前言
笔者目前只学习到BOM的内容,因此所用代码都只限于HTML5、CSS、JS的部分
效果图:
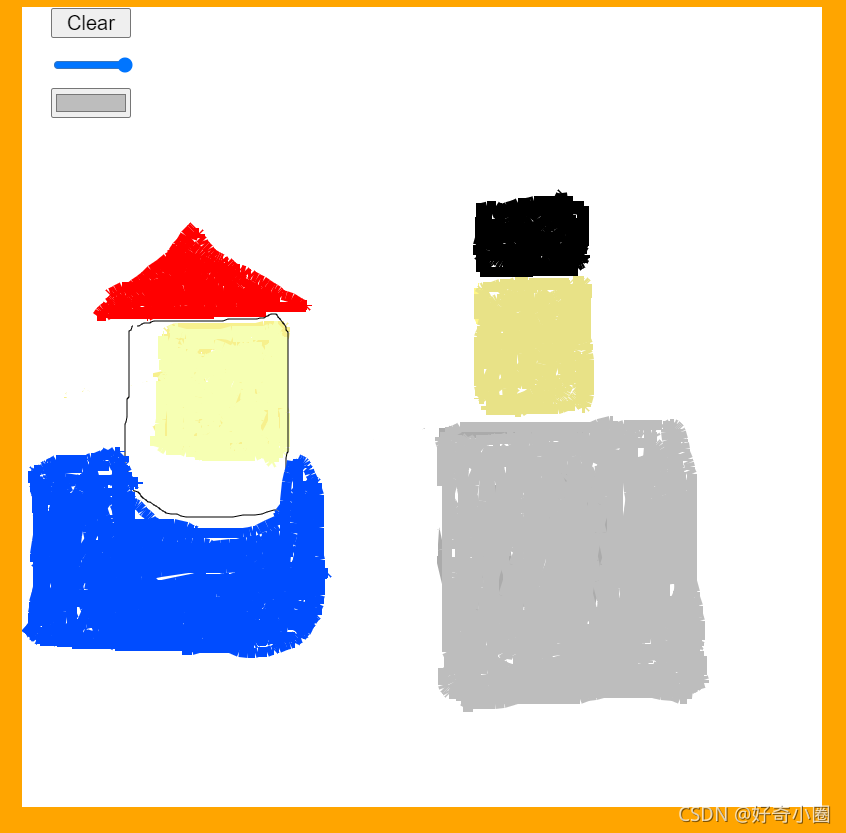

高情商:蜡笔质感
低情商:画笔不连续(我也不清楚怎么改善,还请大佬指教)
一、HTML部分
1、代码
主要指body
<body>
<div id="content">
<!-- 用于选画笔颜色 -->
<label for="color_picker" hidden></label>
<input type="color" id="color_picker" />
<!-- 用于全屏清除 -->
<input type="button" id="clear_button" value="Clear" />
<!-- 用于设定画笔宽度(画笔宽度越大断流的现象越明显) -->
<input type="range" id="line_range" min="1" max="10" />
</div>
<canvas id="canvas">
</canvas>
</body
2、温习
(1)input标签
type:输入的类型,
此处用到了“color”颜色选择;
“button”普通按钮,value可以设置显示的内容;
“range”滑块类型,min和max分别设置最小值和最大值。
(2)label for属性
for 属性规定 label 绑定的表单元素。
(3)canvas标签
Canvas API 提供了一个通过JavaScript 和 HTML的元素来绘制图形的方式。它可以用于动画、游戏画面、数据可视化、图片编辑以及实时视频处理等方面。具体使用在JavaScript部分
二、CSS部分
1、代码
<style>
#canvas {
/*设置居中,画板大小800px*800px(设置于JavaScript部分)*/
position: absolute;
background-color: white;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -400px;
}
input {
/*设置按钮统一样式*/
border-color: 1px #888;
width: 80px;
height: 30px;
}
#clear_button {
/*设置按钮的位置,下同*/
z-index: 10;
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 1px;
font-size: 20px;
}
#line_range {
z-index: 10;
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 41px;
font-size: 20px;
}
#color_picker {
z-index: 10;
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 81px;
font-size: 20px;
}
#content {
position: absolute;
}
/*设置背景颜色*/
body {
background: orange;
}
</style>
2、温习
(1)定位
概念
作为CSS的重要组成,既浮动、定位、过渡之一,定位分为:静态定位(static)、相对定位(relative)、绝对定位(absolute)、固定定位(fixed)、粘性定位(sticky)等。
边偏移
既top、bottom、left、right四个属性,可以用来设置与各个方向的距离
相对定位
子元素为绝对定位时,父元素必须为相对定位,默认为html。
既position:relative;
移动的参照点是自己原来的位置,原来的标准流位置仍然占有,不脱标。
绝对定位
相对于其父移动,在没有设定父元素时,以浏览器为准定位(document文档)。会脱离标准流。
(2)边框border
可用于设置border-width, border-style,和border-color。
(3)盒子模型
以画板大小(Chrome浏览器)为例可见盒子模型的组成
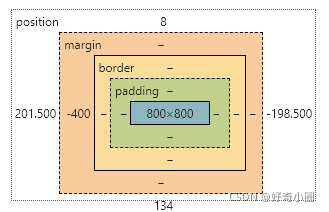
使用
left: 50%;
margin-left: -400px;
即可实现居中对齐
三、JavaScript部分
1、代码
<script>
// 获取用于线宽设置的滑块
var linew = document.querySelector('input[type="range"]');
// 获取canvas标签
let canvas = document.getElementById('canvas');
// 获取2D渲染接口
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// 将渲染颜色设置为 黑色 #000000
ctx.strokeStyle = '#000000';
ctx.setLineDash([]);
//设置画板大小
canvas.setAttribute('height', 800 + 'px');
canvas.setAttribute('width', 800 + 'px');
// 线段开始位置
let startP = { x: 0, y: 0 };
// 线段结束位置
let endP = { x: 0, y: 0 };
// 添加 mousedown 事件
canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', mousedown);
// 添加 mouseup 事件
canvas.addEventListener('mouseup', mouseup);
// 添加 mouseleave 事件
canvas.addEventListener('mouseleave', mouseleave);
function mousedown(e) {
// 将线段开始位置设为鼠标点击的位置
startP = { x: e.clientX - (window.innerWidth - 800) / 2, y: e.clientY };
// 将画笔移到始点
ctx.moveTo(startP.x, startP.y);
console.log('Mouse down.');
ctx.lineWidth = linew.value;
canvas.addEventListener('mousemove', mousemove);
}
function mousemove(e) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(startP.x, startP.y);
// 设置线段终点
endP = { x: e.clientX - (window.innerWidth - 800) / 2, y: e.clientY };
console.log(JSON.stringify(startP) + ',' + JSON.stringify(endP));
// 告诉画笔线段终点位置
ctx.lineTo(endP.x, endP.y);
// 画线段
ctx.stroke();
// 将下一条线段七点设置为当前线段的终点
startP = endP;
ctx.moveTo(startP.x - (window.innerWidth - 800) / 2, startP.y);
}
function mouseup(e) {
console.log('Mouse up.');
canvas.removeEventListener('mousemove', mousemove);
//clearInterval(interval);
}
function mouseleave(e) {
canvas.removeEventListener('mousemove', mousemove);
console.log('Mouse leave.')
}
const color_picker = document.getElementById('color_picker');
color_picker.onchange = function (e) {
console.log('Color changed to.' + color_picker.value);
// 改变画笔颜色
ctx.strokeStyle = color_picker.value;
};
const clear_button = document.getElementById('clear_button');
clear_button.onclick = function (e) {
// 清空画板
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
}
</script>
2、温习
(1)canvas API
菜鸟教程


MDN
Document.getElementById() 方法获取HTML 元素的引用。接着,HTMLCanvasElement.getContext() 方法获取这个元素的context——图像稍后将在此被渲染。
(2)元素获取
document.getElementById(‘输入ID’);通过ID获取
document.querySelector();HTML5新增方法
该方法’.box’获取类,’#nav’获取id,'li’直接获取标签。
(3)鼠标事件与方法监听
上述代码用到了鼠标按下、鼠标抬起、移出元素
// 添加 mousedown 事件
canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', mousedown);
// 添加 mouseup 事件
canvas.addEventListener('mouseup', mouseup);
// 添加 mouseleave 事件
canvas.addEventListener('mouseleave', mouseleave);
总结
还有很多生疏的地方,参考于CSDN