Vue
Vue(读音/vju/, 类似于view) 是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架, 发布于2014年2月。与其它大型框架不同的是, Vue被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用。Vue的核心库只关注视图层, 不仅易于上手, 还便于与第三方库(如:vue-router,vue-resource,vue x) 或既有项目整合。
-
MVVM模式的实现者
-
Model:模型层, 在这里表示JavaScript对象
-
View:视图层, 在这里表示DOM(HTML操作的元素)
-
ViewModel:连接视图和数据的中间件, Vue.js就是MVVM中的View Model层的实现者
-
-
为什么要使用MVVM
MVVM模式和MVC模式一样,主要目的是分离视图(View)和模型(Model),有几大好处
- 低耦合:视图(View)可以独立于Model变化和修改,一个ViewModel可以绑定到不同的View上,当View变化的时候Model可以不变,当Model变化的时候View也可以不变。
- 可复用:你可以把一些视图逻辑放在一个ViewModel里面,让很多View重用这段视图逻辑。
- 独立开发:开发人员可以专注于业务逻辑和数据的开发(ViewMode),设计人员可以专注于页面设计。
- 可测试:界面素来是比较难以测试的,而现在测试可以针对ViewModel来写。
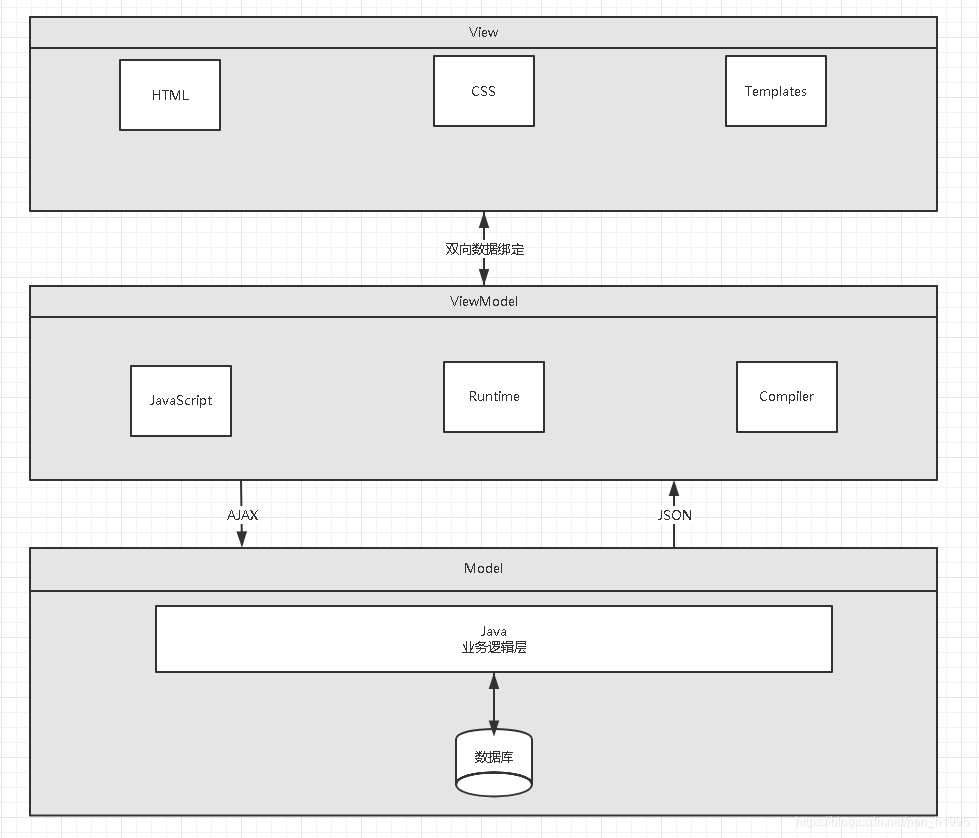
在MVVM架构中, 是不允许数据和视图直接通信的, 只能通过ViewModel来通信, 而View Model就是定义了一个Observer观察者
- ViewModel能够观察到数据的变化, 并对视图对应的内容进行更新
- ViewModel能够监听到视图的变化, 并能够通知数据发生改变
至此, 我们就明白了, Vue.js就是一个MV VM的实现者, 他的核心就是实现了DOM监听与数据绑定
-
为什么要使用Vue.js
-
轻量级, 体积小是一个重要指标。Vue.js压缩后有只有20多kb(Angular压缩后56kb+,React压缩后44kb+)
-
移动优先。更适合移动端, 比如移动端的Touch事件
-
易上手,学习曲线平稳,文档齐全
-
吸取了Angular(模块化) 和React(虚拟DOM) 的长处, 并拥有自己独特的功能,如:计算属性
-
开源,社区活跃度高
-
一,第一个Vue程序
方式一:直接用 script 引入
直接下载并用 <script> 标签引入,Vue 会被注册为一个全局变量。
在开发环境下不要使用压缩版本,不然你就失去了所有常见错误相关的警告!
开发版本包含完整的警告和调试模式
生产版本删除了警告,33.46KB min+gzip
方式二:CDN
对于制作原型或学习,你可以这样使用最新版本:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>
对于生产环境,我们推荐链接到一个明确的版本号和构建文件,以避免新版本造成的不可预期的破坏:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14"></script>
如果你使用原生 ES Modules,这里也有一个兼容 ES Module 的构建文件:
<script type="module">
import Vue from 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.esm.browser.js'
</script>
你可以在 cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue 浏览 NPM 包的源代码。
Vue 也可以在 unpkg 和 cdnjs 上获取 (cdnjs 的版本更新可能略滞后)。
请确认了解不同构建版本并在你发布的站点中使用生产环境版本,把 vue.js 换成 vue.min.js。这是一个更小的构建,可以带来比开发环境下更快的速度体验。
创建项目
1,导入vue.js
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
2,编写页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--视图 view-->
<div id="app">
{{message}}
</div>
<!--<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>-->
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script>
/*模型model*/
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
message:"hello,vue!"
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
3,测试
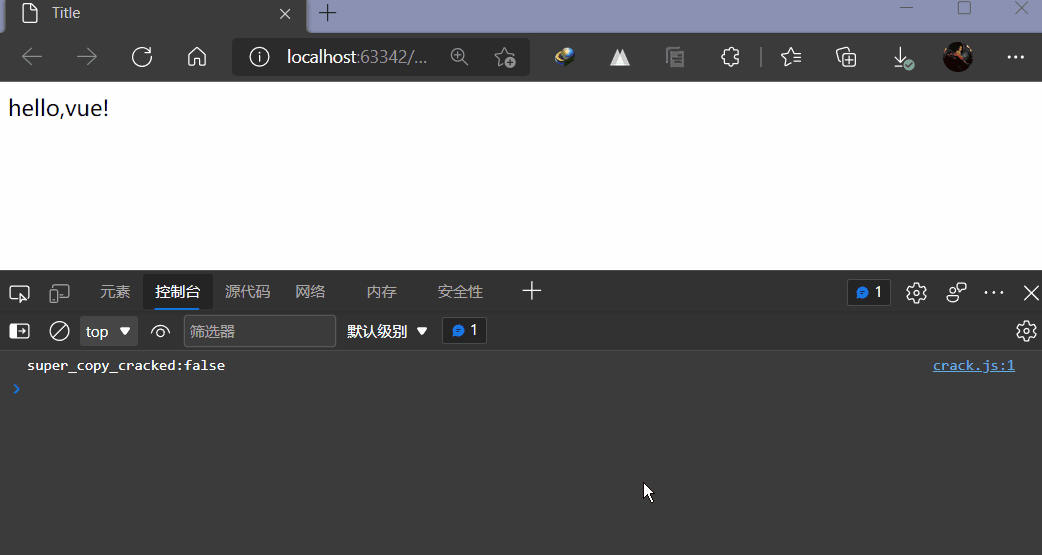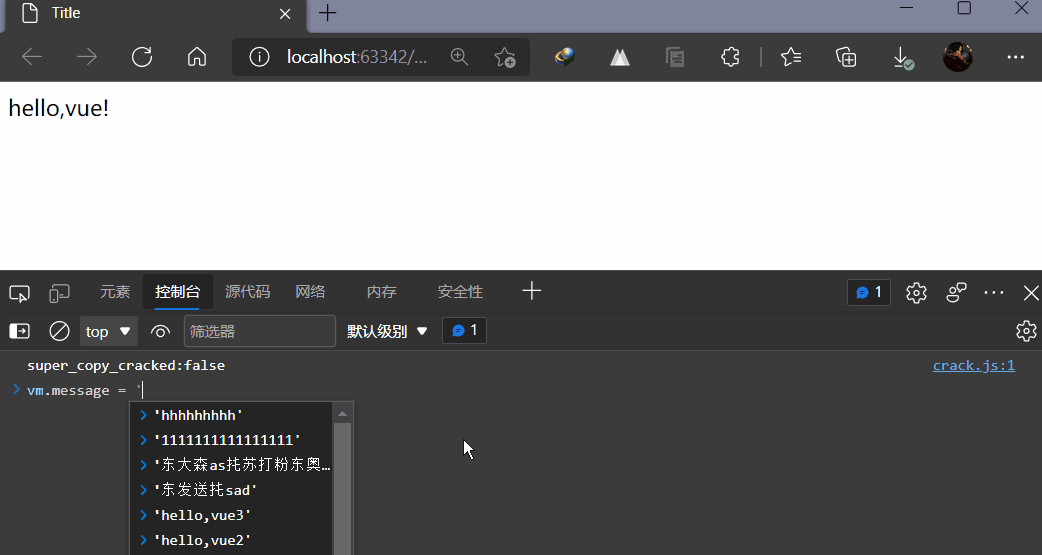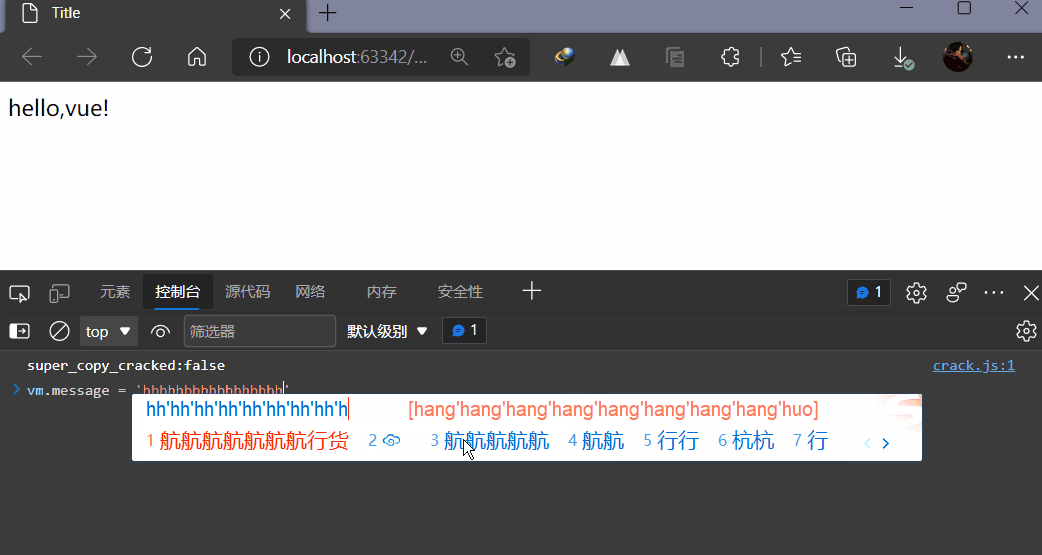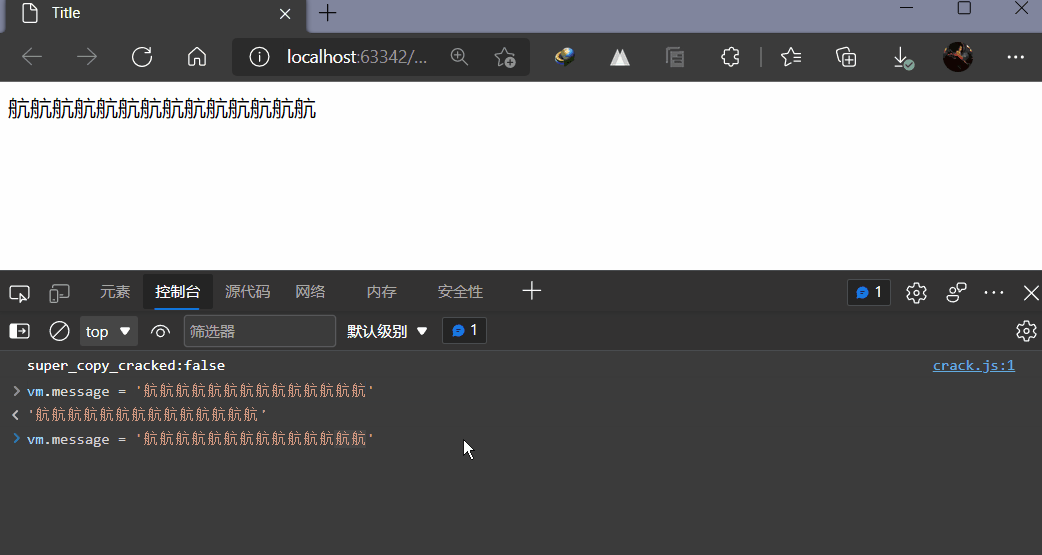
二,指令
2.1,v-bind指令
我们已经成功创建了第一个Vue应用!看起来这跟渲染一个字符串模板非常类似, 但是Vue在背后做了大量工作。现在数据和DOM已经被建立了关联, 所有东西都是响应式的。我们在控制台操作对象属性,界面可以实时更新!
使用v-bind来绑定元素特性!
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--view层:模板-->
<div id="app">
<!-- {{message}}-->
<span v-bind:title="message">
鼠标悬停几秒钟查看此处动态信息
</span>
</div>
<!--<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>-->
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script>
/*模型model,数据*/
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
message:"hello,vue!"
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
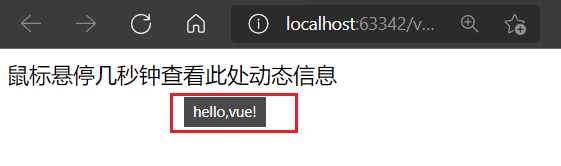
- v-bind等被称为指令。指令带有前缀v以表示它们是Vue提供的特殊特性。
- 它们会在渲染的DOM上应用特殊的响应式行为在这里,该指令的意思是:“将这个元素节点的title特性和Vue实例的message属性保持一致”。
- 打开浏览器控制台, 输入app, message=‘新消息’,就会再一次看到这个绑定了title特性的HTML已经进行了更新。
2.2,条件判断v-if v-else v-else-if
<!--view层:模板-->
<div id="app">
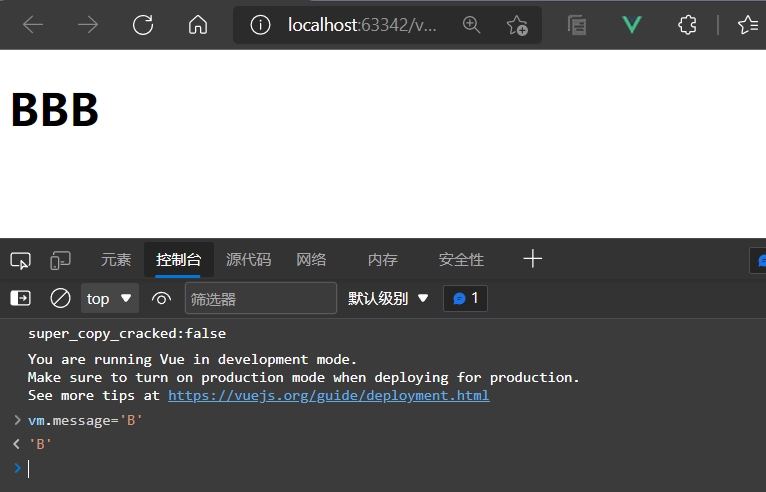
<h1 v-if="message==='A'">AAA</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="message==='B'">BBB</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="message==='C'">CCC</h1>
<h1 v-else>DDD</h1>
</div>
<!--<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>-->
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script>
/*模型model,数据*/
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
message: "A"
}
});
</script>
</body>
2.3,遍历循环 v-for
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--view层:模板-->
<div id="app">
<!-- <p v-for="item in items">-->
<!--可以加下标-->
<p v-for="(item,index) in items">
{{item.message}}--{{index}}
</p>
<!-- msg111--0
msg222--1
msg333--2
-->
</div>
<!--<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>-->
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script>
/*模型model,数据*/
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
items: [
{message: 'msg111'},
{message: 'msg222'},
{message: 'msg333'}
]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.4,事件处理
v-on监听事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--view层:模板-->
<div id="app">
<button v-on:click="sayHi">点击</button>
</div>
<!--<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>-->
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script>
/*模型model,数据*/
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
message: "昂哈哈哈哈哈哈哈"
},
methods: { //方法必须定义在vue的methods中,v-on:绑定事件
sayHi: function (event){
alert(this.message);
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.5,vue的常用属性
el属性
- 用来指示vue编译器从什么地方开始解析 vue的语法,可以说是一个占位符。
data属性
- 用来组织从view中抽象出来的属性,可以说将视图的数据抽象出来存放在data中。
template属性
- 用来设置模板,会替换页面元素,包括占位符。
methods属性
- 放置页面中的业务逻辑,js方法一般都放置在methods中
render属性
- 创建真正的Virtual Dom
computed属性
- 用来计算
- Vue.js 计算属性,计算属性在处理一些复杂逻辑时是很有用的
watch属性
- Vue.js 监听属性 watch,我们可以通过 watch 来响应数据的变化
- watch:function(new,old){} 监听data中数据的变化 两个参数,一个返回新值,一个返回旧值。
三,Vue:表单双绑, 组件
3.1,双向绑定
? Vue.js是一个MVVM框架, 即数据双向绑定, 即当数据发生变化的时候, 视图也就发生变化, 当视图发生变化的时候,数据也会跟着同步变化
- 你可以用
v-model指令在表单input、textarea及select元素上创建双向数据绑定。它会根据控件类型自动选取正确的方法来更新元素。尽管有些神奇, 但v-model本质上不过是语法糖。它负责监听用户的输入事件以更新数据,并对一些极端场景进行一些特殊处理。 - 注意:
v-model会忽略所有表单元素的value、checked、selected特性的初始值而总是将Vue实例的数据作为数据来源。你应该通过JavaScript在组件的data选项中声明初始值!
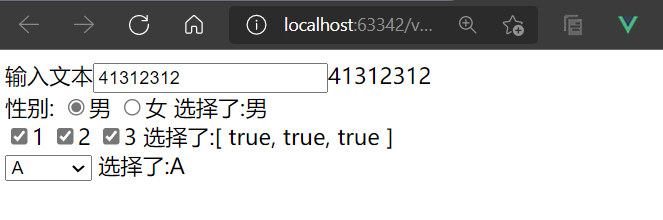
测试
<body>
<!--view层:模板-->
<div id="app">
<!--输入打印-->
<label>
输入文本<input type="text" v-model:value="message"/>{{message}}
</label><br/>
<!--单选框-->
<label>
性别:
<input type="radio" name="sex" value="男" v-model:value="sex"/>男
<input type="radio" name="sex" value="女" v-model:value="sex"/>女
选择了:{{sex}}
</label><br/>
<!--多选框-->
<label>
<input type="checkbox" name="aaa" value="1" v-model:value="box[0]"/>1
<input type="checkbox" name="aaa" value="2" v-model:value="box[1]"/>2
<input type="checkbox" name="aaa" value="3" v-model:value="box[2]"/>3
选择了:{{box}}
</label><br/>
<!--下拉框-->
<label>
<select v-model:aria-valuetext="select">
<option value="" disabled>请选择</option>
<option>A</option>
<option>B</option>
<option>C</option>
</select>
选择了:{{select}}
</label><br/>
</div>
<!--<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>-->
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script>
/*模型model,数据*/
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
message: '123',
sex: '',
select: '',
box: []
}
});
</script>
</body>
3.2,组件
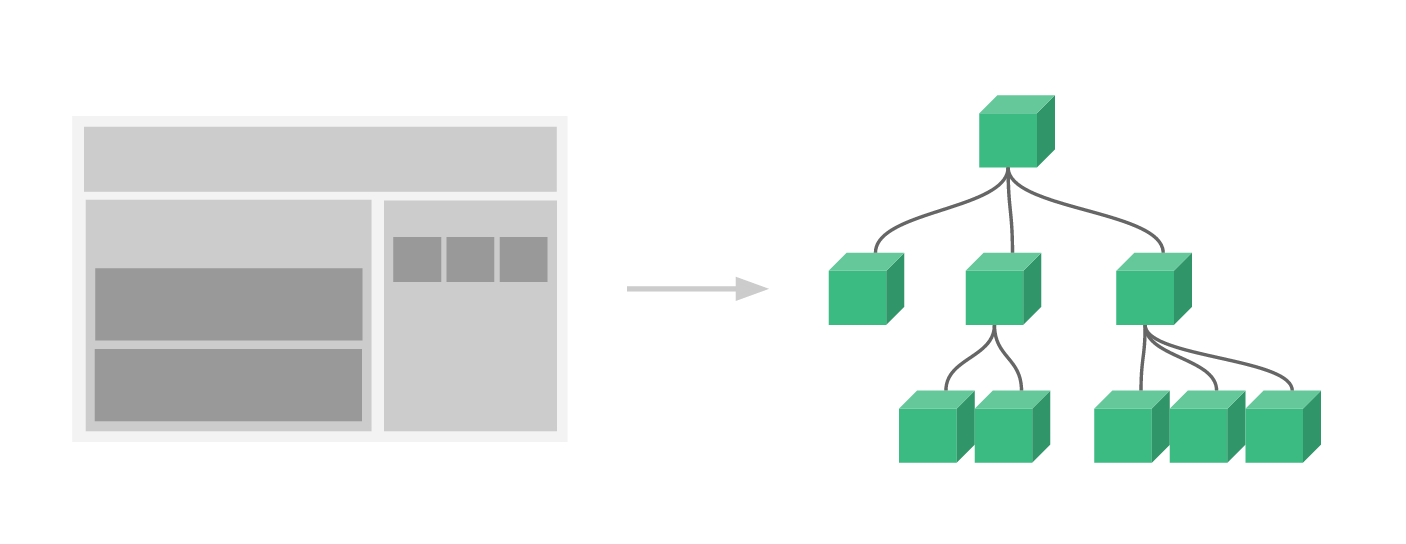
什么是组件
- 组件是可复用的Vue实例,说白了就是一组可以重复使用的模板,跟JSTL的自定义标签、Thymeleaf的th:fragment 等框架有着异曲同工之妙。通常一个应用会以一棵嵌套的组件树的形式来组织:
Vue.component()方法注册组件
- 注意:在实际开发中,我们并不会用以下方式开发组件,而是采用vue-cli创建.vue模板文件的方式开发,以下方法只是为了让大家理解什么是组件。
创建一个组件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--view层:模板-->
<div id="app">
<!--组件: 传递给组件中的值: props-->
<ccc v-for="item in items" v-bind:system="item"></ccc>
<!--把组件想象成一个函数
props为入参
template为要执行的方法
v-bind:xxxx=""就相当于参数赋值
-->
</div>
<!--<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.14/dist/vue.js"></script>-->
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component("ccc",{
props: ['system'],
template: '<p>{{system}}</p>'
})
/*模型model,数据*/
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
items: ["windows","linux","mac"]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
- Vue.component():注册组件
- ccc:自定义组件的名字
- template:组件的模板(自定义标签)
- v-for=“item in items”:遍历我们定义的items数组, item:定义的属性名
- v-bind:system=“item”:绑定传入的props名: system
四,Axios异步通信
什么是Axios
Axios是一个开源的可以用在浏览器端和Node JS的异步通信框架, 她的主要作用就是实现AJAX异步通信,其功能特点如下:
- 从浏览器中创建XMLHttpRequests
- 从node.js创建http请求
- 支持Promise API[JS中链式编程]
- 拦截请求和响应
- 转换请求数据和响应数据
- 取消请求
- 自动转换JSON数据
- 客户端支持防御XSRF(跨站请求伪造)
GitHub:https://github.com/axios/axios
中文文档:http://www.axios-js.com/
为什么要使用Axios
? 由于Vue.js是一个视图层框架并且作者(尤雨溪) 严格准守SoC(关注度分离原则)所以Vue.js并不包含AJAX的通信功能, 为了解决通信问题, 作者单独开发了一个名为vue-resource的插件, 不过在进入2.0版本以后停止了对该插件的维护并推荐了Axios框架。少用jQuery, 因为它操作Dom太频繁!
4.1,创建一个Axios
Vue的生命周期
官方文档:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/instance.html#生命周期图示
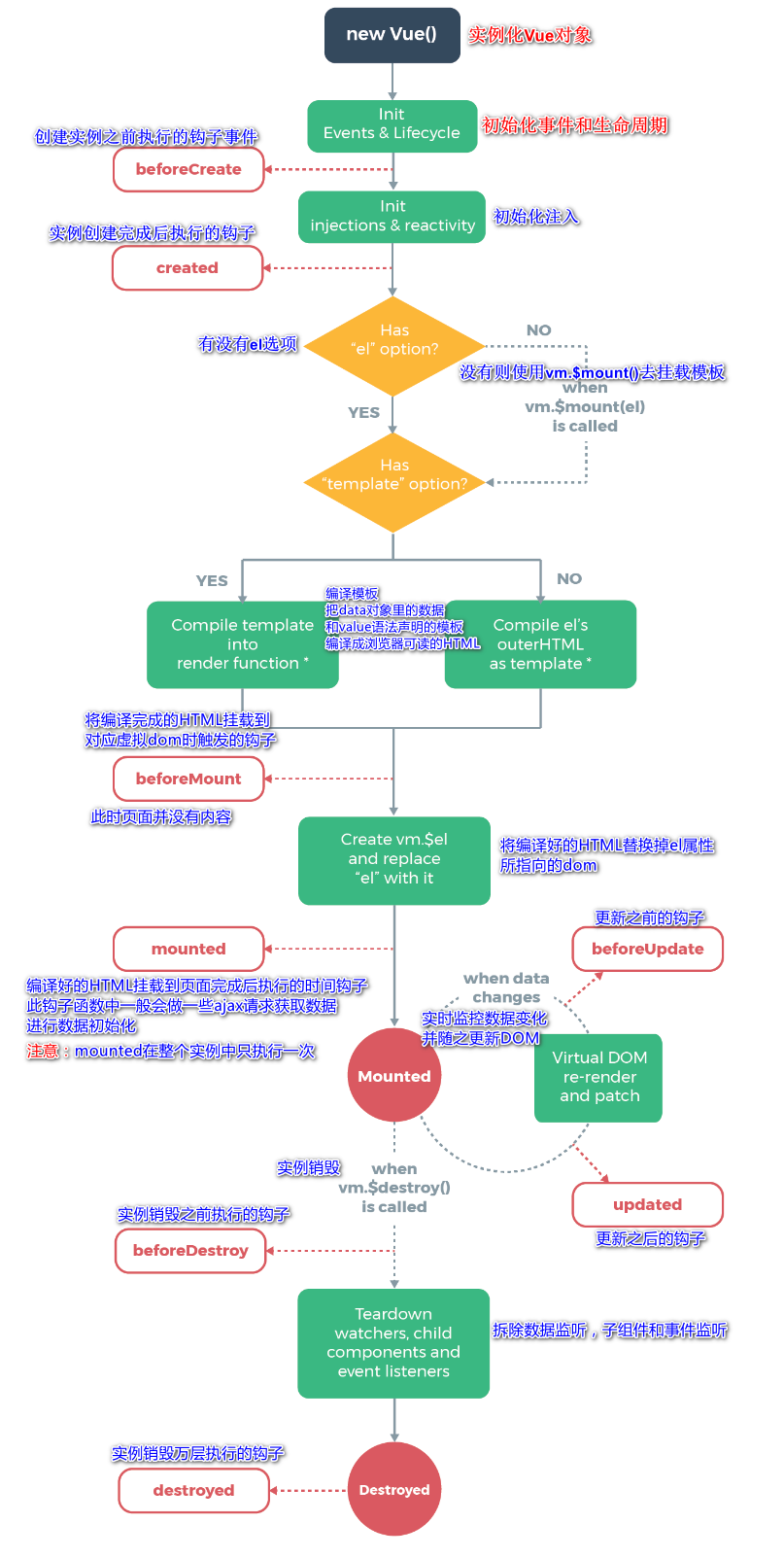
Vue实例有一个完整的生命周期,也就是从开始创建初女台化数据、编译模板、挂载DOM、渲染一更新一渲染、卸载等一系列过程,我们称这是Vue的生命周期。通俗说就是Vue实例从创建到销毁的过程,就是生命周期。
在Vue的整个生命周期中,它提供了一系列的事件,可以让我们在事件触发时注册JS方法,可以让我们用自己注册的JS方法控制整个大局,在这些事件响应方法中的this直接指向的是Vue的实例。
创建data.JSON
{
"name": "狂神说Java",
"url": "https://baidu.com",
"page": 1,
"isNonProfit": true,
"address": {
"street": "含光门",
"city": "陕西西安",
"country": "中国"
},
"links": [
{
"name": "bilibili",
"url": "https://space.bilibili.com/95256449"
},
{
"name": "狂神说Java",
"url": "https://blog.kuangstudy.com"
},
{
"name": "百度",
"url": "https://www.baidu.com/"
}
]
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="vue">
<div>{{data_json.name}}</div>
<a v-bind:href="data_json.url">跳转</a>
</div>
<!--引入js文件-->
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#vue",
data(){
return{
//返回data.json下的所有参数
data_json:{}
}
},
mounted(){//通过钩子函数加载json
axios.get('../data.json').then(response=>(this.data_json=response.data));
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
五,计算属性,内容分发, 自定义事件
5.1,计算属性
什么是计算属性
? 计算属性的重点突出在属性两个字上(属性是名词),首先它是个属性其次这个属性有计算的能力(计算是动词),这里的计算就是个函数:简单点说,它就是一个能够将计算结果缓存起来的属性(将行为转化成了静态的属性),仅此而已;可以想象为缓存!
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="vue">
<!--methods->currentTime1, 要调用方法currentTime1() -->
<p>currentTime1={{currentTime1()}}</p>
<!--computed->currentTime2, 调用属性currentTime2 有缓存,值有跟新才更新-->
<p>currentTime2={{currentTime2}}</p>
</div>
<!--引入js文件-->
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#vue",
data: {
message: "hello"
},
methods: {
currentTime1: function (){
return Date.now();//返回当前时间戳
}
},
computed: { //特色:计算属性
currentTime2: function () {
this.message;
return Date.now();//返回当前时间戳,重名只会调用methods中的方法
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
-
methods:定义方法, 调用方法使用currentTime1(), 需要带括号
-
computed:定义计算属性, 调用属性使用currentTime2, 不需要带括号:this.message是为了能够让currentTime2观察到数据变化而变化
-
如何在方法中的值发生了变化,则缓存就会刷新!可以在控制台使用vm.message=”q in jiang", 改变下数据的值,页面更新
-
结论:
- 调用方法时,每次都需要讲行计算,既然有计算过程则必定产生系统开销,那如果这个结果是不经常变化的呢?此时就可以考虑将这个结果缓存起来,采用计算属性可以很方便的做到这点,计算属性的主要特性就是为了将不经常变化的计算结果进行缓存,以节约我们的系统开销;
5.2,内容分发
在 2.6.0 中,我们为具名插槽和作用域插槽引入了一个新的统一的语法 (即 v-slot 指令)。它取代了 slot 和 slot-scope 这两个目前已被废弃但未被移除且仍在文档中的 attribute。新语法的由来可查阅这份 RFC。
在Vue.js中我们使用元素作为承载分发内容的出口,作者称其为插槽,可以应用在组合组件的场景中
? 比如准备制作一个待办事项组件(todo) , 该组件由待办标题(todo-title) 和待办内容(todo-items)组成,但这三个组件又是相互独立的,该如何操作呢?
第一步: 定义一个待办事项的组件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="vue">
<alert-box>
<box1 v-for="item in items" :system="item"></box1><!--有预留插槽就可以放其他组件-->
</alert-box>
</div>
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
//定义一个组件, <slot></slot>定一个插槽
Vue.component('alert-box',{
template: `
<div class="demo-alert-box">
<strong>系统列表</strong>
<slot></slot>
</div>
`
});
//在定义一个组件box1
Vue.component('box1',{
props: ['system'],
template: `
<div class="demo-alert-box">
{{system}}
</div>
`
});
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#vue",
data: {
items: ["windows","linux","mac"]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
5.3,自定义事件
数据项在Vue的实例中,但删除操作要在组件中完成,那么组件如何才能删除Vue实例中的数据呢?此时就涉及到参数传递与事件分发了,Vue为我们提供了自定义事件的功能很好的帮助我们解决了这个问题;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="vue">
<alert-box>
<!--
v-on:remove_on="removeItems(index), v-on:自定义事件名="绑定vm里的removeItems方法"
-->
<box1 v-for="(item,index) in items" :system="item"
v-bind:item_index="index" v-on:remove_on="removeItems(index)" ></box1><!--有预留插槽就可以放其他组件-->
</alert-box>
</div>
<script src="../vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
//定义一个组件, <slot></slot>定一个插槽
Vue.component('alert-box',{
template: `
<div class="demo-alert-box">
<strong>系统列表</strong>item_index
<slot></slot>
</div>
`
});
//在定义一个组件box1
Vue.component('box1',{
props: ['system','item_index'],
template: `
<div class="demo-alert-box">
{{item_index}}-- {{system}} <button @click="remove">删除{{system}}</button>
</div>
`,
methods: {
remove: function (){ //index可以不用传
this.$emit('remove_on');
}
}
});
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#vue",
data: {
items: ["windows","linux","mac"]
},
methods: {
removeItems: function (index){
console.log('删除了:'+this.items[index])
this.items.splice(index,1);//一次删除一个元素
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
5.4、Vue入门小结
核心:数据驱动,组件化
优点:借鉴了AngularJS的模块化开发和React的虚拟Dom,虚拟Dom就是把Demo操作放到内存中执行;
常用的属性:
- v-if
- v-else-if
- v-else
- v-for
- v-on绑定事件,简写@
- v-model数据双向绑定
- v-bind给组件绑定参数,简写:
组件化:
- 组合组件slot插槽
- 组件内部绑定事件需要使用到
this.$emit("事件名",参数); - 计算属性的特色,缓存计算数据
遵循SoC关注度分离原则,Vue是纯粹的视图框架,并不包含,比如Ajax之类的通信功能,为了解决通信问题,我们需要使用Axios框架做异步通信;
说明
Vue的开发都是要基于NodeJS,实际开发采用Vue-cli脚手架开发,vue-router路由,vuex做状态管理;Vue UI,界面我们一般使用ElementUI(饿了么出品),或者ICE(阿里巴巴出品)来快速搭建前端项目~~
官网:
- https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN
- https://ice.work/
六,第一个vue-cli项目
什么是vue-cli
vue-cli官方提供的一个脚手架,用于快速生成一个vue的项目模板;预先定义好的目录结构及基础代码,就好比咱们在创建Maven项目时可以选择创建一个骨架项目,这个估计项目就是脚手架,我们的开发更加的快速;
项目的功能
- 统一的目录结构
- 本地调试
- 热部署
- 单元测试
- 集成打包上线
安装环境
需要的环境
- Node.js:http://nodejs.cn/download/
安装就是无脑的下一步就好,安装在自己的环境目录下 - Git:https://git-scm.com/doenloads
镜像:https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/git-for-windows/
- 安装Node.js淘宝镜像加速器(cnpm)
# -g 就是全局安装
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
# 或使用如下语句解决npm速度慢的问题
npm install --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
安装vue-cli
cnpm instal @vue-cli
#安装不了vue-cli ,用这个命令可以安装
cnpm install -g vue-cli
#最终使用
cnpm install --global vue-cli
#测试是否安装成功#查看可以基于哪些模板创建vue应用程序,通常我们选择webpack
vue list
导webpack
在自己想安装的位置打开cmd
- vue init webpack 项目名称
手动导webpack
1,下载包 https://github.com/vuejs-templates/webpack ,
2,下载后方到C:\Users\用户\.vue-templates路径下,用户要改成自己的,
.vue-templates如果没有就新建一个文件夹,如果解压后名字手动改成 webpack 不然找不到
3,执行vue init webpack market --offline
C:\Users\Administrator>vue init webpack market --offline
> Use cached template at ~\.vue-templates\webpack
? Target directory exists. Continue? Yes
? Project name vue-demo01
? Project description A Vue.js project
? Author
? Vue build standalone
? Install vue-router? Yes
? Use ESLint to lint your code? Yes
? Pick an ESLint preset Standard
? Set up unit tests No
? Setup e2e tests with Nightwatch? No
? Should we run `npm install` for you after the project has been created? (recommended) no
vue-cli · Generated "market".
# Project initialization finished!
# ========================
To get started:
cd market
npm install (or if using yarn: yarn)
npm run lint -- --fix (or for yarn: yarn run lint --fix)
npm run dev
Documentation can be found at https://vuejs-templates.github.io/webpack
- Project name:项目名称,默认回车即可
- Project description:项目描述,默认回车即可
- Author:项目作者,默认回车即可
- Install vue-router:是否安装vue-router,选择n不安装(后期需要再手动添加)
- Use ESLint to lint your code:是否使用ESLint做代码检查,选择n不安装(后期需要再手动添加)
- Set up unit tests:单元测试相关,选择n不安装(后期需要再手动添加)
- Setupe2etests with Nightwatch:单元测试相关,选择n不安装(后期需要再手动添加)
- Should we run npm install for you after the,project has been created:创建完成后直接初始化,选择n,我们手动执行;运行结果!
下一步执行
-
npm config set registry http://registry.cnpmjs.org(cnpm失败执行这个) -
cnpm install
打包运行
npm run dev
访问

使用idea打开vue项目
七,webpack使用
什么是Webpack
本质上, webpack是一个现代JavaScript应用程序的静态模块打包器(module bundler) 。当webpack处理应用程序时, 它会递归地构建一个依赖关系图(dependency graph) , 其中包含应用程序需要的每个模块, 然后将所有这些模块打包成一个或多个bundle.
模块化的演进
Script标签
<script src = "module1.js"></script>
<script src = "module2.js"></script>
<script src = "module3.js"></script>
这是最原始的JavaScript文件加载方式,如果把每一个文件看做是一个模块,那么他们的接口通常是暴露在全局作用域下,也就是定义在window对象中,不同模块的调用都是一个作用域。
??这种原始的加载方式暴露了一些显而易见的弊端:
- 全局作用域下容易造成变量冲突
- 文件只能按照
<script>的书写顺序进行加载 - 开发人员必须主观解决模块和代码库的依赖关系
- 在大型项目中各种资源难以管理,长期积累的问题导致代码库混乱不堪
CommonsJS
服务器端的NodeJS遵循CommonsJS规范,该规范核心思想是允许模块通过require方法来同步加载所需依赖的其它模块,然后通过exports或module.exports来导出需要暴露的接口。
require("module");
require("../module.js");
export.doStuff = function(){};
module.exports = someValue;
1234
12345
优点:
- 服务器端模块便于重用
- NPM中已经有超过45万个可以使用的模块包
- 简单易用
缺点:
- 同步的模块加载方式不适合在浏览器环境中,同步意味着阻塞加载,浏览器资源是异步加载的
- 不能非阻塞的并行加载多个模块
ES6模块
EcmaScript 6标准增加了JavaScript语言层面的模块体系定义。ES 6模块的设计思想, 是尽量静态化, 使编译时就能确定模块的依赖关系, 以及输入和输出的变量。Commons JS和AMD模块,都只能在运行时确定这些东西。
import "jquery"
export function doStuff(){}
module "localModule"{}
123
优点
- 容易进行静态分析
- 面向未来的Ecma Script标准
缺点
- 原生浏览器端还没有实现该标准
- 全新的命令,新版的Node JS才支持
安装Webpack
WebPack是一款模块加载器兼打包工具, 它能把各种资源, 如JS、JSX、ES 6、SASS、LESS、图片等都作为模块来处理和使用。
??安装:
npm install webpack -g
npm install webpack-cli -g
测试安装成功
webpack -vwebpack-cli -v
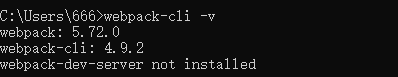
#提示没有安装webpack-dev-server
继续安装
cnpm install webpack-dev-server -g
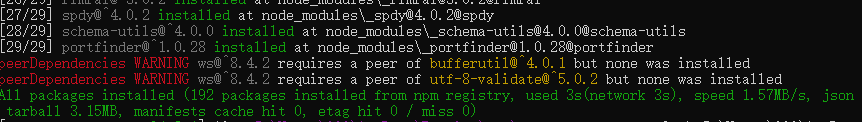
#提示需要安装bufferutilm, utf-8-validate
cnpm install bufferutil@4.0.1 -g
cnpm install utf-8-validate@5.0.2 -g
#上面安装完成继续安装server
cnpm install webpack-dev-server -g
配置
- entry:入口文件, 指定Web Pack用哪个文件作为项目的入口
- output:输出, 指定WebPack把处理完成的文件放置到指定路径
- module:模块, 用于处理各种类型的文件
- plugins:插件, 如:热更新、代码重用等
- resolve:设置路径指向
- watch:监听, 用于设置文件改动后直接打包
module.exports = {
entry:"",
output:{
path:"",
filename:""
},
module:{
loaders:[
{test:/\.js$/,;\loade:""}
]
},
plugins:{},
resolve:{},
watch:true
}
使用webpack
- 创建项目
- hello.js, 用于编写JS模块相关代码
//暴露一个方法
exports.sayHi = function (){
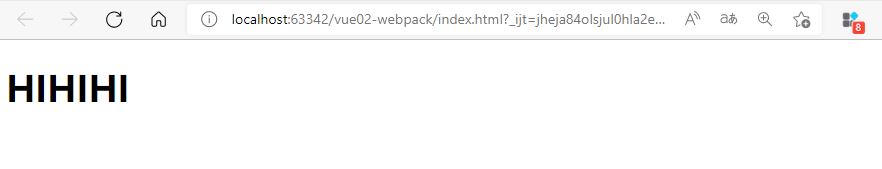
document.write("<h1>HIHIHI</h1>")
};
- index.js的入口文件,用于打包时设置entry属性
let main_hello = require("./hello");
main_hello.sayHi();
- webpack.config.js配置文件,使用webpack命令打包
module.exprots = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: "./js/bundle.js"
},
}
- 命令行输入webpack打包
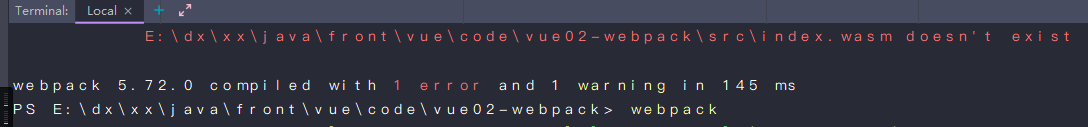
- 生成了main.js
-
新建index.html, 导入main.js
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script src="dist/main.js"></script> </body> </html> -
测试
八,vue-router路由
Vue Router是Vue.js官方的路由管理器。它和Vue.js的核心深度集成, 让构建单页面应用变得易如反掌。包含的功能有:
- 嵌套的路由/视图表
- 模块化的、基于组件的路由配置
- 路由参数、查询、通配符
- 基于Vue js过渡系统的视图过渡效果
- 细粒度的导航控制
- 带有自动激活的CSS class的链接
- HTML5 历史模式或hash模式, 在IE 9中自动降级
- 自定义的滚动行为
8.1,安装
npm install vue-router --save-dev
cnpm install vue-router --save-dev
main.js里导入router
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
Vue.use(VueRouter);
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
- 运行
npm run dev

- 报错估计安装vue-router版本低了
cnpm install vue-router@3.1.5 --save-dev
8.2,使用
1,在components文件夹下新建几个组件
Content.vue
<template>
<h1>Content---内容</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Content"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
login.vue
<template>
<h1>login登录</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "login"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
main.vue
<template>
<h1>main-首页</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "main"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2,新建router文件夹, 创建index.js
- 1,导入路由
import VueRouter from "vue-router"; - 2,导入需要使用的组件
import 组件名 from "路径"; - 3,配置导出路由
- path:相当于跳转路径
- component: 使用的组件名
import Vue from 'vue';
import VueRouter from "vue-router";
import Content from "../components/Content";
import main from "../components/main";
import login from "../components/login";
//安装路由
Vue.use(VueRouter);
//配置导出路由
export default new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
//路由路径
path: '/content',
name: 'inContent',
//跳转路径
component: Content
},
{
//路由路径
path: '/main',
name: 'inMain',
//跳转路径
component: main
},
{
//路由路径
path: '/login',
name: 'login',
//跳转路径
component:login
}
]
});
3,main.js中导入上面创建的路由router
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router' //自动扫描里面的index.js
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
new Vue({
el: '#app',
//配置路由
router,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
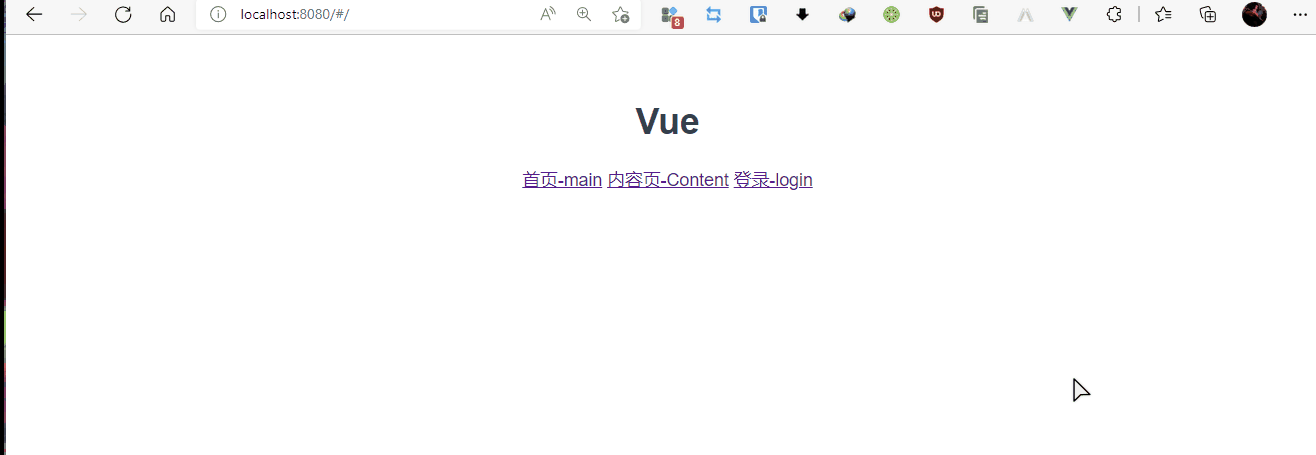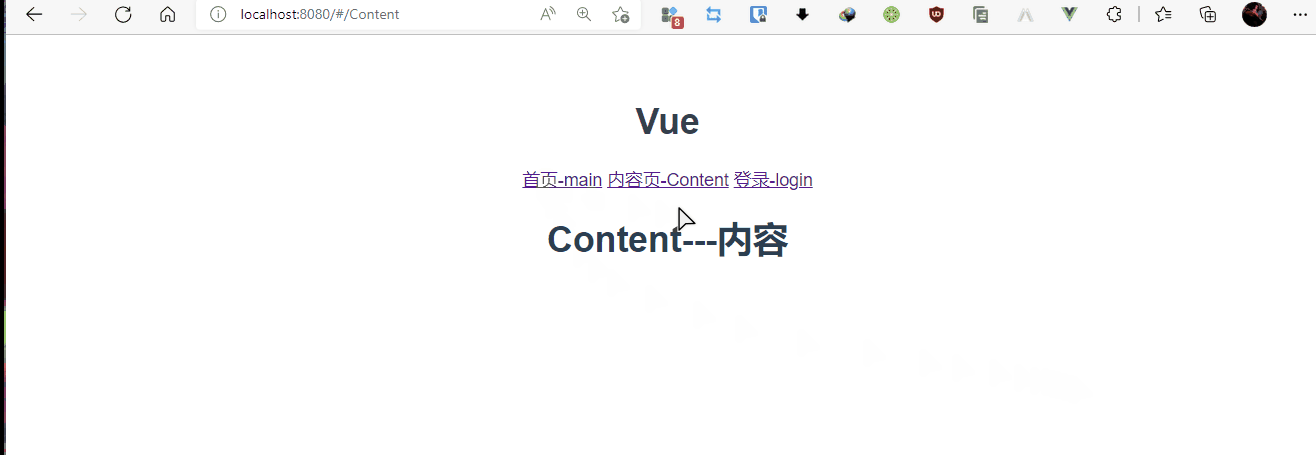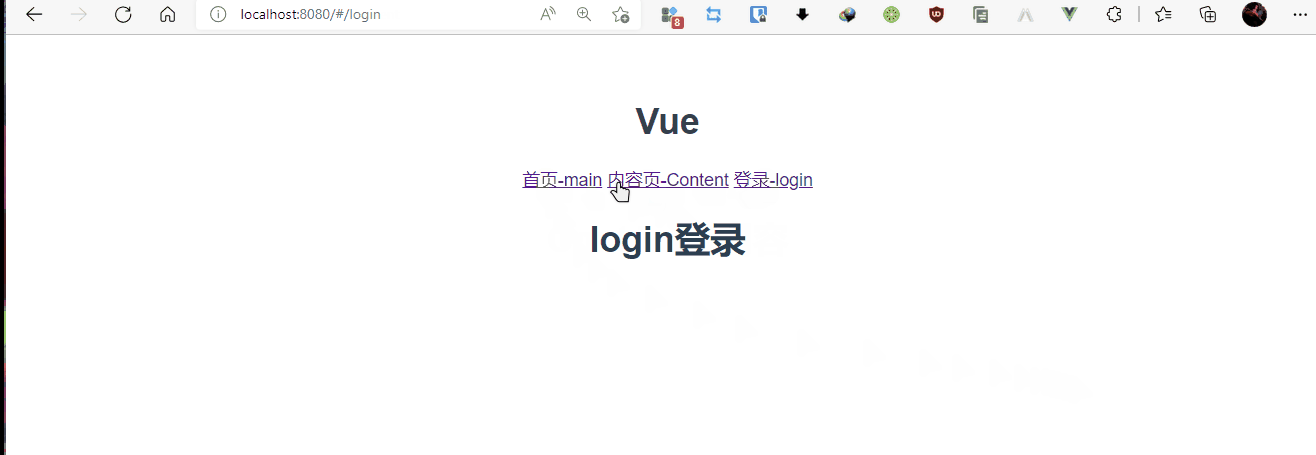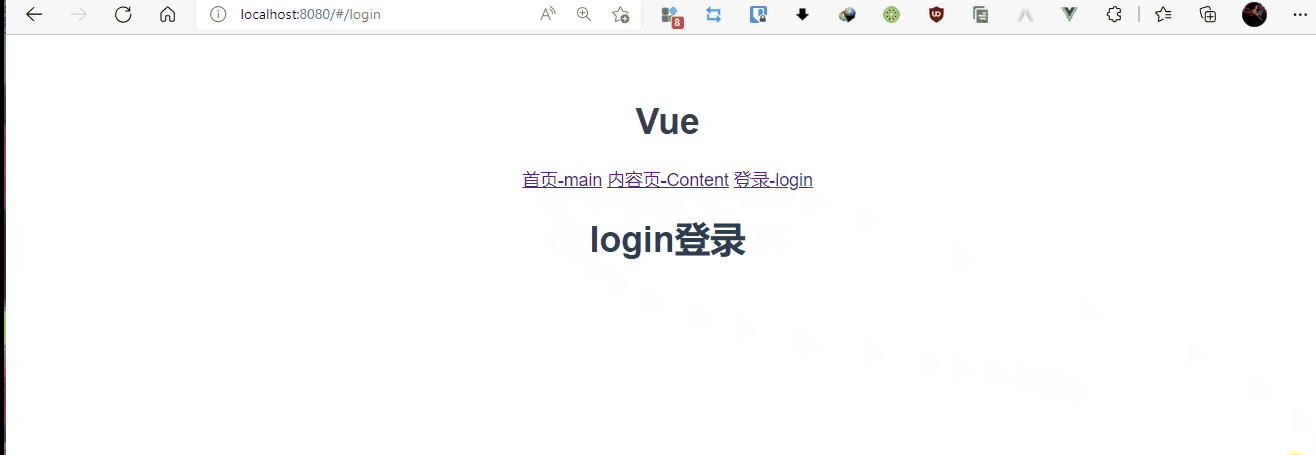
4,App.vue中添加router链接
- 跳转:
router-link to="填路由路径" - 显示:
router-view
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>Vue</h1>
<router-link to="/Content">首页-main</router-link>
<router-link to="/main">内容页-Content</router-link>
<router-link to="/login">登录-login</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
5,发布测试
npm run dev
九,vue+Element UI
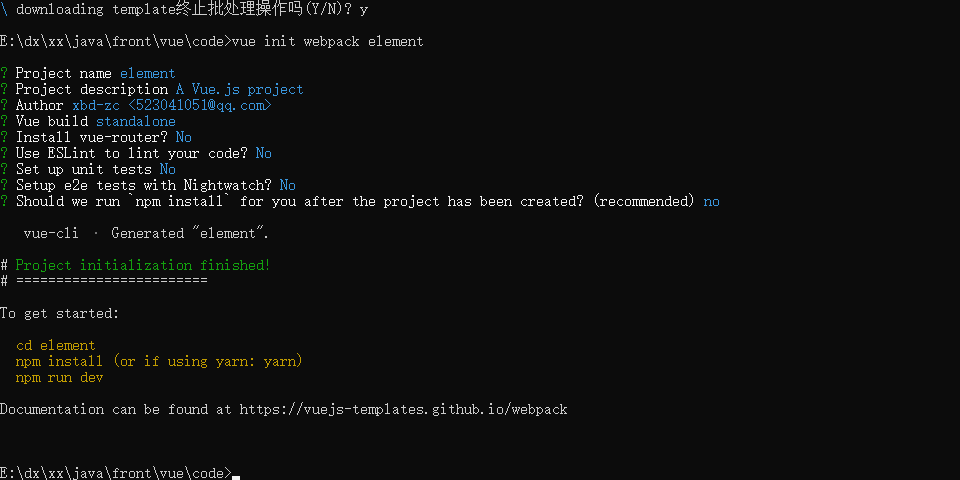
9.1,创建工程
1,创建一个element工程
- 打开cmd初始化:
vue init webpack element
2,安装依赖
#进入工程目录
cd element
#安装vue-routern
#npm install vue-router --save-dev
#我vue版本高的安装3
cnpm install vue-router@3.1.5 --save-dev
#安装element-ui
cnpm i element-ui -S
#安装依赖
cnpm install
# 安装SASS加载器
cnpm install sass-loader node-sass --save-dev
#启功测试
npm run dev
#报错
Error: Cannot find module 'webpack/bin/config-yargs'
Require stack:
- E:\dx\xx\java\front\vue\code\element\node_modules\_webpack-dev-server@2.11.5@webpack-dev-server\bin\webpack-dev-server.js
#解决
package.json中的版本是
"webpack": "^3.6.0",
"webpack-bundle-analyzer": "^2.9.0",
"webpack-dev-server": "^2.9.1",
"webpack-merge": "^4.1.0"
#安装对应版本
npm uninstall webpack-dev-serve
cnpm i webpack-dev-server@2.9.1
cnpm install webpack cli -D
#再执行
npm run dev

9.2,创建登录页面
项目结构
1,新建views文件夹, 添加两个组件
Main.vue
<template>
<h1>首页-Main</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Main"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
Login.vue
<template>
<div>
<el-form ref="loginForm" :model="form" :rules="rules" label-width="80px" class="login-box">
<h3 class="login-title">欢迎登录</h3>
<el-form-item label="账号" prop="username">
<el-input type="text" placeholder="请输入账号" v-model="form.username"/>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="password">
<el-input type="password" placeholder="请输入密码" v-model="form.password"/>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" v-on:click="onsubmit('loginForm')">登录</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
<el-dialog title="温馨提示" :visible.sync="dialogVisible" width="30%" :before-close="handleClose">
<span>请输入账号和密码</span>
<span slot="footer" class="dialog-footer">
<el-button type="primary" @click="dialogVisible = false">确定</el-button>
</span>
</el-dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Login",
data(){
return{
form:{
username:'',
password:''
},
//表单验证,需要在 el-form-item 元素中增加prop属性
rules:{
username:[
{required:true,message:"账号不可为空",trigger:"blur"}
],
password:[
{required:true,message:"密码不可为空",tigger:"blur"}
]
},
//对话框显示和隐藏
dialogVisible:false
}
},
methods:{
handleClose: function () { this.dialogVisible = false; },
onsubmit (formName){
//为表单绑定验证功能
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid)=>{
if(valid){
//使用vue-router路由到指定界面,该方式称为编程式导航
this.$router.push('/main');
}else{
this.dialogVisible=true;
return false;
}
});
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
.login-box{
border:1px solid #DCDFE6;
width: 350px;
margin:180px auto;
padding: 35px 35px 15px 35px;
border-radius: 5px;
-webkit-border-radius: 5px;
-moz-border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 25px #909399;
}
.login-title{
text-align:center;
margin: 0 auto 40px auto;
color: #303133;
}
</style>
2,新建routerw文件夹添加路由
index.js
import Vue from "vue";
import router from 'vue-router';
import Main from "../views/Main";
import Login from "../views/Login";
Vue.use(router);
export default new router({
routes: [
{
path: '/login',
component: Login
},
{
path: '/main',
component: Main
}
]
})
3,main.js导入router,ElementUI
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
//导入router
import router from "./router";
//导入ElementUI
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css';
Vue.use(router);
Vue.use(ElementUI);
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
render: h => h(App)
})
4,App.vue中添加路由视图
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
5,测试
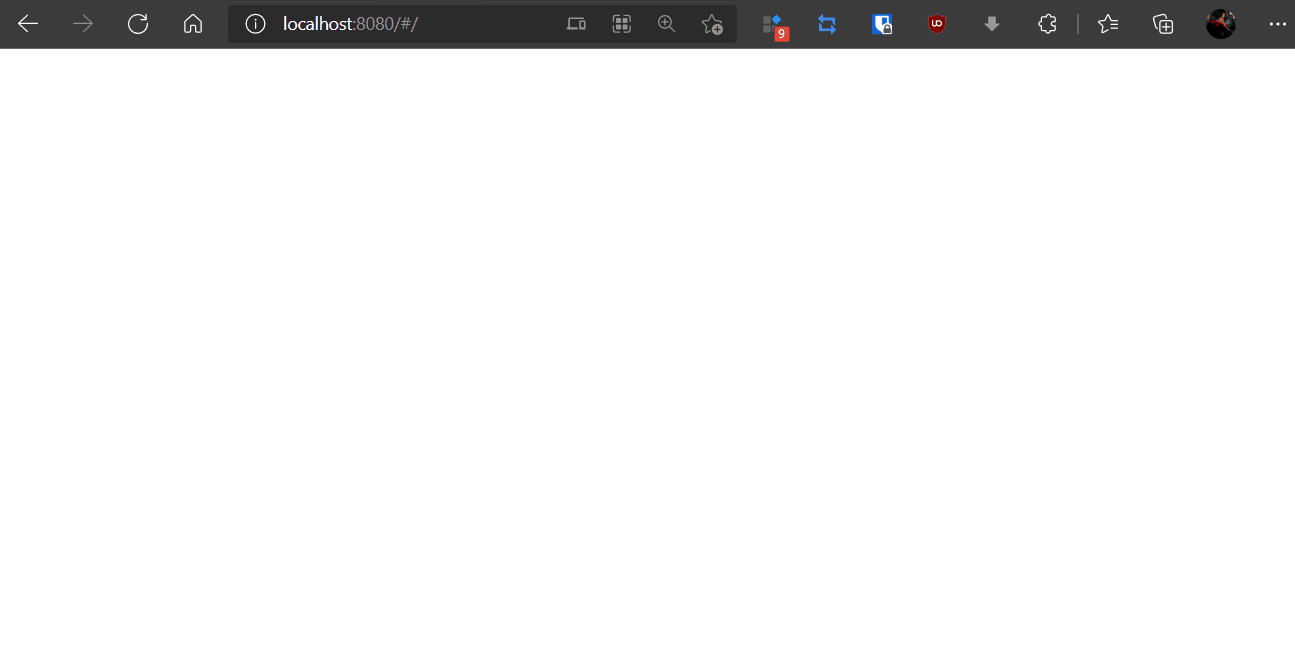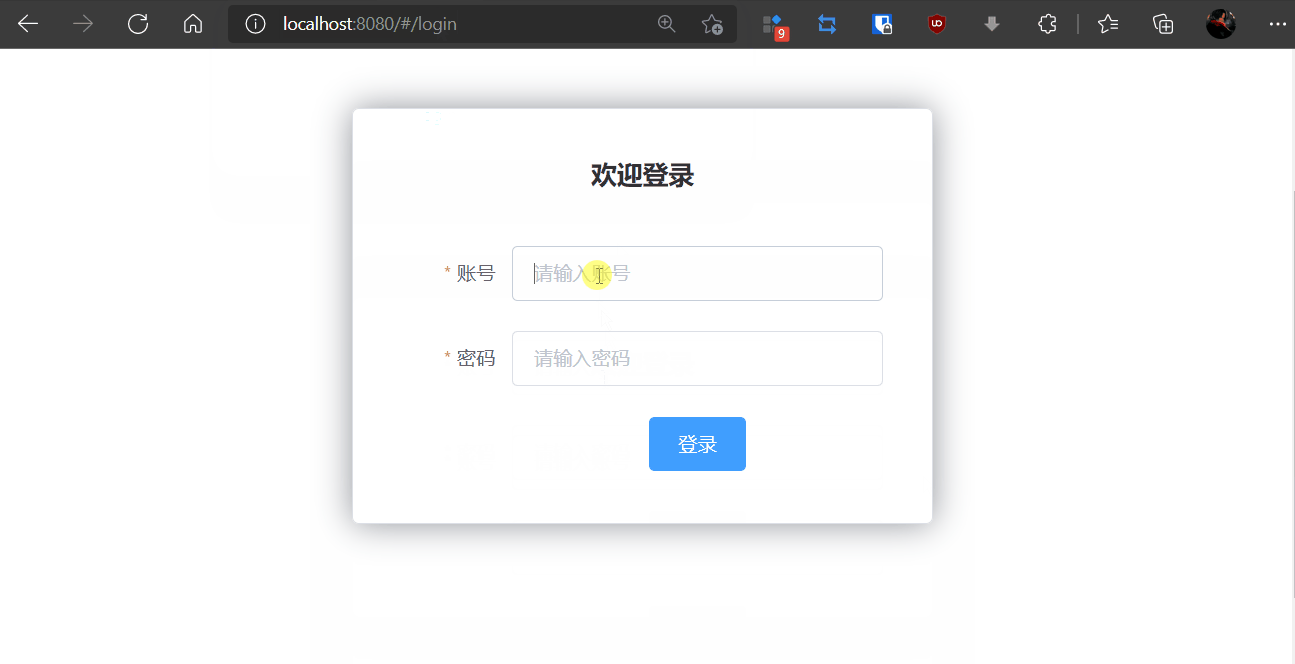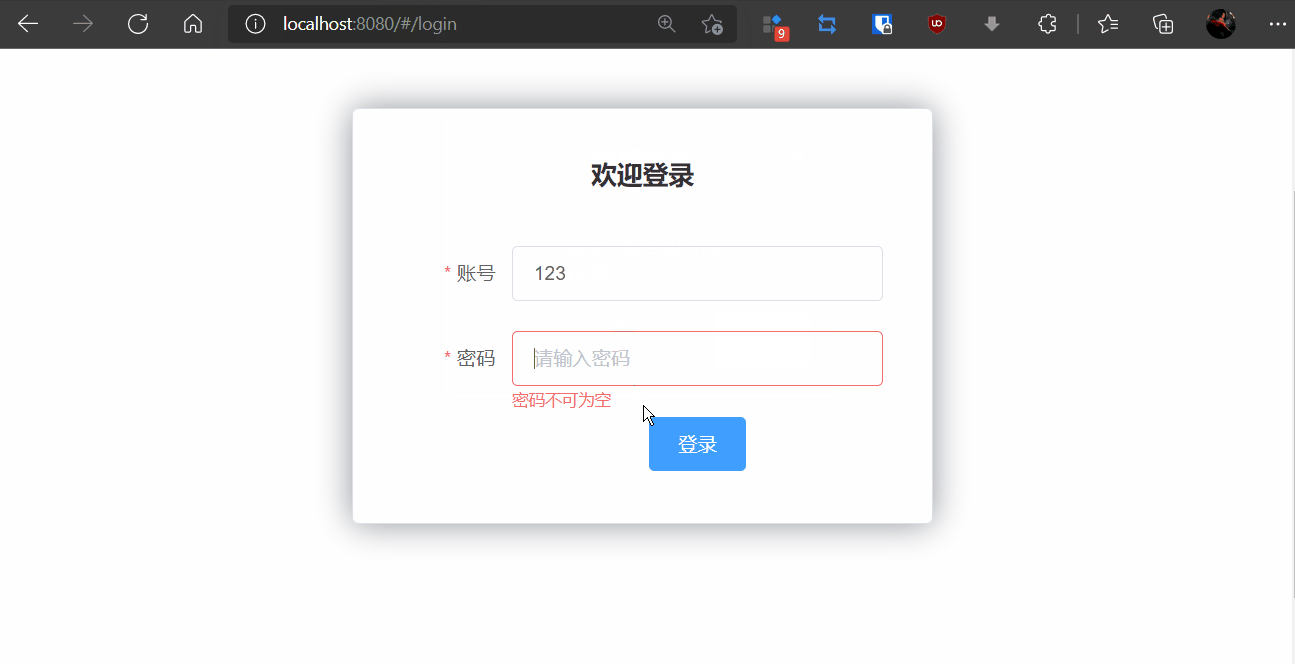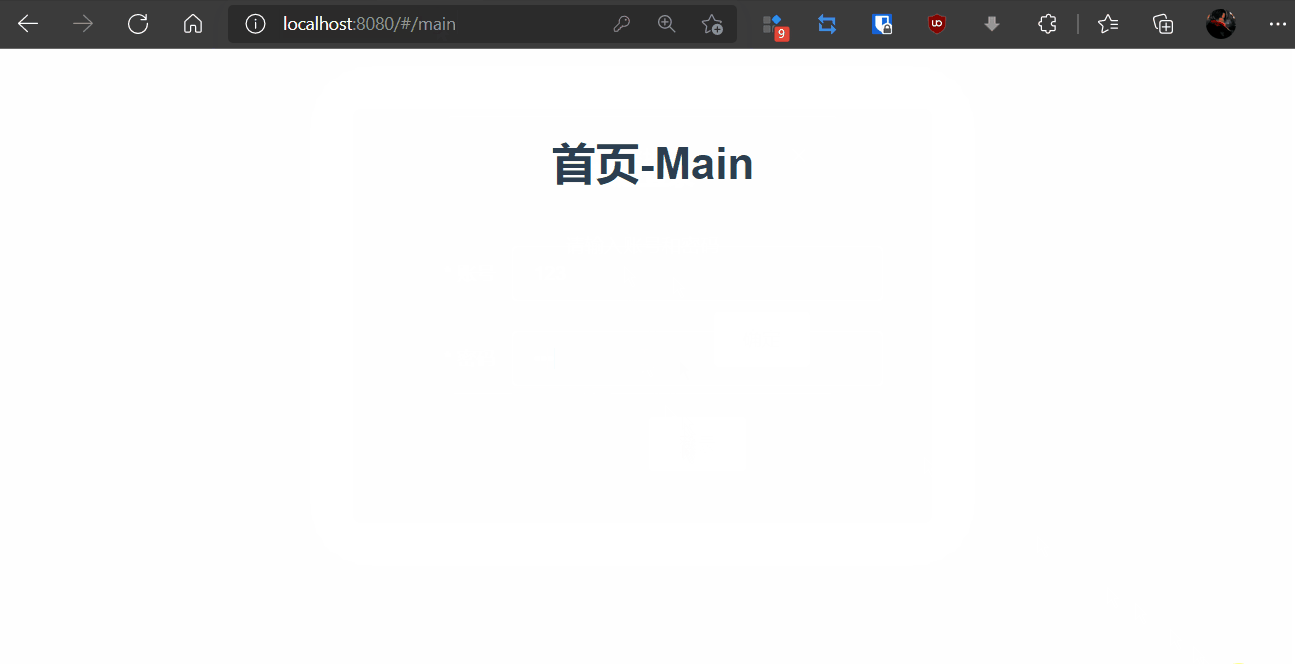
6,npm run dev报错:sass版本问题
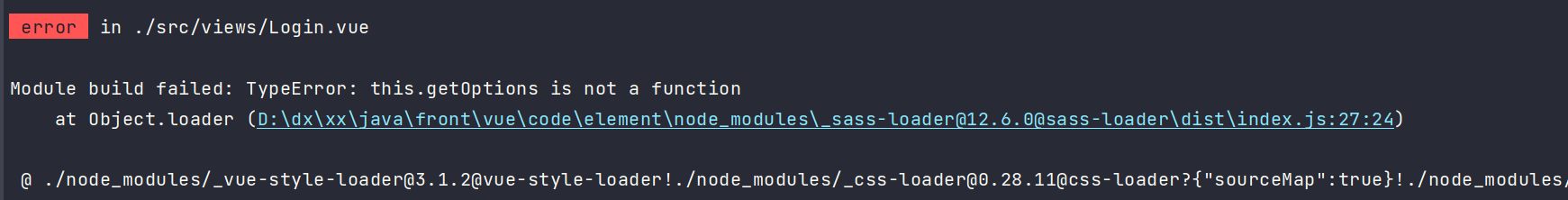
package.json版本降低下
- “node-sass”: “^4.13.1”,
- “sass-loader”: “^7.3.1”,
- 再安装依赖
cnpm install
{
"name": "element",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "A Vue.js project",
"author": "xbd-zc <523041051@qq.com>",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"dev": "webpack-dev-server --inline --progress --config build/webpack.dev.conf.js",
"start": "npm run dev",
"build": "node build/build.js"
},
"dependencies": {
"element-ui": "^2.15.8",
"vue": "^2.5.2",
"webpack-dev-server": "^2.9.1"
},
"devDependencies": {
"autoprefixer": "^7.1.2",
"babel-core": "^6.22.1",
"babel-helper-vue-jsx-merge-props": "^2.0.3",
"babel-loader": "^7.1.1",
"babel-plugin-syntax-jsx": "^6.18.0",
"babel-plugin-transform-runtime": "^6.22.0",
"babel-plugin-transform-vue-jsx": "^3.5.0",
"babel-preset-env": "^1.3.2",
"babel-preset-stage-2": "^6.22.0",
"chalk": "^2.0.1",
"cli": "^1.0.1",
"copy-webpack-plugin": "^4.0.1",
"css-loader": "^0.28.0",
"extract-text-webpack-plugin": "^3.0.0",
"file-loader": "^1.1.4",
"friendly-errors-webpack-plugin": "^1.6.1",
"html-webpack-plugin": "^2.30.1",
"node-notifier": "^5.1.2",
"node-sass": "^4.13.1",
"optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin": "^3.2.0",
"ora": "^1.2.0",
"portfinder": "^1.0.13",
"postcss-import": "^11.0.0",
"postcss-loader": "^2.0.8",
"postcss-url": "^7.2.1",
"rimraf": "^2.6.0",
"sass": "^1.50.1",
"sass-loader": "^7.3.1",
"semver": "^5.3.0",
"shelljs": "^0.7.6",
"uglifyjs-webpack-plugin": "^1.1.1",
"url-loader": "^0.5.8",
"vue-loader": "^13.3.0",
"vue-router": "^3.1.5",
"vue-style-loader": "^3.0.1",
"vue-template-compiler": "^2.5.2",
"webpack": "^3.6.0",
"webpack-bundle-analyzer": "^2.9.0",
"webpack-dev-server": "^2.9.1",
"webpack-merge": "^4.1.0"
},
"engines": {
"node": ">= 6.0.0",
"npm": ">= 3.0.0"
},
"browserslist": [
"> 1%",
"last 2 versions",
"not ie <= 8"
]
}
9.3,路由嵌套
嵌套路由又称子路由,在实际应用中,通常由多层嵌套的组件组合而成。
1,创建用户信息组件,在 views目录下新建user目录,再建两个组件
Profile.vue
<template>
<h1>个人信息</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "UserProfile"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
List.vue
<template>
<h1>用户列表</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "UserList"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2, 修改首页视图,修改 Main.vue 视图组件,此处使用了 ElementUI 布局容器组件
<template>
<div>
<el-container>
<el-aside width="200px">
<el-menu :default-openeds="['1']">
<el-submenu index="1">
<template slot="title"><i class="el-icon-caret-right"></i>用户管理</template>
<el-menu-item-group>
<el-menu-item index="1-1">
<!--插入的地方-->
<router-link to="/user/profile">个人信息</router-link>
</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="1-2">
<!--插入的地方-->
<router-link to="/user/list">用户列表</router-link>
</el-menu-item>
</el-menu-item-group>
</el-submenu>
<el-submenu index="2">
<template slot="title"><i class="el-icon-caret-right"></i>内容管理</template>
<el-menu-item-group>
<el-menu-item index="2-1">分类管理</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="2-2">内容列表</el-menu-item>
</el-menu-item-group>
</el-submenu>
</el-menu>
</el-aside>
<el-container>
<el-header style="text-align: right; font-size: 12px">
<el-dropdown>
<i class="el-icon-setting" style="margin-right: 15px"></i>
<el-dropdown-menu slot="dropdown">
<el-dropdown-item>个人信息</el-dropdown-item>
<el-dropdown-item>退出登录</el-dropdown-item>
</el-dropdown-menu>
</el-dropdown>
</el-header>
<el-main>
<!--在这里展示视图-->
<router-view />
</el-main>
</el-container>
</el-container>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Main"
}
</script>
<style scoped lang="scss">
.el-header {
background-color: #B3C0D1;
color: #333;
line-height: 60px;
}
.el-aside {
color: #333;
}
</style>
3,配置嵌套路由修改router目录下的index.js路由配置文件,使用children放入main中写入子模块
import Vue from "vue";
import router from 'vue-router';
import Main from "../views/Main";
import Login from "../views/Login";
import List from "../views/user/List"
import Profile from "../views/user/Profile";
Vue.use(router);
export default new router({
routes: [
{
path: '/login',
component: Login
},
{
path: '/main',
component: Main,
//嵌套路由
children: [
{
path: '/user/profile',component:Profile
},
{
path: '/user/list',component:List
}
]
}
]
})
4,测试
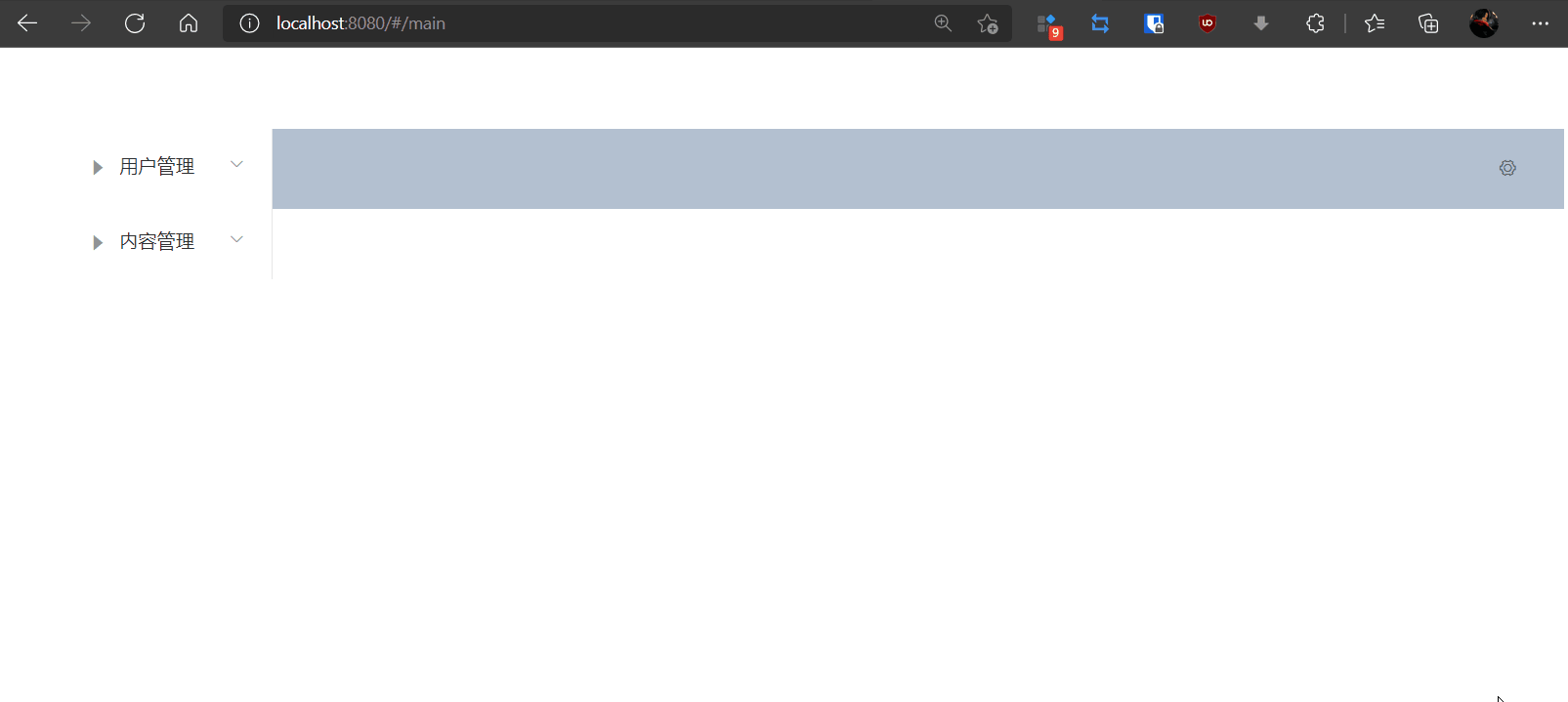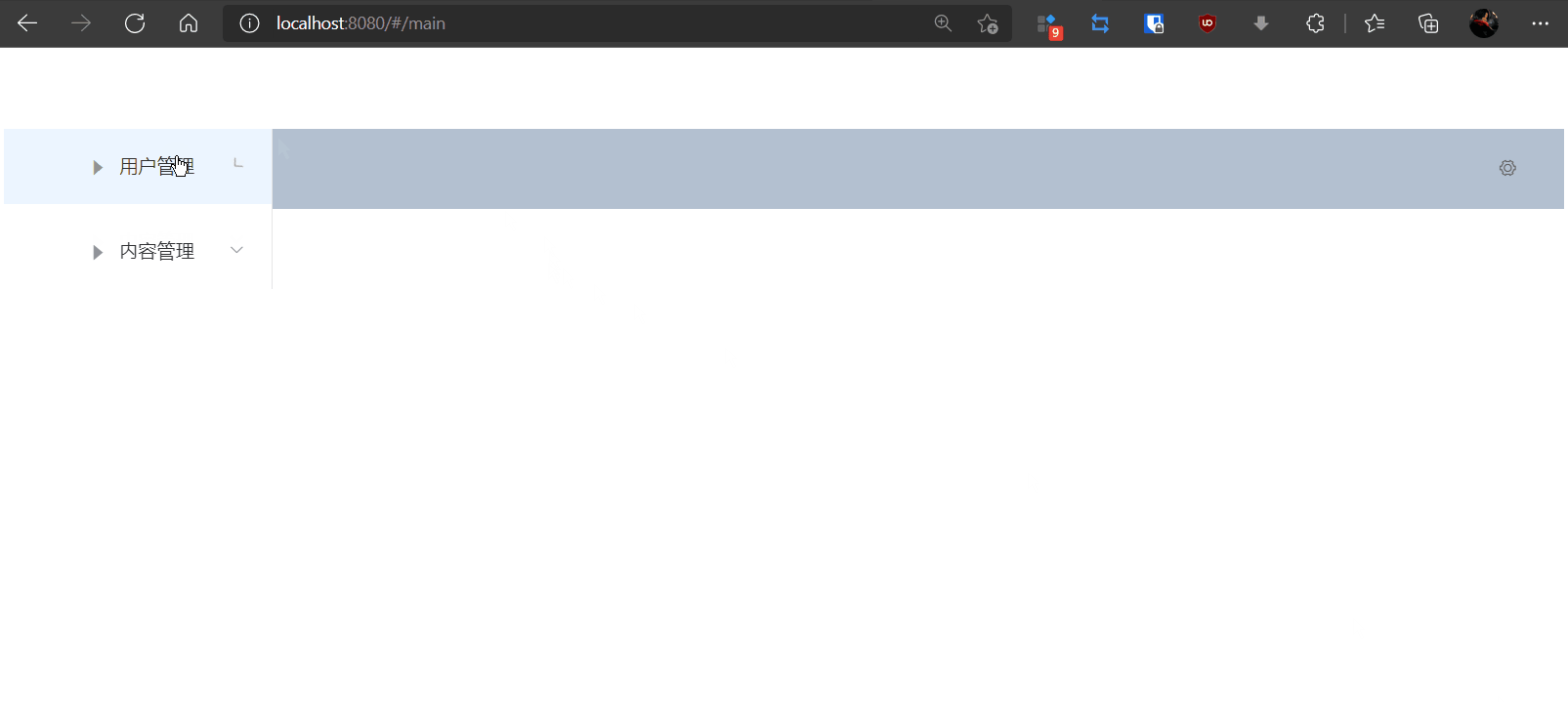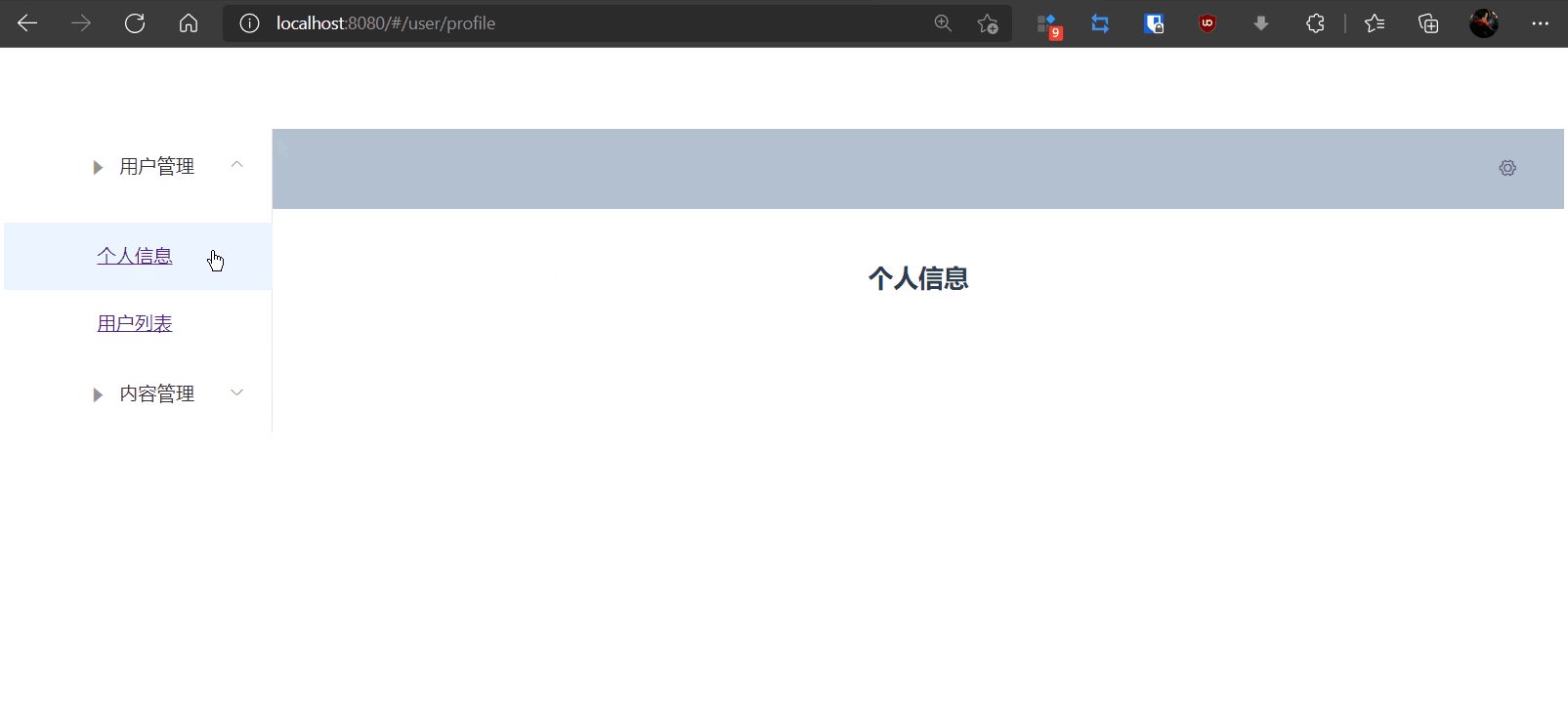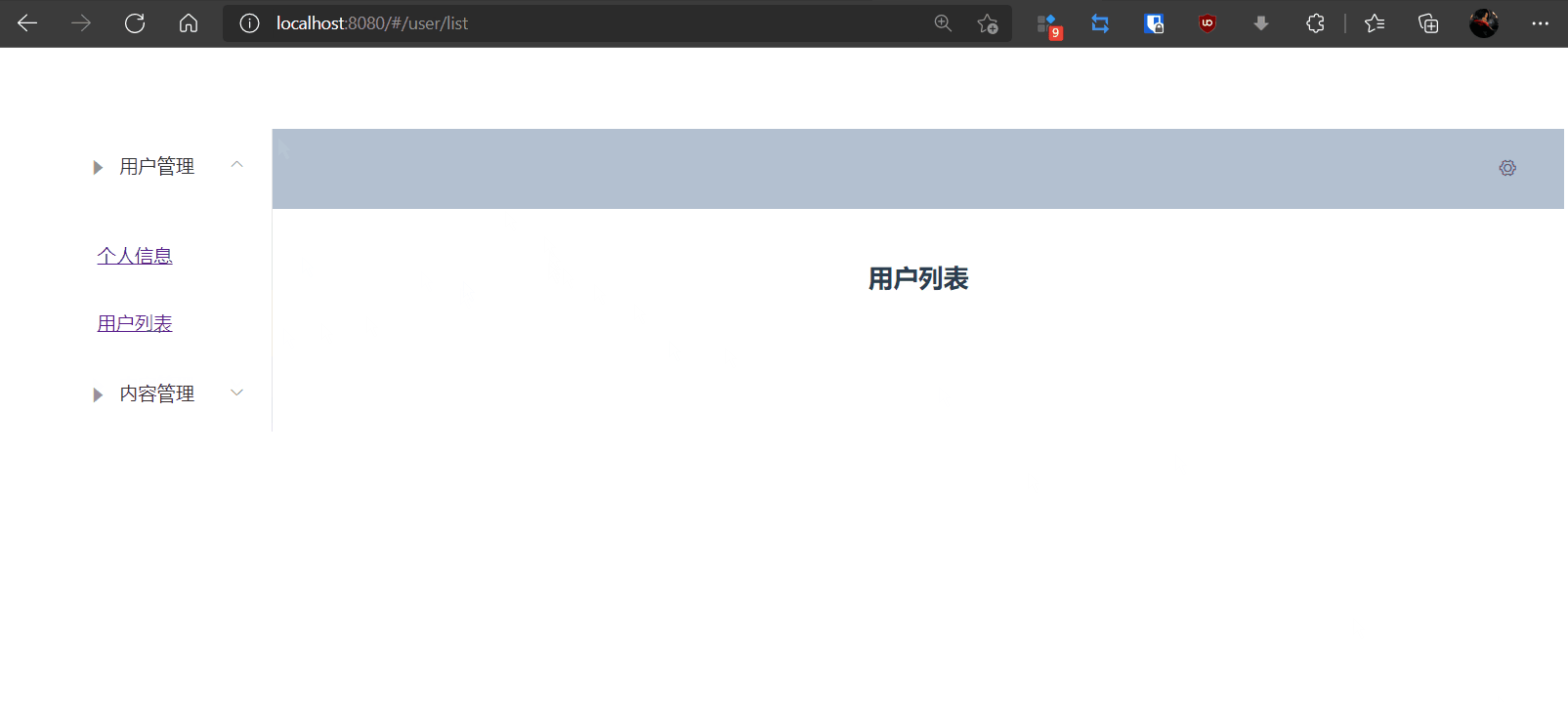
9.4,参数传递
1,views目录下的Main.vue传参
<el-menu-item index="1-1">
<!--name传组件名,params传递参数-->
<router-link :to="{name:'UserProfile',params:{id:1}}">个人信息</router-link>
</el-menu-item>
2,router目录下index.js接收参数
//嵌套路由
children: [
{
path: '/user/profile/:id',
name: 'UserProfile',//遇到的坑: 一定要用引号引起来, 不然找不到
component:UserProfile
},
]
3,views/user/Profile.vue展示参数
<template>
<!--所有的元素必须在同一个标签下面,不能写到外面-->
<div>
<h1>个人信息</h1>
{{$route.params.id}}
</div>
</template>
4,测试
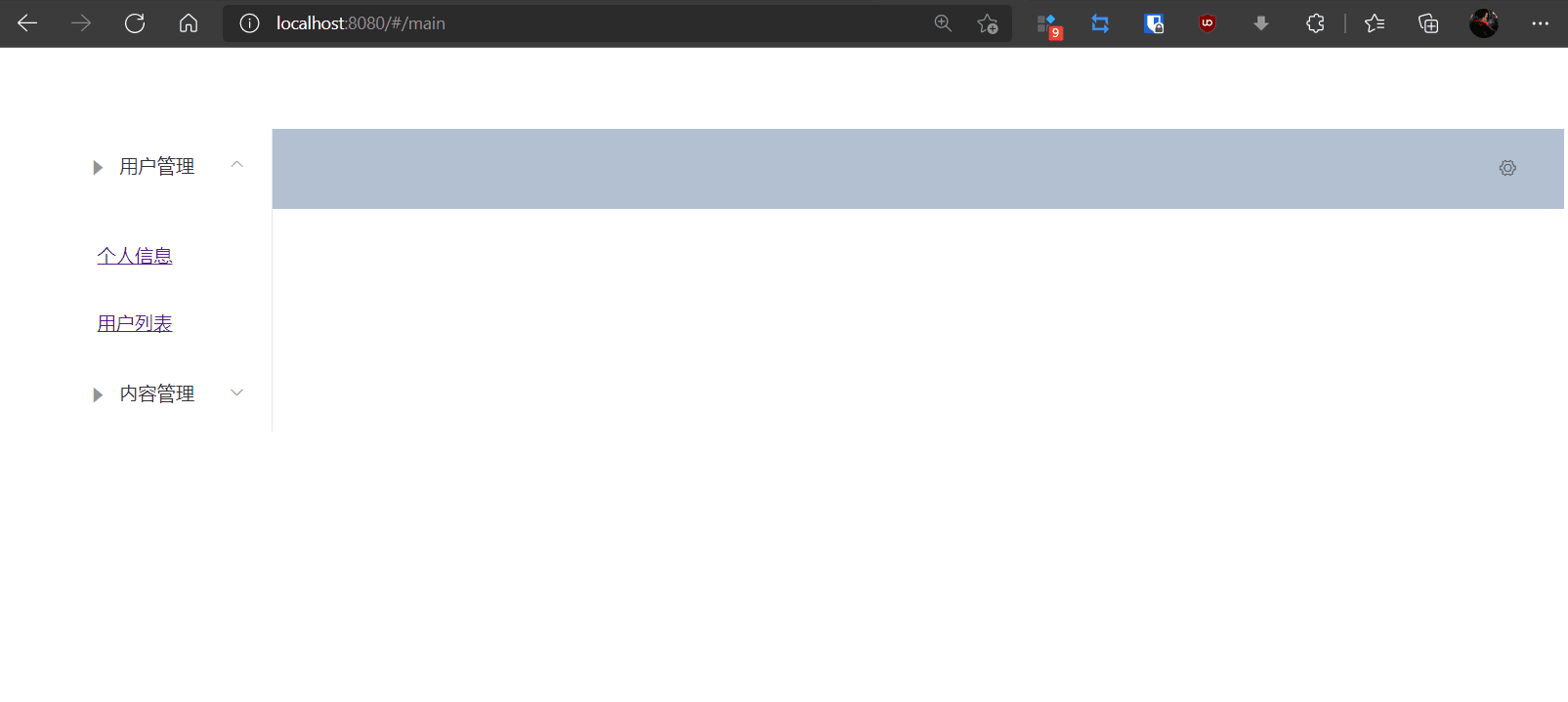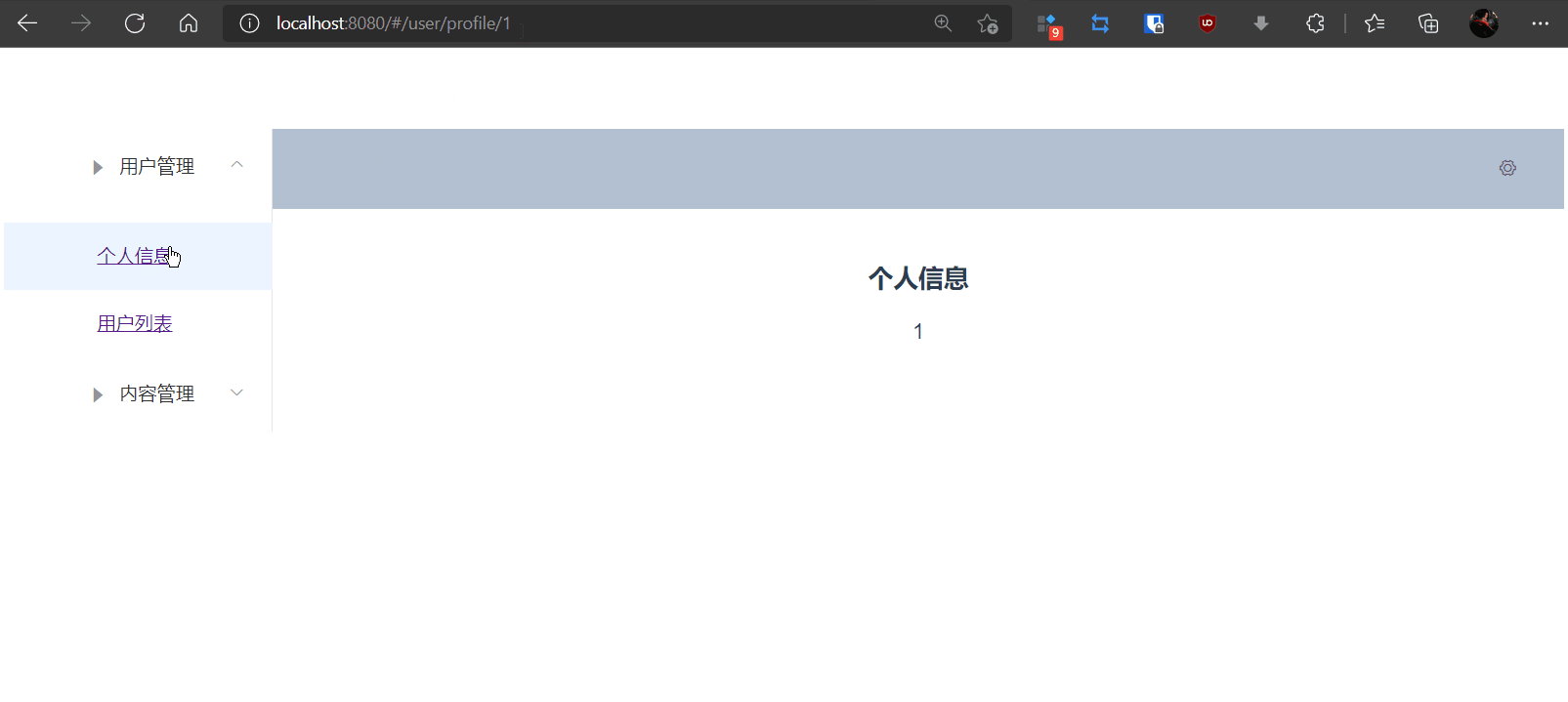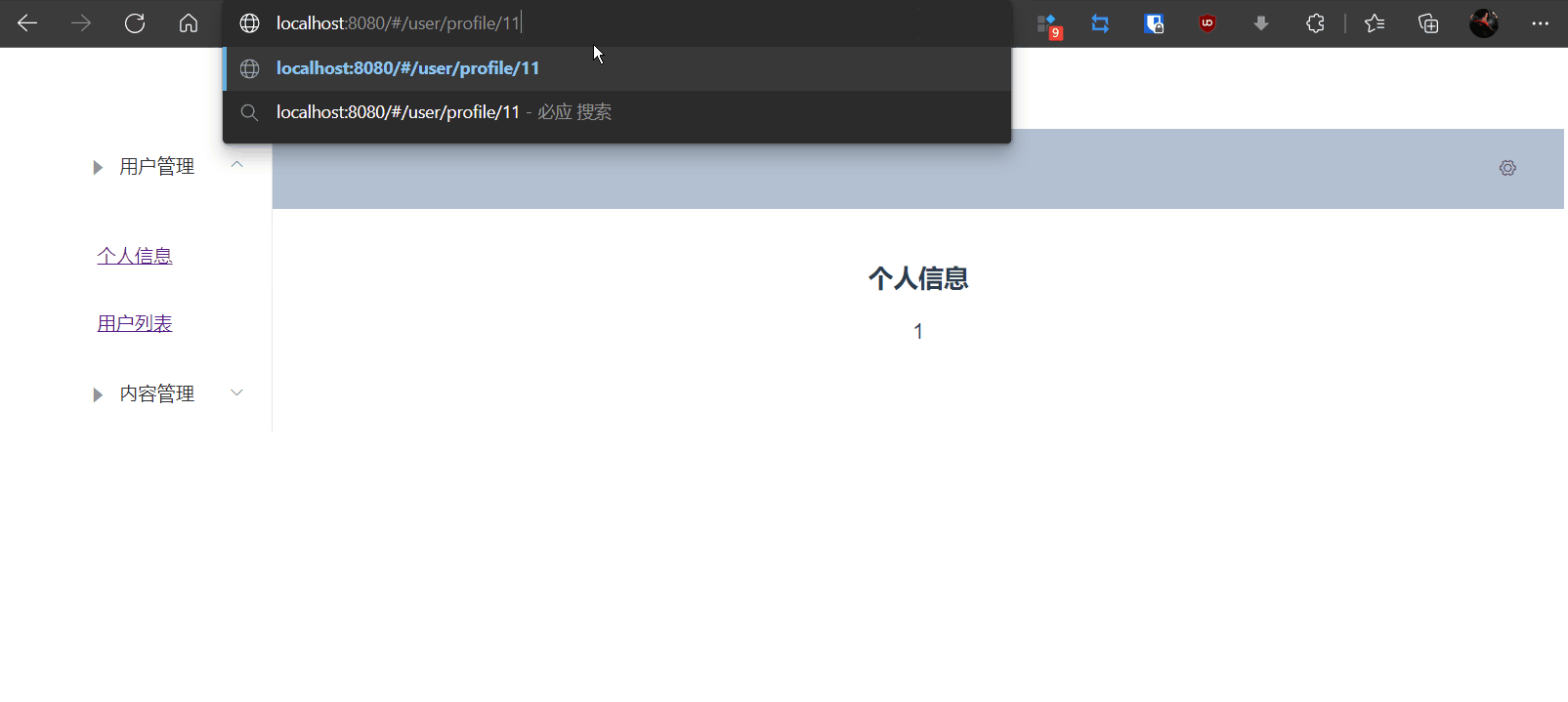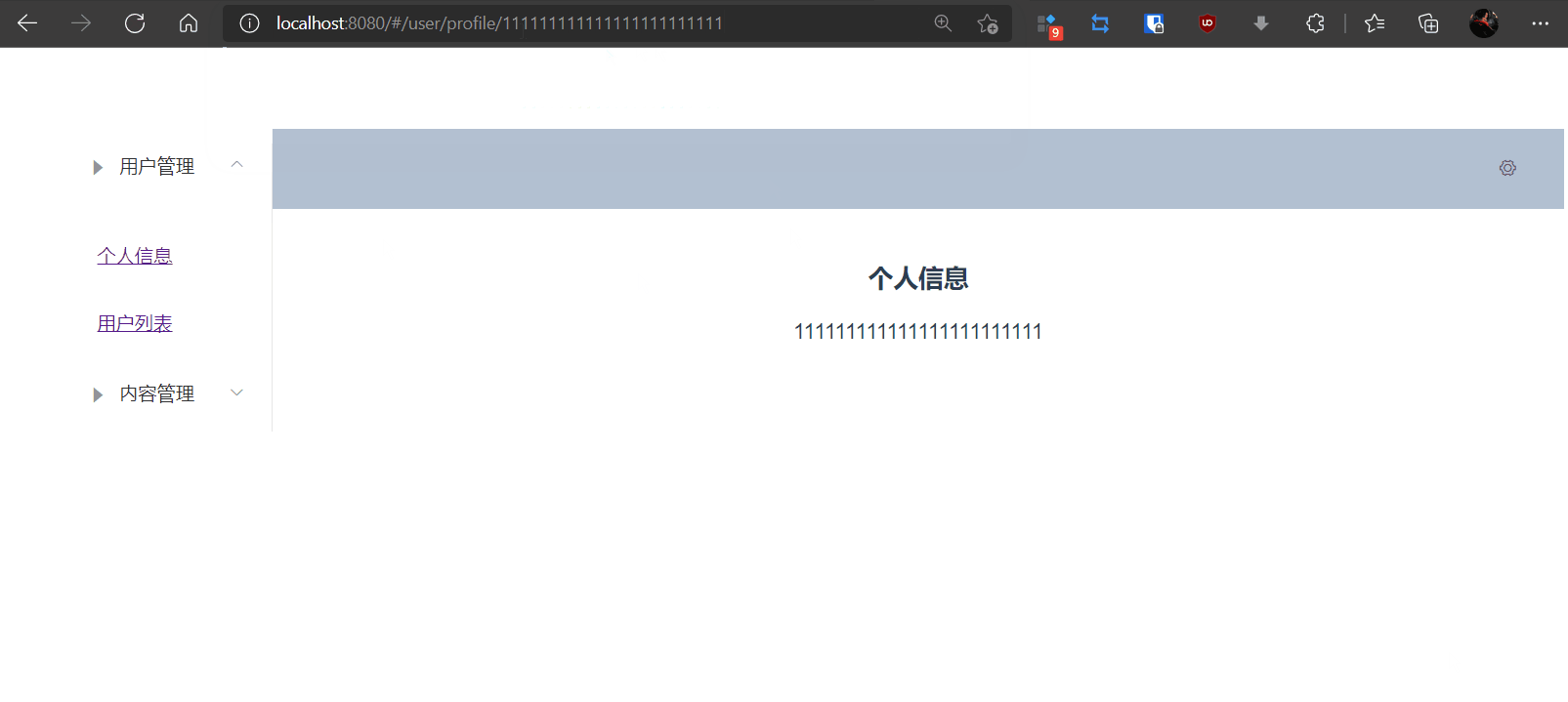
5,通过props传递参数
1,在路由配置中: router下的index.js中的路由属性中增加了 props: true 属性
//嵌套路由
children: [
{
path: '/user/profile/:id',
name: 'UserProfile',//一定要用引号引起来, 不然找不到
component:UserProfile,
props: true
}
]
2,在Profile.vue接收参数
<template>
<!--所有的元素必须在同一个标签下面,不能写到外面-->
<div>
<h1>个人信息</h1>
{{id}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['id'],
name: "UserProfile"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
9.5,重定向
1,在router下面index.js的配置
//嵌套路由
children: [
{
path: '/user/profile/:id',
name: 'UserProfile',//一定要用引号引起来, 不然找不到
component:UserProfile,
props: true
},
{
path: '/user/list',component:UserList
},
{
path: '/goMain',
redirect: '/main'
}
]
- 重定向只需要设置跳转的路径, 不需要组件
2,在/views/Main.vue添加返回主页
<el-menu-item index="1-3">
<router-link to="/goMain">回到主页</router-link>
</el-menu-item>
9.6,路由模式
路由模式有两种
- hash:路径带 # 符号,如 http://localhost/#/login (默认, 不写就是hash)
- history:路径不带 # 符号,如 http://localhost/login
修改路由配置,代码如下:
export default new router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
]
});
9.7,设置404页面
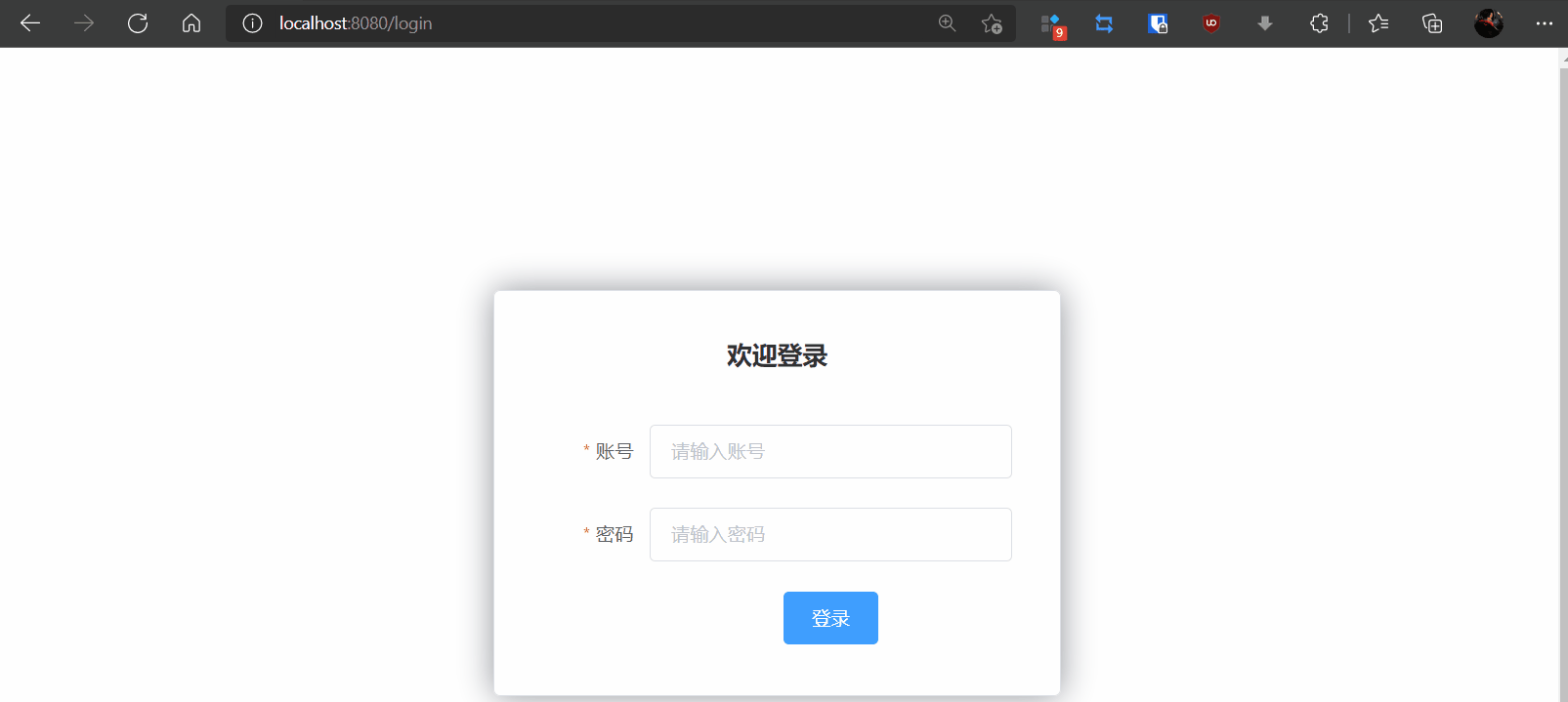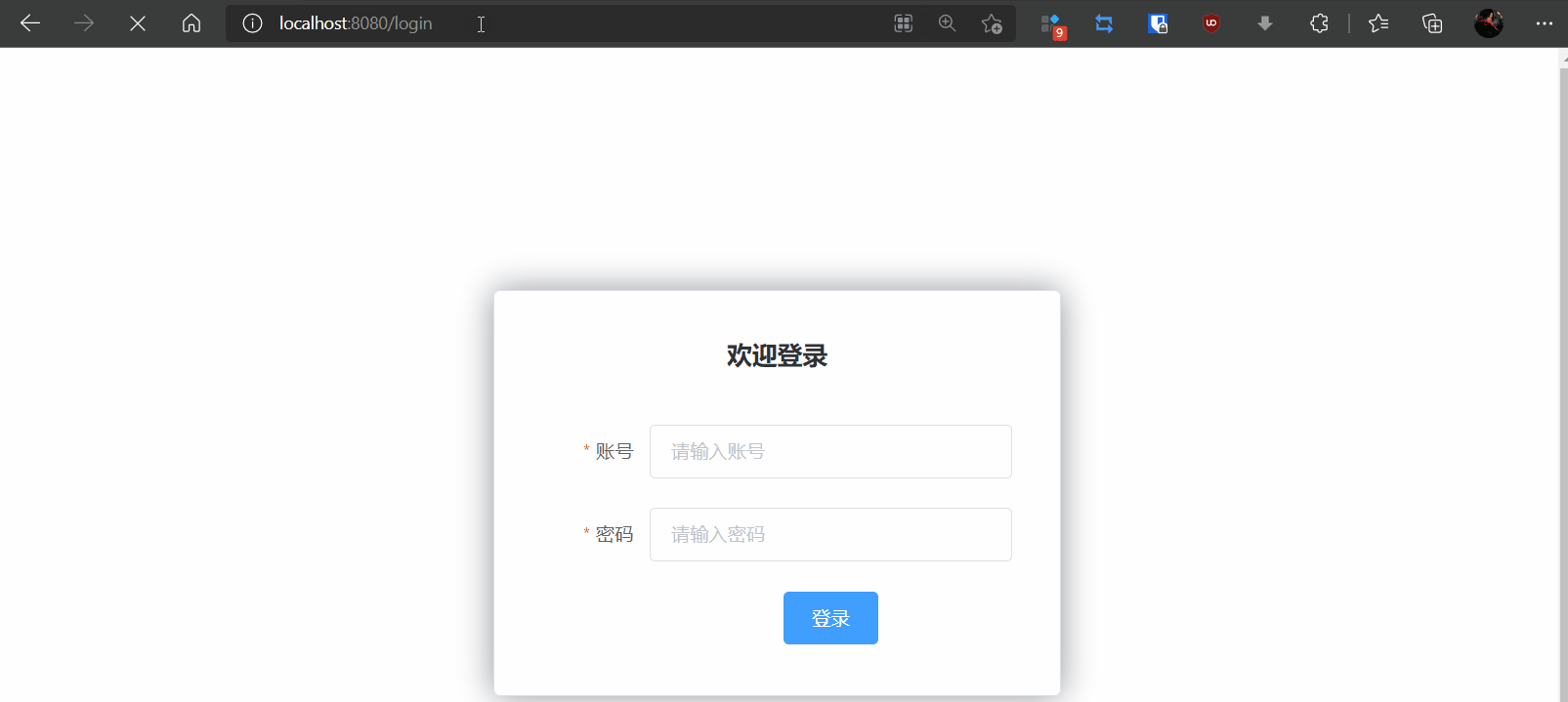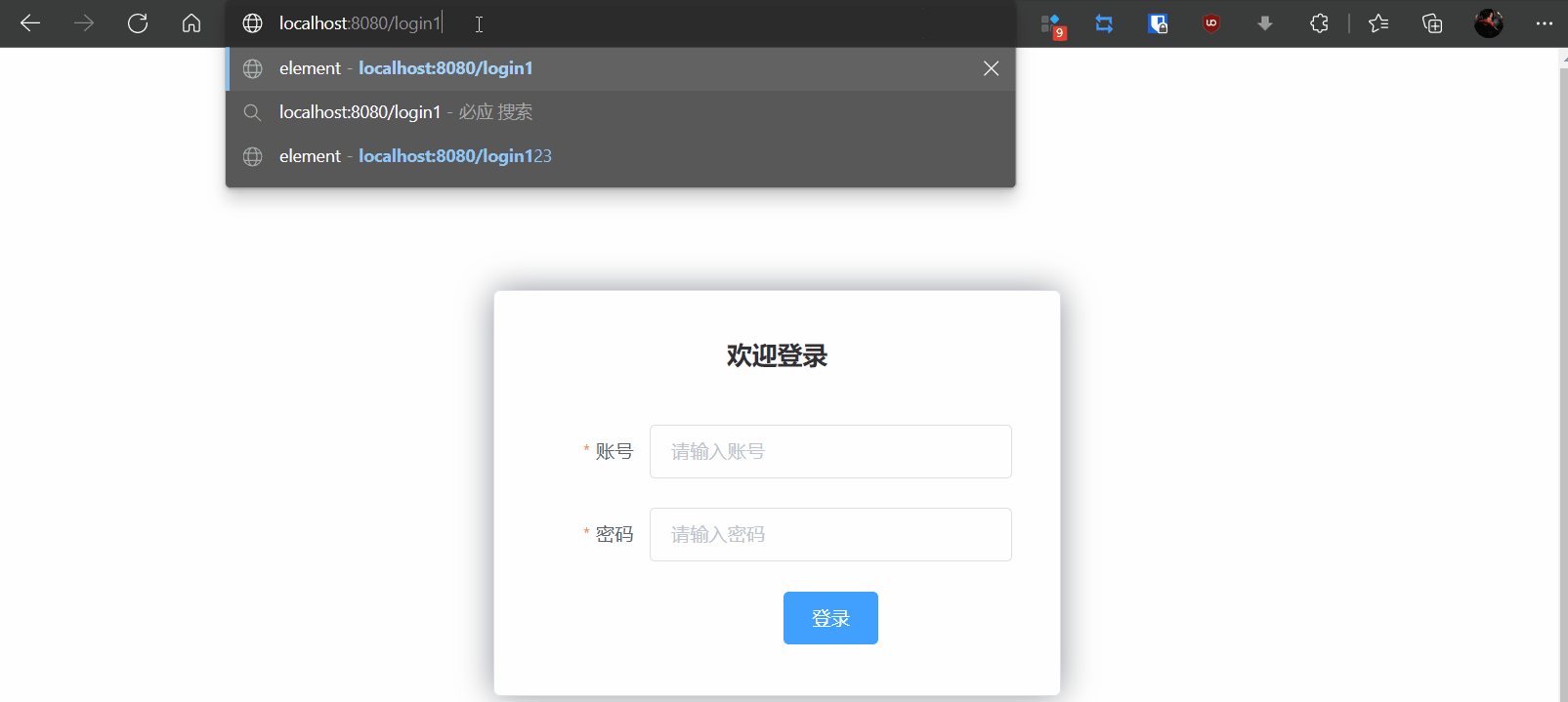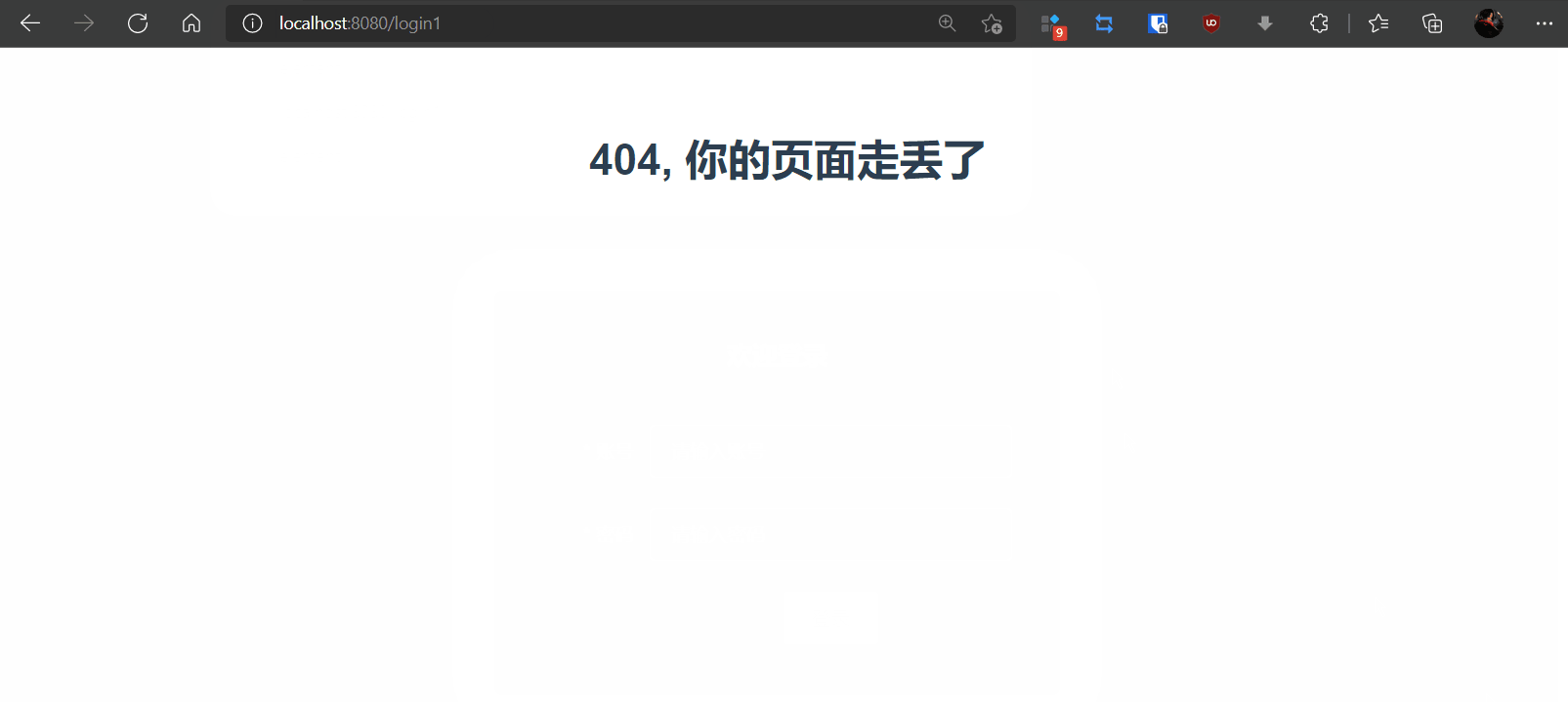
1,views/NotFound.vue创建组件
<template>
<h1>404, 你的页面走丢了</h1>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "NotFound"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2,/router/index.js添加路由
export default new router({
mode:'history',
routes: [
{
path: '/login',
component: Login,
},
{
path: '*',
component: NotFound
},
{
path: '/main/:name',
name: 'Main',
component: Main,
props: true,
},
]
})
3,测试
9.8,路由钩子
- beforeRouteEnter:在进入路由前执行
- beforeRouteLeave:在离开路由前执行
export default {
name: "UserProfile",
beforeRouteEnter: (to, from, next) => {
console.log("准备进入个人信息页");
next();
},
beforeRouteLeave: (to, from, next) => {
console.log("准备离开个人信息页");
next();
}
}
参数说明:
- to:路由将要跳转的路径信息
- from:路径跳转前的路径信息
- next:路由的控制参数
- next() 跳入下一个页面
- next(‘/path’) 改变路由的跳转方向,使其跳到另一个路由
- next(false) 返回原来的页面
- next((vm)=>{}) 仅在 beforeRouteEnter 中可用,vm 是组件实例
9.9,与异步请求Axios
axios中文文档|axios中文网 | axios (axios-js.com)
1,安装Axios:
CommonJS:
cnpm install --save axios vue-axios
将下面代码加入入口文件:
import Vue from 'vue'
import axios from 'axios'
import VueAxios from 'vue-axios'
Vue.use(VueAxios, axios)
2,导入json, /static/mock/data.json
{
"name": "狂神说Java",
"url": "https://baidu.com",
"page": 1,
"isNonProfit": true,
"address": {
"street": "含光门",
"city": "陕西西安",
"country": "中国"
},
"links": [
{
"name": "bilibili",
"url": "https://space.bilibili.com/95256449"
},
{
"name": "狂神说Java",
"url": "https://blog.kuangstudy.com"
},
{
"name": "百度",
"url": "https://www.baidu.com/"
}
]
}
3,钩子中添加获取json方法, /views/user/Profile.vue
<template>
<!--所有的元素必须在同一个标签下面,不能写到外面-->
<div>
<h1>个人信息</h1>
{{id}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['id'],
name: "UserProfile",
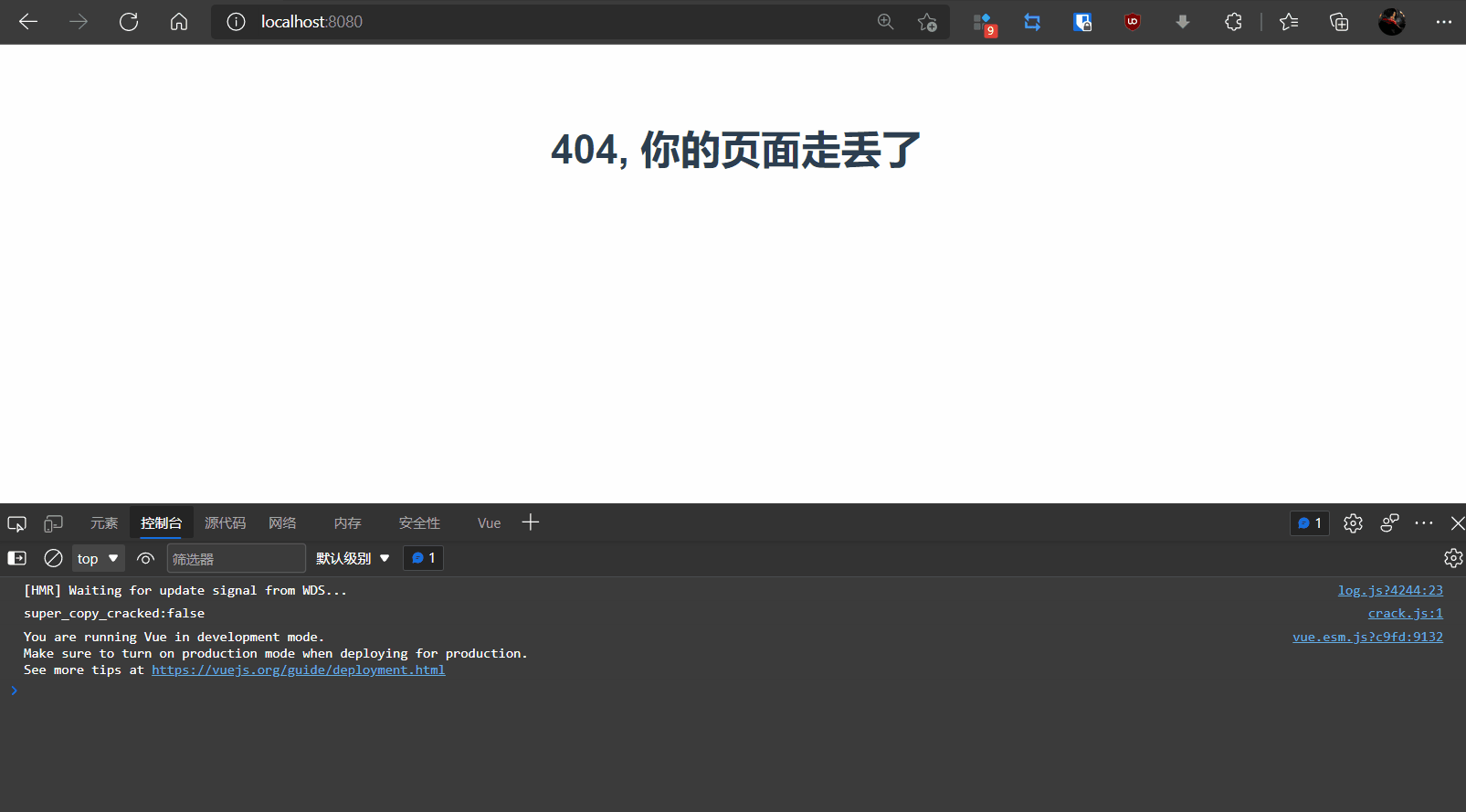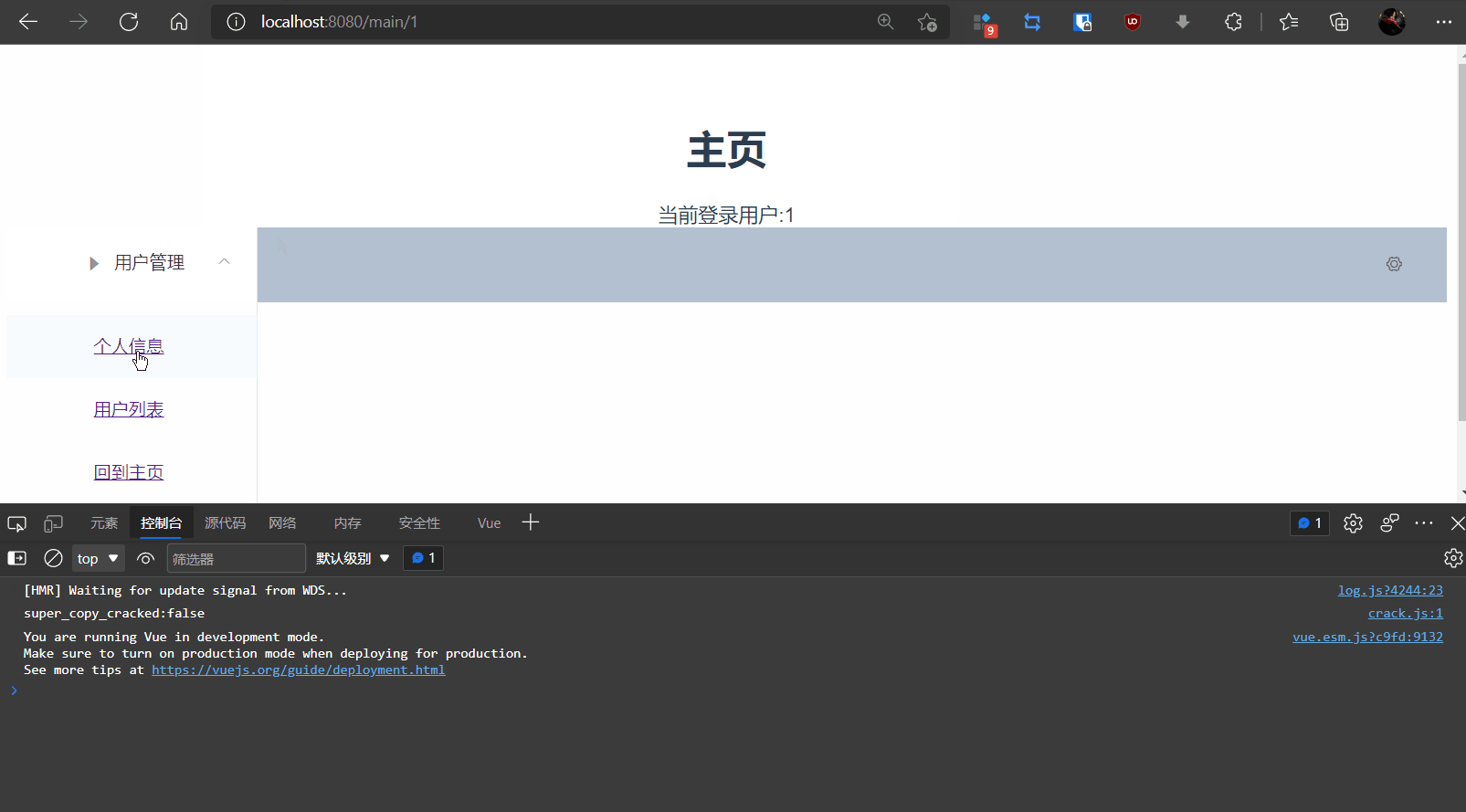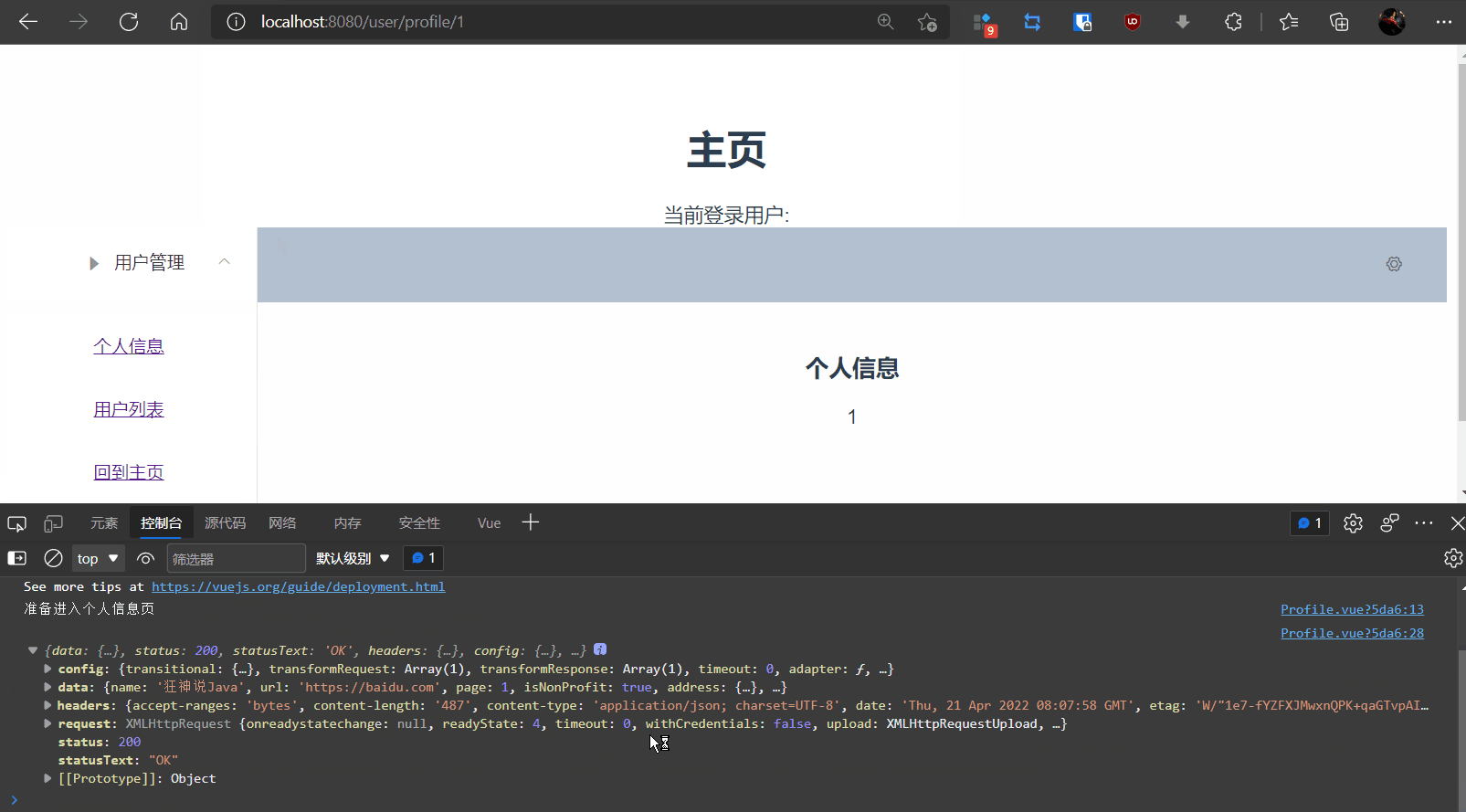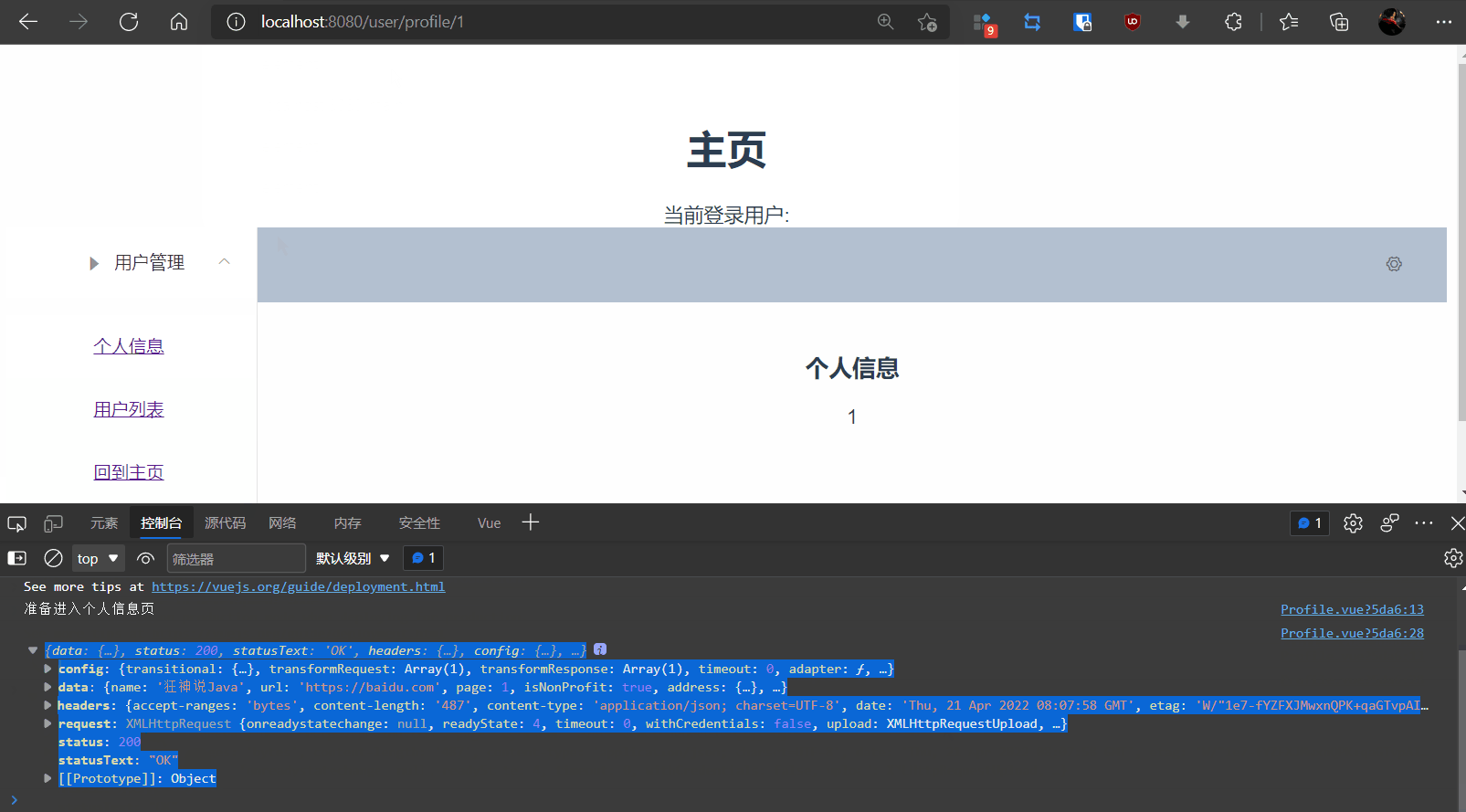
beforeRouteEnter: (to, from, next) => {
console.log("准备进入个人信息页");//加载数据
next(vm => {
vm.getData();
});
},
beforeRouteLeave: (to, from, next) => {
console.log("准备离开个人信息页");
next();
},
methods: {
getData: function (){
this.axios({
method: 'get',
url: 'http://localhost:8080/static/mock/data.json',
}).then(function (response){
console.log(response);
});
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
4,测试