React源码解析————ReactHooks(二)
2021SC@SDUSC
2021SC@SDUSC
ReactHooks
这一次我们将从mount开始,解析ReactHooks,并且将重点围绕四个重点hooks展开,分别是负责组件更新的useState,负责执行副作用useEffect ,负责保存数据的useRef,负责缓存优化的useMemo, 至于useCallback,useReducer原理和那四个重点hooks比较相近,就简单提一嘴,不会再详细解释了。
mountWorkInProgressHook
在组件初始化的时候,每一次hooks执行,如useState(),useRef(),都会调用mountWorkInProgressHook,mountWorkInProgressHook到底做了写什么,让我们一起来分析一下:
function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
mountWorkInProgressHook这个函数做的事情很简单,首先每次执行一个hooks函数,都产生一个hook对象,里面保存了当前hook信息,然后将每个hooks以链表形式串联起来,并赋值给workInProgress的memoizedState。也就证实了上述所说的,函数组件用memoizedState存放hooks链表。
至于hook对象中都保留了那些信息?我这里先分别介绍一下 :
memoizedState: useState中 保存 state 信息 | useEffect 中 保存着 effect 对象 | useMemo 中 保存的是缓存的值和 deps | useRef 中保存的是 ref 对象。
baseQueue : usestate和useReducer中 保存最新的更新队列。
baseState : usestate和useReducer中,一次更新中 ,产生的最新state值。
queue : 保存待更新队列 pendingQueue ,更新函数 dispatch 等信息。
next: 指向下一个 hooks对象。
那么当我们函数组件执行之后,四个hooks和workInProgress将是如图的关系。
下面这个图是从网上找的,如果作者看到请联系我,我会加上出处。
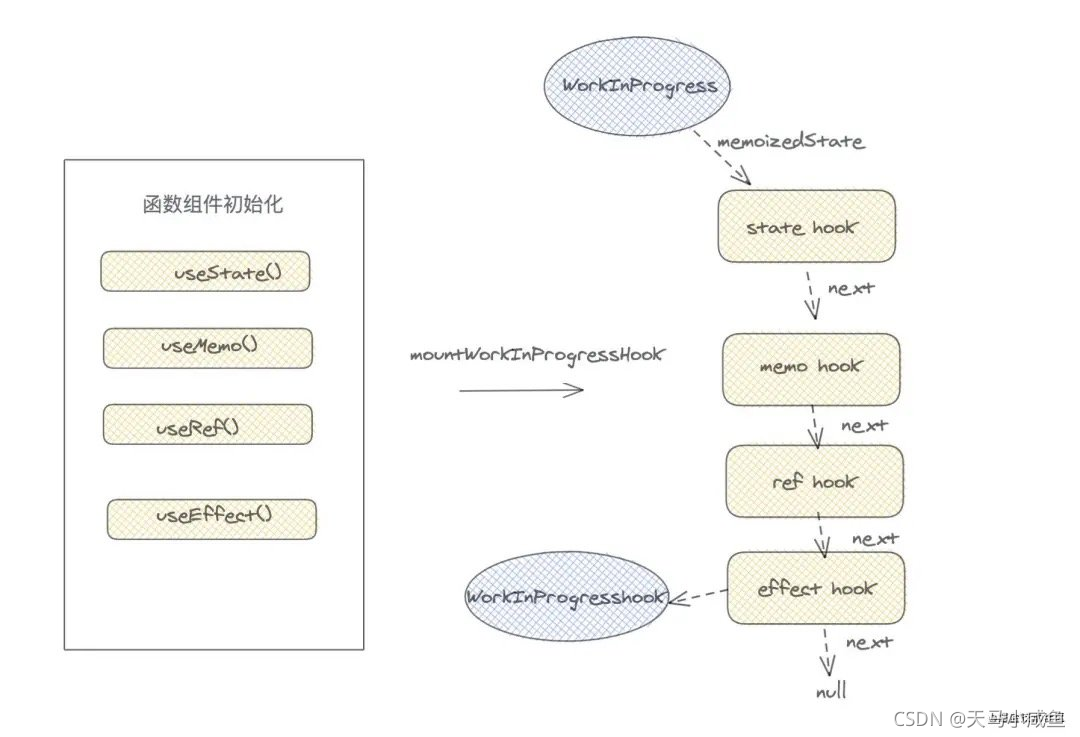
mountState
function mountState(
initialState
){
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
// 如果 useState 第一个参数为函数,执行函数得到state
initialState = initialState();
}
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue = (hook.queue = {
pending: null, // 带更新的
dispatch: null, // 负责更新函数
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer, //用于得到最新的 state ,
lastRenderedState: initialState, // 最后一次得到的 state
});
const dispatch = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind( // 负责更新的函数
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
)))
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
mountState到底做了些什么,首先会得到初始化的state,将它赋值给mountWorkInProgressHook产生的hook对象的 memoizedState和baseState属性,然后创建一个queue对象,里面保存了负责更新的信息。
在无状态组件中,useState和useReducer触发函数更新的方法都是dispatchAction,useState,可以看成一个简化版的useReducer,至于dispatchAction怎么更新state,更新组件的,我们接着往下研究dispatchAction。
在研究之前 我们先要弄明白dispatchAction是什么?
function dispatchAction<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
)
const [ number , setNumber ] = useState(0)
dispatchAction 就是 setNumber , dispatchAction 第一个参数和第二个参数,已经被bind给改成currentlyRenderingFiber和 queue,我们传入的参数是第三个参数action
dispatchAction 无状态组件更新机制
function dispatchAction(fiber, queue, action) {
// 计算 expirationTime 过程略过。
/* 创建一个update */
const update= {
expirationTime,
suspenseConfig,
action,
eagerReducer: null,
eagerState: null,
next: null,
}
/* 把创建的update */
const pending = queue.pending;
if (pending === null) { // 证明第一次更新
update.next = update;
} else { // 不是第一次更新
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
queue.pending = update;
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
/* 判断当前是否在渲染阶段 */
if ( fiber === currentlyRenderingFiber || (alternate !== null && alternate === currentlyRenderingFiber)) {
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = true;
update.expirationTime = renderExpirationTime;
currentlyRenderingFiber.expirationTime = renderExpirationTime;
} else { /* 当前函数组件对应fiber没有处于调和渲染阶段 ,那么获取最新state , 执行更新 */
if (fiber.expirationTime === NoWork && (alternate === null || alternate.expirationTime === NoWork)) {
const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer;
if (lastRenderedReducer !== null) {
let prevDispatcher;
try {
const currentState = queue.lastRenderedState; /* 上一次的state */
const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action); /**/
update.eagerReducer = lastRenderedReducer;
update.eagerState = eagerState;
if (is(eagerState, currentState)) {
return
}
}
}
}
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, expirationTime);
}
}
无论是类组件调用setState,还是函数组件的dispatchAction ,都会产生一个 update对象,里面记录了此次更新的信息,然后将此update放入待更新的pending队列中,dispatchAction第二步就是判断当前函数组件的fiber对象是否处于渲染阶段,如果处于渲染阶段,那么不需要我们在更新当前函数组件,只需要更新一下当前update的expirationTime即可。
如果当前fiber没有处于更新阶段。那么通过调用lastRenderedReducer获取最新的state,和上一次的currentState,进行浅比较,如果相等,那么就退出,这就证实了为什么useState,两次值相等的时候,组件不渲染的原因了,这个机制和Component模式下的setState有一定的区别。
如果两次state不相等,那么调用scheduleUpdateOnFiber调度渲染当前fiber,scheduleUpdateOnFiber是react渲染更新的主要函数。
我们把初始化mountState和无状态组件更新机制讲明白了,接下来看一下其他的hooks初始化做了些什么操作?
mountEffect
当我们调用useEffect的时候,在组件第一次渲染的时候会调用mountEffect方法,这个方法到底做了些什么?
function mountEffect(
create,
deps,
) {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
hook.memoizedState = pushEffect(
HookHasEffect | hookEffectTag,
create, // useEffect 第一次参数,就是副作用函数
undefined,
nextDeps, // useEffect 第二次参数,deps
);
}
每个hooks初始化都会创建一个hook对象,然后将hook的memoizedState保存当前effect hook信息。
有两个memoizedState大家千万别混淆了
1.workInProgress / current 树上的 memoizedState 保存的是当前函数组件每个hooks形成的链表。
2.每个hooks上的memoizedState 保存了当前hooks信息,不同种类的hooks的memoizedState内容不同。
pushEffect
function pushEffect(tag, create, destroy, deps) {
const effect = {
tag,
create,
destroy,
deps,
next: null,
};
let componentUpdateQueue = currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue
if (componentUpdateQueue === null) { // 如果是第一个 useEffect
componentUpdateQueue = { lastEffect: null }
currentlyRenderingFiber.updateQueue = componentUpdateQueue
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
} else { // 存在多个effect
const lastEffect = componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect;
if (lastEffect === null) {
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect.next = effect;
} else {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
lastEffect.next = effect;
effect.next = firstEffect;
componentUpdateQueue.lastEffect = effect;
}
}
return effect;
}
首先创建一个 effect ,判断组件如果第一次渲染,那么创建 componentUpdateQueue ,就是workInProgress的updateQueue。然后将effect放入updateQueue中。
mountReducer
function mountReducer<S, I, A>(
reducer: (S, A) => S,
initialArg: I,
init?: I => S,
): [S, Dispatch<A>] {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
let initialState;
if (init !== undefined) {
initialState = init(initialArg);
} else {
initialState = ((initialArg: any): S);
}
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue: UpdateQueue<S, A> = {
pending: null,
interleaved: null,
lanes: NoLanes,
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: reducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
};
hook.queue = queue;
const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
): any));
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
初始化useReducer和初始化useState很相似,从本质来说,useState 不过就是预置了 reducer 的 useReducer,(所以mountReducer我们不再赘述),通过源码对比,我们能看到 mountState 和 mountReducer 的区别就是 queue 中 lastRenderedReducer 字段
//mountReducer:
const queue = (hook.queue = {
// 与极简实现中的同名字段意义相同,保存update对象
pending: null,
// 保存dispatchAction.bind()的值
dispatch: null,
// 上一次render时使用的reducer
lastRenderedReducer: reducer,
// 上一次render时的state
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
});
//mountState:
const queue = (hook.queue = {
pending: null, // 带更新的
dispatch: null, // 负责更新函数
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer, //用于得到最新的 state ,
lastRenderedState: initialState, // 最后一次得到的 state
});
mountReducer 的 lastRenderedReducer 接收的就是传入你自定义的 reducer;而 mountState 接收的 lastRenderedReducer 是一个预置的 basicStateReducer。
下面我们来看看 basicStateReducer 的实现
function basicStateReducer<S>(state: S, action: BasicStateAction<S>): S {
// $FlowFixMe: Flow doesn't like mixed types
return typeof action === 'function' ? action(state) : action;
}
这也直接证明了 useState 即 reducer 为 basicStateReducer 的 useReducer。
mountMemo
function mountMemo<T>(
nextCreate: () => T,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): T {
// 创建并返回当前hook
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
// 计算value
const nextValue = nextCreate();
// 将value与deps保存在hook.memoizedState
hook.memoizedState = [nextValue, nextDeps];
return nextValue;
}
初始化useMemo,就是创建一个hook,然后执行useMemo的第一个参数,得到需要缓存的值,然后将值和deps记录下来,赋值给当前hook的memoizedState。整体上并没有复杂的逻辑。
mountCallback
function mountMemo<T>(
nextCreate: () => T,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): T {
// 创建并返回当前hook
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
// 计算value
const nextValue = nextCreate();
// 将value与deps保存在hook.memoizedState
hook.memoizedState = [nextValue, nextDeps];
return nextValue;
}
function mountCallback<T>(callback: T, deps: Array<mixed> | void | null): T {
// 创建并返回当前hook
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
// 将value与deps保存在hook.memoizedState
hook.memoizedState = [callback, nextDeps];
return callback;
}
可以看到,与mountCallback这两个唯一的区别是
1.mountMemo会将回调函数(nextCreate)的执行结果作为value保存
2.mountCallback会保存回调函数果作为value保存
mountRef
function mountRef(initialValue) {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const ref = {current: initialValue};
hook.memoizedState = ref;
return ref;
}
mountRef初始化很简单, 创建一个ref对象, 对象的current 属性来保存初始化的值,最后用memoizedState保存ref,完成整个操作。
总结
我们来总结一下初始化阶段,react-hooks做的事情,在一个函数组件第一次渲染执行上下文过程中,每个react-hooks执行,都会产生一个hook对象,并形成链表结构,绑定在workInProgress的memoizedState属性上,然后react-hooks上的状态,绑定在当前hooks对象的memoizedState属性上。对于effect副作用钩子,会绑定在workInProgress.updateQueue上,等到commit阶段,dom树构建完成,在执行每个 effect 副作用钩子。