简化对象和函数写法
【介绍】
ES6 允许在大括号里面,直接写入变量和函数,作为对象的属性和方法。这样的书写更加简洁
let name = "张三";
let talk = function () {
console.log("你好,很高兴见到你");
}
//创建对象
const person = {
// 完整写法
// name:name,
// talk:talk
// 简化写法
name,
talk,
// 声明方法的简化
study() {
console.log("好好学习,天天向上");
}
}
person.talk();
person.study();
箭头函数
【代码示例】
// ES6允许是用箭头(=>)定义函数
//声明一个函数
/*let fn = function () {
}*/
//箭头函数声明一个函数
let fn = (a,b)=>{
return a+b;
}
console.log(fn(1,2));//3
【特性】
1、箭头函数的 this 是静态的,始终指向函数声明时所在作用域下的 this 的值
function getName() {
console.log(this.name);
}
let getName2 = ()=>{
console.log(this.name);
}
window.name = "李四"
const person = {
name : "lisi"
}
//直接调用
getName();//李四
getName2();//李四
//call方法调用
getName.call(person);//lisi
getName2.call(person);//李四
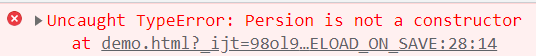
2、不能作为构造实例化对象
/*let Persion = (name, age) => {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
let me = new Persion("张三", 18);
console.log(me);*/
3、不能使用 arguments 变量
普通函数
function fn() {
console.log(arguments);
}
fn(1, 2, 3);
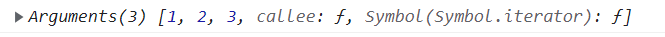
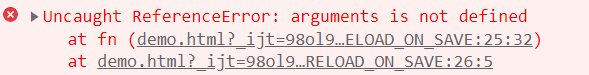
箭头函数就不能使用 arguments
let fn = () => console.log(arguments);
fn(1, 2, 3);
【箭头函数的简写】
1、小括号省略,当形参有且只有一个的时候
//正常写法
let add = (n) => {
return n + n;
}
//简写
let add = n => {
return n + n
}
console.log(add(9));//18
2、省略花括号,当代码体只有一条的时候,此时 return 必须省略,因为语句的执行结果就是返回值
//正常写法
let pow = (n) => {
return n * n;
}
//简写
let pow = n => n * n;
console.log(pow(9));//81
【箭头函数应用1:点击div 2s后改变颜色】
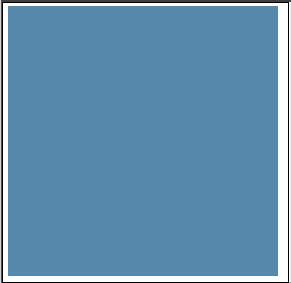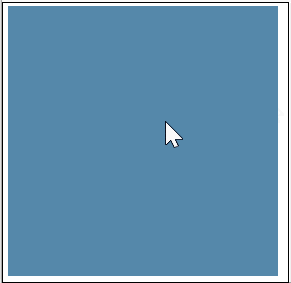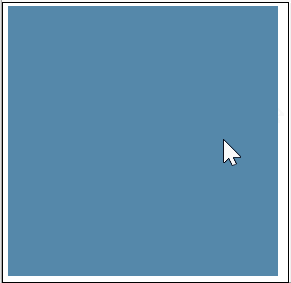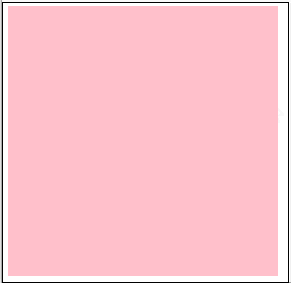
传统写法存在问题
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>箭头函数的实践和应用场景</title>
<style>
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: #58a;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="ad"></div>
<script>
// 需求-1 点击 div 2s 后颜色变成『粉色』
// 获取元素
let ad = document.getElementById('ad');
// 绑定事件
ad.addEventListener("click", function () {
// 传统写法
// 定时器:参数1:回调函数;参数2:时间;
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(this);
this.style.background = 'pink';
}, 2000);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
这种写法是有问题的,因为 setTimeout 中的 this 是指向 window 的,window 没有 style 属性,所以 undefined

传统解决办法:保存一个外层的 this
let ad = document.getElementById('ad');
ad.addEventListener("click", function () {
//保存 this 的值
let _this = this;
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(_this);
_this.style.background = 'pink';
}, 2000);
});
ES6写法:
let ad = document.getElementById('ad');
ad.addEventListener("click", function () {
setTimeout(()=> {
console.log(_this);
this.style.background = 'pink';
}, 2000);
});
箭头函数的 this 是静态的,指向声明时所在作用域下的 this,也就是 ad
【箭头函数应用2:从数组中返回偶数的元素】
之前的写法
const arr = [1, 6, 9, 10, 100, 25];
const result = arr.filter(function (item) {
if (item % 2 === 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
});
console.log(result);//[6, 10, 100]
ES6写法
const arr = [1, 6, 9, 10, 100, 25];
const result = arr.filter(item => {
if (item % 2 === 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
});
//可简写为:
const result = arr.filter(item => item % 2 === 0);
console.log(result);
箭头函数适合与 this 无关的回调:定时器,数组的方法回调
箭头函数不适合与 this 有关的回调:事件回调,对象的方法
参数默认值
ES6允许给函数的参数赋初始值
【特点】
1、形参初始值 具有默认值的参数,一般位置要靠后(潜规则)
function add(a, b, c = 10) {
return a + b + c;
}
let result = add(1, 2);
console.log(result); // 13
2、与解构赋值结合
function connect({host = "127.0.0.1", username, password, port}) {
console.log(host)//localhost
console.log(username)//root
console.log(password)//root
console.log(port)//3306
}
connect({
host: 'localhost',
username: 'root',
password: 'root',
port: 3306
})
rest 参数
ES6 引入 rest 参数,用于获取函数的实参,用来代替 arguments
ES5获取实参的方式
function data() {
console.log(arguments);
}
data("西瓜", "草莓", "芒果");
可以看到接收到的是一个对象

ES6的 rest 参数...args,rest 参数必须放在最后面
function data(...args) {
console.log(args); // fliter some every map
}
data("西瓜", "草莓", "芒果");
可以看到收到的是数组,这样就可以使用操作数组的方法了

