Vue3的官方文档有8个部方面:1基础,2深入组件,3过度动画,4可复用组合,5高阶指南,6工具,7规模化,8无障碍 个部分.
1、基础:
????????安装方式: CDN 下载js npm CLI构建? ?大多数情况下,我们更倾向于使用 Vue CLI 来创建一个配置最小化的 webpack 构建版本。
? ? ? ? 发布地址:npm@next V3.2.31core/CHANGELOG.md at main · vuejs/core · GitHub🖖 Vue.js is a progressive, incrementally-adoptable JavaScript framework for building UI on the web. - core/CHANGELOG.md at main · vuejs/core![]() https://github.com/vuejs/vue-next/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md? ? ? Vue Devtools,?
https://github.com/vuejs/vue-next/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md? ? ? Vue Devtools,?
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
npm install vue@next
npm install -D @vue/compiler-sfc
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue upgrade --next? ? 命令行工具 (CLI)?
? ? Vite 快速构建 Vue 项目?
$ npm init vite@latest <project-name> -- --template vue
$ cd <project-name>
$ npm install
$ npm run dev
📢📢 「重要通知」原淘宝 npm 域名即将停止解析 📢📢
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npmmirror.com介绍:Vue 的核心库只关注视图层,不仅易于上手,还便于与第三方库或既有项目整合。另一方面,当与现代化的工具链以及各种支持类库结合使用时,Vue 也完全能够为复杂的单页应用提供驱动。
创建应用:?每个 Vue 应用都是通过用?createApp?函数创建一个新的应用实例开始的
????????????????????????大多数方法都会返回该同一实例,允许链式
? ? ?根组件:
const RootComponent = {
/* 选项 */
}
const app = Vue.createApp(RootComponent)
const vm = app.mount('#app')
/* mount 不返回应用本身。相反,它返回的是根组件实例。 */ ?property? 可以将用户定义的 property 添加到组件实例中,例如?methods,props,computed,inject?和?setup?,Vue 还通过组件实例暴露了一些内置 property,如?$attrs?和?$emit。这些 property 都有一个?$?前缀,以避免与用户定义的 property 名冲突。
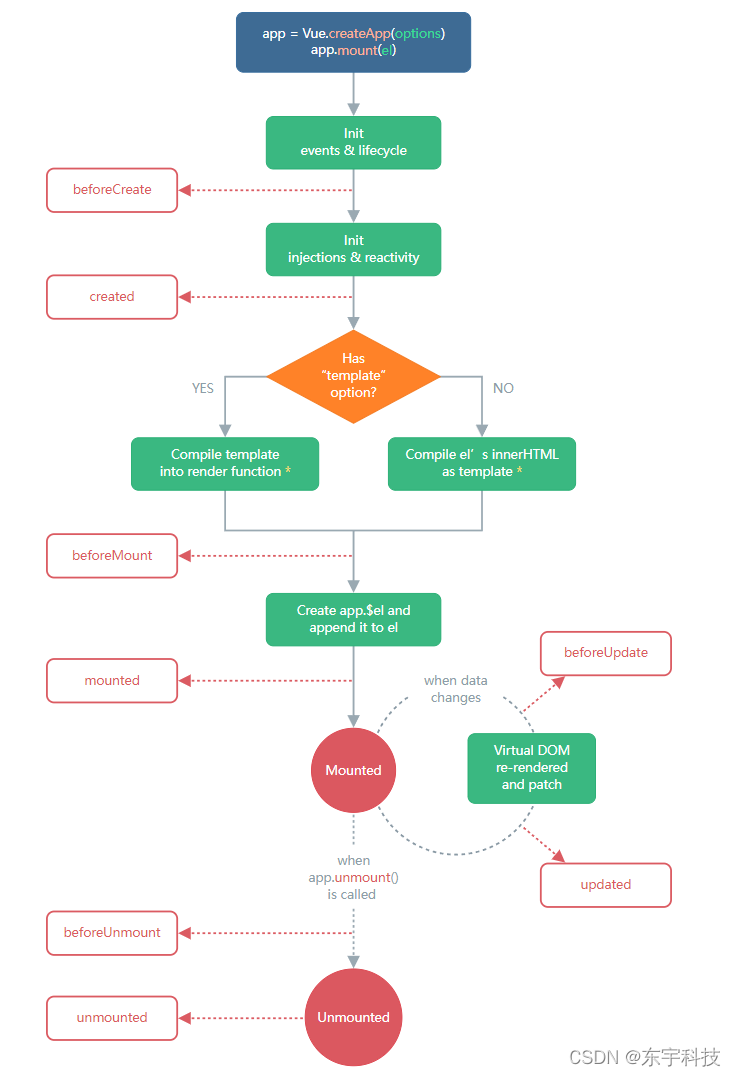
? 生命周期钩子的函数??不要在选项 property 或回调上使用箭头函数
模版语法:? 你也可以不用模板,直接写渲染 (render) 函数,使用可选的 JSX 语法?
<span>Message: {{ msg }}</span>
<span v-once>这个将不会改变: {{ msg }}</span> 执行一次性地插值
为了输出真正的 HTML,你需要使用v-html
<span v-html="rawHtml"></span> 容易导致 XSS 攻击 attribute?
<div v-bind:id="dynamicId"></div>
{{ number + 1 }}
{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}
{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}
<div v-bind:id="'list-' + id"></div>
<!-- 这是语句,不是表达式:-->
{{ var a = 1 }}
<!-- 流程控制也不会生效,请使用三元表达式 -->
{{ if (ok) { return message } }}指令:
<p v-if="seen">现在你看到我了</p>
<a v-bind:href="url"> ... </a>
<a v-on:click="doSomething"> ... </a>
<a v-bind:[attributeName]="url"> ... </a>
当 eventName 的值为 "focus" 时,v-on:[eventName] 将等价于 v-on:focus
<a v-on:[eventName]="doSomething"> ... </a>?修饰符:
<form v-on:submit.prevent="onSubmit">...</form>Vue 为?v-bind?和?v-on?这两个最常用的指令,提供了特定简写
<a v-bind:href="url"> ... </a>
<!-- 缩写 -->
<a :href="url"> ... </a>
<!-- 动态参数的缩写 -->
<a :[key]="url"> ... </a>
<a v-on:click="doSomething"> ... </a>
<!-- 缩写 -->
<a @click="doSomething"> ... </a>
<!-- 动态参数的缩写 -->
<a @[event]="doSomething"> ... </a>模板表达式都被放在沙盒中,只能访问一个受限的全局变量列表,如?Math?和?Date。你不应该在模板表达式中试图访问用户定义的全局变量?
Data Property:
data?选项是一个函数 并以?$data?的形式存储在组件实例中
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { count: 4 }
},
methods: {
increment() {
// `this` 指向该组件实例 Vue 自动为 methods 绑定 this
this.count++
}
}
})
const vm = app.mount('#app')
// 修改 vm.count 的值也会更新 $data.count
vm.count = 5
console.log(vm.$data.count) // => 5
// 反之亦然
vm.$data.count = 6
console.log(vm.count) // => 6
vm.increment()Vue 你应该避免使用?$?前缀??_?前缀。?
Vue 没有内置支持防抖和节流,但可以使用?Lodash?等库来实现
<script src="https://unpkg.com/lodash@4.17.20/lodash.min.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.createApp({
methods: {
// 用 Lodash 的防抖函数
click: _.debounce(function() {
// ... 响应点击 ...
}, 500)
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
对于可复用组件,可以在生命周期钩子的 created 里添加该防抖函数
app.component('save-button', {
created() {
// 使用 Lodash 实现防抖
this.debouncedClick = _.debounce(this.click, 500)
},
unmounted() {
// 移除组件时,取消定时器
this.debouncedClick.cancel()
},
methods: {
click() {
// ... 响应点击 ...
}
},
template: `
<button @click="debouncedClick">
Save
</button>
`
})计算属性:?不同的是计算属性将基于它们的响应依赖关系缓存。计算属性只会在相关响应式依赖发生改变时重新求值。这就意味着只要?author.books?还没有发生改变,多次访问?publishedBookMessage?时计算属性会立即返回之前的计算结果,而不必再次执行函数
// ...
computed: {
fullName: {
// getter
get() {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
},
// setter
set(newValue) {
const names = newValue.split(' ')
this.firstName = names[0]
this.lastName = names[names.length - 1]
}
}
}
// ...侦听器?
watch: {
// 每当 question 发生变化时,该函数将会执行
question(newQuestion, oldQuestion) {
if (newQuestion.indexOf('?') > -1) {
this.getAnswer()
}
}
},增强的ClassStyle?
<div :class="{ active: isActive }"></div>
这个 class 存在与否将取决于 data property isActive 的 truthiness。
<div
class="static"
:class="{ active: isActive, 'text-danger': hasError }"
></div>
或者定义个对象,对象的计算属性也行
<div :class="classObject"></div>
data() {
return {
classObject: {
active: true,
'text-danger': false
}
}
}
或者数组:
<div :class="[activeClass, errorClass]"></div>
data() {
return {
activeClass: 'active',
errorClass: 'text-danger'
}
}
<div :class="[{ active: isActive }, errorClass]"></div>
<div id="app">
<my-component class="baz"></my-component>
</div>
<div :style="styleObject"></div>
data() {
return {
styleObject: {
color: 'red',
fontSize: '13px'
}
}
}条件渲染:?
<h1 v-if="awesome">Vue is awesome!</h1>
<h1 v-else>Oh no 😢</h1>
<template v-if="ok"> 类是block
<h1>Title</h1>
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
</template>
v-else 元素必须紧跟在带 v-if 或者 v-else-if 的元素的后面,否则它将不会被识别
v-show 的元素始终会被渲染并保留在 DOM 中。v-show 只是简单地切换元素的 CSS 。
如果需要非常频繁地切换,则使用 v-show 较好;如果在运行时条件很少改变,则使用 v-if 较好。
当 v-if 与 v-for 一起使用时,v-if 具有比 v-for 更高的优先级列表渲染:
<ul id="array-rendering">
<li v-for="item in items">
//<li v-for="(item, index) in items">
//<div v-for="item of items"></div>
{{ item.message }}
</li>
</ul>?也可以用?v-for?来遍历一个对象的 property。
<li v-for="value in myObject">
{{ value }}
</li>
<li v-for="(value, name) in myObject">
{{ name }}: {{ value }}
</li>
<li v-for="(value, name, index) in myObject">
{{ index }}. {{ name }}: {{ value }}
</li>
<div v-for="item in items" :key="item.id">
<!-- v-for 的 key。请用字符串或数值类型的值。 -->
</div>
push()pop()shift()unshift()splice()sort()reverse()当使用非变更方法时,可以用新数组替换旧数组:?
example1.items = example1.items.filter(item => item.message.match(/Foo/))你可能认为这将导致 Vue 丢弃现有 DOM 并重新渲染整个列表。幸运的是,事实并非如此。Vue 为了使得 DOM 元素得到最大范围的重用而实现了一些智能的启发式方法,所以用一个含有相同元素的数组去替换原来的数组是非常高效的操作。?
<my-component
v-for="(item, index) in items"
:item="item"
:index="index"
:key="item.id"
></my-component>下面是一个简单的 todo 列表的完整例子:?
<div id="todo-list-example">
<form v-on:submit.prevent="addNewTodo">
<label for="new-todo">Add a todo</label>
<input
v-model="newTodoText"
id="new-todo"
placeholder="E.g. Feed the cat"
/>
<button>Add</button>
</form>
<ul>
<todo-item
v-for="(todo, index) in todos"
:key="todo.id"
:title="todo.title"
@remove="todos.splice(index, 1)"
></todo-item>
</ul>
</div>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
newTodoText: '',
todos: [
{
id: 1,
title: 'Do the dishes'
},
{
id: 2,
title: 'Take out the trash'
},
{
id: 3,
title: 'Mow the lawn'
}
],
nextTodoId: 4
}
},
methods: {
addNewTodo() {
this.todos.push({
id: this.nextTodoId++,
title: this.newTodoText
})
this.newTodoText = ''
}
}
})
app.component('todo-item', {
template: `
<li>
{{ title }}
<button @click="$emit('remove')">Remove</button>
</li>
`,
props: ['title'],
emits: ['remove']
})
app.mount('#todo-list-example')事件处理?
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
name: 'Vue.js'
}
},
methods: {
greet(event) {
// `methods` 内部的 `this` 指向当前活动实例
alert('Hello ' + this.name + '!')
// `event` 是原生 DOM event
if (event) {
alert(event.target.tagName)
}
}
}
}).mount('#event-with-method')?
<button @click="warn('Form cannot be submitted yet.', $event)">
Submit
</button>
<!-- 这两个 one() 和 two() 将执行按钮点击事件 -->
<button @click="one($event), two($event)">
Submit
</button>
// ...
methods: {
warn(message, event) {
// 现在可以访问到原生事件
if (event) {
event.preventDefault()
}
alert(message)
}
}
?修饰符:
<!-- 阻止单击事件继续冒泡 -->
<a @click.stop="doThis"></a>
<!-- 提交事件不再重载页面 -->
<form @submit.prevent="onSubmit"></form>
<!-- 修饰符可以串联 -->
<a @click.stop.prevent="doThat"></a>
<!-- 只有修饰符 -->
<form @submit.prevent></form>
<!-- 添加事件监听器时使用事件捕获模式 -->
<!-- 即内部元素触发的事件先在此处理,然后才交由内部元素进行处理 -->
<div @click.capture="doThis">...</div>
<!-- 只当在 event.target 是当前元素自身时触发处理函数 -->
<!-- 即事件不是从内部元素触发的 -->
<div @click.self="doThat">...</div>
使用修饰符时,顺序很重要;相应的代码会以同样的顺序产生。因此,用 @click.prevent.self 会阻止元素本身及其子元素的点击的默认行为,而 @click.self.prevent 只会阻止对元素自身的点击的默认行为。
<!-- 点击事件将只会触发一次 -->
<a @click.once="doThis"></a>
<!-- 滚动事件的默认行为 (即滚动行为) 将会立即触发, -->
<!-- 而不会等待 `onScroll` 完成, -->
<!-- 以防止其中包含 `event.preventDefault()` 的情况 -->
<div @scroll.passive="onScroll">...</div><!-- 只有在 `key` 是 `Enter` 时调用 `vm.submit()` -->
<input @keyup.enter="submit" />
<input @keyup.page-down="onPageDown" />
.enter .tab .delete (捕获“删除”和“退格”键) .esc .space
.up .down .left .right
.ctrl .alt .shift .meta
meta 对应 command 键 (?)。在 Windows 系统键盘 meta 对应 Windows 徽标键 (?)
<!-- Alt + Enter -->
<input @keyup.alt.enter="clear" />
<!-- Ctrl + Click -->
<div @click.ctrl="doSomething">Do something</div>
<!-- 即使 Alt 或 Shift 被一同按下时也会触发 -->
<button @click.ctrl="onClick">A</button>
<!-- 有且只有 Ctrl 被按下的时候才触发 -->
<button @click.ctrl.exact="onCtrlClick">A</button>
<!-- 没有任何系统修饰符被按下的时候才触发 -->
<button @click.exact="onClick">A</button>
.left .right .middle表单输入绑定:
v-model?会忽略所有表单元素的?value、checked、selected?attribute 的初始值。它将始终将当前活动实例的数据作为数据来源。你应该通过 JavaScript 在组件的?data?选项中声明初始值。.
- text 和 textarea 元素使用?
value?property 和?input?事件; - checkbox 和 radio 使用?
checked?property 和?change?事件; - select 字段将?
value?作为 prop 并将?change?作为事件。
<input v-model="message" placeholder="edit me" />
<p>Message is: {{ message }}</p>
<span>Multiline message is:</span>
<p style="white-space: pre-line;">{{ message }}</p>
<br />
<textarea v-model="message" placeholder="add multiple lines"></textarea>
<!-- bad -->
<textarea>{{ text }}</textarea>
<!-- good -->
<textarea v-model="text"></textarea>
<input type="checkbox" id="checkbox" v-model="checked" />
<label for="checkbox">{{ checked }}</label>
<div id="v-model-multiple-checkboxes">
<input type="checkbox" id="jack" value="Jack" v-model="checkedNames" />
<label for="jack">Jack</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="john" value="John" v-model="checkedNames" />
<label for="john">John</label>
<input type="checkbox" id="mike" value="Mike" v-model="checkedNames" />
<label for="mike">Mike</label>
<br />
<span>Checked names: {{ checkedNames }}</span>
</div>
<div id="v-model-radiobutton">
<input type="radio" id="one" value="One" v-model="picked" />
<label for="one">One</label>
<br />
<input type="radio" id="two" value="Two" v-model="picked" />
<label for="two">Two</label>
<br />
<span>Picked: {{ picked }}</span>
</div>
<div id="v-model-select-dynamic" class="demo">
<select v-model="selected">
<option v-for="option in options" :value="option.value">
{{ option.text }}
</option>
</select>
<span>Selected: {{ selected }}</span>
</div>
<div id="v-model-select" class="demo">
<select v-model="selected">
<option disabled value="">Please select one</option>
<option>A</option>
<option>B</option>
<option>C</option>
</select>
<span>Selected: {{ selected }}</span>
</div><!-- 在“change”时而非“input”时更新 -->
<input v-model.lazy="msg" />
<input v-model.number="age" type="text" />
<input v-model.trim="msg" />?组件基础:?组件是带有名称的可复用实例
// 创建一个Vue 应用
const app = Vue.createApp({})
// 定义一个名为 button-counter 的新全局组件
app.component('button-counter', {
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
template: `
<button @click="count++">
You clicked me {{ count }} times.
</button>`
})Prop 是你可以在组件上注册的一些自定义 attribute
<div id="blog-posts-events-demo" class="demo">
<div :style="{ fontSize: postFontSize + 'em' }">
<blog-post
v-for="post in posts"
:key="post.id"
:title="post.title"
@enlarge-text="postFontSize += 0.1"
></blog-post>
</div>
</div>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
posts: [
{ id: 1, title: 'My journey with Vue'},
{ id: 2, title: 'Blogging with Vue'},
{ id: 3, title: 'Why Vue is so fun'}
],
postFontSize: 1
}
}
})
app.component('blog-post', {
props: ['title'],
template: `
<div class="blog-post">
<h4>{{ title }}</h4>
<button @click="$emit('enlargeText', 0.1)">
Enlarge text
</button>
</div>
`
})
app.mount('#blog-posts-events-demo')创建支持?v-model?的自定义输入组件?
<input v-model="searchText" />
等价于
<input :value="searchText" @input="searchText = $event.target.value" />
<custom-input
:model-value="searchText"
@update:model-value="searchText = $event"
></custom-input>
app.component('custom-input', {
props: ['modelValue'],
emits: ['update:modelValue'],
template: `
<input
:value="modelValue"
@input="$emit('update:modelValue', $event.target.value)"
>
`
})
该组件实现 v-model 的另一种方法是使用 computed 来定义 getter 和 setter。
app.component('custom-input', {
props: ['modelValue'],
emits: ['update:modelValue'],
template: `
<input v-model="value">
`,
computed: {
value: {
get() {
return this.modelValue
},
set(value) {
this.$emit('update:modelValue', value)
}
}
}
})当它用于原生 HTML 元素时,is?的值必须以?vue:?开头,才可以被解释为 Vue 组件。这是避免和原生自定义元素混淆。?HTML attribute 名不区分大小写
app.component('blog-post', {
props: ['postTitle'],
template: `
<h3>{{ postTitle }}</h3>
`
})<!-- 在 HTML 中则是横线字符分割 -->
<blog-post post-title="hello!"></blog-post>组件注册
组件名:全部 - 小写??kebab-case(短横线分隔命名) ?[k??b?b]
当使用 PascalCase (首字母大写命名) 定义一个组件时,你在引用这个自定义元素时两种命名法都可以使用。也就是说?<my-component-name>?和?<MyComponentName>?都是可接受的。注意,尽管如此,直接在 DOM (即非字符串的模板) 中使用时只有 kebab-case 是有效的。
import ComponentA from './ComponentA.vue'
export default {
components: {
ComponentA
}
// ...
}模块系统?
import ComponentA from './ComponentA'
import ComponentC from './ComponentC'
export default {
components: {
ComponentA,
ComponentC
}
// ...
}prop的值类型?静态或动态
props: {
title: String,
likes: Number,
isPublished: Boolean,
commentIds: Array,
author: Object,
callback: Function,
contactsPromise: Promise // 或任何其他构造函数
}<blog-post v-bind="post"></blog-post>
<blog-post v-bind:id="post.id" v-bind:title="post.title"></blog-post>
post: {
id: 1,
title: 'My Journey with Vue'
}单向数据流? ?父级 prop 的更新会向下流动到子组件中,但是反过来则不行。?
props: ['size'],
computed: {
normalizedSize() {
return this.size.trim().toLowerCase()
}
}
注意在 JavaScript 中对象和数组是通过引用传入的,所以对于一个数组或对象类型的 prop 来说,在子组件中改变这个对象或数组本身将会影响到父组件的状态,且 Vue 无法为此向你发出警告。作为一个通用规则,应该避免修改任何 prop,包括对象和数组,因为这种做法无视了单向数据绑定,且可能会导致意料之外的结果。prop 指定验证 组件实例创建之前进行验证,实例的 property (如?data、computed?等) 在?default?或?validator?函数中是不可用的
camelCase (驼峰命名法) 的 prop 名需要使用其等价的 kebab-case (短横线分隔命名) 命名
app.component('my-component', {
props: {
// 基础的类型检查 (`null` 和 `undefined` 值会通过任何类型验证)
String Number Boolean Array Object Date Function Symbol
propA: Number,
// 多个可能的类型
propB: [String, Number],
// 必填的字符串
propC: {
type: String,
required: true
},
// 带有默认值的数字
propD: {
type: Number,
default: 100
},
// 带有默认值的对象
propE: {
type: Object,
// 对象或数组的默认值必须从一个工厂函数返回
default() {
return { message: 'hello' }
}
},
// 自定义验证函数
propF: {
validator(value) {
// 这个值必须与下列字符串中的其中一个相匹配
return ['success', 'warning', 'danger'].includes(value)
}
},
// 具有默认值的函数
propG: {
type: Function,
// 与对象或数组的默认值不同,这不是一个工厂函数——这是一个用作默认值的函数
default() {
return 'Default function'
}
}
}
})非 prop 的 attribute 将自动添加到根节点的 attribute 中?
?
<div id="date-picker" class="demo">
<date-picker @change="showChange"></date-picker>
</div>
const app = Vue.createApp({
methods: {
showChange(event) {
console.log(event.target.value) // 将打印所选选项的值
}
}
})
通过将 inheritAttrs 选项设置为 false,你可以使用组件的 $attrs 将 attribute 应用到其它元素上,
app.component('date-picker', {
inheritAttrs: false,
template: `
<div class="date-picker">
<input type="datetime-local" v-bind="$attrs" />
</div>
`
})组件上的?v-model?使用?modelValue?作为 prop 和?update:modelValue?作为事件。?
<my-component v-model:title="bookTitle"></my-component>
app.component('my-component', {
props: {
title: String
},
emits: ['update:title'],
template: `
<input
type="text"
:value="title"
@input="$emit('update:title', $event.target.value)">
`
})
多个 v-model 绑定
<user-name
v-model:first-name="firstName"
v-model:last-name="lastName"
></user-name>
app.component('user-name', {
props: {
firstName: String,
lastName: String
},
emits: ['update:firstName', 'update:lastName'],
template: `
<input
type="text"
:value="firstName"
@input="$emit('update:firstName', $event.target.value)">
<input
type="text"
:value="lastName"
@input="$emit('update:lastName', $event.target.value)">
`
})添加到组件?v-model?的修饰符将通过?modelModifiers?prop 提供给组件?
<my-component v-model.capitalize="myText"></my-component>
app.component('my-component', {
props: {
modelValue: String,
modelModifiers: {
default: () => ({})
}
},
emits: ['update:modelValue'],
template: `
<input type="text"
:value="modelValue"
@input="$emit('update:modelValue', $event.target.value)">
`,
created() {
console.log(this.modelModifiers) // { capitalize: true }
}
})插槽内容待续。。?