一、Bootstrap Carousel
-
vscode进行多行光标操作:
Shift + Alt + (拖动鼠标) 列(框)选择 Column (box) selection
Ctrl + Shift + Alt +(箭头键) 列(框)选择 Column (box) selection
Ctrl + Shift + Alt + PgUp / PgDown 列(框)选择页上/下 Column (box) selection page up/down -
slide 悬浮停顿,设置速度等
<div id="carouselExampleSlidesOnly" class="carousel slide" data-bs-ride="carousel" data-interval="1000" data-pause="hover">
<div class="carousel-inner">
<div class="carousel-item active" style="background-color:pink">
<img src="..." class="d-block w-100" alt="...">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item" style="background-color:blue">
<img src="..." class="d-block w-100" alt="...">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item" style="background-color:yellow">
<img src="..." class="d-block w-100" alt="...">
</div>
</div>
</div>
.carousel-item{
height: 500px;
}
- 带左右键控制的carousel
<div id="carouselExampleControls" class="carousel slide" data-bs-ride="carousel">
<div class="carousel-inner">
<div class="carousel-item active" style="background-color:pink">
<img src="..." class="d-block w-100" alt="...">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item" style="background-color:blue">
<img src="..." class="d-block w-100" alt="...">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item" style="background-color:yellow">
<img src="..." class="d-block w-100" alt="...">
</div>
</div>
<button class="carousel-control-prev" type="button" data-bs-target="#carouselExampleControls" data-bs-slide="prev">
<span class="carousel-control-prev-icon" aria-hidden="true"></span>
<span class="visually-hidden">Previous</span>
</button>
<button class="carousel-control-next" type="button" data-bs-target="#carouselExampleControls" data-bs-slide="next">
<span class="carousel-control-next-icon" aria-hidden="true"></span>
<span class="visually-hidden">Next</span>
</button>
</div>
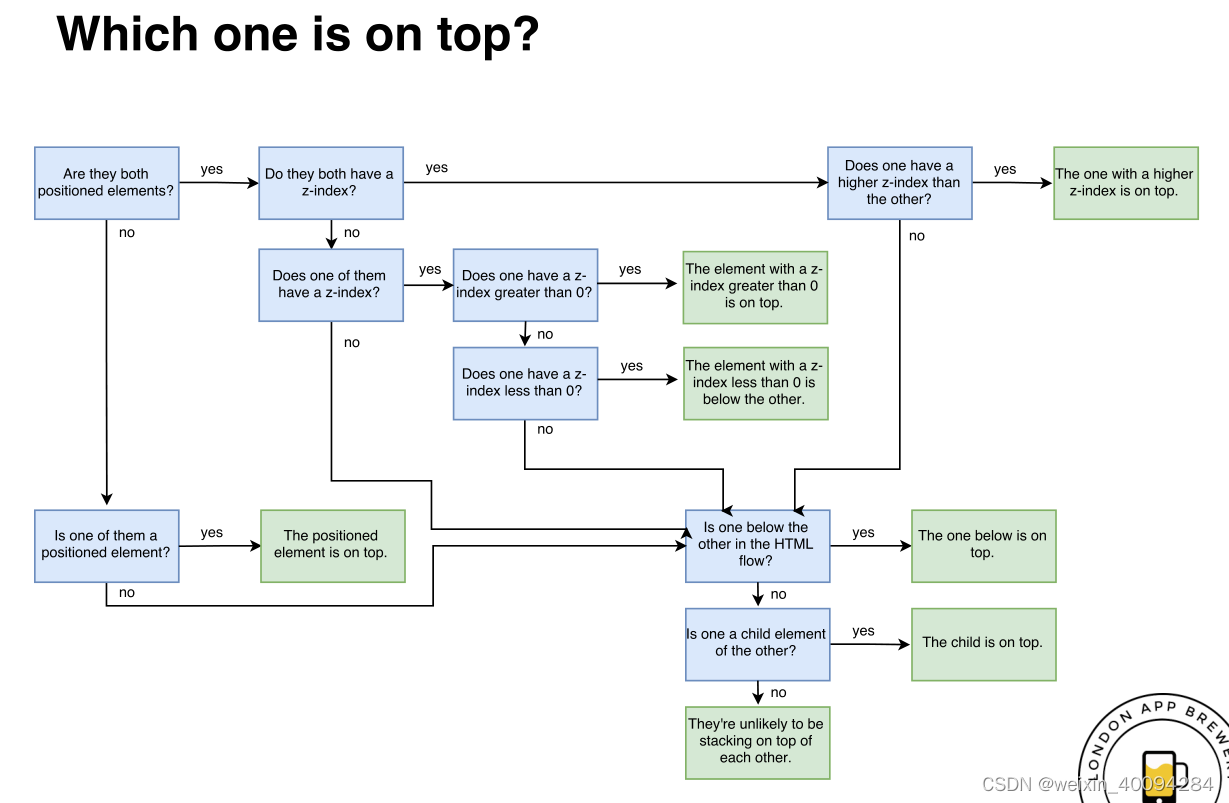
二、CSS-Z index
HTML natural stacking order:当element的position都有设置,code中先有的element在距离屏幕最远的地方,后有的element叠加在先有的element之上。
css-z index: 所有element默认z index是0, 如果z index是-1,代表在其他元素的后面(距离屏幕更远);如果z index是1,代表在其他元素的上面(距离屏幕更近)
注意:css-z index生效的条件是,element的position都有设置,无论是absolute,fixed,或者relative;如果position没有设置,则z index没用
三、media query
对移动化需求:
- 建立一个独立于电脑端的网站:m.xxx.com
或者 2. make the website responsive
<h1> Hello World!</h1>
@media print{
h1{
color:red;
}
}
在打印时会变成红色
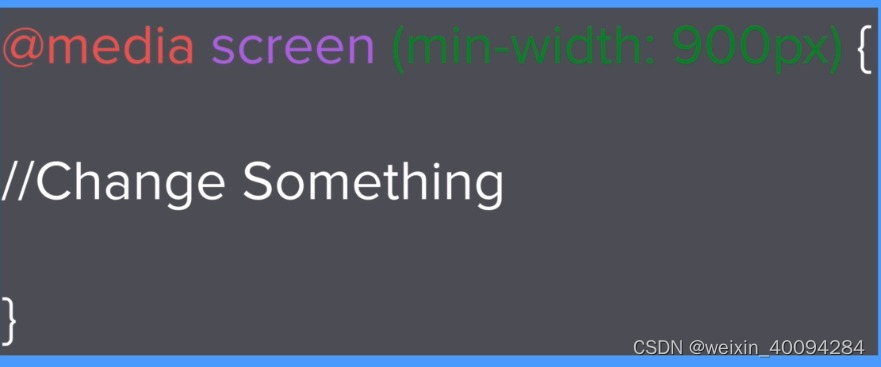
media query:
@media<type><feature>
media query是个query,它首先check《type》《feature》是否满足,满足再执行操作:
h1{
font-size:30px;
}
@media (max-width:900px){
h1{
font-size:60px;
}
}
则在分辨率横向<=900px时,执行60px的字号;>900时,执行30px的字号
分辨:显示器分辨率,浏览器,viewport(网站在屏幕显示的尺寸)
四、nav bar设置地址
给nav bar的href填入#id,可使其跳转到对应的section。
五、code refactoring
DRY:don’t repeat yourself
相反,WET:we enjoy typing
实际应用:
- h1, h2,…h6{font-family} 然后在各个section相应标题有变化的地方,重起一个class,对其进行规定
- 各处text-align是center,直接在body中规定,其他处可删除。再对个别text-align是left的地方做出规定。
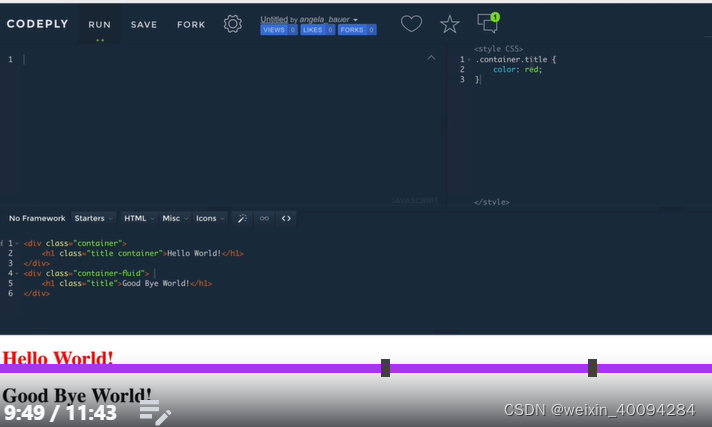
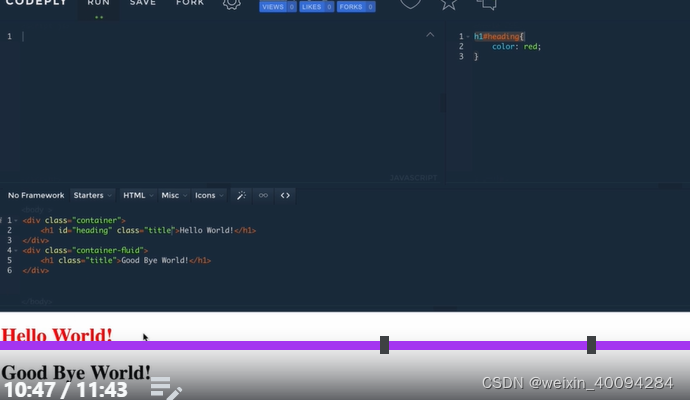
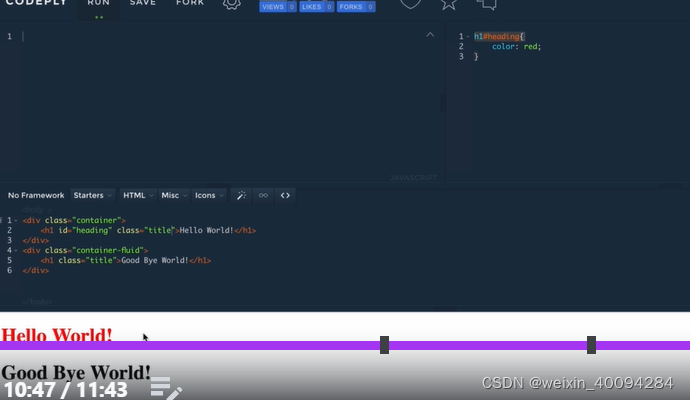
六、advanced CSS—combined selectors:
#id. className{
}
对一个section id下的class做出规定,而不影响其他的同名class
- 多selectors:

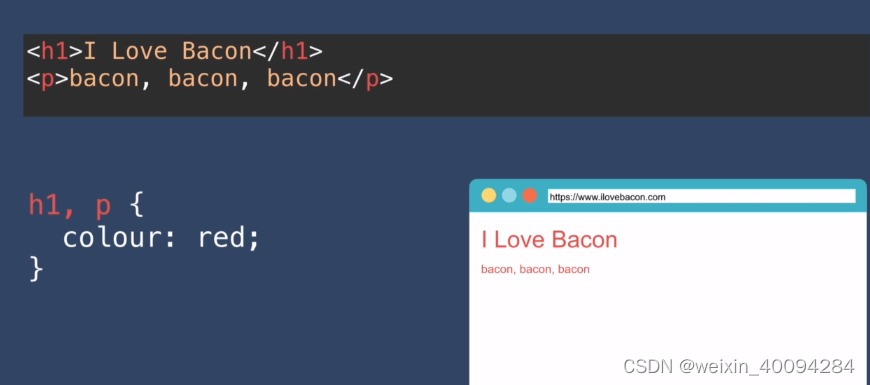
- 层级selectors:


这种一般就直接#title: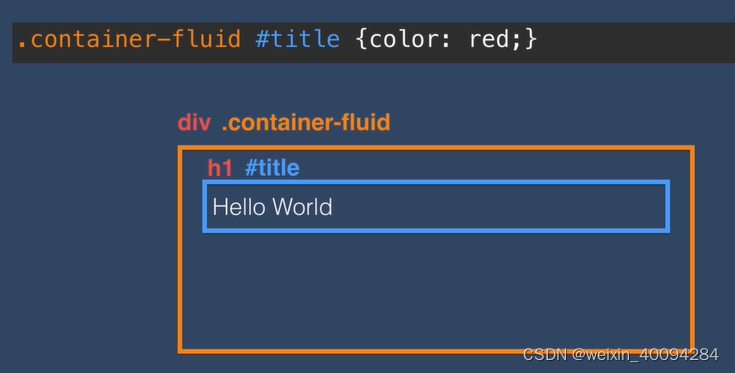
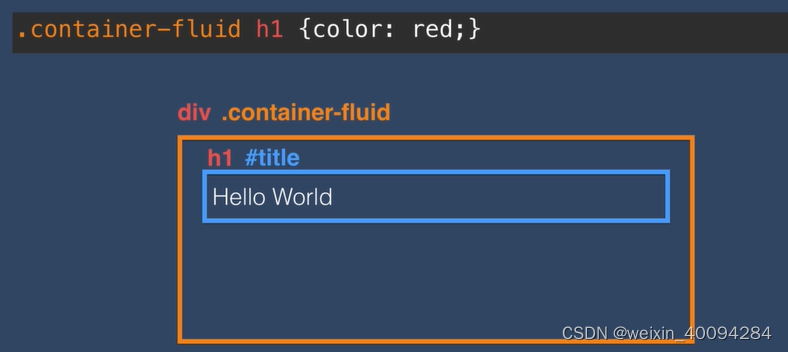
从右往左看,右边是child,左边是parent:

- combined selectors

或者

但二者是都对于同一个element起作用。

有空格的是母子关系:
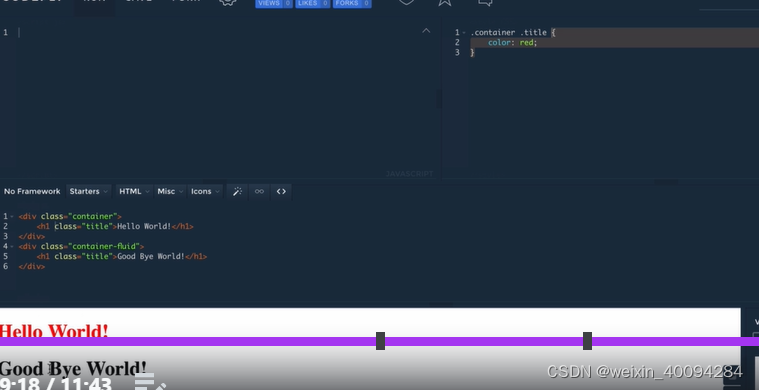
无空格的指class名需要同时满足:
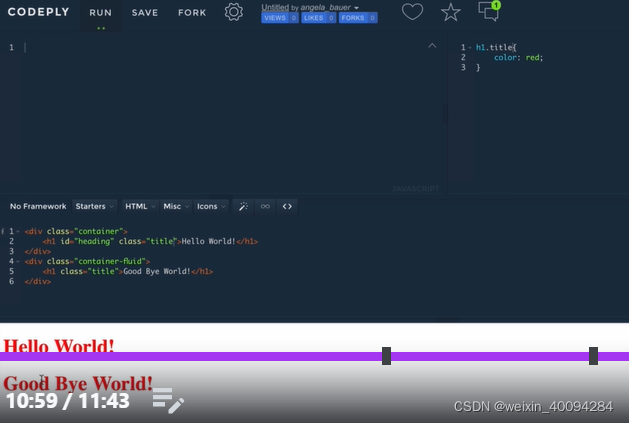
七、selector priority
- 对同一个element的css规定,后面的会代替前面的:
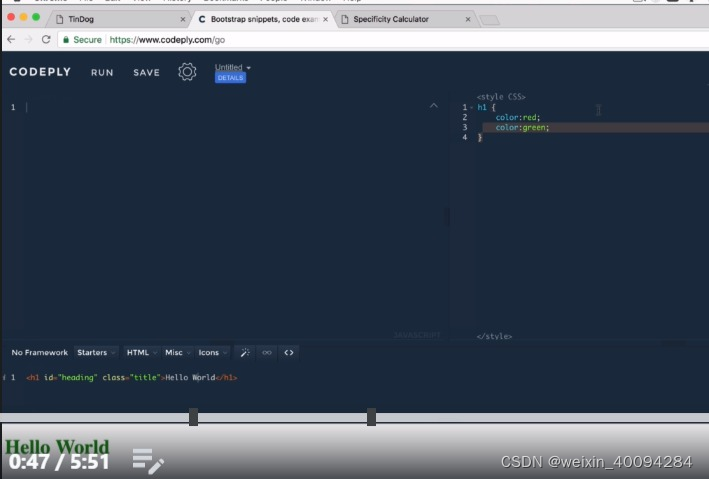
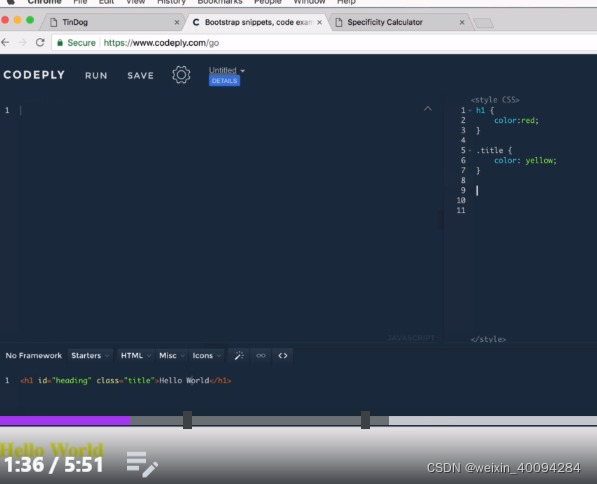
- 更specific的、更高hierarchy的具有priority,比如单条的id比class更高,执行更specific的css:
- inline的设定总是要高于css的
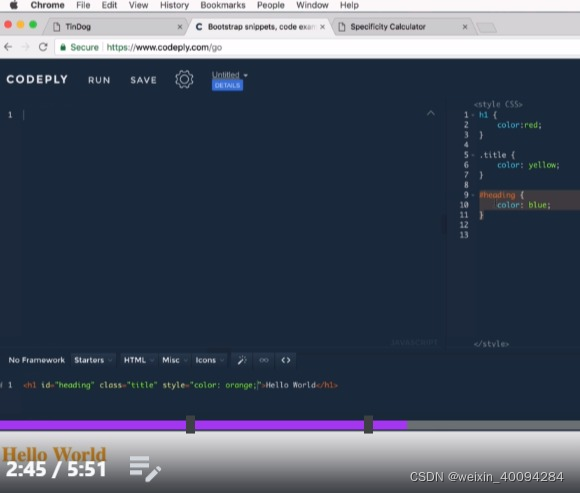
- 避免rules conflict:
1)节俭使用id,能用class的地方尽量都用class,实在需要用id再用id,如section id–需要nav定位到对方
2)class名只用一个,eg big-heading后不要再取名big name等等
3)尽量避免使用inline style=“…”