commit阶段
上节讲到了rootFiber完成completeWork的时候,返回了一个状态,为RootInCompleted,表示工作完成。调用finishConcurrentRender方法,该方法会调用commitRoot,开启commit阶段。
现在回顾一下,我们的fiber结构是
// App组件
const App: React.FC = () => {
return <DD />;
};
// DD组件
class DD extends Component {
render() {
return <div>123</div>;
}
}
那么fiber结构应该是
rootFiber.child => App fiber
App fiber.child => DD fiber
DD fiber.child => div fiber
看看finishConcurrentRender方法
//完成了render阶段之后,开启commit阶段
finishConcurrentRender(root, exitStatus, lanes);
root是FiberRoot,exitStatus是RootInCompleted,表示完成状态。
finishConcurrentRender
function finishConcurrentRender(root, exitStatus, lanes) {
switch(exitStatus){
case RootInProgress:
case RootFatalErrored: {throw new Error('Root did not complete. This is a bug in React.')}
case RootCompleted: commitRoot(root, workInProgressRootRecoverableErrors); break;
...
}
}
可以看到,finishConcurrentRender主要就是完成了对exitStatus的判断,如果状态不对就抛出错误。然后调用commitRoot方法,开启commit阶段。
commitRoot
commitRoot会调用commitRootImpl方法,该方法时commit阶段的主要方法。
commitRootImpl方法
commitRootImp主要做了一下六件事情。
- 1 开始执行dom操作之前,将所有effects执行完毕。
- 2 before-mutation之前的阶段,全局变量重置,调度useEffect
function commitRootImpl(
root: FiberRoot,
recoverableErrors: null | Array<mixed>,
renderPriorityLevel: EventPriority
) {
// --------before-mutation-之前的阶段-start-------
const finishedWork = root.finishedWork; // rootFiber
const lanes = root.finishedLanes; //优先级
// 重置FiberRoot的属性
root.finishedWork = null;
root.finishedLanes = NoLanes;
// 重置变量
root.callbackNode = null;
root.callbackPriority = NoLane;
//开始调度useEffect
if (
(finishedWork.subtreeFlags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags ||
(finishedWork.flags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags
) {
if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
// 赋值全局变量,表示有useEffect的副作用
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true;
pendingPassiveEffectsRemainingLanes = remainingLanes;
// 以普通优先级调度useEffect
scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => {
flushPassiveEffects();
// This render triggered passive effects: release the root cache pool
// *after* passive effects fire to avoid freeing a cache pool that may
// be referenced by a node in the tree (HostRoot, Cache boundary etc)
return null;
});
}
}
......
}
- 3 before-mutation阶段,调用commitBeforeMutationEffects
- 4 mutation阶段,调用commitMutationEffects
- 5 layout阶段, 调用commitLayoutEffects
function commitRootImpl(
root: FiberRoot,
recoverableErrors: null | Array<mixed>,
renderPriorityLevel: EventPriority
) {
// --------before-mutation-之前的阶段-start-------
......
// 判断是否有effects影响需要更新
const subtreeHasEffects = ....// 子树是否有更新
const rootHasEffect = .... // root是否有更新
if (subtreeHasEffects || rootHasEffect) {
//因为commit是同步的,优先级也是最高的
const previousPriority = getCurrentUpdatePriority();
setCurrentUpdatePriority(DiscreteEventPriority); //设置最高优先级
// -----------------beforeMutation阶段------------------
const shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur = commitBeforeMutationEffects(
root,
finishedWork
);
// ------------mutation阶段------------------
commitMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes);
// 切换RootFiber.current
root.current = finishedWork;
// ------------layout阶段----------------
commitLayoutEffects(finishedWork, root, lanes);
if (__DEV__) {
if (enableDebugTracing) {
logLayoutEffectsStopped();
}
}
}
- 6 layout之后阶段,如果有useEffect的effects,就赋值给全局变量rootWithPendingPassiveEffects,useEffect的调度函数通过上面去获取effectLists,执行对应的useEffects函数。调用ensureRootIsScheduled最后判断还有没有更新没执行
function commitRootImpl(
root: FiberRoot,
recoverableErrors: null | Array<mixed>,
renderPriorityLevel: EventPriority
) {
// --------before-mutation-之前的阶段-start-------
......
// 判断是否有effects影响需要更新
const subtreeHasEffects = ....// 子树是否有更新
const rootHasEffect = .... // root是否有更新
if (subtreeHasEffects || rootHasEffect) {
//因为commit是同步的,优先级也是最高的
const previousPriority = getCurrentUpdatePriority();
setCurrentUpdatePriority(DiscreteEventPriority); //设置最高优先级
// -----------------beforeMutation阶段------------------
// ------------mutation阶段------------------
// ------------layout阶段----------------
....
// -------------------layout之后--start-------------------
const rootDidHavePassiveEffects = rootDoesHavePassiveEffects;
if (rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) { // 有useEffect的effects
// This commit has passive effects. Stash a reference to them. But don't
// schedule a callback until after flushing layout work.
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = false;
rootWithPendingPassiveEffects = root; //将root赋值给rootWithPendingPassiveEffects,useEffect执行的时候会通过他来获取effectList
pendingPassiveEffectsLanes = lanes;
}
...
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now()); //确保额外的工作正在调度
// If layout work was scheduled, flush it now.
flushSyncCallbacks();
...
}
commit阶段完成。
接着看对应的每个阶段做的事情。
before-mutation之前
//当rootWithPendingPassiveEffects不为空的时候,表示有effect 执行effectList上的副作用,直到effectLists上值为null
do {
flushPassiveEffects();
} while (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null); //mount的时候为null,
const finishedWork = root.finishedWork; // rootFiber
const lanes = root.finishedLanes; //优先级
// 重置FiberRoot的属性
root.finishedWork = null;
root.finishedLanes = NoLanes;
// 重置变量
root.callbackNode = null;
root.callbackPriority = NoLane;
if (
(finishedWork.subtreeFlags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags ||
(finishedWork.flags & PassiveMask) !== NoFlags
) {
if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
// 赋值全局变量,表示有useEffect的副作用
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true;
pendingPassiveEffectsRemainingLanes = remainingLanes;
scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => { // 以普通优先级调度useEffect
flushPassiveEffects();
// This render triggered passive effects: release the root cache pool
// *after* passive effects fire to avoid freeing a cache pool that may
// be referenced by a node in the tree (HostRoot, Cache boundary etc)
return null;
});
}
}
可以看到,主要就是三件事情
- 如果rootWithPendingPassiveEffects有值,就调度flushPassiveEffects,调度useEffect
- 重置全局变量
- 如果有useEffect的相关effects,就调用scheduleCallback,以普通优先级调度flushPassiveEffects
flushPassiveEffects最终会调用
export function flushPassiveEffects(): boolean {
if (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null) {
// 调用UseEffect的销毁函数
commitPassiveUnmountEffects(root.current);
// 调用useEffect函数
commitPassiveMountEffects(root, root.current);
}
}
调度useEffect的销毁和执行函数。
rootWithPendingPassiveEffects是在layout阶段之后被赋值的。
before-mutation阶段
- 根据effectList链表获取有副作用的fiber
- 类组件执行instance.getSnapShotBeforeUpdate,将返回值挂载到instance上面。
export function commitBeforeMutationEffects(
root: FiberRoot,
firstChild: Fiber // workInprogress rootFiber
) {
...
nextEffect = firstChild;
commitBeforeMutationEffects_begin();
..
return shouldFire;
}
firstCHild就是rootFiber,对于commit阶段,他就是第一个要处理的子节点。
调用commitBeforeMutationEffects_begin
function commitBeforeMutationEffects_begin() {
// 开启while循环
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
const child = fiber.child;
if (
// mount的时候只有rootFiber身材有flags,所以第一次mount,nextEffect最后会被赋值到App
(fiber.subtreeFlags & BeforeMutationMask) !== NoFlags &&
child !== null
) {
ensureCorrectReturnPointer(child, fiber);
nextEffect = child;
} else {
commitBeforeMutationEffects_complete();
}
}
开启while循环,遍历effectLists链表,获取到最后一个有副作用的子节点。
mount的时候需要注意,因为只有rootFiber会有flags标记,所以第一次循环,会走if条件,将App fiber赋值给nextEffect。
第二次循环因为App fiber没有flags标记,所以走else条件,commitBeforeMutationEffects_complete
function commitBeforeMutationEffects_complete() {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
// 开启while循环
const fiber = nextEffect;
commitBeforeMutationEffectsOnFiber(fiber);
const sibling = fiber.sibling;
if (sibling !== null) {
ensureCorrectReturnPointer(sibling, fiber.return);
nextEffect = sibling;
return;
}
// 下一个while循环条件
nextEffect = fiber.return;
}
}
commitBeforeMutationEffects_complete也开启一个while循环,从下往上处理每一个有flags的fiber。调用commitBeforeMutationEffectsOnFiber
function commitBeforeMutationEffectsOnFiber(finishedWork: Fiber) {
const current = finishedWork.alternate; //获取rooFiber的alternate也就是current rootFiber
const flags = finishedWork.flags; //获取rootFiber的effectTag
if ((flags & Snapshot) !== NoFlags) {
//有flags标记的fiber才会执行
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
..
case ClassComponent: {
if (current !== null) {
const prevProps = current.memoizedProps; //旧的props
const prevState = current.memoizedState; //旧的state
const instance = finishedWork.stateNode; //获取类组件的实例
// 调用类组件的getSnapshotBeforeUpdate函数
const snapshot = instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(
finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type
? prevProps
: resolveDefaultProps(finishedWork.type, prevProps),
prevState
);
// 将返回的快照值保存在实例的__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate上,到时候赋值给componentDidUpdate
instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate = snapshot;
}
break;
}
}
}
}
这里主要处理了类组件,执行了getSnapshotBeforeUpdate生命周期,将返回值挂载到
instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate上。
mutation阶段
主要调用了commitMutationEffects函数,mutation阶段是操作dom的阶段。
commitMutationEffects(root, finishedWork, lanes);
function commitMutationEffects_begin(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes){
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
// 删除操作
const deletions = fiber.deletions;
if (deletions !== null) {
for (let i = 0; i < deletions.length; i++) {
commitDeletion(root, childToDelete, fiber); //对于删除的fiber
}
}
const child = fiber.child;
// 跟before-mutation阶段一样的判断条件
if ((fiber.subtreeFlags & MutationMask) !== NoFlags && child !== null) {
ensureCorrectReturnPointer(child, fiber);
nextEffect = child;
} else {
commitMutationEffects_complete(root, lanes);
}
}
}
commitMutationEffects_begin函数的while循环,跟before-mutation阶段的一样判断条件。这里多了一个对于删除节点的操作。
对于删除的节点,存在fiber.deletion上。调用commitDeletion进行删除。
commitDeletion调用commitNestedUnmounts函数。
主要执行对dom的删除。
function commitNestedUnmounts(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
root: Fiber,
nearestMountedAncestor: Fiber
){
// 递归删除所有子节点,将子节点都调用一次commitUnmount函数。
while (true) {
commitUnmount(finishedRoot, node, nearestMountedAncestor);
if (
node.child !== null &&
(!supportsMutation || node.tag !== HostPortal)
) {
node.child.return = node;
node = node.child;
continue;
}
if (node === root) {
return;
}
while (node.sibling === null) {
if (node.return === null || node.return === root) {
return;
}
node = node.return;
}
node.sibling.return = node.return;
node = node.sibling;
}
}
function commitUnmount(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
current: Fiber,
nearestMountedAncestor: Fiber
){
switch (current.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:{
const updateQueue: FunctionComponentUpdateQueue | null =
(current.updateQueue: any);
if (updateQueue !== null) {
const lastEffect = updateQueue.lastEffect;
if (lastEffect !== null) {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
let effect = firstEffect;
do {
// 调用useLyaoutEffect的销毁函数
const { destroy, tag } = effect;
if (destroy !== undefined) {
....
safelyCallDestroy(current, nearestMountedAncestor, destroy);
...
}
}
}
effect = effect.next;
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
}
}
return;
}
.....
// 对于类组件
case ClassComponent: {
safelyDetachRef(current, nearestMountedAncestor);
const instance = current.stateNode;
if (typeof instance.componentWillUnmount === "function") {
safelyCallComponentWillUnmount(
current,
nearestMountedAncestor,
instance
);
}
return;
}
....
}
....
}
- useLayoutEffect是以链表的形式存放在fiber.updateQueue.lastEffect之上。这里对于函数组件的操作就是获取所有effects,调用其销毁函数destroy。记住,useLayoutEffect销毁函数是在mutation阶段执行的。
- 对于类组件,处理ref,调用类组件的componentWillUnMount函数。
commitMutationEffects_complete
跟before-mutation阶段一样
function commitMutationEffects_complete(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes) {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
// 开启while循环
const fiber = nextEffect;
...
commitMutationEffectsOnFiber(fiber, root, lanes);
...
const sibling = fiber.sibling;
if (sibling !== null) {
ensureCorrectReturnPointer(sibling, fiber.return);
nextEffect = sibling;
return;
}
nextEffect = fiber.return;
}
}
开启while循环,执行所有的有flags的fiber,调用commitMutationEffectsOnFiber函数
// mutation阶段主要执行的函数
function commitMutationEffectsOnFiber(
finishedWork: Fiber, // fiber
root: FiberRoot, //FiberROot
lanes: Lanes
) {
const flags = finishedWork.flags; //effectTag
// 有ref的effectTag
if (flags & Ref) {
const current = finishedWork.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
commitDetachRef(current); //清除ref
}
}
// 判断当前的fiber要做啥操作
const primaryFlags = flags & (Placement | Update | Hydrating);
switch (primaryFlags) {
case Placement: {
// 新增
commitPlacement(finishedWork);
finishedWork.flags &= ~Placement;
break;
}
case PlacementAndUpdate: {
// 新增并且修改
commitPlacement(finishedWork);
finishedWork.flags &= ~Placement;
// Update
const current = finishedWork.alternate;
commitWork(current, finishedWork);
break;
}
...
case Update: {
// 修改
const current = finishedWork.alternate;
commitWork(current, finishedWork);
break;
}
}
}
commitMutationEffectsOnFiber主要处理了包含有ref的flags的fiber,先清除老的ref,等到layout阶段再赋值新的ref
function commitDetachRef(current: Fiber) {
const currentRef = current.ref;
if (currentRef !== null) {
if (typeof currentRef === "function") {
if (
enableProfilerTimer &&
enableProfilerCommitHooks &&
current.mode & ProfileMode
) {
...
currentRef(null);
}
} else {
currentRef(null);
}
} else {
currentRef.current = null;
}
}
可以看到如果ref是函数,就传入null,如果不是,就将其置为null。
接着是处理新增和修改的fiber。
新增主要调用 commitPlacement(finishedWork);
修改主要调用 commitWork(current, finishedWork);
commitPlacement
function commitPlacement(finishedWork: Fiber): void {
if (!supportsMutation) {
return;
}
// 获取非组件的父级fiber对象,只有非组件的才能插入
const parentFiber = getHostParentFiber(finishedWork);
// 判断父级fiber的类型
switch (parentFiber.tag) {
case HostComponent: {
const parent: Instance = parentFiber.stateNode;
//获取兄弟节点
const before = getHostSibling(finishedWork);
// insert或append插入到到父级上
insertOrAppendPlacementNode(finishedWork, before, parent);
break;
}
.....
}
}
对于新增的节点,会获取父级非组件fiber,因为组件是没有dom的然后获取兄弟节点。判断是insert还是append。
// 新增节点操作
function insertOrAppendPlacementNode(
node: Fiber, // 当前fiber
before: ?Instance, //兄弟节点
parent: Instance //父亲节点
): void {
const { tag } = node;
const isHost = tag === HostComponent || tag === HostText; //是不是原生标签或者是文本节点
if (isHost) {
//如果是原生标签或者是文本节点
const stateNode = node.stateNode;
if (before) {
// 有兄弟,调用insertBefore
insertBefore(parent, stateNode, before);
} else {
//否则调用append
appendChild(parent, stateNode);
}
} else if (tag === HostPortal) {
...
} else {
// 那就是组件了,组件就要将他的所有儿子都插入dom中
const child = node.child;
if (child !== null) {
insertOrAppendPlacementNode(child, before, parent);
let sibling = child.sibling;
while (sibling !== null) {
insertOrAppendPlacementNode(sibling, before, parent);
sibling = sibling.sibling;
}
}
}
}
insertOrAppendPlacementNode也很暴力,如果是div p 等原生标签或者是文本节点,如果有兄弟就使用insertBefore,如果没有就是用appendChild。
如果是组件的话,组件是没有dom的,要将组件的所有子dom遍历插入到当前dom节点来。递归调用insertOrAppendPlacementNode
commitWork
function commitWork(current: Fiber | null, finishedWork: Fiber): void {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
...
case FunctionComponent:{
commitHookEffectListUnmount(
HookInsertion | HookHasEffect,
finishedWork,
finishedWork.return
);
....
}
}
}
组件修改,调用useLayoutEffet的销毁函数。
所以mutation阶段做的事情就是
- 遍历循环有flags的fiber,对于有ref的,先清除ref的内容。
- 对于删除的fiber,先清除ref,如果hi函数组件,就调用useLayoutEffect的销毁函数,如果是类组件,就调用componentWillUnMount函数
- 对于新增的fiber,通过获取父级和兄弟判断调用insert还是append方法。
- 对于修改的fiber,函数组件执行useLayoutEffect的销毁函数。对于原生div标签,调用commitUpdate
export function commitUpdate(
domElement: Instance,
updatePayload: Array<mixed>,
type: string,
oldProps: Props,
newProps: Props,
internalInstanceHandle: Object,
): void {
// 通过修改props修改内容
updateProperties(domElement, updatePayload, type, oldProps, newProps);
updateFiberProps(domElement, newProps);
}
layout阶段
layout阶段对应dom刚刚操作之后。调用 commitLayoutEffects(finishedWork, root, lanes);
跟before-mutation一样的通过while循环,遍历所有有flags的fiber
function commitLayoutEffects_begin(
subtreeRoot: Fiber,
root: FiberRoot,
committedLanes: Lanes
) {
..
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
const firstChild = fiber.child;
// 循环找到最下边的有flags的fiber
if ((fiber.subtreeFlags & LayoutMask) !== NoFlags && firstChild !== null) {
ensureCorrectReturnPointer(firstChild, fiber);
nextEffect = firstChild;
} else {
commitLayoutMountEffects_complete(subtreeRoot, root, committedLanes);
}
}
}
如上,判断条件跟之前两个阶段一样,调用commitLayoutMountEffects_complete
function commitLayoutMountEffects_complete(
subtreeRoot: Fiber,
root: FiberRoot,
committedLanes: Lanes
) {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const fiber = nextEffect;
if ((fiber.flags & LayoutMask) !== NoFlags) {
commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(root, current, fiber, committedLanes);
}
const sibling = fiber.sibling;
if (sibling !== null) {
ensureCorrectReturnPointer(sibling, fiber.return);
nextEffect = sibling;
return;
}
nextEffect = fiber.return;
}
}
如上,通过while循环,遍历所有有flags的fiber,执行commitLayoutEffectOnFiber方法
function commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
current: Fiber | null,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedLanes: Lanes
): void {
if ((finishedWork.flags & LayoutMask) !== NoFlags) {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
...
case FunctionComponent:{
startLayoutEffectTimer();
// 调度useLayoutEffect的create函数 layout阶段传入的数是5,用来调用uselayoutEffect
commitHookEffectListMount(
HookLayout | HookHasEffect,
finishedWork
);
}
}
}
对于函数组件,调用useLayoutEffect的执行函数,需要注意的是,useEffect跟useLayoutEffect是一样的,都是产生一个effects。如
const App: React.FC = () => {
React.useEffect(function Effect(){
debugger
console.log('useEffect');
},[])
React.useLayoutEffect(function LayoutEffect(){
console.log('useLayoutEffect');
}, [])
return <DD />;
};
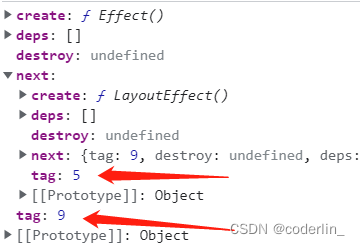
useEffect产生的effect,他的tag是9,对于useLayoutEffect,产生的effect,tag是5。他们是以环状单链表的形式存放在fiber.updateQueue.lastEffect上。
他们的执行函数都commitHookEffectListMount,通过传入的参数以及effect的tag判断当前要执行的是哪种类型。
对于useLayoutEffect,useEffect的create不会被执行,只会执行useLayoutEffect的create。useEffect是以异步的形式调用的,useLayoutEffect是同步执行的。
接着回到正题,对于commitLayoutEffectOnFiber,如果是类组件
function commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
current: Fiber | null,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedLanes: Lanes
): void {
if ((finishedWork.flags & LayoutMask) !== NoFlags) {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
...
case ClassComponent: {
const instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
if (finishedWork.flags & Update) {
if (!offscreenSubtreeWasHidden) {
// 类组件,调用componentDidMount
instance.componentDidMount();
} else {
const prevProps =
finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type
? current.memoizedProps
: resolveDefaultProps(
finishedWork.type,
current.memoizedProps
);
const prevState = current.memoizedState;
try {
startLayoutEffectTimer();
// 类组件,调用componentDidUpdate
instance.componentDidUpdate(
prevProps,
prevState,
instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate //before-mutation阶段调用的getSnaoShotBeforeUpdate的返回值
);
}
}
}
}
// 如果还存在任务队列
const updateQueue: UpdateQueue<*> | null =
(finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
if (updateQueue !== null) {
// 调用render方法的第三个参数。
commitUpdateQueue(finishedWork, updateQueue, instance);
}
break;
}
}
}
- 对于class组件,调用componentDidMount或者是componentDidUpdate,并且传入了 instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate也就是before-mutation阶段调用的getSnaoShotBeforeUpdate的返回值
最后调用了commitUpdateQueue方法,该方法主要也就是调用了一些回调函数,如render的第三个参数。
-
而对于原生组件,主要就是处理了一些比如输入框的autoFocus属性和img的src属性。
case HostComponent: { const instance: Instance = finishedWork.stateNode; if (current === null && finishedWork.flags & Update) { const type = finishedWork.type; const props = finishedWork.memoizedProps; commitMount(instance, type, props, finishedWork); } break; }export function commitMount( domElement: Instance, type: string, newProps: Props, internalInstanceHandle: Object, ): void { switch (type) { case 'button': case 'input': case 'select': case 'textarea': if (newProps.autoFocus) { ((domElement: any): | HTMLButtonElement | HTMLInputElement | HTMLSelectElement | HTMLTextAreaElement).focus(); } return; case 'img': { if ((newProps: any).src) { ((domElement: any): HTMLImageElement).src = (newProps: any).src; } return; } } }
最后,处理ref
function commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
current: Fiber | null,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedLanes: Lanes
){
....
// 处理ref
if (!enableSuspenseLayoutEffectSemantics || !offscreenSubtreeWasHidden) {
...
if (finishedWork.flags & Ref) {
commitAttachRef(finishedWork);
}
}
}
调用commitAttachRef方法
function commitAttachRef(finishedWork: Fiber) {
const ref = finishedWork.ref;
if (ref !== null) {
const instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
let instanceToUse;
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case HostComponent:
instanceToUse = getPublicInstance(instance);
break;
default:
instanceToUse = instance;
}
if (typeof ref === "function") {
let retVal;
retVal = ref(instanceToUse);
}else {
ref.current = instanceToUse;
}
}
}
-
如果re不为空,并且是原生标签,直接获取dom信息赋值给ref.current。
-
如果ref是函数,并且不是原生标签,那么就执行ref函数,并且传入fiber.stateNode。
-
如果ref不是函数,那么就直接赋值fiber.stateNode,对于类组件是实例,对于函数组件是null。
至此,layout阶段完毕。
layout阶段做的事情:
- 对于函数组件,执行useLayoutEffect的create
- 对于类组件,调用componentDidMount/componentDidUpdate,并且调用一些回调函数,比如render的第三个参数
- 对于原生组件,处理一些特殊属性。
- 对于ref,直接赋值。
layout阶段之后
function commitRootImp(){
...
// -------------------layout之后--start-------------------
const rootDidHavePassiveEffects = rootDoesHavePassiveEffects;
if (rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) { // 有useEffect的effects
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = false;
rootWithPendingPassiveEffects = root;
pendingPassiveEffectsLanes = lanes;
}
// 在调用一次ensureRootIsScheduled, 确保如果有额外的工作的话,那么他们也需要调度
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
// If layout work was scheduled, flush it now.
flushSyncCallbacks();
...
}
layout阶段之后做的事情,主要是对全局变量赋值,比如rootWithPendingPassiveEffects,他是刚才说before-mutation阶段之前,调度flushPassiveEffects函数要执行的重要遍历
export function flushPassiveEffects(): boolean {
if (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null) {
const root = rootWithPendingPassiveEffects;
return flushPassiveEffectsImpl();
.....
}
return false;
}
等到schedulecallback执行flushPassiveEffects的时候,rootWithPendingPassiveEffects就有值了,而flushPassiveEffectsImpl最终会调用commitHookEffectListMount函数,这次才是真正执行useEffect。由于flushPassiveEffects是通过scheduleCallback注册的,而schedule模块是通过postMesssage实现的,所以最快,flushPassiveEffects函数也是在下一帧执行宏任务的时候执行。这也是为什么useEffect是异步的原因。
因为useLayoutEffect是在commit阶段完成销毁和执行函数的,他们是同步的,而useEffect是后面帧才执行的。
然后layout阶段之后还调用了一次ensureRootIsScheduled,确保commti产生的额外的任务可以被调度。
最后
上面说过finishConcurrentRender调用了commitRoot函数开启了commit阶段,那么执行完之后
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(){
...
//完成了render阶段之后,开启commit阶段
finishConcurrentRender(root, exitStatus, lanes);
....
// 每次执行完performConcurrentWorkOnRoot都会调用ensureRootIsScheduled来判断当前是否有更高优先级的任务需要调度
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
//如果没有更高优先级或者当前任务就是最高优先级的,继续返回该任务
if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) {
// The task node scheduled for this root is the same one that's
// currently executed. Need to return a continuation.
// performConcurrentWorkOnRoot是ScheduleCallback注册的函数,而ScheduleCallback执行的时候,需要通过返回来确定该任务是否继续执行
// 这里通过ensureRootIsScheduled调度之后,发现root上面挂载的任务还是当前这个任务,表示当前的任务依然是最高优先级的。
// 所以,需要返回当前的任务给ScheduleCallback,以表示当前任务依然是最高优先级,需要执行。
return performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root);
}
//当调用ensureRootIsScheduled调度之后,如果有更高优先级的,或者任务都执行完毕了,那么这里返回null给scheduleCallback
// 表示当前任务已经结束,当Schedule执行注册的函数performConcurrentWorkOnRoot,结果是Null的时候,他会认为该任务已经结束。
// 会将该任务从最小堆中取出,然后继续调度,看有没有更高优先级的任务,注意,Schedule和React里面有各自的调度系统
return null;
}
最后还是会调用ensureRootIsScheduled,判断有没有新的任务,而没有任务之后
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) {
//正在工作的任务
const existingCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
// Check if any lanes are being starved by other work. If so, mark them as
// expired so we know to work on those next.
markStarvedLanesAsExpired(root, currentTime);
//当前调度的任务的优先级
const nextLanes = getNextLanes(
root,
root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes
);
// 如果当前调度的任务优先级是NoLanes,不需要调度,直接刷新全局变量,并且取消当前的工作的任务
if (nextLanes === NoLanes) {
// Special case: There's nothing to work on.
if (existingCallbackNode !== null) {
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode);
}
root.callbackNode = null;
root.callbackPriority = NoLane;
return;
}
....
}
它会将root.callbackNode = null;重置全局变量。然后直接return。那么在
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(){
... // 获取调度的任务
const originalCallbackNode = root.callbackNode;
....
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now());
//如果没有更高优先级或者当前任务就是最高优先级的,继续返回该任务
if (root.callbackNode === originalCallbackNode) {
// The task node scheduled for this root is the same one that's
// currently executed. Need to return a continuation.
// performConcurrentWorkOnRoot是ScheduleCallback注册的函数,而ScheduleCallback执行的时候,需要通过返回来确定该任务是否继续执行
// 这里通过ensureRootIsScheduled调度之后,发现root上面挂载的任务还是当前这个任务,表示当前的任务依然是最高优先级的。
// 所以,需要返回当前的任务给ScheduleCallback,以表示当前任务依然是最高优先级,需要执行。
return performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root);
}
//当调用ensureRootIsScheduled调度之后,如果有更高优先级的,或者任务都执行完毕了,那么这里返回null给scheduleCallback
// 表示当前任务已经结束,当Schedule执行注册的函数performConcurrentWorkOnRoot,结果是Null的时候,他会认为该任务已经结束。
// 会将该任务从最小堆中取出,然后继续调度,看有没有更高优先级的任务,注意,Schedule和React里面有各自的调度系统
return null;
}
这个if条件的判断就会使false,然后直接返回null。而scheduleCallback收到null之后,他会认为当前任务已经完成,所以就清空任务,至此,一次完整的react执行完毕。
