前言
在B站上看了js的视频,一边看一边写笔记,好记性不如烂笔头,总结了一些比较常用的知识点。发到csdn上就当作备份。前面的一些较简单所以没有写,只写了一些我认为容易忘记的知识点,有错的地方欢迎指点。总字数:6666字
JavaScript
1.数值转换
Boolean() // 布尔型 非0即真
Number() // 转换为数字 只有纯数字字符串才能转,不然就是NaN
parseInt() // 转换为int 取整3.14->3 为字符串时100a->100 开头不是数字则NaN
// 转换为十进制 parseInt(nmuber,进制)
parseFloat() // 转换为float 取浮点数
Math.ceil() // 向上取整 3.1->4
2.作用域
查找变量从最近父级查找,逐层向上
let 作用域为最近{}内
3.存储数据
对象数据类型,键值对集合,json
4.数组
1.设置数组长度
// 例子:数组length-1 =>作用:可以用来删除最后的元素
arr.length = 长度
2.从后面加数据
// 返回数组长度
push(value)
3.在前面加数据
// 返回长度
unshift(value)
4.删除最后一个
// 返回被删除的元素
pop()
5.删除第一个
// 返回被删除的元素
shift()
6.数组反转
// 返回反转后的数组
reverse()
7.删除若干数据
// 删除若干数据,并选择是否插入。默认值(0,0,没有) 返回新数组(被删除的数据)
splice(开始索引,多少个,value)
8.数组排序
// 什么都不传就两个两个换。返回排序好的数组
sort() //例如:1,2,3,4 => 2,1,4,3
// 从小到大排序
sort(function(a,b){return a - b})
// 从大到小排序
sort(function(a,b){return b - a})
9.拼接成字符串
// join(连接符)。将数组用连接符连接成字符串,返回字符串
join('-') // 例如:1,2,3 => 1-2-3
10.拼接数组
// concat(其他数组)将其他数组与数组拼接。返回拼接好的数组
arr1.concat(arr2)
11.截取数组
// 默认(0,数组长度),返回截取的新数组,包前不包后
slice(开始索引,结束索引)
11.查找value在数组的索引
// 有该数据则返回第一次出现的索引。没有则返回-1
indexOf(value)
12.遍历数组
// item 是数组每一个元素,index 是索引,arr是数组。参数可以不写,没有返回值
forEach(function(item,index,arr){})
13.映射数组
// 返回新的数组
map(function(item,index,arr){return item*10}) // 将数组每一个元素*10
14.过滤数组
// 返回过滤好的新数组
filter(function(item,index,arr){return item>150}) // 将数组小于150的元素删除
15.判断是否每一项都满足条件
// 返回布尔值
every(function(item,index,arr){return item>150}) // 判断是否大于150
16.判断是否有某一项都满足条件
// 返回布尔值
some(function(item,index,arr){return item>150}) // 判断是否有满足大于150的元素
5.字符串
1.获取对应索引位置的字符
// 返回字符
charAt(索引)
2.将字符串的所有字母转换成小写
// 返回转好的字符串
toLowerCase()
3.将字符串的所有字母转换成大写
// 返回转好的字符串
toUpperCase()
4.将字符串第一个满足的内容更换
// 返回字符串。注意:第一个
replace(换下内容,换上内容)
5.去除首尾空格
// 返回字符串
trim()
6.按照分隔符切割组成一个数组
// 返回数组
split(分隔符)
// 多个分隔符(x,y是分隔符)
split(/x|y/)
// 若分隔符是. 要加[]
split(/[.]|y/)
7.截取字符串
有三个方法:
substr(开始索引,个数)
substring(开始索引,结束索引)
slice(开始索引,结束索引)
// 示例
var arr = "01234567"
var res1 = substr(1,6) // 结果为123456,1是开始索引,6是6个字符
var res2 = substring(1,6) // 结果12345,1是开始索引,6是结束索引。包前不包后
var res3 = slice(1,6) // 结果12345,1是开始索引,6是结束索引。包前不包后
6.数字常用方法
1.获取0~1之间的随机小数。
// 返回小数。包前不包后,即可以获取到0,不可以获取到1
Math.random()
2.对数字进行四舍五入取整
// 返回整数
Math.round(value)
3.对数字进行向上取整
// 返回整数
Math.ceil(value)
4.对数字进行向下取整
// 返回整数。相对于去小数
Math.floor(value)
5.对数字进行取幂运算
// 返回结果
Math.pow(底数,指数)
// 例如2的5次方
Math.pow(2,5)
6.对数字进行二次方根运算
// 返回结果
Math.sqrt(value)
// 例如根号4
Math.sqrt(4)
7.对数字进行绝对值运算
// 返回结果
Math.abs()
8.获取若干数字中的最大值
// 返回最大值。
Math.max(value1,value2,...)
9.获取若干数字中的最小值
// 返回最小值。
Math.min(value1,value2,...)
10.得到一个近似Π(派:3.14159…)的值
// 返回值
Math.PI
11.示例:
// 获取0~x之间的随机整数,
var a = Math.random()*(x+1)
var result = Math.floor(a)
// 获取x~y之间的随机整数
var b = Math.random()*(y-x+1)
var result1 = Math.floor(b)+x
7.时间常用方法
var time = new data()
time.getFullYear() // 获取年
time.getMonth() // 获取月份
time.getDate() // 获取日期
time.getHours() // 获取小时
time.getMinutes() // 获取分钟
time.getSeconds() // 获取秒
time.getDay() // 获取星期 0~6 周日到周六
time.getTime() // 获取时间戳 1970/1/1 00:00:00 距离今天的毫秒
// 获取时间差函数
function getDiff(time1,time2){
// 获取时间戳
var ms1 = time1.getTime()
var ms1 = time1.getTime()
// 两个时间戳相减的秒数,向上取整忽略毫秒
var sub = Math.celi((ms2-ms1)/1000)
//换算,向下取整
var day = Math.floor(sub / (60 * 60 * 24))
var hours = Math.floor(sub % (60 * 60 *24) / (60 * 60))
var minutes = Math.floor(sub % (60*60) / 60)
var seconds = sub % 60
return {day:day,hours:hours,minutes:minutes,seconds:seconds}
}
8.BOM操作
操作浏览器
8.1获取浏览器窗口尺寸
// 获取浏览器可视窗口的宽度 包括滚动条
window.innerWidth
// 获取浏览器可视窗口的高度
window.innerHeight
8.2 浏览器的弹出层
// 提示框
window.alert('value')
// 询问框 有返回值,确定true,取消false
window.confirm('value')
// 输入框 有返回值,确定输入的东西,取消null
window.prompt('value')
8.3 开启和关闭标签页
// 开启
window.open('地址/url')
// 关闭当前
window.close()
8.4 浏览器常见事件
// 资源加载完毕
window.onload = function(){}
//可视尺寸改变
window.onresize = function(){}
// 滚动条位置改变
window.onscroll = function(){}
8.5 浏览器的历史记录操作
// 回退页面
window.history.back()
// 前进页面
window.history.forward()
8.6 浏览器卷去的尺寸
有滚动条时,页面隐藏的部分尺寸
// 卷去的高度
document.documentElement.scrollTop //页面有<!DOCTYPE html>
document.body.scrollTop //页面没有<!DOCTYPE html>
//卷去的宽度
document.documentElement.scrollLeft
document.body.scrollLeft
// 卷去的高度/宽度 兼容写法
var height = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop
8.7 浏览器滚动到
// left 浏览器卷去的宽度, top 浏览器卷去的高度 ,瞬间移动
window.scrollTo(left,top)
//平滑滚动
window.scrollTo({
left:xx,
top:yy,
behavior:'smooth' //平滑滚动
})
9.定时器
有返回值,返回第几个定时器,不区分定时器类型
1.间隔定时器(按照指定周期毫秒,去执行指定代码)
setInterval(function(){
// 要执行的代码
},1000)
2.延时定时器(在固定的时间毫秒后执行一次代码)
setTimeout(function(){
// 要执行的代码
},1000)
3.关闭定时器,不区分定时器类型
// 语法一
clearInterval(要关闭的定时器返回值)
// 语法二
clearTimeout(要关闭的定时器返回值)
10.DOM
操作文档流相关内容的属性和方法
10.1 获取元素
// 根据id获取元素。有-对应元素,没有-null
document.getElementById('id名称')
// 根据类名获取元素。获取文档流中所有类名对应的元素,返回伪数组
document.getElementsByClassName('类名')
// 根据元素标签名获取。获取文档流中所有标签名对应的元素,返回伪数组
document.getElementsByTagName('标签名')
// 根据选择器获取一个,获取文档流中满足条件的第一个元素
document.querySelector('选择器') //选择器 .nav
// 根据选择器选择一组,获取文档流中所有满足条件的元素,返回伪数组
document.querySelectorAll('选择器')
10.2 操作元素内容
// 文本内容
// 获取
元素.innerText
//设置 覆盖/替换
元素.innerText = '新内容'
// 超文本内容
//获取
元素.innerHTML
//设置 覆盖/替换
元素.innerHTML = '新内容'
10.3 操作元素属性
// 原生属性(标签自带的属性)
//获取
元素.属性
//设置
元素.属性 = '新内容'
// 自定义属性(自己设定的一些属性)
//获取
元素.getAttribute('属性名')
//设置
元素.setAttribute('属性名','属性值')
//删除
元素.removeAttribute('属性名')
// 注意:以上方法一般不用做操作元素 类名 和 样式
10.4 操作元素类名
//获取
元素.className
//设置
元素.className = '新类名'
10.5 操作元素行内样式
// 获取
元素.style.样式名
// 设置
元素.style.样式名 = '样式值' //有中划线-的样式,写成驼峰,如backgroundColor
10.6 获取元素非行内样式
// 获取 可以获取非行内样式,也可以获取行内样式,只能获取不能设置
window.getComputedStyle(元素).样式名
10.7 节点操作
// 创建节点,创建一个指定的标签元素,返回节点
document.createElement('标签名称')
// 插入节点向后插入,把子节点放在父节点的内部,并且放在最后的位置
父节点.appendChild(子节点)
// 插入节点向前插入,把子节点放在父节点的内部,放在指定位置
父节点.insertBefore(要插入的子节点,哪个子节点前面)
// 删除节点,删除指定的节点
父节点.removeChild(子节点)
// 删除节点
节点.remove()
// 替换节点
父节点.replaceChild(换上节点,换下节点)
// 克隆节点 true/false
节点.cloneNode(是否克隆后代节点)
// 1.获取元素尺寸,元素 内容 + padding + border 区域的尺寸
元素.offsetHeight
元素.offsetWidth
// 2.获取元素尺寸,元素 内容 + padding 区域的尺寸
元素.clientHeight
元素.clientWidth
11.事件类型
- 图错误点:contextmenu 是右键单击
事件对象,有函数提供,在函数里面用形参接收即可
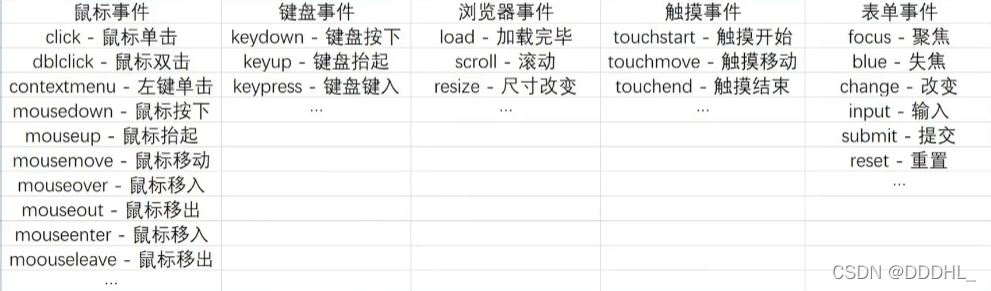
补充:
offsetX 和 offsetY 相对于促发事件元素,鼠标的坐标信息
clientX 和 clientY 相对于可视窗口,鼠标的坐标信息
pageX 和 pageY 相对于整个页面文档流,鼠标的坐标信息
2.浏览器相应事件的机制

先从外层传递到里层(事件捕获阶段),最后传出来(事件冒泡阶段)
3.阻止事件传播
事件对象.stopPropagation()
4.事件委托
使用事件对象的target可以知道点击的是哪个元素
ul.onclick = function(e){
if(e.target.tagName === 'LI'){
console.log('你点击的是LI')
}
}
12.面向对象
创建工厂
构造函数 首字母大写 与new连用 (内置构造函数Object)
不要随便return。return基本数据类型无效;return复杂数据类型比如数组,构造函数无效。
function Person(){
this.name = 'jack'
}
var obj = new Person() // 小括号不写也行,不推荐不写
如果构造函数里面有函数,每个对象都会新建一个函数
解决方案:使用原型prototype属性,是一个对象。
属性写在构造函数体内,方法写在构造函数的原型上,如果属性不变,也写在原型上
// 所有实例化对象都会加上这个方法
function Person(){}
Person.prototype.sayHi = function(){} //sayHi 方法名
Person.prototype.a = 110
13.原型链
用 "proto"串联起来的对象链状结构
对象访问机制:先去自己身上找,没有就去proto上找,逐级查找 最高级Object的proto,没有就返回undefined
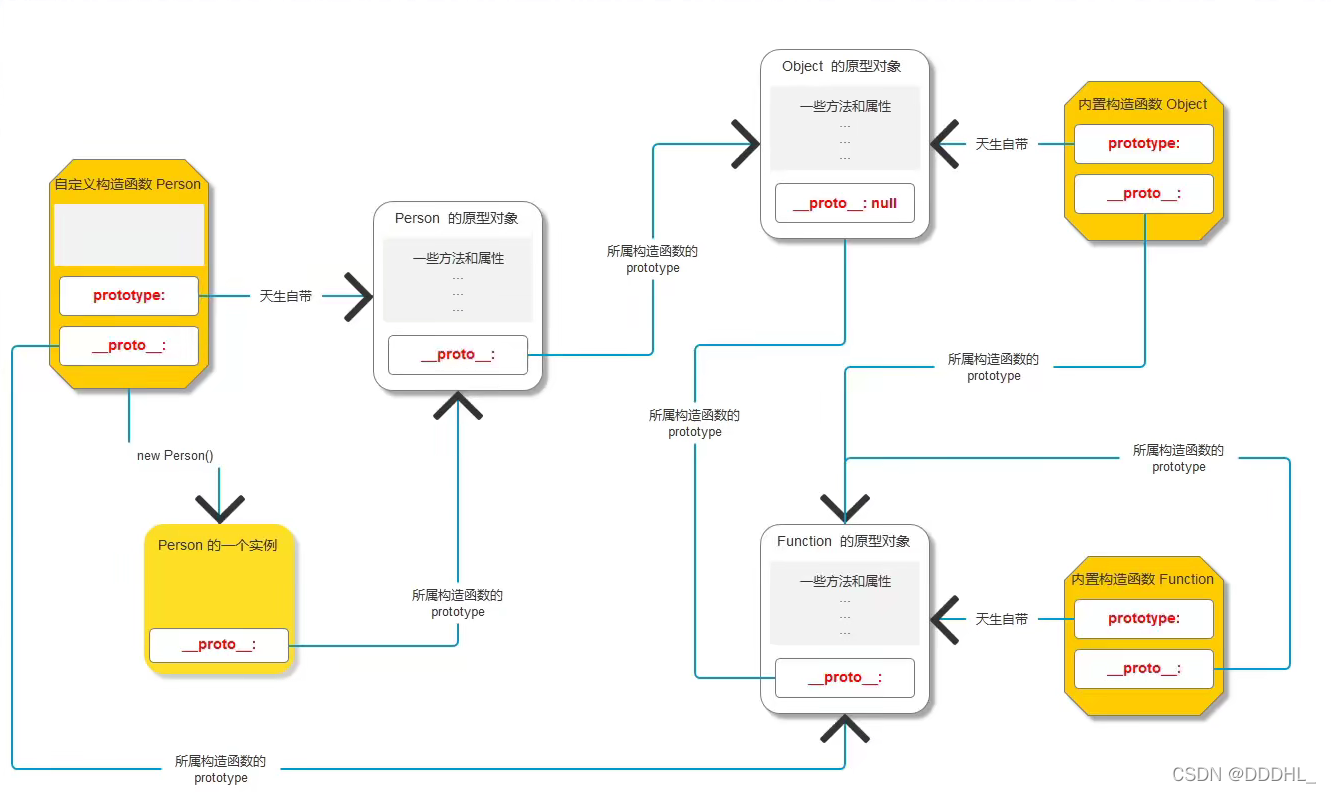
14.ES6
14.1 新增变量命名
ES6以前用var ES6新增let/const
var 函数作用域

14.2 箭头函数
ES6对函数表达式的简写(声明式函数不能使用)就是把function变成=>
var fn1 = function(){}
var fn1 = ()=>{}
// 1.只有一个形参时,可以不写()
var fn1 = function(a){}
var fn1 = a=>{}
// 2.只有一句话时,可以不写{} 会把这句话的结果当做返回值
var fn1 = function(a,b){return a+b}
var fn1 = (a,b)=> a+b
// 3.箭头函数没有arguments
// 4.箭头函数内部没有this,用的是外部作用域的this
14.3 解构赋值
// 解构数组,使用[]
let arr[a,b] = ['1','2']
console.log(a) // 1
console.log(b) // 2
// 解构对象,使用{}
let obj = {name:lhd, id:10}
let{name,id} = obj
console.log(name) //lhd
console.log(id) //10
// 解构对象起别名
let{name:a} = obj //a=lhd
14.4 模板字符串
可以换行,直接在字符串内解析变量
var str = `ab`
var str = `a
b`
// 解析变量
var age = 18
var str = `我今年${age}岁` // 输出我今年18岁
14.5 展开运算符
展开数组 = 去除[]
var arr = [1,2,3]
console.log(arr) //输出数组
console.log(...arr) //输出1,2,3
// 作用1:合并数组
var arr = [1,2,3]
var arr1 = [4,5,6]
var arr2 = [...arr,...arr1] // 输出数组[1,2,3,4,5,6]
// 作用2:给函数传递参数
var arr1 = [10,20,5,6]
var max = Math.max(...arr1) //输出最大值,max()不能直接放数组
展开对象 = 去除{}
// 作用1:用来复制对象。注意:有相同成员,...obj要放在前面,不然会被obj的覆盖
var obj = {name:lhd}
var obj1 = {
id:10,
...obj
}
14.6 类语法
ES6的语法写构造函数,解决之前写构造函数需要分开写的缺点
// 之前的写法
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.sayHi = function(){ console.log('hello world')}
// 静态属性与方法
Person.a = 100
Person.go = function(){ console.log('go') }
// 实例化对象
var p1 = new Person('lhd','19')
console.log(p1) // 输出对象
p1.sayHi() // 输出hello world
console.log(p1.a) // 输出100
Person.go() // 输出go
var p2 = Person('lhd','19') // 注意:不报错,但不能实例化对象
// ES6 写法
class Person{
// 这里按照 ES5 的构造函数体书写
constructor(name,age){
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
// 直接写原型的函数
sayHi(){ console.log('hello world')}
// 静态属性 + static
static a = 100
// 静态方法
static go() = function(){ console.log('go') }
}
// 实例化对象
var p1 = new Person('lhd','19')
console.log(p1)
p1.sayHi()
var p2 = Person('lhd','19') // 注意:报错,一定要用new
console.log(Person.a)
Person.go()
15.立即执行函数
立即执行函数前面的语句必须有分号
(function(){
// xx
}())
16.请求接口
后端给予接口文档,按照接口文档写
16.1 Ajax
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('GET','XXX',true) //请求方式、请求地址、是否异步
xhr.onload = function(){
//返回的是字符串
console.log(xhr.responseText)
//想拿json,要解析
var res = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText)
}
xhr.send()
16.2 GET和POST的区别
GET直接在open函数地址内拼接
xhr.open('GET','xxx?name=lhd&id=10',true) //请求方式、请求地址、是否异步
POST在send函数内写参数,并且要特殊说明
// 语法:xhr.setRequestHeader('content-type',你传递的参数格式) 后端给参数格式
xhr.setRequestHeader('content-type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
xhr.send('name='+lhd+'&id='+age)
16.3 阻止form表单的默认提交行为
loginForm.onsubmit = function(e){
e.preventDefault()
}
17.jQuery
一个大型的简单的第三方类库,对DOM操作进行封装,引入后暴露两个全局变量 $ 和 jquery
17.1 选择器
(返回元素集合)
$('选择器')
17.2 筛选器
$('选择器').筛选器名称()

17.3 操作文本内容
$(‘div’) = 选中div
3.1 html() 等价于原生 JS 的 innerHTML
// 获取
$('div').html()
// 设置
$('div').html('你要设置的内容')
// 可以识别并解析 html 结构字符串
$('div').html('<h2>hello world<h2>')
3.2 text() 等价于原生 JS 的 innerText
// 获取
$('div').text()
// 设置 不可以解析
$('div').text('hello world')
3.3 val() 等价于原生 JS 中 value
// 获取
$('input').val()
// 设置
$('input').val('你要设置的内容')
17.4 操作元素类名
4.1 addClass() 新增类名
$('div').addClass('要添加的类名')
4.2 removeClass() 删除类名
$('div').removeClass('要删除的类名')
4.3 toggleClass() 切换类名
本身有这个类名,那就是删除,如果本身没有这个类名,那就是添加
// 假设div中有a b c d 三个类名
var btn = document.querySelector('button')
btn.onclick = function(){
$('div').toggleClass('box')
}
// 点击一次,添加box到class中,点击第二次,删除box
17.5 操作元素样式
1.css()
// 获取,可以获取行内和非行内样式。
// 元素集合.css(你要获取的样式名称)
$('div').css('width') //获取div的宽
//设置,注意:样式单位是 px 时,可以省略 px
//元素集合.css(样式名,样式值)
$('div').css('width', '300px') //设置div宽为300px
$('div').css('width', 300)
2.css 批量设置样式
// 元素集合.css({ 所有要设置的样式 })
$('div').css({
width:260,
height:320,
'background-color':'purple'
})
17.6 操作元素属性
1.arrt()
// 一般用于操作元素的自定义属性。直接出现在元素的标签里
// 获取自定义属性hello
$('div').attr('hello')
// 设置自定义属性hello
$('div').attr('hello') = 100
2.removeAttr()
// 删除自定义属性hello
$('div').removeAttr('hello')
3.prop()
// 操作元素原生属性时,会直接出现在元素标签里
// 操作自定义属性时,不会直接出现在元素标签里,会响应在元素对象上
// 注意:prop()不能获取元素标签上原有的自定义属性,只能获取prop()自己设定的自定义属性
// 获取原生和自定义属性
$('div').prop('id')
$('div').prop('hello')
// 设置原生和自定义属性
$('div').prop('id') = 1
$('div').prop('hello') = 100
4.removeProp()
// 不能删除原有的自定义属性和原生属性,只能删除prop()设定的自定义属性
$('div').prop('hello') = 100
$('div').removeProp('hello')
17.7 获取元素尺寸

1.width()、height()
// 获取内容区域的尺寸
$('div').width() // 300
$('div').height() // 300
2.innerWidth()、innerHeight()
// 获取内容和 padding 区域尺寸
$('div').innerWidth() // 340
$('div').innerHeight() // 340
3.outerWidth()、outerHeight()
// 获取内容、padding 和 border 区域尺寸
$('div').outerWidth() // 380
$('div').outerHeight() // 380
4.outerWidth(true)、outerHeight(true)
// 获取内容、padding 、border 和 margin 尺寸
// 假设设定margin为20px
$('div').outerWidth(true) // 420
$('div').outerHeight(true) // 420
17.8 获取元素偏移量
1.offset()
// 获取元素相对于页面左上角的坐标位置
// 返回值是对象数据类型 {top:xx,left:xx}
$('div').offset()
2.position()
// 获取元素定位的位置
// 返回值是对象数据类型 {top:xx,left:xx}
// 注意:如果定位设置的是right,bottom,会自动转成top,left
$('div').position()
17.9 绑定事件
1.on()
1-1 基础绑定事件
// 语法:元素集合.on('事件类型','事件处理函数')
$('div').on('click',function(){ console.log('点击div') })
1-2 事件委托绑定事件
// 语法:元素集合.on('事件类型',选择器,事件处理函数)
// 把事件绑定给 div 元素,当你在 div 内的 p 元素触发事件时,执行事件处理函数
// 相对于把 p 元素的事件委托给 div 元素来绑定
$('div').on('click','p',function(){ console.log('点击p') })
1-3 批量绑定事件
// 语法:元素集合.on({事件类型1:处理函数, 事件类型2:处理函数})
// 注意:不能进行事件委托了
$('div').on({
click: function(){ console.log('鼠标点击') }
mouseover: function(){ console.log('鼠标移入') }
mouseout: function(){ console.log('鼠标移出') }
})
2.one()
one() 与 on() 绑定事件的方式一样,区别就是 one() 只能执行一次
2-1 基础绑定事件
$('div').one('click', function(){ console.log('只触发一次') })
2-2 事件委托
$('div').one('click','p', function(){ console.log('只触发一次') })
2-2 批量绑定事件
$('div').one({
click: function(){ console.log('鼠标点击,只触发一次') }
mouseover: function(){ console.log('鼠标移入,只触发一次') }
mouseout: function(){ console.log('鼠标移出,只触发一次') }
})
3.hover()
jQuery 里面一个特殊的事件
// 语法:元素集合.hover(移入时触发的函数,移出时触发的函数)
// 只传一个函数时,会在移入移出都触发这个函数
$('div').hover(
function (){ console.log('鼠标移入') }
function (){ console.log('鼠标移出') }
)
4.常用事件函数
jQuery 把我们最常用的一些事件,单独做成了事件函数
我们通过调用这些事件函数,来达到绑定事件的效果
如 click(),mouseover(),mouseout(),change() …
$('div').click(function(){ console.log('鼠标点击') })
17.10 事件的解绑和触发
1.off() 事件解绑
1-1 解绑全部事件处理函数
// 准备事件处理函数
function A() { console.log('A事件处理函数') }
function B() { console.log('B事件处理函数') }
function C() { console.log('C事件处理函数') }
// 给 div 元素绑定事件
$('div')
.click(A)
.click(B)
.click(C)
// 事件解绑 语法:元素集合.off(事件类型)
// 把 div 的 click 事件对应的所有事件处理函数全部移除
$('div').off('click')
1-2 解绑指定事件处理函数
// 语法:元素集合.off(事件类型,要解绑的事件处理函数)
// 会把 div 的 click 事件对应的 B 事件处理函数移除
$('div').off('click',B)
2.trigger() 事件触发
// 语法:元素集合.trigger(事件类型)
// 触发 div 元素的 click 事件处理函数
$('div').trigger('click')
17.11 基本动画
1.hide() 隐藏动画
2.show() 显示动画
3.toggle() 切换动画
? => 本身如果是显示的,就切换成隐藏
? => 本身如果是隐藏的,就切换成显示
三个函数都有三个参数,分布是运动时间、运动曲线、运动结束后的回调函数
// 1.只写一个参数:运动时间,单位ms
$('div').hide(1000)
$('div').show(1000)
$('div').toggle(1000)
// 2.参数都写上
$('div').hide(1000,'linear', function(){ console.log('动画结束') })
$('div').show(1000,'linear', function(){ console.log('动画结束') })
$('div').toggle(1000,'linear', function(){ console.log('动画结束') })
17.12 折叠动画
与上面动画的使用方法一致,只是隐藏和显示的效果不同
基本动画相对于把宽高都同时缩小到左上角,折叠动画则是只改变高度,由下向上缩小
1.slideDown() 隐藏动画
2.slideUp() 显示动画
3.slideToggle() 切换动画
? => 本身如果是显示的,就切换成隐藏
? => 本身如果是隐藏的,就切换成显示
三个函数都有三个参数,分布是运动时间、运动曲线、运动结束后的回调函数
// 1.只写一个参数:运动时间,单位ms
$('div').slideDown(1000)
$('div').slideUp(1000)
$('div').slideToggle(1000)
// 2.参数都写上
$('div').slideDown(1000,'linear', function(){ console.log('动画结束') })
$('div').slideUp(1000,'linear', function(){ console.log('动画结束') })
$('div').slideToggle(1000,'linear', function(){ console.log('动画结束') })
17.13 渐隐渐显动画
与上面动画的使用方法一致,只是隐藏和显示的效果不同
相对于改变透明度,让元素慢慢消失
1.fadeIn() 隐藏动画
2.fadeOut() 显示动画
3.fadeToggle() 切换动画
? => 本身如果是显示的,就切换成隐藏
? => 本身如果是隐藏的,就切换成显示
以上三个函数都有三个参数,分布是运动时间、运动曲线、运动结束后的回调函数
4.fadeTo(运动时间,指定透明度,运动曲线,回调函数) 改变元素的透明度为指定值
// 1.只写一个参数:运动时间,单位ms
$('div').fadeIn(1000)
$('div').fadeOut(1000)
$('div').fadeToggle(1000)
// 2.参数都写上
$('div').fadeIn(1000,'linear', function(){ console.log('动画结束') })
$('div').fadeOut(1000,'linear', function(){ console.log('动画结束') })
$('div').fadeToggle(1000,'linear', function(){ console.log('动画结束') })
// 3.fadeTo() 改变透明度
$('div').fadeTo(1000,0.68,'linear',function(){console.log('运动到指定透明度') })
17.14 综合动画函数
animate() 有四个参数
=>第一个:要运动的样式,以一个对象数据类型传递
=>第二个:运动时间
=>第三个:运动曲线
=>第四个:运动结束的回调函数
注意:关于 颜色 和 transform 相关的样式不能运动
$('div').animate({
width:500,
height:600
},1000,'linear',function(){console.log('运动结束')})
17.15 运动结束函数
不停点击按钮使动画变化时,会记录次数,即使你停下来也还在继续变化直到执行完所有次数
1.stop()
=>当任何一个元素执行了stop方法后,会立即结束当前所有运动。
=>目前运动到那什么位置,就停留在什么位置。
=>一般对于结束动画的时候,都是在运动开始之前
// 基本用法
$('div').stop()
// 假设有个按钮id为btn,点击切换动画
$("#btn").click(function(){
// 加上stop()后,连续点击,只要不点击了,就只执行到本次的结束,不会继续执行所有次数
$('div').stop().toggle(2000)
})
2.finish()
会立即结束当前所有运动,直接去到动画的结束位置
// 基本用法
$('div').finish()
// 利用完成动画函数书写动画函数
$("#btn").click(function(){
// 每一次触发时,都会把之前的动画瞬间完成,只执行本次最新的动画
$('div').finish().toggle(200)
})
17.16 ajax
语法:$.ajax({ 本次发送 ajax 的配置项 })
配置项:
1.url:必填,表示请求地址
2.method:选填,默认是 GET ,表示请求方式
3.data:选填,默认是 ’ ’ ,表示携带给后端的参数
5.dataType:选填,默认自动识别,表示后端返回给你的数据类型
6.async:选填,默认是 true,表示是否异步
7.success:选填,表示请求成功的回调函数
8.error:选填,表示请求失败的回调函数
// 演示 发送两个数据给后端
$.ajax({
url:'http://localhost:8888/test',
method:'POST',
data:{name:'lhd',id:'19'},
dataType:'JSON',
async:'true',
success:function(res){
console.log(res) //输出后端给你的json
}
})
总结:看视频写笔记养成好习惯