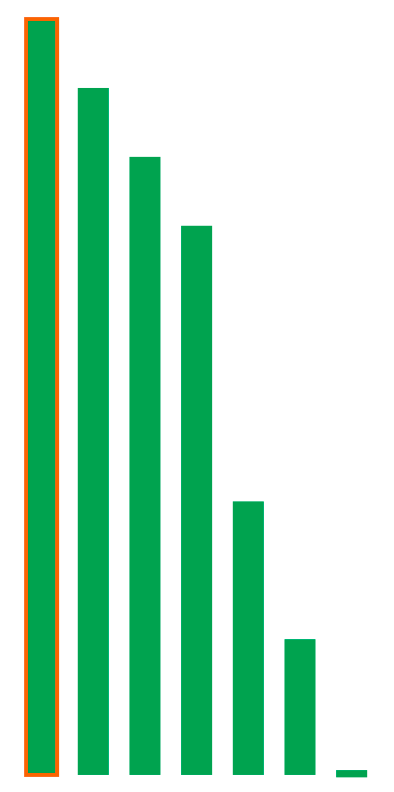 所以了解一个前端组件库最核心还是需要弄懂一个 `<Button />` 跑通背后所需要的各种准备工作,也就是上图中的第一根高柱,而开发一个组件库首先也应该专注于设计让至少一个 `Button` 跑通的方案。 # Button 背后的技术链  我们以 [Naive UI ](https://github.com/TuSimple/naive-ui "Naive UI ")为研究对象,来详细剖析其 `<Button />` 实现背后的各种原理,原因有比较直观的 2 点: 1. ?其技术栈以 Vite 、Vue3、TypeScript 为主,符合笔者最近的技术栈 ## 从模板出发 想了解一个组件,第一件事情当然是了解它的骨架了,也就是我们常说的 HTML/JSX 相关内容了,首先看一下 Naive UI 的 Button 组件的模板: ``` ? name: 'Button', ? props: {}, ? setup(props) {}, ? render() { ? ? // 第一部分 ? ? // n ? ? const { $slots, mergedClsPrefix, tag: Component } = this; ? ? const children = flatten(getSlot(this)); ? ? return ( ? ? ? <Component? ? ? ? ? ref="selfRef" ? ? ? ? // 第二部分 ? ? ? ? class={[ ? ? ? ? ? `${mergedClsPrefix}-button`, ? ? ? ? ? `${mergedClsPrefix}-button--${this.type}-type`, ? ? ? ? ? { ? ? ? ? ? ? [`${mergedClsPrefix}-button--disabled`]: this.disabled, ? ? ? ? ? ? [`${mergedClsPrefix}-button--block`]: this.block, ? ? ? ? ? ? [`${mergedClsPrefix}-button--pressed`]: this.enterPressed, ? ? ? ? ? ? [`${mergedClsPrefix}-button--dashed`]: !this.text && this.dashed, ? ? ? ? ? ? [`${mergedClsPrefix}-button--color`]: this.color, ? ? ? ? ? ? [`${mergedClsPrefix}-button--ghost`]: this.ghost, // required for button group border collapse ? ? ? ? ? }, ? ? ? ? ]} ? ? ? ? tabindex={this.mergedFocusable ? 0 : -1} ? ? ? ? type={this.attrType} ? ? ? ? style={this.cssVars} ? ? ? ? disabled={this.disabled} ? ? ? ? onClick={this.handleClick} ? ? ? ? onBlur={this.handleBlur} ? ? ? ? onMousedown={this.handleMouseDown} ? ? ? ? onKeyup={this.handleKeyUp} ? ? ? ? onKeydown={this.handleKeyDown} ? ? ? ? > ? ? ? ? // 第三部分 ? ? ? ? {$slots.default && this.iconPlacement === "right" ? ( ? ? ? ? ? <div class={`${mergedClsPrefix}-button__content`}>{children}</div> ? ? ? ? ) : null} ? ? ? ? // 第四部分 ? ? ? ? <NFadeInExpandTransition width> ? ? ? ? ? {{ ? ? ? ? ? ? default: () => ? ? ? ? ? ? ? $slots.icon || this.loading ? ( ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <span ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? class={`${mergedClsPrefix}-button__icon`} ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? style={{ ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? margin: !$slots.default ? 0 : "", ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }} ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? > ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <NIconSwitchTransition> ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? {{ ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? default: () => ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? this.loading ? ( ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <NBaseLoading ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? clsPrefix={mergedClsPrefix} ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? key="loading" ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? class={`${mergedClsPrefix}-icon-slot`} ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? strokeWidth={20} ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? /> ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ) : ( ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? <div ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? key="icon" ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? class={`${mergedClsPrefix}-icon-slot`} ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? role="none" ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? > ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? {renderSlot($slots, "icon")} ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? </div> ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ), ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }} ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? </NIconSwitchTransition> ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? </span> ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ) : null, ? ? ? ? ? }} ? ? ? ? </NFadeInExpandTransition> ? ? ? ? // 第三部分 ? ? ? ? {$slots.default && this.iconPlacement === "left" ? ( ? ? ? ? ? <span class={`${mergedClsPrefix}-button__content`}>{children}</span> ? ? ? ? ) : null} ? ? ? ? // 第五部分 ? ? ? ? {!this.text ? ( ? ? ? ? ? <NBaseWave ref="waveRef" clsPrefix={mergedClsPrefix} /> ? ? ? ? ) : null} ? ? ? ? // 第六部分 ? ? ? ? {this.showBorder ? ( ? ? ? ? ? <div ? ? ? ? ? ? aria-hidden ? ? ? ? ? ? class={`${mergedClsPrefix}-button__border`} ? ? ? ? ? ? style={this.customColorCssVars} ? ? ? ? ? /> ? ? ? ? ) : null} ? ? ? ? // 第六部分 ? ? ? ? {this.showBorder ? ( ? ? ? ? ? <div ? ? ? ? ? ? aria-hidden ? ? ? ? ? ? class={`${mergedClsPrefix}-button__state-border`} ? ? ? ? ? ? style={this.customColorCssVars} ? ? ? ? ? /> ? ? ? ? ) : null} ? ? </Component> ? ? ) ? } }); 可以看到,上述的主要展示出了 `<Button />` 组件的模板部分,基于 Vue3 的 `defineComponent` 来定义组件,基于 `render` 方法使用 JSX 的形式来编写模板,其中模板部分又主要分为 6 部分,在代码中以注释的方式标注出: 1. ?主要是取属性相关,主要有三个属性:`$slots` 、`mergedClsPrefix` 、`tag` ,其中 `$slots` 在 Vue 领域内类似孩子节点所属的对象,`mergedClsPrefix` 则为整个组件库的命名空间前缀,在 Naive UI 中这个前缀为 `n` ,`tag` 则表示此组件应该以什么样的标签进行展示,默认是 `<button />` ,你也可以换成 `<a />` ,让按钮长得像一个链接  2. ?主要是定义 `Button` 相关的属性: ? ? 1. ?其中 `class` 则根据传进来的属性来判定属于哪种 `type`:`primary` 、`info` 、`warning` 、`success` 、`error` ,以及当前处于什么状态:`disabled` 、`block` 、`pressed` 、`dashed` 、`color` 、`ghost` ,根据这些 `type` 和状态给予合适的类名,从而为组件定义对应类名所属的 CSS 样式  3. ?主要是决定在 `iconPlacement` 为 `left` 、`right` 时,组件孩子节点的展示形式,即图标在左和右时,孩子节点分布以 `<span />` 或 `<div />` 标签的形式展示,当为 `right` 时,设置为 `<div />` 则是为了更好的处理布局与定位  4. ?为图标相关内容,`NFadeInExpandTransition` 为控制 Icon 出现和消失的过渡动画,`NIconSwitchTransition` 则是控制 `loading` 形式的 Icon 和其他 Icon 的切换过渡动画  5. ?当按钮不以 `text` 节点的形式展示时,其上应该有处理反馈的波纹,通过上述视频也可以看到在点按钮时会有对应的波纹效果来给出点击反馈,如下图展示为类文本形式,在点击时就不能出现波纹扩散效果  6. ?主要是通过 `<div />` 去模拟组件的边框:`border` 和 `state-border` ,前者主要静态、默认的处理边框颜色、宽度等,后者则是处理在不同状态下:`focus` 、`hover` 、`active` 、`pressed` 等下的 `border` 样式 可以通过一个实际的例子看一下这两者所起的作用: ``` ? ? border: var(--border); } .n-button .n-button__border, .n-button .n-button__state-border { ? ? position: absolute; ? ? left: 0; ? ? top: 0; ? ? right: 0; ? ? bottom: 0; ? ? border-radius: inherit; ? ? transition: border-color .3s var(--bezier); ? ? pointer-events: none; } .n-button:not(.n-button--disabled):hover .n-button__state-border { ? ? border: var(--border-hover); } .n-button:not(.n-button--disabled):pressed .n-button__state-border { ? ? border: var(--border-pressed); } style attribute { ? ? --bezier: ; ? ? --bezier-ease-out: ; ? ? --border: 1px ?; ? ? --border-hover: 1px ?; ? ? --border-pressed: 1px ?; ? ? --border-focus: 1px ?; ? ? --border-disabled: 1px ?; } 可以看到 `state-border` 主要是处理一些会动态变化的效果,如在 `hover` 、`pressed` 等状态下的边框展示效果,而 `border` 则负责初始默认的效果。 了解了主要模板相关的内容之后,你可能对在讲解整个模板中出现频度最高的一个内容表示疑惑,即: - ? `${mergedClsPrefix}-button` 为什么会有这么奇怪的 CSS 类写法?以及在给组件赋值属性时: - ? `style``={``this``.cssVars}` 一个典型的例子为: ``` ? // default type ? color: "#0000", ? colorHover: "#0000", ? colorPressed: "#0000", ? colorFocus: "#0000", ? colorDisabled: "#0000", ? textColor: textColor2, } 为什么需要赋值一堆的 CSS Variables? 如果你对这几个问题疑惑不解,并想探求其背后的原理,那么此时你应该舒一口气,然后保持专注继续阅读文章下一部分内容:样式的组织艺术。 ## 样式的组织艺术 在组件库这个领域,绝大部分时间都花在如何更好的、更加自定义的组织整体的样式系统。 而 Naive UI 这个框架有个有意思的特性,它不使用任何预处理、后处理样式语言如 Less/Sass/PostCSS 等,而是自造了为框架而生、且框架无关、带 SSR 特性的类 CSS in JS 的方案:[css-render](https://github.com/07akioni/css-render "css-render"),并给予这个方案设计了一套插件系统,目前主要有两个插件: - ? [vue3-ssr](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@css-render/vue3-ssr "vue3-ssr") 本文中主要专注于 CSR 方面的讲解,所以只会关注 `plugin-bem` 相关的内容。 css-render 目前的基本使用场景为搭配 `plugin-bem` 插件使用,编写基于 BEM 风格的、易于组织的类 CSS in JS 代码,至于这里为什么说是 “类” CSS in JS 解决方案,后续会进行讲解。 当我们安装了对应的包之后: ``` 可以按照如下形式来使用: ``` import bem from '@css-render/plugin-bem' const cssr = CssRender() const plugin = bem({ ? blockPrefix: '.ggl-' }) cssr.use(plugin) // 为 cssr 注册 bem 插件 const { cB, cE, cM } = plugin const style = cB( ? 'container', ? [ ? ? cE( ? ? ? 'left, right',? ? ? ? { ? ? ? ? width: '50%' ? ? ? } ? ? ), ? ? cM( ? ? ? 'dark',? ? ? ? [ ? ? ? ? cE( ? ? ? ? ? 'left, right', ? ? ? ? ? { ? ? ? ? ? ? backgroundColor: 'black' ? ? ? ? ? } ? ? ? ? ) ? ? ? ] ? ? ) ? ] ) // 查看渲染的 CSS 样式字符串 console.log(style.render()) // 将样式挂载到 head 标签里面,可以提供 options style.mount(/* options */) // 删除挂载的样式 style.unmount(/* options */) 上述的 Log 的效果如下: ``` .ggl-container .ggl-container__right { ? width: 50%; } .ggl-container.ggl-container--dark .ggl-container__left,? .ggl-container.ggl-container--dark .ggl-container__right{ ? background-color: black; } 可以看到上述代码主要使用了 `cB` 、`cE` 、 `cM` 函数来进行各种标签、样式的嵌套组合,来达到定义规范 CSS 类和对应样式的效果,为了更近一步讲解这个库的作用以及它在 Naive UI 中所达到的效果,我们有必要先了解一下什么是 BEM。 ### 什么是 BEM? B(Block)、E(Element)、M(Modifier),即块、元素与修饰符,是一种广泛使用的对 HTML/CSS 里面使用到的类命名规范: ``` .btn {} ?/* 依赖块的元素 */? .btn__price {} .btn__text {} ?/* 修改块状态的修饰符 */ .btn--orange {}? .btn--big {} - ? 上述中块(Block),即 `btn` ,代表一个抽象的最顶级的新组件,即块里面不能包含块,也被视为一棵树中的父节点,使用 `.btn` 表示 上述的 CSS 形式反映到 HTML 里面,会得到如下结构: ``` ? <span class="btn__price">¥9.99</span> ? <span class="btn__text">订购</span> </a> 使用这种 BEM 形式的类命名风格基本有如下几种优点: 1. ?可以表示几乎所有的元素及其从属关系,且关系明确、语义明确 ``` .btn { ? text-decoration: none; ? background-color: white; ? color: #888; ? border-radius: 5px; ? display: inline-block; ? margin: 10px; ? font-size: 18px; ? text-transform: uppercase; ? font-weight: 600; ? padding: 10px 5px; } /* Element */ .btn__price { ? background-color: white; ? color: #fff; ? padding-right: 12px; ? padding-left: 12px; ? margin-right: -10px; /* realign button text padding */ ? font-weight: 600; ? background-color: #333; ? opacity: .4; ? border-radius: 5px 0 0 5px; } /* Element */ .btn__text { ? padding: 0 10px; ? border-radius: 0 5px 5px 0; } /* Modifier */ .btn--big { ? font-size: 28px; ? padding: 10px; ? font-weight: 400; } /* Modifier */ .btn--blue { ? border-color: #0074D9; ? color: white; ? background-color: #0074D9; } /* Modifier */ .btn--orange { ? border-color: #FF4136; ? color: white; ? background-color: #FF4136; } /* Modifier */ .btn--green { ? border-color: #3D9970; ? color: white; ? background-color: #3D9970; } body { ? font-family: "fira-sans-2", sans-serif; ? background-color: #ccc; } 上述只需要修改修饰符 `orange` 、`green` 、`blue` 、`big` 等,就可以获得不同的效果:  ### CSS Render 是如何运作的? CSS Render 本质上是一个 CSS 生成器,然后提供了 `mount` 和 `unmount` API,用于将生成的 CSS 字符串挂载到 HTML 模板里和从 HTML 里面删除此 CSS 样式标签,它借助 BEM 命名规范插件和 CSS Variables 来实现 Sass/Less/CSS-in-JS 形式的方案,可以减少整体 CSS 的重复逻辑和包大小。 了解了 BEM 和上述关于 CSS Render 的介绍之后,我们再来回顾一下以下的代码: ``` import bem from '@css-render/plugin-bem' const cssr = CssRender() const plugin = bem({ ? blockPrefix: '.ggl-' }) cssr.use(plugin) // 为 cssr 注册 bem 插件 const { cB, cE, cM } = plugin const style = cB( ? 'container', ? [ ? ? cE( ? ? ? 'left, right',? ? ? ? { ? ? ? ? width: '50%' ? ? ? } ? ? ), ? ? cM( ? ? ? 'dark',? ? ? ? [ ? ? ? ? cE( ? ? ? ? ? 'left, right', ? ? ? ? ? { ? ? ? ? ? ? backgroundColor: 'black' ? ? ? ? ? } ? ? ? ? ) ? ? ? ] ? ? ) ? ] ) // 查看渲染的 CSS 样式字符串 console.log(style.render()) // 将样式挂载到 head 标签里面,可以提供 options style.mount(/* options */) // 删除挂载的样式 style.unmount(/* options */) 上述代码主要做了如下工作: 1. ?初始化 CSS Render 实例,然后初始化 BEM 插件实例,并为整体样式类加上 `.ggl-` 前缀 1. ?从 BEM 插件里面导出相关的 `cB` 、`cE` 、`cM` 方法,然后基于这三个方法遵从 BEM 的概念进行样式类的排列、嵌套、组合来形成我们最终的样式类和对应的样式 ? ? 1. ?首先是 `cB` ,定义某个顶层块元素为 `container` 了解了上述的层级嵌套关系之后,我们就可以写出上述 `style` 进行 `render` 之后的效果: ``` .ggl-container .ggl-container__left,? .ggl-container .ggl-container__right { ? width: 50%; } // .ggl- 前缀,以及 cB('container', [cM('dark', [cE('left, right', { backgroundColor: 'black' } )])]) .ggl-container.ggl-container--dark .ggl-container--left,? .ggl-container.ggl-container--dark .ggl-container__right { ?background-color: black; } 可以看到 `cM` 定义的修饰符,其实是直接修饰块,也就是在类生成上会是 `.ggl-container.ggl-container--dark` 与父块的类直接写在一起,属于修饰关系,而不是从属关系。 ### Naive UI 的样式组织  Naive UI 在样式组织上主要遵循如下逻辑,依然以 Button 为例: - ? 挂载 CSS Variables,这里存在默认的变量和用户传进来自定义的变量,将 `cssVars` 传给标签的 `style` 字段来挂载 通过上面三步走的方式,就可以定义好 Button 相关的所有类、样式,并通过 CSS Variables 支持主题定制、主题重载等功能。 上述三步走主要是在 `setup` 函数里面调用 `useTheme` 钩子,处理 Button 相关样式挂载和全局默认样式挂载,然后处理 CSS Variables 定义和使用: ``` ? name: "Button", ? props: buttonProps, ? setup(props) { ? ? const themeRef = useTheme( ? ? ? "Button", ? ? ? "Button", ? ? ? style, ? ? ? buttonLight, ? ? ? props, ? ? ? mergedClsPrefixRef ? ? ); ? ?? ? ? return { ? ? ? // 定义边框颜色相关 ? ? ? customColorCssVars: computed(() => {}), ? ? ? // 定义 字体、边框、颜色、大小相关 ? ? ? cssVars: computed(() => {}), ? ? } ? } ? render() { ? ? // 定义 button 相关的 CSS 变量 ? ? <Component style={this.cssVars}> ? ? ? // 定义边框颜色独有的 CSS 变量 ? ? ? <div class={`${mergedClsPrefix}-button__border`} style={this. customColorCssVars} /> ? ? ? <div class={`${mergedClsPrefix}-button__state-border`} style={this. customColorCssVars} /> ? ? </Component> ? } }); #### 挂载 Buttn 相关样式 Button 相关样式挂载与全局样式挂载相关的内容存在于 `Button` 组件的 `setup` 方法里面的 `useTheme` Hooks,`useTheme` 是一个如下结构的钩子函数: ``` type ThemeCommonVars = typeof { primaryHover: '#36ad6a', errorHover: '#de576d', ... } // Button 独有的 CSS Variable 类型 type ButtonThemeVars = ThemeCommonVars & { /* ?Button 相关的 CSS Variables 的类型 */ } // Theme 的类型 interface Theme<N, T = {}, R = any> { ? // 主题名 ? name: N ? // 主题一些通用的 CSS Variables ? common?: ThemeCommonVars ? // 相关依赖组件的一些 CSS Variables,如 Form 里面依赖 Button,对应的 Button ? // 需要包含的 CSS Variables 要有限制 ? peers?: R ? // 主题自身的一些个性化的 CSS Variables ? self?: (vars: ThemeCommonVars) => T } // Button Theme 的类型 type ButtonTheme = Theme<'Button', ButtonThemeVars > interface GlobalThemeWithoutCommon { ? Button?: ButtonTheme ? Icon?: IconTheme } // useTheme 方法传入 props 的类型 type UseThemeProps<T> = Readonly<{ ? // 主题相关变量,如 darkTheme ? theme?: T | undefined ? // 主题中可以被重载的变量 ? themeOverrides?: ExtractThemeOverrides<T> ? // 内建主题中可以被重载的变量 ? builtinThemeOverrides?: ExtractThemeOverrides<T> }> // 最终合并的 Theme 的类型 type MergedTheme<T> = T extends Theme<unknown, infer V, infer W> ? ? { ? ? ? common: ThemeCommonVars ? ? ? self: V ? ? ? ?// 相关依赖组件的一些 CSS Variables,如 Form 里面依赖 Button,对应的 Button ? ? ? // 需要包含的 CSS Variables 要有限制 ? ? ? peers: W ? ? ? ?// 相关依赖组件的一些 CSS Variables,如 Form 里面依赖 Button,对应的 Button ? ? ? // 需要包含的 CSS Variables 要有限制,这些 CSS Variables 中可以被重载的变量 ? ? ? peerOverrides: ExtractMergedPeerOverrides<T> ? ? } ? : T useTheme<N, T, R>( ? resolveId: keyof GlobalThemeWithoutCommon, ? mountId: string, ? style: CNode | undefined, ? defaultTheme: Theme<N, T, R>, ? props: UseThemeProps<Theme<N, T, R>>, ? // n ? clsPrefixRef?: Ref<string | undefined> ) => ComputedRef<MergedTheme<Theme<N, T, R>>> 可以看到,`useTheme` 主要接收 6 个参数: - ? `resolveId` 用于定位在全局样式主题中的键值,这里是 `'Button'` `useTheme` 返回一个合并了内建样式、全局定义的关于 Button 相关的样式、用户自定义样式三者的样式合集 `ComputedRef<MergedTheme<Theme<N, T, R>>>` 。 了解了 `useTheme` 钩子函数的输入与输出之后,可以继续来看一下其函数主体逻辑: ``` ? resolveId, ? mountId, ? style, ? defaultTheme, ? props, ? clsPrefixRef ) { ? if (style) { ? ? const mountStyle = () => { ? ? ? const clsPrefix = clsPrefixRef?.value; ? ? ? style.mount({ ? ? ? ? id: clsPrefix === undefined ? mountId : clsPrefix + mountId, ? ? ? ? head: true, ? ? ? ? props: { ? ? ? ? ? bPrefix: clsPrefix ? `.${clsPrefix}-` : undefined, ? ? ? ? }, ? ? ? }); ? ? ? globalStyle.mount({ ? ? ? ? id: "naive-ui/global", ? ? ? ? head: true, ? ? ? }); ? ? }; ? ? onBeforeMount(mountStyle); ? } ? const NConfigProvider = inject(configProviderInjectionKey, null); ? const mergedThemeRef = computed(() => { ? ? const { ? ? ? theme: { common: selfCommon, self, peers = {} } = {}, ? ? ? themeOverrides: selfOverrides = {}, ? ? ? builtinThemeOverrides: builtinOverrides = {}, ? ? } = props; ? ? const { common: selfCommonOverrides, peers: peersOverrides } = ? ? ? selfOverrides; ? ? const { ? ? ? common: globalCommon = undefined, ? ?? ? ? ? ? common: globalSelfCommon = undefined, ? ? ? ? self: globalSelf = undefined, ? ? ? ? peers: globalPeers = {}, ? ? ? } = {}, ? ? } = NConfigProvider?.mergedThemeRef.value || {}; ? ? const { ? ? ? common: globalCommonOverrides = undefined, ? ? ?= {}, ? ? } = NConfigProvider?.mergedThemeOverridesRef.value || {}; ? ? const { ? ? ? common: globalSelfCommonOverrides, ? ? ? peers: globalPeersOverrides = {}, ? ? } = globalSelfOverrides; ? ? const mergedCommon = merge( ? ? ? {}, ? ? ? selfCommon || globalSelfCommon || globalCommon || defaultTheme.common, ? ? ? globalCommonOverrides, ? ? ? globalSelfCommonOverrides, ? ? ? selfCommonOverrides ? ? ); ? ? const mergedSelf = merge( ? ? ? // {}, executed every time, no need for empty obj ? ? ? (self || globalSelf || defaultTheme.self)?.(mergedCommon), ? ? ? builtinOverrides, ? ? ? globalSelfOverrides, ? ? ? selfOverrides ? ? ); ? ? return { ? ? ? common: mergedCommon, ? ? ? self: mergedSelf, ? ? ? peers: merge({}, defaultTheme.peers, globalPeers, peers), ? ? ? peerOverrides: merge({}, globalPeersOverrides, peersOverrides), ? ? }; ? }); ? return mergedThemeRef; } 可以看到 `useTheme` 主体逻辑包含两个部分: - ? 第一部分为挂载 `button` 相关的样式到 `clsPrefix + mountId` ,包含 `button` 相关的样式类骨架,以及挂载全局通用样式到 `naive-ui/global` ,并且这个样式的挂载过程是在 `onBeforeMount` 钩子调用时,对应到之前讲解的样式挂载顺序就可以理清楚了: ? ? - ? 顺序为 `setup` 里面返回 CSS Variables,然后通过标签的 `style` 注册 CSS Variables - ? 第二部分为将用户自定义的主题、内部配置的主题进行整合生成新的主题变量集 ? ? - ? 用户自定义的主题 `props` :包含 `theme` 、`themeOverrides` 、`builtinThemeOverrides` 接下来着重讲解关于这两部的具体代码和相关变量的含义。 第一部分中的 `button` 相关的样式如下: ``` import fadeInWidthExpandTransition from "../../../_styles/transitions/fade-in-width-expand.cssr"; import iconSwitchTransition from "../../../_styles/transitions/icon-switch.cssr"; export default c([ ? cB( ? ? "button", ? ? ` ? ? font-weight: var(--font-weight); ? ? line-height: 1; ? ? font-family: inherit; ? ? padding: var(--padding); ? ? // .... 更多的定义 ? ? `, [ ? ? // border ,边框相关的样式类骨架 ? ? ? cM("color", [ ? ? ? ? cE("border", { ? ? ? ? ? borderColor: "var(--border-color)", ? ? ? ? }), ? ? ? ? cM("disabled", [ ? ? ? ? ? cE("border", { ? ? ? ? ? ? borderColor: "var(--border-color-disabled)", ? ? ? ? ? }), ? ? ? ? ]), ? ? ? ? cNotM("disabled", [ ? ? ? ? ? c("&:focus", [ ? ? ? ? ? ? cE("state-border", { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? borderColor: "var(--border-color-focus)", ? ? ? ? ? ? }), ? ? ? ? ? ]), ? ? ? ? ? c("&:hover", [ ? ? ? ? ? ? cE("state-border", { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? borderColor: "var(--border-color-hover)", ? ? ? ? ? ? }), ? ? ? ? ? ]), ? ? ? ? ? c("&:active", [ ? ? ? ? ? ? cE("state-border", { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? borderColor: "var(--border-color-pressed)", ? ? ? ? ? ? }), ? ? ? ? ? ]), ? ? ? ? ? cM("pressed", [ ? ? ? ? ? ? cE("state-border", { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? borderColor: "var(--border-color-pressed)", ? ? ? ? ? ? }), ? ? ? ? ? ]), ? ? ? ? ]), ? ? ? ]), ? ? ? // icon 相关的样式类骨架 ? ? ? cE( ? ? ? ? "icon", ? ? ? ? ` ? ? ? margin: var(--icon-margin); ? ? ? margin-left: 0; ? ? ? height: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? width: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? max-width: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? font-size: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? position: relative; ? ? ? flex-shrink: 0; ? ? `, ? ? ? ? [ ? ? ? ? ? cB( ? ? ? ? ? ? "icon-slot", ? ? ? ? ? ? ` ? ? ? ? height: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? ? width: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? ? position: absolute; ? ? ? ? left: 0; ? ? ? ? top: 50%; ? ? ? ? transform: translateY(-50%); ? ? ? ? display: flex; ? ? ? `, ? ? ? ? ? ? [ ? ? ? ? ? ? ? iconSwitchTransition({ ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? top: "50%", ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? originalTransform: "translateY(-50%)", ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }), ? ? ? ? ? ? ] ? ? ? ? ? ), ? ? ? ? ? fadeInWidthExpandTransition(), ? ? ? ? ] ? ? ? ), ? ? ? // content 子元素内容相关的样式类骨架 ? ? ? cE( ? ? ? ? "content", ? ? ? ? ` ? ? ? display: flex; ? ? ? align-items: center; ? ? ? flex-wrap: nowrap; ? ? `, ? ? ? ? [ ? ? ? ? ? c("~", [ ? ? ? ? ? ? cE("icon", { ? ? ? ? ? ? ? margin: "var(--icon-margin)", ? ? ? ? ? ? ? marginRight: 0, ? ? ? ? ? ? }), ? ? ? ? ? ]), ? ? ? ? ] ? ? ? ), ? ? ? // 更多的关于 backgroundColor、base-wave 点击反馈波纹,icon,content,block 相关的样式定义 ? ? ], ? ? // 动画、过渡相关的样式类骨架 ? ? c("@keyframes button-wave-spread", { ? ? from: { ? ? ? boxShadow: "0 0 0.5px 0 var(--ripple-color)", ? ? }, ? ? to: { ? ? ? // don't use exact 5px since chrome will display the animation with glitches ? ? ? boxShadow: "0 0 0.5px 4.5px var(--ripple-color)", ? ? }, ? }), ? c("@keyframes button-wave-opacity", { ? ? from: { ? ? ? opacity: "var(--wave-opacity)", ? ? }, ? ? to: { ? ? ? opacity: 0, ? ? }, ? }), ]); 上面的 CSS Render 相关的代码最终会产出类型下面的内容: ``` ? ? font-weight: var(--font-weight); ? ? line-height: 1; ? ? font-family: inherit; ? ? padding: var(--padding); ? ? transition: ? ? ? color .3s var(--bezier), ? ? ? background-color .3s var(--bezier), ? ? ? opacity .3s var(--bezier), ? ? ? border-color .3s var(--bezier); ?? } .n-button.n-button--color .n-button__border { ? border-color: var(--border-color); } .n-button.n-button--color.n-button--disabled .n-button__border { ? border-color: var(--border-color-disabled); } .n-button.n-button--color:not(.n-button--disabled):focus .n-button__state-border { ? border-color: var(--border-color-focus); } .n-button .n-base-wave { ? ? ? pointer-events: none; ? ? ? top: 0; ? ? ? right: 0; ? ? ? bottom: 0; ? ? ? left: 0; ? ? ? animation-iteration-count: 1; ? ? ? animation-duration: var(--ripple-duration); ? ? ? animation-timing-function: var(--bezier-ease-out), var(--bezier-ease-out); ? ?? } .n-button .n-base-wave.n-base-wave--active { ? z-index: 1; ? animation-name: button-wave-spread, button-wave-opacity; } .n-button .n-button__border, .n-button .n-button__state-border { ? ? ? position: absolute; ? ? ? left: 0; ? ? ? top: 0; ? ? ? right: 0; ? ? ? bottom: 0; ? ? ? border-radius: inherit; ? ? ? transition: border-color .3s var(--bezier); ? ? ? pointer-events: none; ? ?? } .n-button .n-button__icon { ? ? ? margin: var(--icon-margin); ? ? ? margin-left: 0; ? ? ? height: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? width: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? max-width: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? font-size: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? position: relative; ? ? ? flex-shrink: 0; ? ?? } .n-button .n-button__icon .n-icon-slot { ? ? ? ? height: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? ? width: var(--icon-size); ? ? ? ? position: absolute; ? ? ? ? left: 0; ? ? ? ? top: 50%; ? ? ? ? transform: translateY(-50%); ? ? ? ? display: flex; ? ? ?? } .n-button .n-button__icon.fade-in-width-expand-transition-enter-active { ? ? ? overflow: hidden; ? ? ? transition: ? ? ? ? opacity .2s cubic-bezier(.4, 0, .2, 1) .1s, ? ? ? ? max-width .2s cubic-bezier(.4, 0, .2, 1), ? ? ? ? margin-left .2s cubic-bezier(.4, 0, .2, 1), ? ? ? ? margin-right .2s cubic-bezier(.4, 0, .2, 1); ? ?? } .n-button .n-button__content { ? ? ? display: flex; ? ? ? align-items: center; ? ? ? flex-wrap: nowrap; ? ?? } .n-button .n-button__content ~ .n-button__icon { ? margin: var(--icon-margin); ? margin-right: 0; } .n-button.n-button--block { ? ? ? display: flex; ? ? ? width: 100%; ? ?? } .n-button.n-button--dashed .n-button__border, .n-button.n-button--dashed .n-button__state-border { ? border-style: dashed !important; } .n-button.n-button--disabled { ? cursor: not-allowed; ? opacity: var(--opacity-disabled); } @keyframes button-wave-spread { ? from { ? ? box-shadow: 0 0 0.5px 0 var(--ripple-color); ? } ? to { ? ? box-shadow: 0 0 0.5px 4.5px var(--ripple-color); ? } } @keyframes button-wave-opacity { ? from { ? ? opacity: var(--wave-opacity); ? } ? to { ? ? opacity: 0; ? } } 可以看到 `button` 相关的样式使用 BEM 命名风格处理了各种场景: - ? border 与 state-border ,关于 disabled、pressed、hover 、active 等状态下的样式 ``` ? border-color: var(--border-color-focus); } - ? 按钮被点击时出现波纹的样式 `.n-button .n-base-wave` 同时可以看到在样式中为各种属性预留了对应的 CSS Variables,包括 box-shadow 的 `--ripple-color` ,icon 宽高的 `--icon-size` ,过渡动画 `transition` 的 `--bezier` ,这些变量是为后面定制各种样式、主题留出空间。 即在设计一个组件库的样式系统时,组件相关的样式模板使用 BEM 风格提前就定义好,然后对于需要定制的主题相关的变量等通过 CSS Variables 来进行个性化的更改,达到定制主题的效果。 #### 挂载全局样式 全局相关的样式主要是一些简单的基础配置,代码如下: ``` import commonVariables from "../common/_common"; export default c( ? "body", ? ` ? margin: 0; ? font-size: ${commonVariables.fontSize}; ? font-family: ${commonVariables.fontFamily}; ? line-height: ${commonVariables.lineHeight}; ? -webkit-text-size-adjust: 100%; `, ? [ ? ? c( ? ? ? "input", ? ? ? ` ? ? font-family: inherit; ? ? font-size: inherit; ? ` ? ? ), ? ] ); 主要为 `margin` 、`font-size` 、`font-family` 、`line-height` 等相关的内容,是为了兼容浏览器所必要进行的 CSS 代码标准化,比较典型的有 [Normalize.css: Make browsers render all elements more consistently.](https://necolas.github.io/normalize.css/ "Normalize.css: Make browsers render all elements more consistently.")。 其中 `commonVariables` 如下: ``` ? fontFamily: ? ? 'v-sans, system-ui, -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, "Segoe UI", sans-serif, "Apple Color Emoji", "Segoe UI Emoji", "Segoe UI Symbol"', ? fontFamilyMono: "v-mono, SFMono-Regular, Menlo, Consolas, Courier, monospace", ? fontWeight: "400", ? fontWeightStrong: "500", ? cubicBezierEaseInOut: "cubic-bezier(.4, 0, .2, 1)", ? cubicBezierEaseOut: "cubic-bezier(0, 0, .2, 1)", ? cubicBezierEaseIn: "cubic-bezier(.4, 0, 1, 1)", ? borderRadius: "3px", ? borderRadiusSmall: "2px", ? fontSize: "14px", ? fontSizeTiny: "12px", ? fontSizeSmall: "14px", ? fontSizeMedium: "14px", ? fontSizeLarge: "15px", ? fontSizeHuge: "16px", ? lineHeight: "1.6", ? heightTiny: "22px", ? heightSmall: "28px", ? heightMedium: "34px", ? heightLarge: "40px", ? heightHuge: "46px", ? transformDebounceScale: "scale(1)", }; 上述的通用变量是 UI 组件库向上构建的一些最基础的 “原材料”,也是默认不建议修改的、业界的最佳实践,如定义 `size` 有 5 类,分别为 `tiny` 、`small` 、`medium` 、`large` 、`huge` ,定义字体、代码字体 等。 #### 定义与注册 CSS Variables 这块的主要代码为: ``` const mergedThemeRef = computed(() => { const { ? theme: { common: selfCommon, self, peers = {} } = {}, ? themeOverrides: selfOverrides = {}, ? builtinThemeOverrides: builtinOverrides = {}, } = props; const { common: selfCommonOverrides, peers: peersOverrides } = ? selfOverrides; const { ? common: globalCommon = undefined, ? [resolveId]: { ? ? common: globalSelfCommon = undefined, ? ? self: globalSelf = undefined, ? ? peers: globalPeers = {}, ? } = {}, } = NConfigProvider?.mergedThemeRef.value || {}; const { ? common: globalCommonOverrides = undefined, ? [resolveId]: globalSelfOverrides = {}, } = NConfigProvider?.mergedThemeOverridesRef.value || {}; const { ? common: globalSelfCommonOverrides, ? peers: globalPeersOverrides = {}, } = globalSelfOverrides; const mergedCommon = merge( ? {}, ? selfCommon || globalSelfCommon || globalCommon || defaultTheme.common, ? globalCommonOverrides, ? globalSelfCommonOverrides, ? selfCommonOverrides ); const mergedSelf = merge( ? // {}, executed every time, no need for empty obj ? (self || globalSelf || defaultTheme.self)?.(mergedCommon), ? builtinOverrides, ? globalSelfOverrides, ? selfOverrides ); return { ? common: mergedCommon, ? self: mergedSelf, ? peers: merge({}, defaultTheme.peers, globalPeers, peers), ? peerOverrides: merge({}, globalPeersOverrides, peersOverrides), }; 首先是从通过 `inject` 拿到 `configProviderInjectionKey` 相关的内容,其中 `configProviderInjectionKey` 相关内容定义在如下: ``` ? mergedRtlRef, ? mergedIconsRef, ? mergedComponentPropsRef, ? mergedBorderedRef, ? mergedNamespaceRef, ? mergedClsPrefixRef, ? mergedLocaleRef: computed(() => { ? ? // xxx ? }), ? mergedDateLocaleRef: computed(() => { ? ? // xxx ? }), ? mergedHljsRef: computed(() => { ? ? // ... ? }), ? mergedThemeRef, ? mergedThemeOverridesRef }) 可以看到包含 rtl、icon、border、namespace、clsPrefix、locale(国际化)、date、theme、themeOverrides 等几乎所有的配置,而这里主要是想拿到主题相关的配置: - ? `mergedThemeRef` :可调整的主题,如 ``` ? <n-config-provider :theme="darkTheme"> ? ? <app /> ? </n-config-provider> </template> <script> ? import { darkTheme } from 'naive-ui' ? export default { ? ? setup() { ? ? ? return { ? ? ? ? darkTheme ? ? ? } ? ? } ? } </script> - ? `mergedThemeOverridesRef` :可调整的主题变量,如 ``` ? ? common: { ? ? ? primaryColor: '#FF0000' ? ? }, ? ? Button: { ? ? ? textColor: '#FF0000' ? ? ? backgroundColor: '#FFF000', ? ? }, ? ? Select: { ? ? ? peers: { ? ? ? ? InternalSelection: { ? ? ? ? ? textColor: '#FF0000' ? ? ? ? } ? ? ? } ? ? } ? ? // ... ? } 上述的这两者有主要包含全局 `common` 相关的,以及 `Button` 中 `common` 相关的统一变量、`self` 相关的 Button 自定义的一些变量,以及 `Button` 在与其他组件使用时涉及相关限制的 `peers` 变量。 从 `useTheme` 钩子函数中返回 `themeRef` 之后,`themeRef` 相关的内容会拿来组装 Button 涉及到的各种样式,主要从以下四个方向进行处理: - ? `fontProps` ``` ? // fontProps ? // colorProps ? // borderProps ? // sizeProps ?? ? return { ? // 处理 动画过渡函数、透明度相关的变量 ? ? "--bezier": cubicBezierEaseInOut, ? ? ? "--bezier-ease-out": cubicBezierEaseOut, ? ? ? "--ripple-duration": rippleDuration, ? ? ? "--opacity-disabled": opacityDisabled, ? ? ? "--wave-opacity": waveOpacity, ? ? ? // 处理字体、颜色、边框、大小相关的变量 ? ? ...fontProps, ? ? ...colorProps, ? ? ...borderProps, ? ? ...sizeProps, ? }; }); `fontProps` 相关代码如下: ``` const { ? self, } = theme; const { ? rippleDuration, ? opacityDisabled, ? fontWeightText, ? fontWeighGhost, ? fontWeight, } = self; const { dashed, type, ghost, text, color, round, circle } = props; ? ? ? ? // font const fontProps = { ? fontWeight: text ? ? ? fontWeightText ? ? : ghost ? ? ? fontWeighGhost ? ? : fontWeight, }; 主要判断当 Button 以 text 节点进行展示时、以透明背景进行展示时、标准状态下的字体相关的 CSS 变量与值。 `colorProps` 相关代码如下 ``` ? "--color": "initial", ? "--color-hover": "initial", ? "--color-pressed": "initial", ? "--color-focus": "initial", ? "--color-disabled": "initial", ? "--ripple-color": "initial", ? "--text-color": "initial", ? "--text-color-hover": "initial", ? "--text-color-pressed": "initial", ? "--text-color-focus": "initial", ? "--text-color-disabled": "initial", }; if (text) { ? const { depth } = props; ? const textColor = ? ? color || ? ? (type === "default" && depth !== undefined ? ? ? ? self[createKey("textColorTextDepth", String(depth))] ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorText", type)]); ? colorProps = { ? ? "--color": "#0000", ? ? "--color-hover": "#0000", ? ? "--color-pressed": "#0000", ? ? "--color-focus": "#0000", ? ? "--color-disabled": "#0000", ? ? "--ripple-color": "#0000", ? ? "--text-color": textColor, ? ? "--text-color-hover": color ? ? ? ? createHoverColor(color) ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorTextHover", type)], ? ? "--text-color-pressed": color ? ? ? ? createPressedColor(color) ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorTextPressed", type)], ? ? "--text-color-focus": color ? ? ? ? createHoverColor(color) ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorTextHover", type)], ? ? "--text-color-disabled": ? ? ? color || self[createKey("textColorTextDisabled", type)], ? }; } else if (ghost || dashed) { ? colorProps = { ? ? "--color": "#0000", ? ? "--color-hover": "#0000", ? ? "--color-pressed": "#0000", ? ? "--color-focus": "#0000", ? ? "--color-disabled": "#0000", ? ? "--ripple-color": color || self[createKey("rippleColor", type)], ? ? "--text-color": color || self[createKey("textColorGhost", type)], ? ? "--text-color-hover": color ? ? ? ? createHoverColor(color) ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorGhostHover", type)], ? ? "--text-color-pressed": color ? ? ? ? createPressedColor(color) ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorGhostPressed", type)], ? ? "--text-color-focus": color ? ? ? ? createHoverColor(color) ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorGhostHover", type)], ? ? "--text-color-disabled": ? ? ? color || self[createKey("textColorGhostDisabled", type)], ? }; } else { ? colorProps = { ? ? "--color": color || self[createKey("color", type)], ? ? "--color-hover": color ? ? ? ? createHoverColor(color) ? ? ? : self[createKey("colorHover", type)], ? ? "--color-pressed": color ? ? ? ? createPressedColor(color) ? ? ? : self[createKey("colorPressed", type)], ? ? "--color-focus": color ? ? ? ? createHoverColor(color) ? ? ? : self[createKey("colorFocus", type)], ? ? "--color-disabled": color || self[createKey("colorDisabled", type)], ? ? "--ripple-color": color || self[createKey("rippleColor", type)], ? ? "--text-color": color ? ? ? ? self.textColorPrimary ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColor", type)], ? ? "--text-color-hover": color ? ? ? ? self.textColorHoverPrimary ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorHover", type)], ? ? "--text-color-pressed": color ? ? ? ? self.textColorPressedPrimary ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorPressed", type)], ? ? "--text-color-focus": color ? ? ? ? self.textColorFocusPrimary ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorFocus", type)], ? ? "--text-color-disabled": color ? ? ? ? self.textColorDisabledPrimary ? ? ? : self[createKey("textColorDisabled", type)], ? }; } 主要处理在四种形式:普通、text 节点、ghost 背景透明、dashed 虚线形式下,对不同状态 标准 、`pressed` 、`hover` 、`focus`、 `disabled` 等处理相关的 CSS 属性和值 `borderProps` 相关的代码如下: ``` ? "--border": "initial", ? "--border-hover": "initial", ? "--border-pressed": "initial", ? "--border-focus": "initial", ? "--border-disabled": "initial", }; if (text) { ? borderProps = { ? ? "--border": "none", ? ? "--border-hover": "none", ? ? "--border-pressed": "none", ? ? "--border-focus": "none", ? ? "--border-disabled": "none", ? }; } else { ? borderProps = { ? ? "--border": self[createKey("border", type)], ? ? "--border-hover": self[createKey("borderHover", type)], ? ? "--border-pressed": self[createKey("borderPressed", type)], ? ? "--border-focus": self[createKey("borderFocus", type)], ? ? "--border-disabled": self[createKey("borderDisabled", type)], ? }; } 主要处理在以 text 形式进行展示和普通形式展示下,五种不同状态 标准 、`pressed` 、`hover` 、`focus` 、`disabled`等情况下的处理。 这里 `borderProps` 其实主要是定义整个 `border` 属性,而边框颜色相关的属性其实是通过 `setup` 里面的 `customColorCssVars` 进行定义的,代码如下: ``` ? ? const { color } = props; ? ? if (!color) return null; ? ? const hoverColor = createHoverColor(color); ? ? return { ? ? ? "--border-color": color, ? ? ? "--border-color-hover": hoverColor, ? ? ? "--border-color-pressed": createPressedColor(color), ? ? ? "--border-color-focus": hoverColor, ? ? ? "--border-color-disabled": color, ? ? }; ? }) `sizeProps` 相关的代码如下: ``` ? "--width": circle && !text ? height : "initial", ? "--height": text ? "initial" : height, ? "--font-size": fontSize, ? "--padding": circle ? ? ? "initial" ? ? : text ? ? ? "initial" ? ? : round ? ? ? paddingRound ? ? : padding, ? "--icon-size": iconSize, ? "--icon-margin": iconMargin, ? "--border-radius": text ? ? ? "initial" ? ? : circle || round ? ? ? height ? ? : borderRadius, }; 主要处理 `width` 、`height` 、`font-size` 、`padding` 、`icon` 、`border` 相关的大小内容,其中 `margin` 在挂载全局默认样式的时候进行了处理,默认为 0。 #### 小结 通过上面三步走: 1. ?挂载 button 相关的样式类骨架,留出大量 CSS Variables 用于自定义样式 我们就成功应用 CSS Render、 BEM plugin、CSS Variables 完成了 Button 整体样式的设计,它既易于理解、还易于定制。 不过也值得注意的是,纵观上述组件中样式的处理逻辑,只定义在 `setup` 里,也少用生命周期相关的钩子,其实也可以看出 CSS Render 的主要使用场景:即事先将所有的情况都规范好,相关的 CSS Variables 都预设好,然后给出 ## 必要的事件处理也不能少 Naive UI 主要提供了以下几类事件的处理: - ? `mousedown` : `handleMouseDown` 可以来分别看一下其中的代码: `handleMouseDown` : ``` ? e.preventDefault(); ? if (props.disabled) { ? ? return; ? } ? if (mergedFocusableRef.value) { ? ? selfRef.value?.focus({ preventScroll: true }); ? } }; 主要处理 `disabled` 情况下不响应、以及如果可以 `focus` 情况下,调用 `selfRef` 进行 focus,并激活对应的样式。 `handleKeyUp` : ``` ? switch (e.code) { ? ? case "Enter": ? ? case "NumpadEnter": ? ? ? if (!props.keyboard) { ? ? ? ? e.preventDefault(); ? ? ? ? return; ? ? ? } ? ? ? enterPressedRef.value = false; ? ? ? void nextTick(() => { ? ? ? ? if (!props.disabled) { ? ? ? ? ? selfRef.value?.click(); ? ? ? ? } ? ? ? }); ? } }; 主要处理 `Enter` 、`NumpadEnter` 键,判断是否支持键盘处理,并在合适的情况下激活按钮点击。 `handleKeyDown` : ``` ? switch (e.code) { ? ? case "Enter": ? ? case "NumpadEnter": ? ? ? if (!props.keyboard) return; ? ? ? e.preventDefault(); ? ? ? enterPressedRef.value = true; ? } }; 主要处理 `Enter` 、`NumpadEnter` 键,判断是否支持键盘处理,并在合适的情况下更新 `enterPressedRef` 的值,标志当前是 `keydown` 过。 `handleClick` : ``` ? if (!props.disabled) { ? ? const { onClick } = props; ? ? if (onClick) call(onClick, e); ? ? if (!props.text) { ? ? ? const { value } = waveRef; ? ? ? if (value) { ? ? ? ? value.play(); ? ? ? } ? ? } ? } }; 根据状态调用对应的点击处理函数,以及非 text 节点下播放按钮的点击波纹动效。 `handleBlur` : ``` ? enterPressedRef.value = false; }; 更新 `enterPressedRef` 的值,标志当前是 blur 了。 # 总结与展望 本文通过一层层、源码级剖析了 Naive UI 的 Button 完整过程,可以发现对于组件库这个领域来说,绝大部分的构思都是花在如何设计可扩展的样式系统上,从 Ant Design、Element UI 使用 Less 来组织样式系统,再到 Material Design 使用 CSS-in-JS,如 `styled-components` 来组织样式系统,再到现在 Naive UI 使用 CSS Render 来组织样式系统,虽然组织样式系统的形式繁多,但实际上就我理解而言,在设计样式类、对应的样式、样式的扩展和主题定制上应该大体保持相似。 如果你能通过这篇杂乱的文章理解了 Button 运行的整个过程,还保持着对 Naive UI 整体的源码、工程化方向建设的兴趣,你完全可以按照这个逻辑去理解其他组件的设计原理,正如我在开始放的那张图一样,你了解整体代码的过程中会感觉越来越简单:  了解优秀库的源码设计、研读大牛的源码可以帮助我们了解业界最佳实践、优秀的设计思想和改进编写代码的方式,成为更加优秀的开发者,你我共勉💪! |
|
|
| JavaScript知识库 最新文章 |
| ES6的相关知识点 |
| react 函数式组件 & react其他一些总结 |
| Vue基础超详细 |
| 前端JS也可以连点成线(Vue中运用 AntVG6) |
| Vue事件处理的基本使用 |
| Vue后台项目的记录 (一) |
| 前后端分离vue跨域,devServer配置proxy代理 |
| TypeScript |
| 初识vuex |
| vue项目安装包指令收集 |
|
|
| 上一篇文章 下一篇文章 查看所有文章 |
|
|
开发:
C++知识库
Java知识库
JavaScript
Python
PHP知识库
人工智能
区块链
大数据
移动开发
嵌入式
开发工具
数据结构与算法
开发测试
游戏开发
网络协议
系统运维
教程: HTML教程 CSS教程 JavaScript教程 Go语言教程 JQuery教程 VUE教程 VUE3教程 Bootstrap教程 SQL数据库教程 C语言教程 C++教程 Java教程 Python教程 Python3教程 C#教程 数码: 电脑 笔记本 显卡 显示器 固态硬盘 硬盘 耳机 手机 iphone vivo oppo 小米 华为 单反 装机 图拉丁 |
| 360图书馆 购物 三丰科技 阅读网 日历 万年历 2026年3日历 | -2026/3/6 15:21:19- |
|
| 网站联系: qq:121756557 email:121756557@qq.com IT数码 |