HTML、CSS、JS以及JQuery总结:
现在的HTML主要是实现内容的呈现,CSS是对内容进行布局和装饰,JS以及jQuery是对内容的操作,即实现内容的动态改变。
前后端的交互,现在学到的主要是HTML的form表单:
<form action="url" method="GET | POST" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="f">? //如果有file类型字段,form标签中要有enctype="multipart/form-data"
<input type="submit">
</form>
能够向后台传递个字段主要有:input标签 type=“text、radio、checkbox、file、hidden、password”等,select标签,textarea标签,这几个标签必须设置name属性,name的值就是设置传递数据的key,标签的value是传递的数据的值,后台接收的是字典,key就是前端标签的name值,value就是前端标签的value值。
CSS主要的是float:
清除浮动——:after的用法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.left{
float: left;
}
.container{
background-color: rosybrown;
}
.container .item{
width: 180px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #336699;
border: 1px solid red;
}
.clearfix:after{
content: "ooo"; /*//增加的内容,在页面上显示,但不能选定*/
display: block; /*以块级标签显示*/
clear: both; /*清除浮动,撑起外层div*/
visibility: hidden; /*不想显示content增加的内容,但是占据位置,display:none则是不显示内容,也不占据位置*/
height: 0; /*这样浏览器上外观显示就没有ooo这个内容,也不占位置了,但在文档流中还有的*/
}
/*//.container:after 是在container标签内部的沉底部位增加内容*/
/*以后只要在对应的标签中增加class=“clearfix”就能撑起这个标签,好处是一直在标签的最底部增加,即使是动态增加子标签*/
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container clearfix">
<div class="item left"></div>
<div class="item left"></div>
<div class="item left"></div>
<div class="item left"></div>
<!-- <div style="clear: both"></div> /* 以前的做法,在.container内部增加一个div,清除浮动,撑起container*/-->
</div>
</body>
</html>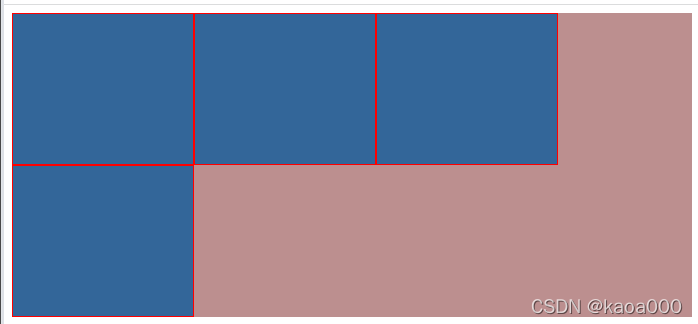
1、已知外层高度,内元素浮动时,外层按照已知已设置的高度被撑开
2、未知外层高度
? ? ? ? -- 原来做法:在内元素沉底位置增加<div style="clear:both";> </div>
? ? ? ? -- 推荐做法:写一个样式,如上的:
? ? ? ??.clearfix:after{
? ? ? ? ? ? content: "ooo";?
? ? ? ? ? ? display: block;
? ? ? ? ? ? clear: both; ?
? ? ? ? ? ? visibility: hidden;
? ? ? ? ? ? height: 0;
? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ??然后在需要的标签上增加class为clearfix就可以。
hover的应用:
.c1{
? ? background-color:red;
}
.c1:hover{
? ? background-color:pink;
}
以上样式,当鼠标放在.c1标签上时,背景色变为pink;鼠标移出标签,背景色变为red。
.c1:hover .c2{
? ? background-color:blue;
}
以上样式,是当鼠标放在c1上时,c2的样式改变。
实现一个鼠标进入和离开时改变的例子:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.clearfix:after{
content: "ooo";
display: block;
clear: both;
visibility: hidden;
height: 0;
}
.container{
background-color: red;
}
.container .item{
width: 180px;
height: 150px;
background-color: #336699;
border: 1px solid red;
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;//加上这一条,是为了给遮罩层定位用的
}
.left{
float: left;
}
.container .item:hover{ /*当鼠标放在item标签上时,item自身改变*/
border: 1px solid yellow;
}
.container .item .text {
display: none;
}
.container .item:hover .text{
display: block;
}/*当鼠标选中item时,item下的text标签发生改变*/
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container clearfix">
<div class="item left">
<div class="bg">
<img src="1.jpg" style="height: 150px;width: 180px">
</div>
<div class="text">
<div style="z-index:9;position: absolute;left: 0;right: 0;top:0;bottom: 0;background-color: deeppink;opacity: 0.4;"></div>
//上面的div为遮罩层,其定位,需要一个position:relative
<div style="z-index:10;position: absolute;left: 0;right: 0;top: 0;bottom: 0;color: yellow">内容介绍</div>
//上面的div为遮罩层上的文字层,其定位,也需要一个position:relative
</div>
</div>
<div class="item left">
<div class="bg">
<img src="1.jpg" style="height: 150px;width: 180px">
</div>
<div class="text">
<div style="z-index:9;position: absolute;left: 0;right: 0;top:0;bottom: 0;background-color: deeppink;opacity: 0.4;"></div>
//上面的div定位,需要一个position:relative
<div style="z-index:10;position: absolute;left: 0;right: 0;top: 0;bottom: 0;color: yellow">内容介绍</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="item left">
<div class="bg">
<img src="1.jpg" style="height: 150px;width: 180px">
</div>
<div class="text">
<div style="z-index:9;position: absolute;left: 0;right: 0;top:0;bottom: 0;background-color: deeppink;opacity: 0.4;"></div>
//上面的div定位,需要一个position:relative
<div style="z-index:10;position: absolute;left: 0;right: 0;top: 0;bottom: 0;color: yellow">内容介绍</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>?主要应用了:hover .class
另一个应用:类似下拉菜单栏的例子:

?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
*{
margin: 0;
}
.left{
float: left;
}
.right{
float: right;
}
.pg-header{
height: 48px;
background-color: #336699;
color: white;
line-height: 48px;
}
.pg-header .logo{
width: 200px;
align-content: center;
margin-left: 10px;
}
.pg-header .user{
padding: 0 40px;
height: 48px;
position: relative;
}
.pg-header .user:hover{
background-color: palegoldenrod;
}
.pg-header .user .au img{
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
margin-top: 4px;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.pg-header .user .more{
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
top: 48px;
right: 16px;
border: 1px solid red;
background-color: #b4b4b4;
display: none;
z-index: 90;
}
.pg-header .user .more a{
display: block;
}
.pg-header .user:hover .more{
display: block;
}
.pg-body .body-menu{
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid forestgreen;
}
.pg-body .body-content{
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
bottom: 0;
left: 210px;
right: 0;
border: 1px solid forestgreen;
overflow: auto;
z-index: 10;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="pg-header">
<div class="logo left">后台管理页面布局演示</div>
<div class="user right">
<a class="au">
<img src="1.jpg">
</a>
<div class="more">
<a>我的信息</a>
<a>注销</a>
<a>更多信息</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="pg-body">
<div class="body-menu"></div>
<div class="body-content"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>JavaScript总结补充:
作用域和作用域链:
Java/C#中,代码块作为作用域,Python中以函数作为作用域。
而JavaScript中,以函数作为作用域;函数在被调用之前,作用域链已经存在。
<script>
? ? ? ? ? ? xo = 'alex';
? ? ? ? ? ? function f1(){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? var xo = 'eric';
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? function f2(){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? console.log(xo);
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? return f2
? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? ? ? var xxxxx = f1()
? ? ? ? ? ? xxxxx()
? ? ? ? ? ? // eirc
</script>
?声明提前:
?function func(){?
? ? ? ? ? ? console.log(ox);
? ? ? ? ? ? var ox = ' ?'
? ? ? ? ? ? var ox = ' ?'
? ? ? ? }
??func()
jQuery:找元素(直接,间接);操作(属性、增加、删除、修改。。。)
事件绑定方式:
DOM下绑定事件:
1)、<p id="p1" οnclick="func1(this);">hello p</p>
2)、var?ele=document.getElementById("p1");
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ele.οnclick=function(){alert (this.innerHTML);}
jQuery下绑定事件:
1)、$("p").click(function(){$(this).css("color","red");})
$(document).ready(function(){? ?}? ?//当js代码放在HTNL文档开头时,使用这个格式等待HTML加载完成在执行代码,就不会出现元素找不到的情况。
简写方式:$(function(){? ?})
事件相对于DOM,将前面的on去掉
2)、$("p").bind("click",function(){})? //不推荐使用了
3)、$("P").on("click","li",function(){})
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>11111</li>
<li>22222</li>
<li>33333</li>
<li>44444</li>
</ul>
<input type="button" value="+" onclick="add();">
<p>pppppppppppppppp</p>
<script src="jquery-3.6.0.js"></script>
<script>
function add() {
$("ul").append("<li>555555</li>");
}
// $("ul li").click(function () {
// alert(456);
// })
// //上面的绑定事件的方式,为直接使用事件click(),对动态添加的标签无法绑定
$("ul").on("click","li",function () {
alert(666);
})
//上面的绑定事件方式,为使用on方式,动态添加的元素也能生效。
function myHandler(event) {
alert(event.data.foo);
}
$("p").on("click",{foo:"bar"},myHandler);
//上面标签绑定事件,传递一个字典作为参数,在事件函数中,定义event参数,通过event来获取这个参数
</script>
</body>
</html>
?on方式的绑定,叫做事件委托,将绑定到li上的事件,委托给ul。on有四个参数。
面板拖动示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div style="border: 1px solid #ddd;width: 600px;position: absolute">
<div id="title" style="background-color: black;height: 40px;color: white">
标题
</div>
<div style="height: 300px;">
内容
</div>
</div>
<script src="jquery-3.6.0.js"></script>
<script>
$("#title").mouseover(function () {
$(this).css("cursor","move").mousedown(function (event) {
var start_x = event.screenX;
var start_y = event.screenY;
var parent_left = $(this).parent().offset().left;
var parent_top = $(this).parent().offset().top;
$(this).on("mousemove",function (event2) {
var new_x = event2.screenX;
var new_y = event2.screenY;
var new_parent_x = parent_left + new_x - start_x;
var new_parent_y = parent_top + new_y -start_y;
$(this).parent().css("left",new_parent_x+"px");
$(this).parent().css("top",new_parent_y+"px");
}).mouseup(function () {
$(this).off("mousemove");
});
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
鼠标按住标题栏拖动
?动画显示隐藏示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>hello world</p>
<input id="show" type="button" value="显示">
<input id="hide" type="button" value="隐藏">
<input id="toggle" type="button" value="切换">
<script src="jquery-3.6.0.js"></script>
<script>
$("#show").click(function () {
$("p").show(2000);
})//显示,有一个慢动作的拉幕效果
$("#hide").click(function () {
$("p").hide(2000);
})//隐藏,有一个慢动作的收幕效果
$("#toggle").click(function () {
$("p").toggle(5000);
})//实现上述显示和隐藏功能,当前是显示的,则隐藏,当前是隐藏的则显示
</script>
</body>
</html>淡入淡出动画示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1" style="display: none;width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: forestgreen;"></div>
<input id="In" type="button" value="fadeIn">
<input id="Out" type="button" value="fadeOut">
<input id="Toggle" type="button" value="fadeToggle">
<input id="To" type="button" value="fadeTo">
<script src="jquery-3.6.0.js"></script>
<script>
$("#In").click(function () {
$("div").fadeIn(2000);
})
$("#Out").click(function () {
$("div").fadeOut(2000);
})
$("#Toggle").click(function () {
$("div").fadeToggle(2000);
})
$("#To").click(function () {
$("div").fadeTo(2000,0.3);
})//最后出来的背景透明度为0.3
</script>
</body>
</html>滑动动画:slideDown()、slideUp()、slideToggle()
回调函数:
$("#show").click(function () {
? ? ? ? $("p").show(2000,function(){ 。。。? });?
? ? })
当show方法2秒完成后,即show方法完成了动作,然后调用函数,这里的function就是回调函数,即定义的动作或事件完成后,再调用的函数。
jQuery扩展:使用extend()方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>hello pppp</p>
<script src="jquery-3.6.0.js"></script>
<script>
$.extend({
getmax:function (a,b) {
return a>b ? a:b;
}
});//直接在jQuery上扩展,调用时是$加上点调用
alert($.getmax(5,6));
$.fn.extend({
print:function () {
alert($(this).html());
}
});//这种扩展,调用时必须是一个标签
$("p").print();
</script>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var f = function (a) {
alert(a);
};
f(123);
//上下等同
(function (a) {
alert(a);
})(123);
//将扩展方法放在自执行函数中,属于私有域,避免重名变量冲突
(function () {
$.fn.extend({
print:function(){
console.log($(this).html());
};
});
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>