vuejs量化知识
1、邂逅vuejs
1.1、vuejs的特点
- 解耦视图和数据
- 可复用的组件
- 前端的路由技术(vue-route)
- 状态管理(vue-x)
- 虚拟DOM
1.2、vue.js的安装
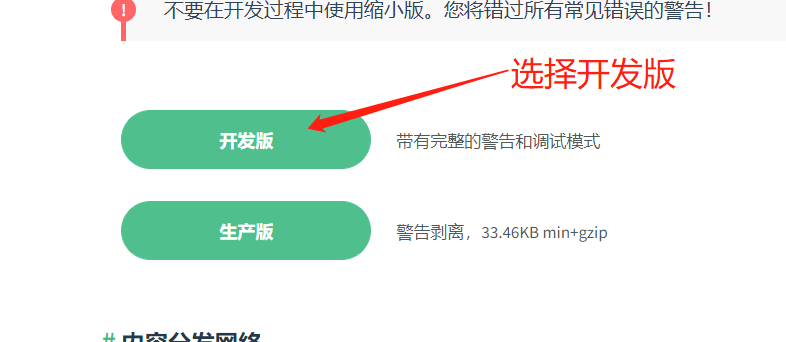
常见的安装的方式
-
CDN的引入(建议的话使用开发版本)
-
下载和引入
- 下载地址: https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/installation.html 。
-
NPM安装
- 后续都是使用这个方式
1.3、初识vue.js
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">{{message}}</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello world'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.4、vue的列表显示(v-for遍历)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue的列表显示</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">{{message}}
<ul>
<!-- 对数组进行遍历-->
<li v-for="item in movies">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var app =new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好啊',
movies:['海贼王','火影忍者','星际穿越','大话西游'],
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

1.5、计数器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue案例-计数器</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>当前计数:{{counter}}</h2>
<!-- v-on设置事件-->
<button v-on:click="counter++">+</button>
<button v-on:click="counter--">-</button>
<!-- 进行函数的绑定-->
<button v-on:click="add">点击</button>
<button v-on:click="sub">点击</button>
</div>
<script>
var app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
counter:0,
},
methods:{
//在methods设置函数,并且也是按照对象的方式进行存储
add:function (){
alert("add被执行");
this.counter++;
},
sub:function (){
console.log("--被执行");
this.counter--;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

1.6、理解vue的mvvm(Model View ViewModel)
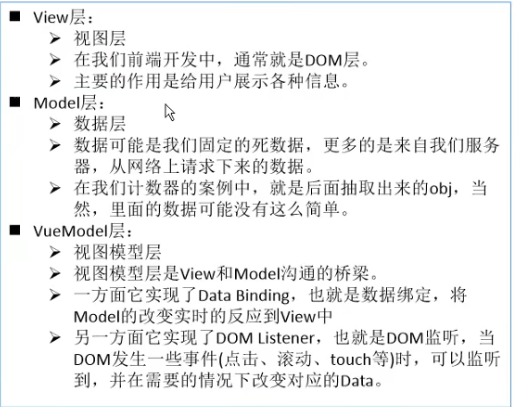
vue实例中的添加的属性的属性值的类型
- del:
- 类型:Sring||HTMLElement
- 作用:决定之后Vue实例会管理哪一个DOM
- data:
- 类型:Object(对象类型)|function(函数类型)组件之中data必须是一个函数
- 作用:Vue实例对应的数据对象
- methods:
- 类型:{[key:string],function}其放置的一些函数
- 作用:定义属于Vue的一些方法,可以在其他的地方进行使用,也可以在指令中进行调用
方法和函数的区别:
- 方法:method
- 函数:function
- 在类里面的一般称为方法,直接定义的是函数
1.7、Vue的生命周期
生命周期:事物从的诞生到消亡的过程。
vue的生命周期函数:
- created:function(){}
- mounted:function(){}
- beforeCreate:function(){}
1.8、插值操作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>{{method}}</h2>
<!-- 通过这种方式进行字符串的拼接-->
<h2>{{firstName+''+lastName}}</h2>
<!--可以通过此进行简单的数字运算-->
<h2>{{counter*2}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
var app =new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
method:'你好世界',
name:'李四',
role:'老师',
lastName:'学工办主任',
firstName:'bryant',
counter:100
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

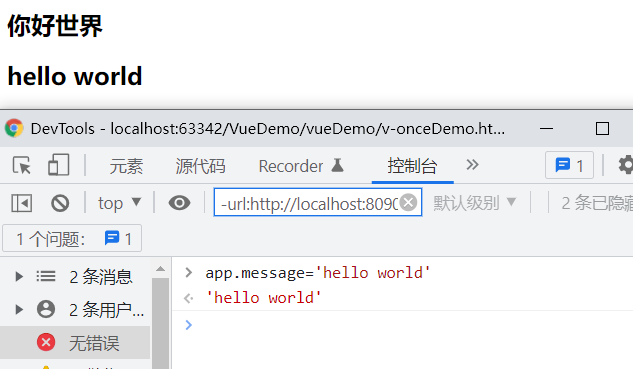
1.8.1、v-once指令的使用
当指令使用的时候,只会显示最初的数据,当数据发生改变的时候,数据依然显示最原始的数据,不会随之改变。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-once语法的使用</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2 v-once>{{message}}</h2>
<h2 >{{message}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
var app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好世界'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.8.2、v-html指令的使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-once语法的使用</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 通过这个标签进行html代码的接收-->
<h2 v-html="url"></h2>
</div>
<script>
var app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好世界',
url:"<a href='http://www.baidu.com'>百度一下</a>"
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.8.3、v-text指令的使用(不常用)
注:一般不推荐使用,容易对拼接的字符串进行覆盖
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-text</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 通过这个标签进行html代码的接收-->
<h2 v-html="url"></h2>
<!-- 通过v-text来获取数据中的内容,但是一般不使用-->
<h2 v-text="message"></h2>
</div>
<script>
var app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好世界',
url:"<a href='http://www.baidu.com'>百度一下</a>"
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.8.4、v-pre标签的使用(不常用)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-pre标签的使用</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- pre标签的使用,当所接受的数据不需要进行解析的时候采用-->
<h2 v-pre>{{message}}</h2>
<h2>{{message}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
var app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好世界',
url:"<a href='http://www.baidu.com'>百度一下</a>"
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.8.5、v-cloak标签的使用(一般不用)
保证所监视的标签部分却ing由vue.js代码部分的运行
1.9、v-bind的使用
对象语法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-once语法的使用</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<style>
.test{
color: red;
font-weight: bolder;
font-size: 20px;
font-family: '威雅软黑';
}
.test1{
background-color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- v-bind在标签内获取相关的数据-->
<a v-bind:href="url">点击一下</a>
<!-- 简写的方式-->
<a :href="url">点击一下</a>
<!-- 类标签的绑定-->
<h2 v-bind:class="active">{{message}}</h2>
<!-- 通过修改Boolean值来修改class中的值,在进行class的动态获取的时候,我们仍然可以进行class的写定-->
<h2 v-bind:class="{test:isTest,test1:isTest1}">{{message}}</h2>
<button v-on:click="bt"></button>
</div>
<script>
var app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好世界',
url:'http://www.baidu.com',
active:'test',
isTest:true,
isTest1:true,
},
methods:{
bt:function (){
//进行值的取反
this.isTest=!this.isTest;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
数组语法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-once语法的使用</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<style>
.test{
color: red;
font-weight: bolder;
font-size: 20px;
font-family: '威雅软黑';
}
.test1{
background-color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 通过函数的方式,对class进行赋值-->
<h2 v-bind:class="getClass()">{{message}}</h2>
<button v-on:click="bt"></button>
</div>
<script>
var app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好世界',
url:'http://www.baidu.com',
isTest:true,
isTest1:true,
},
methods:{
bt:function (){
//进行值的取反
this.isTest=!this.isTest;
},
//通过函数的形式,对class推送数组
getClass:function (){
//注意:一定要写this,时刻保证自己所取的参数为自己的
return {test:this.isTest,test1:this.isTest1}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
动态绑定样式
对象语法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 通过v-bind动态的绑定属性额style的值-->
<!-- <h1 :style="{key:value,key1:value1}">{{message}}</h1>-->
<h1 :style="{color:size}">{{message}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello world',
size:"red",
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
数组语法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 通过数组对标签的样式进行修改-->
<h1 :style="[baseStyle,baseStyle1]">{{message}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello world',
size:"red",
baseStyle:{
fontSize:"50px",
color:"red"
},
baseStyle1:{
backgroundColor:"black"
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html >
2、计算属性computed
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>计算属性的使用</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 获取数据时对数据进行处理整合-->
<!-- 第一种方法-->
<h1>{{message+" "+name}}</h1>
<!-- 第二种方法-->
<h1>{{message}} {{name}}</h1>
<!-- 第三种方式 通过函数进行整合-->
<h1>{{realName()}}</h1>
<!-- 通过计算属性进行数据整合-->
<h1>{{fullName}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'李',
name:'四'
},
computed:{
fullName:function (){
return this.message+" "+this.name;
}
},
methods:{
realName:function (){
return this.message+" "+this.name;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
复杂操作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">总价:{{num}}</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
Books:[
{name:"算法大全",price:119,author:'张三'},
{name:"java全解",price:98,author:'张三'},
{name:"算法导论",price:57,author:'张三'}
]
},
computed:{
num:function (){
var num1=0;
for (var i=0; i<this.Books.length;i++){
num1=num1+this.Books[i].price;
}
return num1;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
注:在vue中,计算属性(computed)具有缓存,当执行第一次的时候,所产生的结果会存放在内存之中,当再次使用结果的时候直接在内存中读取,但是methods不具有缓存效果,当再次使用数据结果的时候,需要再次执行,效率不高

2.1、计算属性的setter与getter
在computed(计算属性)中存在setter与getter方法
2.2、ES6中常见的一些方法
2.2.1、let/var的使用
- 在ES6中设立的参数,当设立的参数需要变化的时候我们使用let
- 当我们设立的参数不进行变化的时候,我们使用const(const的指定的对象,对象是不可以进行修改的,但是对象中的内容可以进行修改)
注:let与var的区别
let具有块级作用域,但是var却不存在。
2.3、事件监听(v-on)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>事件监听</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>{{message}}</h2>
<!-- v-on的简写-->
<button @click="add">+</button>
<button @click="sub">-</button>
</div>
<script>
const appp=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:0
},
methods:{
add:function (){
this.message++;
},
sub:function (){
this.message--;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
监听事件的参数的传递
- 在事件监听的时候,所写的方法如果不需要进行参数的传递,我们可以省掉方法中的小括号。
- 传参的两种情况:
- 直接传输常量写死
- .传递一个参数,但是参数的值需要在vue实例中的data中进行体现。否则胡报错
v-on修饰符的使用
- Vue提供的修饰符
- .stop–调用event。stopPropagation()
- .prevent – 调用 event.preventDefault()
- .{keyCode | keyAlias} --只当事件从特定的建触发时才会回调
- .native – 监听组件根元素的原生事件
- .once – 只触发一次回调。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-on的修饰符的使用</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!--当给一个元素的与他的父元素一块设置了事件时,当触发子元素的事件活带动父元素的事件一块启动-->
<div @click="divClick">
<!-- 通过修饰符对相关的函数进行叫停-->
<button @click.stop="btnClick">按钮</button>
</div><br/>
<!-- .prevent修饰符的使用-->
<!-- 屏蔽某些元素自带的事件-->
<!-- 例子:input标签的submit具有自己的提交功能,.prevent可以进行屏蔽-->
<form action="baidu">
<input type="submit" value="提交" @click.prevent="inputClick">
</form>
<!-- 监听键盘的键帽的点击-->
<input type="text" @keyup="keyUp">
<!-- .once修饰符-->
<button @click.once="btn2Click">按钮2</button>
</div>
<script>
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello world'
},
methods:{
btnClick:function (){
alert('你好世界');
},
divClick:function (){
alert('你好世界hhhhhhhh');
},
inputClick:function (){
alert("进行数据的提交");
},
keyUp:function (){
alert("点击了一下");
},
btn2Click:function (){
alert("只能点击一次")
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.4、条件判断、循环
2.4.1、v-if、v-else、v-else-if
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-if的使用</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2 v-if="isAction">{{message}}</h2>
<h2 v-else>{{message1}}</h2>
<h2 v-if="score>=90">优秀</h2>
<h2 v-else-if="score>=80">良好</h2>
<h2 v-else-if="score>=60">及格</h2>
<h2 v-else>不及格</h2>
</div>
<script>
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello world',
message1:'hhhhhh',
score:85,
isAction:false
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
案例:切换登录的方式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>第一个小案例</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 在进行切换账号进行登录的时候,可以通过属性,来防止其中input标签的复用-->
<span v-if="isShow">
<label>账号登录</label>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入账号" key="username"/>
</span>
<span v-else>
<label>邮箱登录</label>
<input type="email" placeholder="请输入邮箱" key="email"/>
</span>
<button @click="btn">切换登录方式</button>
</div>
<script>
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
isShow:true
},
methods:{
btn:function (){
// alert("你好世界");
this.isShow=!this.isShow
console.log(this.isShow)
// alert(this.isShow)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
在进行切换账号进行登录的时候,可以通过属性,来防止其中input标签的复用
2.4.2、v-if与v-show的区别
v-if:当v-if的值魏flase时,包含他的元素根本不存在dom之中
v-show:当v-show的值魏flase时,包含他的元素只是添加了一个行内的样式,将包含他的元素给隐藏起来了。
当需要切换的频率很高的时候,我们采用v-show,当频率不高的时候,我们采用v-if
2.4.3、v-for
官方推荐:当我们在使用v-for的时候我们尽量给相关的标签添加一个:key的属性,使其更好的复用。
常用的方法
- push往数组之中存放数据
- pop删除一个数组中的最后一个数据
- shift删除数组中的第一个数据
- unshift,在数组最前面添加元素(可以同时添加多个元素)
- splice():删除元素、插入元素、替换元素
- 删除元素:第二个参数传入的是你要删除几个元素
- 对数组进行赋值,在vue中自带的vue.set(this.name,‘index’,‘value’)
案例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>第一个案例</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<style>
.test1{
color: red;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-bind:class="{test1:currentIndex===index}" v-for="(item,index) in message" @click="test(index)">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
const app=new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
message:['猫和老鼠','舒克贝塔','黑猫警长','火影忍者'],
currentIndex: 0,
},
methods:{
test:function (index){
this.currentIndex=index;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

2.4.4、图书购买系统
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>购物车</title>
<link type="text/css" href="index.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div v-if="books.length>0">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>出版日期</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>购买数量</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(item,index) in books">
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.data}}</td>
<!-- 使用过滤器-->
<td>{{item.price | filterBefore}}</td>
<td>
<button @click="disincress(index)" v-bind:disabled="item.count<=1">-</button>
{{item.count}}
<button @click="incress(index)">+</button>
</td>
<td>
<button @click="remove(index)">移除</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>总价:{{totalPrice | filterBefore}}</h3>
</div>
<div v-else>
<h1>购物车空空如也,快去看看吧!!!!</h1>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
css
table {
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
}
th,td{
padding: 8px 16px;
border: 1px solid #e9e9e9;
text-align: left;
}
th{
background-color: #f7f7f7;
color: #5c6b77;
font-weight: 600;
}
js
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
books:[
{
id:1,
name:'算法导论',
data:'2006-9',
price:85,
count:1
},
{
id:2,
name:'UNIX编程艺术',
data:'2006-2',
price: 55.00,
count:1
},
{
id:3,
name:'代码大全',
data:'2006-3',
price: 128.00,
count:1
}
]
},
//过滤器,可以自动传参数,
filters:{
filterBefore:function (price){
return "¥"+price.toFixed(2);
}
},
//函数、方法
methods:{
//通过下边对数组内的内容进行修改
disincress:function (index){
let i=this.books[index].count
this.books[index].count=i-1
},
incress:function (index){
let i=this.books[index].count
this.books[index].count=i+1
},
remove:function (index){
// alert('进入了这个方法');
this.books.splice(index,1);
}
},
//计算属性
computed:{
totalPrice:function (){
let totalPrice=0;
for (let i=0; i<this.books.length;i++){
let num =this.books[i].count * this.books[i].price;
totalPrice=totalPrice+num;
}
return totalPrice;
}
}
})
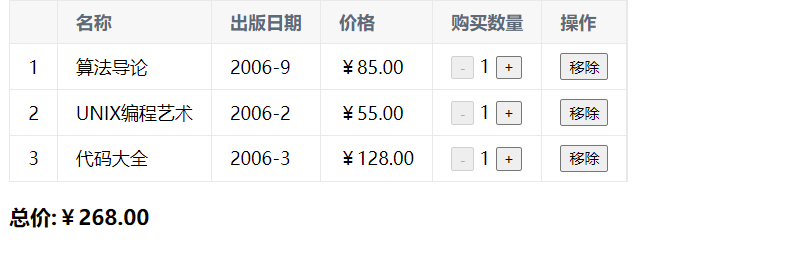
当全部移除之后呈现一下的情况

2.5、v-model表单绑定(是一个双向绑定)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-model的使用</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="message">
{{message}}
</div>
<script>
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好啊'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.5.1、v-model结合radio
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-model与radio的结合</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<label for="man">
<input type="radio" id="man" name="sex" value="男" v-model="sex"/>男
</label>
<label for="woman">
<input type="radio" id="woman" name="sex" v-model="sex" value="女"/>女
</label>
<h1>您的性别是:{{sex}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好世界',
sex:''
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

2.5.2、v-model与checkbox的结合使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-model与checkbox结合</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!--checkbox单选-->
<label for="test1">
<input type="checkbox" id="test1" value="同意协议" v-model="agree" >同意协议
</label>
<h2>你选择的是{{agree}}</h2>
<button v-bind:disabled="!agree">下一步</button>
<!-- 多选框-->
<input type="checkbox" value="篮球" v-model="hobbyes">篮球
<input type="checkbox" value="足球" v-model="hobbyes">足球
<input type="checkbox" value="乒乓球" v-model="hobbyes">乒乓球
<input type="checkbox" value="排球" v-model="hobbyes">排球
<h1>你选择的爱好是{{hobbyes}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello world',
agree:false,
//注意采用数组的形式进行接收
hobbyes:[]
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

注:在进行多选框的数据存储的时候,一定要采用数组的形式进行数据的接收
2.5.3、v-model与select的结合使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>v-model与select结合</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 选择一个-->
<select name="abc" v-model="fruit">
<option value="苹果" >苹果</option>
<option value="香蕉" >香蕉</option>
<option value="留恋" >榴莲</option>
<option value="葡萄" >葡萄</option>
</select>
<h1>您选择的说过是:{{fruit}}</h1>
<!-- 多选-->
<select name="abc" v-model="fruits" multiple>
<option value="苹果" >苹果</option>
<option value="香蕉" >香蕉</option>
<option value="留恋" >榴莲</option>
<option value="葡萄" >葡萄</option>
</select>
<h1>您选择的说过是:{{fruits}}</h1>
</div>
<script>
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello world',
fruit:"香蕉",
fruits:[]
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

修饰符
- lazy:在进行值的双向绑定的时候,当input的焦点失去的时候才会有值的互换。
- number:默认v-model输入的值都是String类型
- [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-r5IkQdYB-1648715189976)(…/AppData/Roaming/Typora/typora-user-images/image-20220215102937895.png)]
- trim:v-model.trim去掉空格
2、组件化开发
2.1、组件化的基本使用
组件化的使用必须是在vue实例的范围之内
作用,可以很大程度的提高代码的复用
- 创建组件构造器对象
- 注册组件
- 使用组件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>组件化的基本使用</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<test></test>
</div>
<script>
<!-- 创建组件的构造器-->
const cpnC=Vue.extend({
template:
"<div>" +
"<h1>我是标题</h1>" +
"<p>我是内容111111</p>"+
"<p>我是内容222222</p>"+
"</div>"
});
//注册组件
Vue.component('test',cpnC)
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'hello world'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

2.2、全局组件和局部组件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>注册组件的语法糖简写</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js" ></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cpn1></cpn1>
<cpn2></cpn2>
</div>
<script>
<!-- 全局作用与的组件的简写-->
Vue.component('cpn1',{
template:"<div>" +
"<h1>我是全局作用域的标题</h1>" +
"<p>我是内容</p>"+
"</div>"
})
//局部作用域的组件的简写
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
components:{
'cpn2':{
template: "<div>" +
"<h1>我是局部作用域的标题</h1>" +
"<p>这是内容1111111</p>"+
"</div>"
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

2.3、组件模板抽离的方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>组件模板抽离方法</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cpn></cpn>
<my-cpn></my-cpn>
</div>
<template id="cpn2">
<div>
<h1>我是标题</h1>
<p>我是内容1111222</p>
</div>
</template>
<script type="text/x-template" id="cpn1">
<div>
<h1>我是标题</h1>
<p>我是内容1111111</p>
</div>
</script>
<script>
Vue.component('cpn',{
template:"#cpn2",
})
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
components:{
'my-cpn':{
template: '#cpn'
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.4、组件数据的获取
注:在vue中,组件时一个独立的模块,组件中的数据无法直接在vue的实例之中直接获取。
组件数据的存放的位置
- 组件对象也有一个data属性(也可以有methods属性)
- 只是这个data属性必须是一个函数
- 而且这个函数返回类型是一个对象,对象内部保存着数据
2.4.1、组件中的data为什么必须是函数
注:因为组件的存在可以使代码进行多次的复用,如果直接对data中写入数据时,会产生组件之间的数据的相互的影响,但是通过函数来解决,则会避免这个问题,通过函数进行数据的返回,类似于在内存中开辟一个新的地址,之后各个值之间互不影响
2.5、父子组件通信,父传子(props)
父级向子级元素传递数据的方式
- 通过props向子组件传递数据
- 通过时间进行数据的传递
props数据验证的类型
- String
- Number
- Boolean
- Array
- Object
- Date
- Function
- Symbol
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>父级向子级进行数据传输</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<cpn v-bind:cmmessage="message" v-bind:cmmoves="moves"></cpn>
</div>
<div id="app1">
<cpn1 v-bind:cmmoves1="moves1"></cpn1>
</div>
<template id="test">
<div>
{{cmmessage}}
<ul>
<li v-for="item in cmmoves">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<template id="test1">
<ul >
<li v-for="item1 in cmmoves1">{{item1}}</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
<!-- 常见的写法-->
const ctn={
template: '#test',
//对数据类型进行相应的限制
props:{
cmmessage:String,
cmmoves:Array
}
}
//进行设置默认值
const ctn1={
template: '#test1',
props:{
cmmessage1:{
type:String,
// 设置默认值
default:'aaa',
// 设为必须传入参数
required:true
},
cmmoves1:{
//设置数据类型
type:Array,
//default: [] //在vue的2.5.17以上的版本这个写法格式胡出现错误
// default: function (){
// return [];
// }
}
}
}
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
message:'你好世界',
moves:['海贼王','火影忍者','七龙珠','不良人','魔道祖师'],
},
components:{
'cpn':ctn,
'cpn1':ctn1
}
})
const app1=new Vue({
el:'#app1',
data:{
moves1:['天龙八部','射雕英雄传','神雕侠侣'],
},
components:{
'cpn1':ctn1
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
props驼峰标识
在进行v-bind绑定的时候,在vue中式不支持驼峰标识的
解决方式:在大写字母前边通过-进行连接,之后大写字母改成小写字母
子级向父级传输数据(需要进行自定义事件)****$(emit)进行传输
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>子组件向父级组件传输</title>
<script src="../js/vue.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 在自己进行自定义函数的时候,函数的名字一定要与$emit中的设定的函数名字一样-->
<hello @submites1="submites2"></hello>
</div>
<!--设置组件-->
<template id="test1s">
<div>
<h1>11111</h1>
<button @click="submites(item)" v-for="item in books">{{item.name}}</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const ct={
template:'#test1s',
// 组件中的数据必须是一个函数
data:function (){
return{
books:[
{
id:111,
name:'古代史学文书'
},
{
id:222,
name:"现代史学文书"
},
{
id:333,
name:'道家文化'
},
{
id:444,
name:'儒家文化'
}
]
}
},
methods:{
submites:function (item){
// alert("点击的按钮式"+item)
//用过$emit来进行参数的传递和函数的反射
this.$emit("submites1",item)
}
}
}
const app=new Vue({
el:'#app',
//进行组件注册
components:{
'hello':ct
},
//创建函数
methods: {
submites2:function (item){
console.log("所接收的数据是"+item)
console.log(this.submites2)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.6、父子组件通信,结合双向绑定
2.7、js模块化即调用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>js模块化</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--为避免在引用多个js文件时,js文件中设定的参数重复而引发的问题,我们采用将js代码模块化-->
<!--通过设定type的类型,将索引入的js的文件设为独立的模块,type的类型一定得是module-->
<script type="module" src="./aa.js"></script>
<script type="module" src="./bb.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
aa.js 内容的导出
//通过export直接将函数getSum进行导出,保证该函数在其他的js文件中仍然可以被调用
export function getSum(sum,sum1){
return sum+sum1;
}
export let name="小明"
//通过export对aa.js文件中所设的的函数进行以对象的当时进行导出
let name1="小李"
function getSum1(num1,num2){
return num1*num2;
}
export {name1,getSum1}
export class parent{
run(){
alert("小王跑步得了一个第一")
}
}
bb.js内容的导入
//对aa.js文件中导出的函数进行调用
import {getSum,name} from "./aa.js";
//对函数进行相应的调用
// alert(getSum(10,20))
console.log(getSum(10, 20));
//对设定的参数进行相应的调用
// alert(name)
console.log(name);
//都如export一对象的形式导出的相关的函数
import {name1,getSum1} from "./aa.js";
// alert(name1)
// alert(getSum1(10,20))
//当我们导出的参数和函数的数量非常多的时候我们通过*来代替所有的函数和参数通过as来对导入的对象进行封装
import * as aaa from "./aa.js" //在进行导入其他的js文件的时候建议将其他js文件的文件的名称写全,文件后缀一丁要加上
alert(aaa.getSum1(20,30));
alert(aaa.name1)
let parent =new aaa.parent()
alert(parent.run())
3、脚手架
3.1、简介
vue的一种架构
4、路由
4.1、路由的搭建框架
-
下载router插件
npm install router --save -
查看是否下载成功package.json
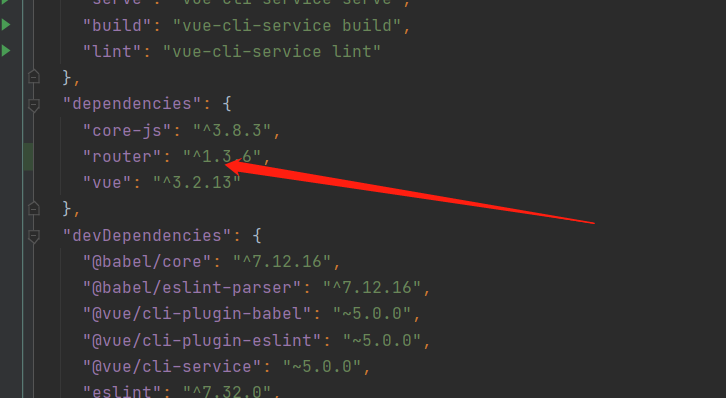
-
在src目录下创建router目录并在里面书写index.js文件
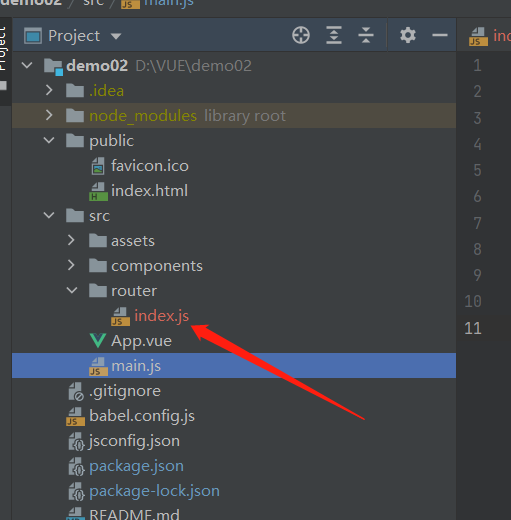
-
在index.js文件中进行相关的配置并进行导出
//配置路由相关的路由 // eslint-disable-next-line no-unused-vars import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Vue from 'vue' //通过Vue.use来安装插件 Vue.use(VueRouter) //创建路由对象 const routers=[]; // eslint-disable-next-line no-unused-vars const router =new VueRouter({ //在其中配置映射关系 routers:routers }) //讲router挂在到vue实例中 // 进行导出 export {router} -
在mian.js文件中的vue实例中进行配置
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import router from './router/index' Vue.config.productionTip=false new Vue({ el:'#app', router:router, render:h =>h(App) })
export {name1,getSum1}
export class parent{
run(){
alert(“小王跑步得了一个第一”)
}
}
**bb.js内容的导入**
```js
//对aa.js文件中导出的函数进行调用
import {getSum,name} from "./aa.js";
//对函数进行相应的调用
// alert(getSum(10,20))
console.log(getSum(10, 20));
//对设定的参数进行相应的调用
// alert(name)
console.log(name);
//都如export一对象的形式导出的相关的函数
import {name1,getSum1} from "./aa.js";
// alert(name1)
// alert(getSum1(10,20))
//当我们导出的参数和函数的数量非常多的时候我们通过*来代替所有的函数和参数通过as来对导入的对象进行封装
import * as aaa from "./aa.js" //在进行导入其他的js文件的时候建议将其他js文件的文件的名称写全,文件后缀一丁要加上
alert(aaa.getSum1(20,30));
alert(aaa.name1)
let parent =new aaa.parent()
alert(parent.run())
3、脚手架
3.1、简介
vue的一种架构
4、路由
4.1、路由的搭建框架
-
下载router插件
npm install router --save -
查看是否下载成功package.json
[外链图片转存中…(img-caho3uAR-1648715189978)]
-
在src目录下创建router目录并在里面书写index.js文件
[外链图片转存中…(img-Fs3AQ1PR-1648715189979)]
-
在index.js文件中进行相关的配置并进行导出
//配置路由相关的路由 // eslint-disable-next-line no-unused-vars import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Vue from 'vue' //通过Vue.use来安装插件 Vue.use(VueRouter) //创建路由对象 const routers=[]; // eslint-disable-next-line no-unused-vars const router =new VueRouter({ //在其中配置映射关系 routers:routers }) //讲router挂在到vue实例中 // 进行导出 export {router} -
在mian.js文件中的vue实例中进行配置
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import router from './router/index' Vue.config.productionTip=false new Vue({ el:'#app', router:router, render:h =>h(App) })