setup细节
-
setup执行的时机
-
在beforeCreate之前执行(一次), 此时组件对象还没有创建
-
this是undefined, 不能通过this来访问data/computed/methods / props
-
其实所有的composition API相关回调函数中也都不可以
<template> <h1>父组件-----</h1> <h3>{{ msg }}</h3> <button @click="msg += '+'">更新数据</button> <hr /> <Child :msg="msg"/> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent, ref } from "vue"; import Child from "./components/child.vue"; export default defineComponent({ name: "App", components: { Child, }, setup() { const msg = ref("abcdef"); return { msg } }, }); </script><template> <h1>子组件</h1> <h3>{{msg}}</h3> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent } from "vue"; export default defineComponent({ name: "Child", props: ["msg"], beforeCreate() { console.log("beforeCreate"); console.log(this.msg); }, setup() { console.log("setup"); console.log(this); } }); </script>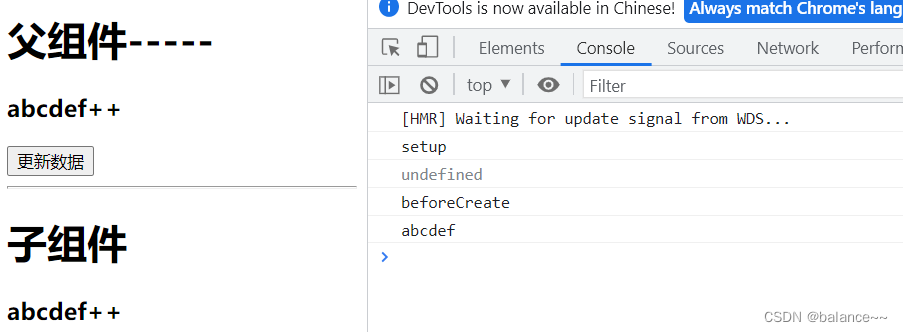
-
-
setup的返回值
- 一般都返回一个对象: 为模板提供数据, 也就是模板中可以直接使用此对象中的所有属性/方法
- 返回对象中的属性会与data函数返回对象的属性合并成为组件对象的属性
- 返回对象中的方法会与methods中的方法合并成为组件对象的方法
- 如果有重名, setup优先
- 注意:
- 一般不要混合使用: methods中可以访问setup提供的属性和方法, 但在setup方法中不能访问data和methods
- setup不能是一个async函数: 因为async函数返回值是promise,而不是return,模板看不到return对象中的属性数据
<template> <h1>{{a1}} -- {{a2}}</h1> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent, ref } from "vue"; export default defineComponent({ name: "Child", setup() { let a1 = ref("a1") let fn1 = () => { console.log("setup中的方法"); } return { a1, fn1 } }, mounted() { // 检验有没有两个方法 console.log(this); }, data() { return { a2: "a2" } }, methods: { fn2() { console.log("methods中的方法"); } } }); </script>
-
setup的参数
-
setup(props, context) / setup(props, {attrs, slots, emit})
-
props: 包含props配置声明且传入了的所有属性的对象
-
attrs: 包含没有在props配置中声明的属性的对象, 相当于 this.$attrs
-
slots: 包含所有传入的插槽内容的对象, 相当于 this.$slots
-
emit: 用来分发自定义事件的函数, 相当于 this.$emit
<template> <h1>父组件-----</h1> <h3>{{ msg }}</h3> <button @click="msg += '+'">更新数据</button> <hr /> <Child :msg="msg" xxx="xxx" @fn="fn"/> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent, ref } from "vue"; import Child from "./components/child.vue"; export default defineComponent({ name: "App", components: { Child, }, setup() { const msg = ref("abcdef"); function fn(str: string) { msg.value += str } return { msg, fn } }, }); </script><template> <h1>子组件</h1> <h3>{{msg}}</h3> <button @click="emitFn()">分发事件</button> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent } from "vue"; export default defineComponent({ name: "Child", props: ["msg"], setup(props, context) { // context可以直接解构为{ attrs, slots, emit } // props是一个对象,里面包含父组件向子组件传递的数据,props接收的所有数据 console.log(props, context); // context -> emit function emitFn() { context.emit("fn", "子组件传来的") } return { emitFn } } }); </script>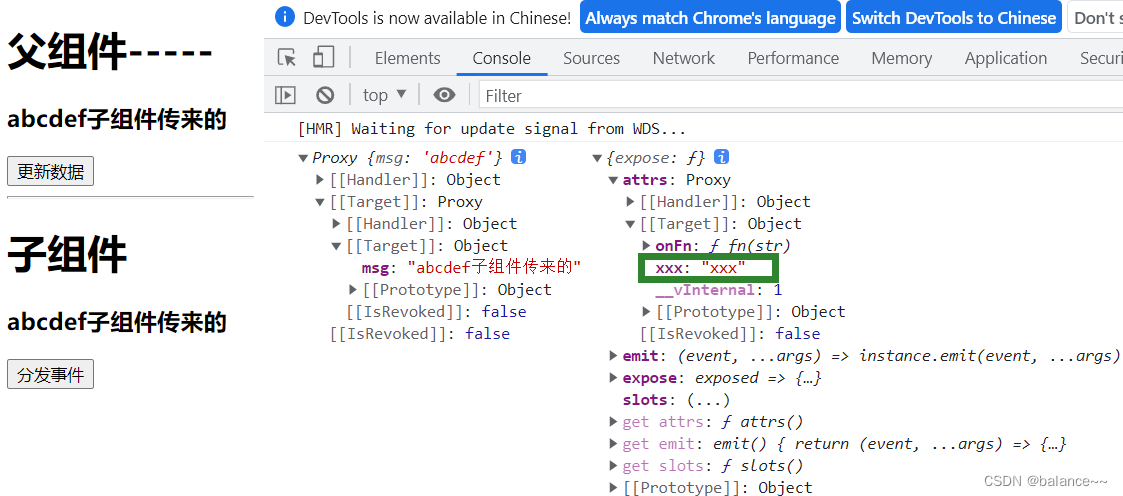
-
reactive与ref细节
-
是Vue3的 composition API中2个最重要的响应式API
-
ref用来处理基本类型数据, reactive用来处理对象(递归深度响应式)
-
如果用ref对象/数组, 内部会自动将对象/数组转换为reactive的代理对象
-
ref内部: 通过给value属性添加getter/setter来实现对数据的劫持
-
reactive内部: 通过使用Proxy来实现对对象内部所有数据的劫持, 并通过Reflect操作对象内部数据
-
ref的数据操作: 在js中要.value, 在模板中不需要(内部解析模板时会自动添加.value)
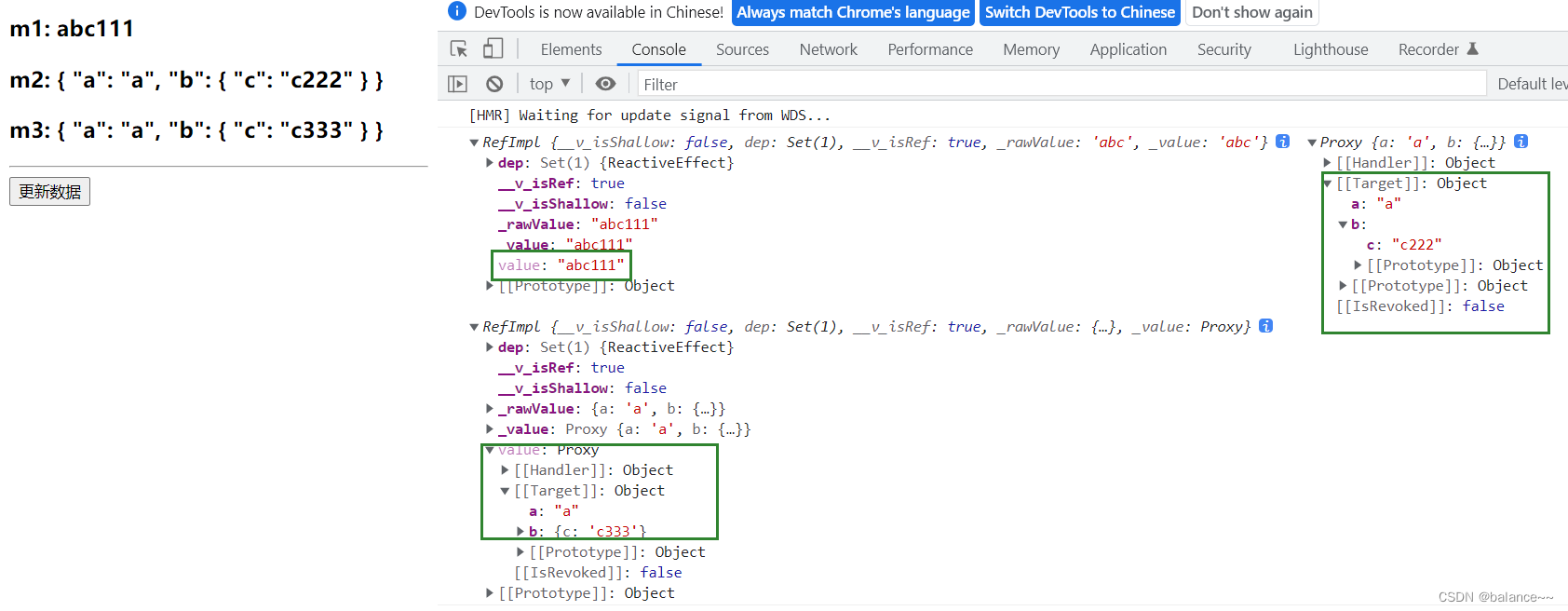
<template> <h3>m1: {{m1}}</h3> <h3>m2: {{m2}}</h3> <h3>m3: {{m3}}</h3> <hr> <button @click="updata">更新数据</button> </template> <script lang="ts"> import { defineComponent, reactive, ref } from "vue"; export default defineComponent({ name: "App", setup() { // 通过ref的方式设置数据 let m1 = ref("abc") let m2 = reactive({ a: 'a', b: { c: 'c' } }) // ref 传入对象? let m3 = ref({ a: 'a', b: { c: 'c' } }) let updata = function() { console.log(m1, m2, m3); m1.value += "111" m2.b.c += "222" m3.value.b.c += "333" } return { m1, m2, m3, updata } }, }); </script>