上代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body{
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
background-color: #333;
}
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-top: calc(50vh - 100px);
background-color: pink;
font-size: 20px;
line-height: 22px;
border: 10px solid red;
padding: 50px;
}
span{
color: blue;
}
b{
color: red;
}
/* .fa{
position: relative;
} */
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="fa">
<div class="box">
请把鼠标 放上来
</div>
</div>
<script>
document.querySelector(".box").addEventListener('mousemove',function(e){
console.dir(this);
// clientHeight: 200
// clientLeft: 0
// clientTop: 0
// clientWidth: 300
// offsetHeight: 200
// offsetLeft: 642
// offsetParent: body
// offsetTop: 137
// offsetWidth: 300
let clientWidth=this.clientWidth
let clientHeight=this.clientHeight
let clientLeft=this.clientLeft
let clientTop=this.clientTop
let offsetHeight=this.offsetHeight
let offsetWidth=this.offsetWidth
let offsetLeft=this.offsetLeft
let offsetTop=this.offsetTop
let offsetParent=this.offsetParent
this.innerHTML=`
<span>元素的可视区大小(padding+content)</span><br/>
clientWidth<b>${clientWidth}</b>,clientHeight<b>${clientHeight}</b><br/>
<span>元素可视区的位置(border的宽度)</span><br/>
clientLeft<b>${clientLeft}</b>,clientTop<b>${clientTop}</b><br/>
<span>元素的本身大小(border+padding+content)</span><br/>
offsetWidth<b>${offsetWidth}</b>,offsetHeight<b>${offsetHeight}</b><br/>
<span>元素的本身位置(根据定位元素)</span><br/>
offsetLeft<b>${offsetLeft}</b>,offsetTop<b>${offsetTop}</b><br/>
<span>元素的本身位置的 定位元素(定位元素 元素父级中 第一个 非static 的定位元素 都没有时候指向body)</span><br/>
offsetParent<b>${offsetParent.nodeName}</b><br/>
`
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
效果图
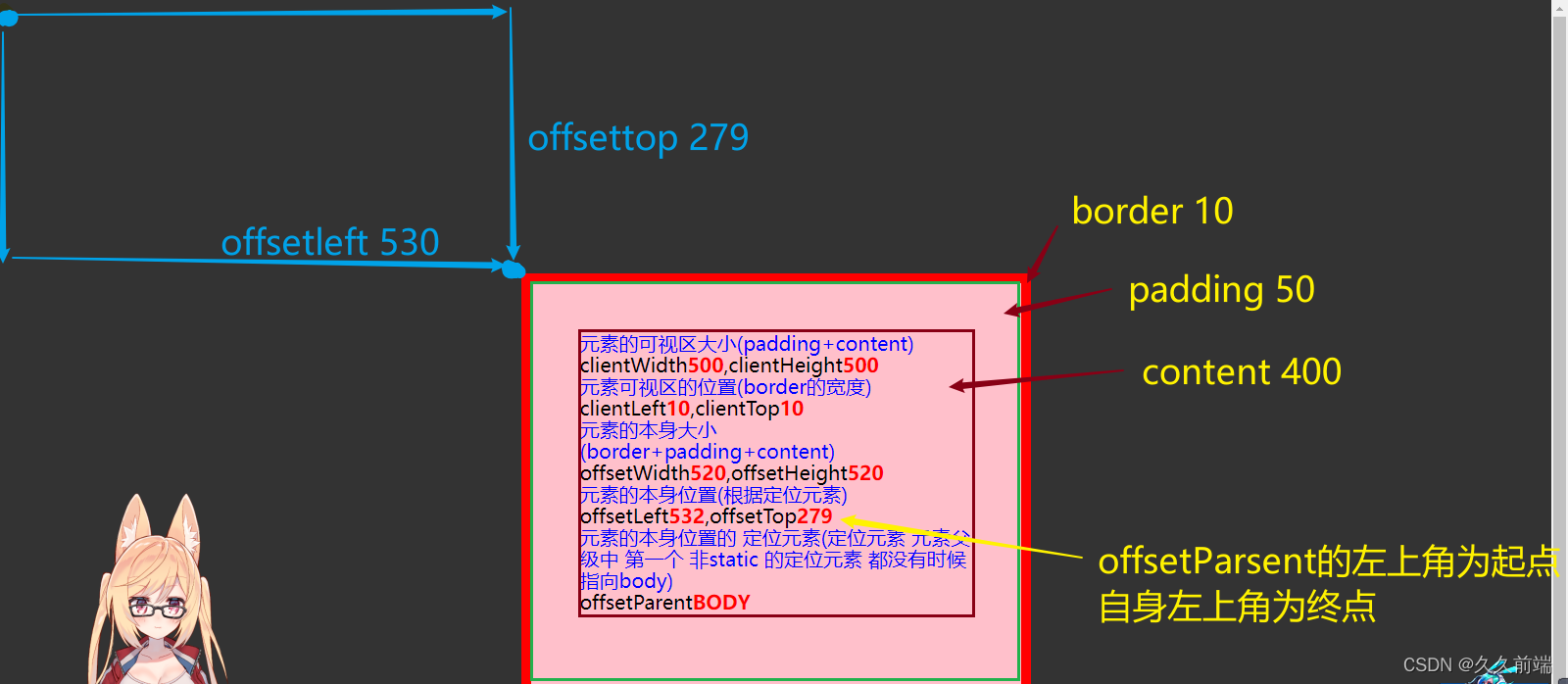

- 1.元素的可视区大小(padding+content)
clientWidth500,clientHeight500
- 2.元素可视区的位置(border的宽度)
clientLeft10,clientTop10
- 3.元素的本身大小(border+padding+content)
offsetWidth520,offsetHeight520
- 4.元素的本身位置(根据定位元素)
offsetLeft532,offsetTop279
- 5.元素的本身位置的 定位元素(定位元素 元素父级中 第一个 非static 的定位元素 都没有时候指向body)
offsetParentBODY
元素位置相对于body视口
Element.getBoundingClientRect()
该Element.getBoundingClientRect()方法返回一个 对象,该DOMRect对象提供有关元素大小及其相对于视口的位置的信息。
句法
domRect = element.getBoundingClientRect();
返回值是一个DOMRect对象,它是包含整个元素的最小矩形,包括它的填充和边框宽度。, left, top, right, bottom, x,y和属性描述了整个矩形的位置和大小(以像素为单位)width。和height以外的属性 相对于视口的左上角。 widthheight
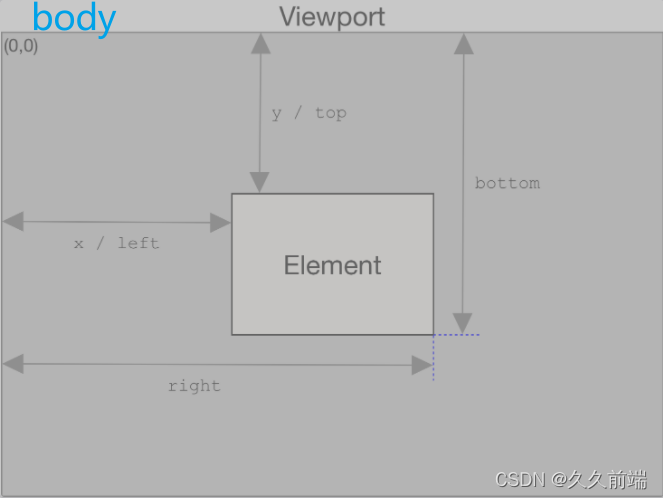
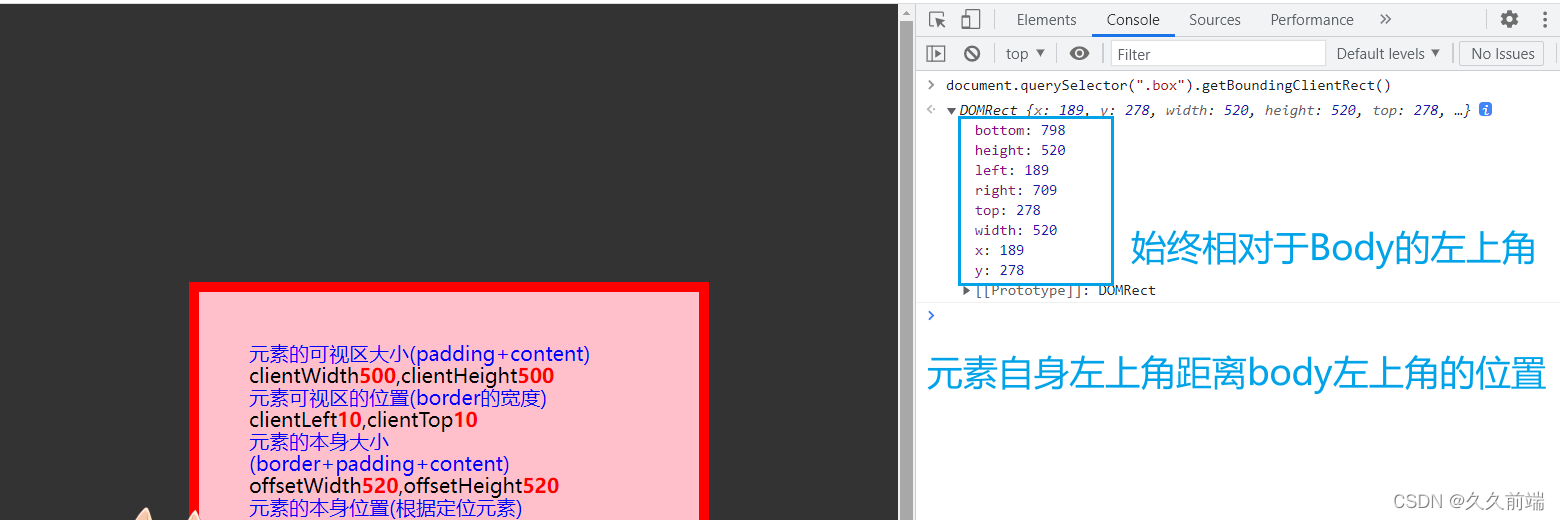
通过这些数据你可以清晰的判断元素是否出现在窗口中