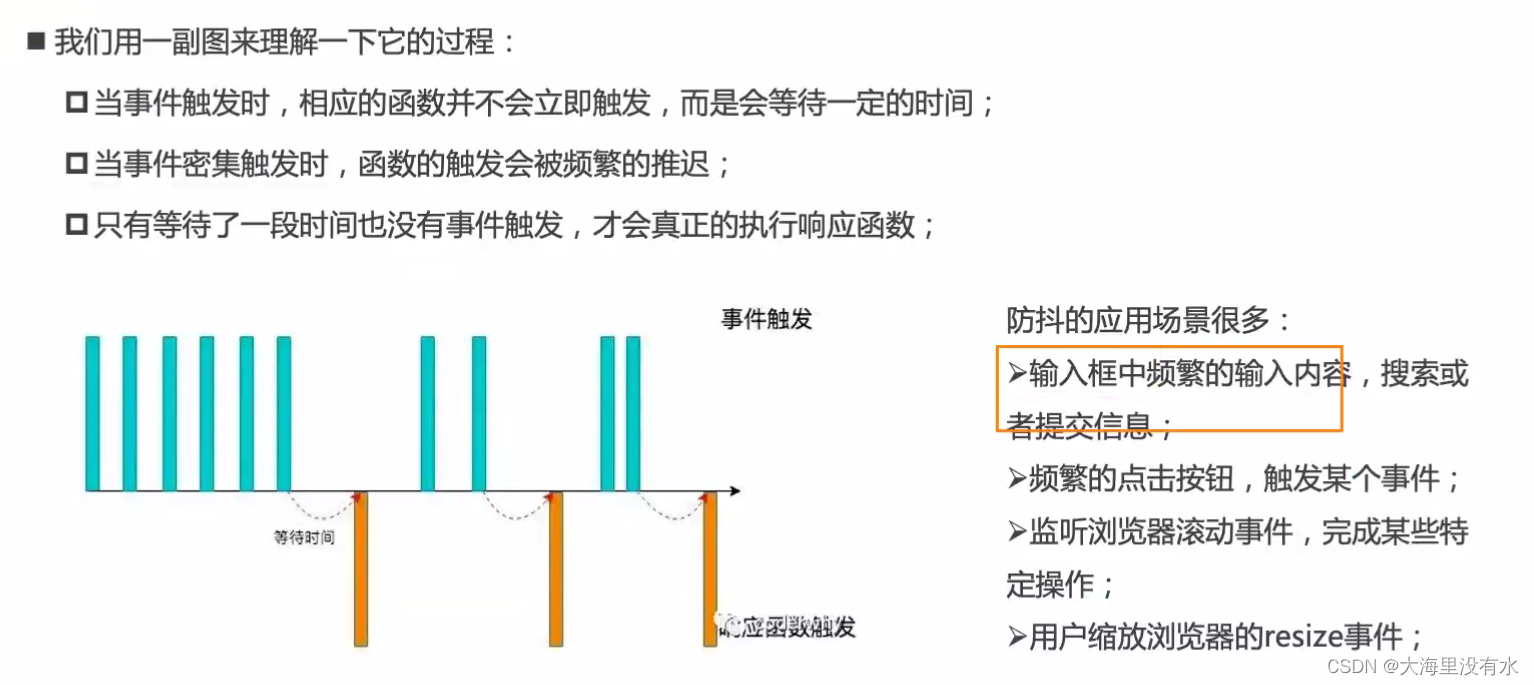
一、防抖
1、应用场景: 搜索联想 - 应用防抖

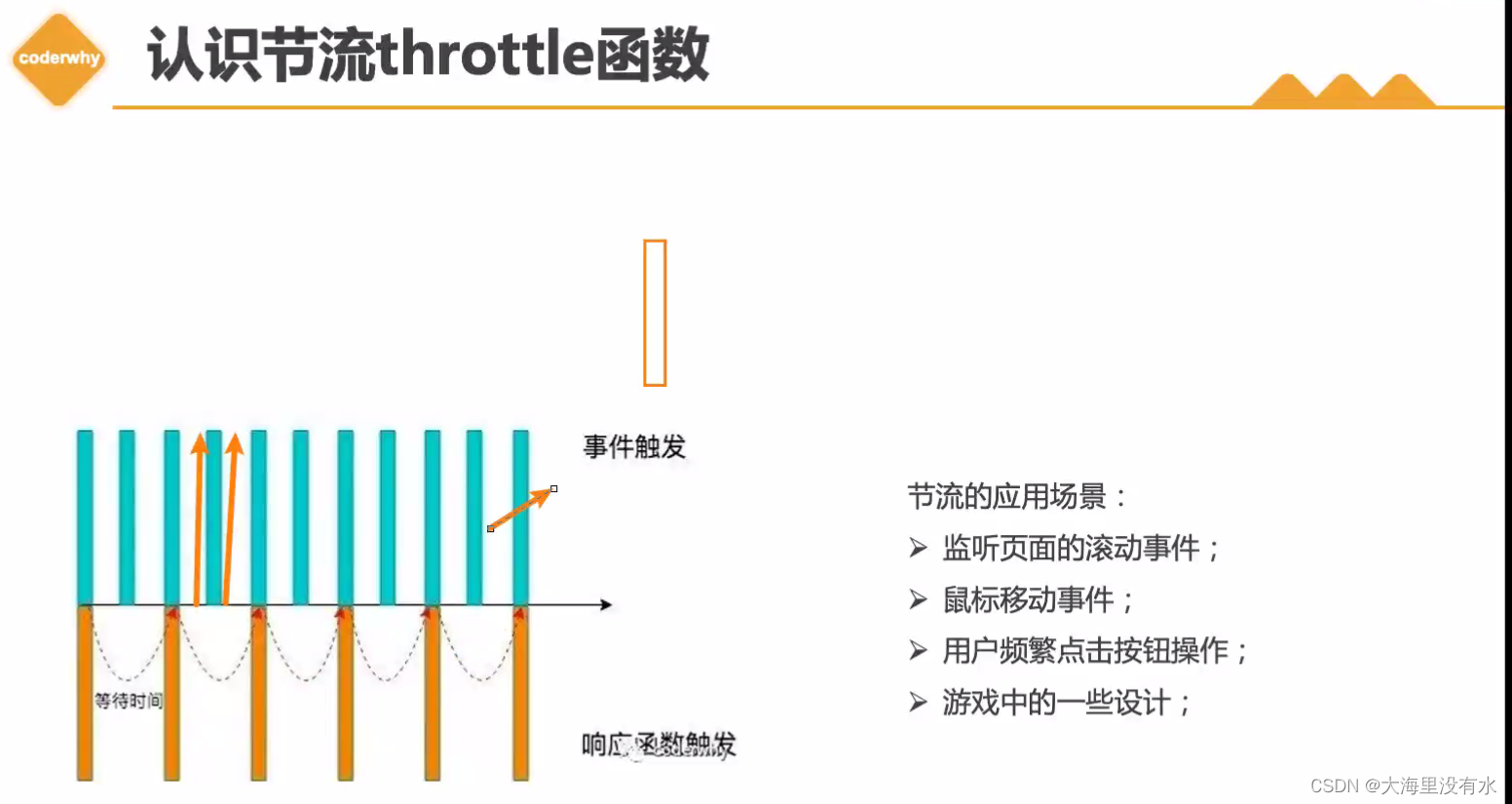
二、节流

三、UnderScore库实现 防抖 节流
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/underscore.js/1.13.4/underscore-min.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEL = document.querySelector("input");
let counter = 0;
// 对这个函数防抖. 就是不断向后延迟,如果用户继续输的话
// inputEL.oninput = function () {
// console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`);
// };
// 1、使用underscore进行防抖处理
const inputChange = function () {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`);
};
// inputEL.oninput = _.debounce(inputChange, 500);
// 节流: 按照一定的频率触发
// 2、使用underscore进行节流处理
inputEL.oninput = _.throttle(inputChange, 2000);
</script>
</body>
</html>
四、自己实现 防抖
1、版本1:debounce基本实现
function debounce(fn, delay) {
// 1、定义一个定时器,保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null;
// 2、真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function (...args) {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的函数
// fn(); // 这么执行,相当于独立函数调用。所以this就指向了window,event指向了undefined
fn.apply(this, args);
}, delay);
};
return _debounce;
}
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<!-- <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/underscore.js/1.13.4/underscore-min.js"></script> -->
<script src="./1.debounce基本实现.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEL = document.querySelector("input");
let counter = 0;
// 对这个函数防抖. 就是不断向后延迟,如果用户继续输的话
// inputEL.oninput = function () {
// console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`);
// };
// 1、使用underscore进行防抖处理
const inputChange = function (event) {
// this:是元素对象, event.我们实现的有问题。
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`, this, event);
};
// inputEL.oninput = _.debounce(inputChange, 500);
inputEL.oninput = debounce(inputChange, 500);
// 节流: 按照一定的频率触发
// 2、使用underscore进行节流处理
// inputEL.oninput = throttle(inputChange, 2000);
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、版本2:debounce立即执行 - (希望第一次立即执行)
function debounce(fn, delay, immediate = false) {
// 1、定义一个定时器,保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null;
let isInvoke = false;
// 2、真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function (...args) {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
// 判断是否需要立即执行
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
fn.apply(this, args);
isInvoke = true;
} else {
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的函数
// fn(); // 这么执行,相当于独立函数调用。所以this就指向了window,event指向了undefined
fn.apply(this, args);
isInvoke = false;
}, delay);
}
};
return _debounce;
}
3、版本3:debounce取消功能
function debounce(fn, delay, immediate = false) {
// 1、定义一个定时器,保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null;
let isInvoke = false;
// 2、真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function (...args) {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
// 判断是否需要立即执行
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
fn.apply(this, args);
isInvoke = true;
} else {
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的函数
// fn(); // 这么执行,相当于独立函数调用。所以this就指向了window,event指向了undefined
fn.apply(this, args);
isInvoke = false;
timer = null;
}, delay);
}
};
// 封装取消功能
_debounce.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
isInvoke = false;
};
return _debounce;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<!-- <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/underscore.js/1.13.4/underscore-min.js"></script> -->
<!-- <script src="./1.debounce基本实现.js"></script> -->
<!-- <script src="./2.debounce-immediate立即执行.js"></script> -->
<script src="./3.debounce-取消功能.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEL = document.querySelector("input");
let counter = 0;
// 对这个函数防抖. 就是不断向后延迟,如果用户继续输的话
// inputEL.oninput = function () {
// console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`);
// };
// 1、使用underscore进行防抖处理
const inputChange = function (event) {
// this:是元素对象, event.我们实现的有问题。
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`, this, event);
};
// inputEL.oninput = _.debounce(inputChange, 500);
// inputEL.oninput = debounce(inputChange, 500, true);
const debounceChange = debounce(inputChange, 500, true);
inputEL.oninput = debounceChange;
// 节流: 按照一定的频率触发
// 2、使用underscore进行节流处理
// inputEL.oninput = throttle(inputChange, 2000);
// 取消功能
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("#cancel");
cancelBtn.onclick = () => {
debounceChange.cancel();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
4、版本4:debounce函数返回值
function debounce(fn, delay, immediate = false, resultCallback) {
// 1、定义一个定时器,保存上一次的定时器
let timer = null;
let isInvoke = false;
// 2、真正执行的函数
const _debounce = function (...args) {
// 取消上一次的定时器
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
// 判断是否需要立即执行
if (immediate && !isInvoke) {
const result = fn.apply(this, args);
if (resultCallback) resultCallback(result);
isInvoke = true;
} else {
// 延迟执行
timer = setTimeout(() => {
// 外部传入的函数
// fn(); // 这么执行,相当于独立函数调用。所以this就指向了window,event指向了undefined
const result = fn.apply(this, args);
if (resultCallback) resultCallback(result);
isInvoke = false;
timer = null;
}, delay);
}
};
// 封装取消功能
_debounce.cancel = function () {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
isInvoke = false;
};
return _debounce;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<!-- <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/underscore.js/1.13.4/underscore-min.js"></script> -->
<!-- <script src="./1.debounce基本实现.js"></script> -->
<!-- <script src="./2.debounce-immediate立即执行.js"></script> -->
<!-- <script src="./3.debounce-取消功能.js"></script> -->
<script src="./4.debounce-函数返回值.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEL = document.querySelector("input");
let counter = 0;
// 对这个函数防抖. 就是不断向后延迟,如果用户继续输的话
// inputEL.oninput = function () {
// console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`);
// };
// 1、使用underscore进行防抖处理
const inputChange = function (event) {
// this:是元素对象, event.我们实现的有问题。
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`, this, event);
// 拿返回值
return "aaa";
};
// inputEL.oninput = _.debounce(inputChange, 500);
// inputEL.oninput = debounce(inputChange, 500, true);
const debounceChange = debounce(inputChange, 500, false, (res) => {
console.log("拿到真正函数的返回值", res);
});
inputEL.oninput = debounceChange;
// 节流: 按照一定的频率触发
// 2、使用underscore进行节流处理
// inputEL.oninput = throttle(inputChange, 2000);
// 取消功能
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("#cancel");
cancelBtn.onclick = () => {
debounceChange.cancel();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
五、自己实现 节流
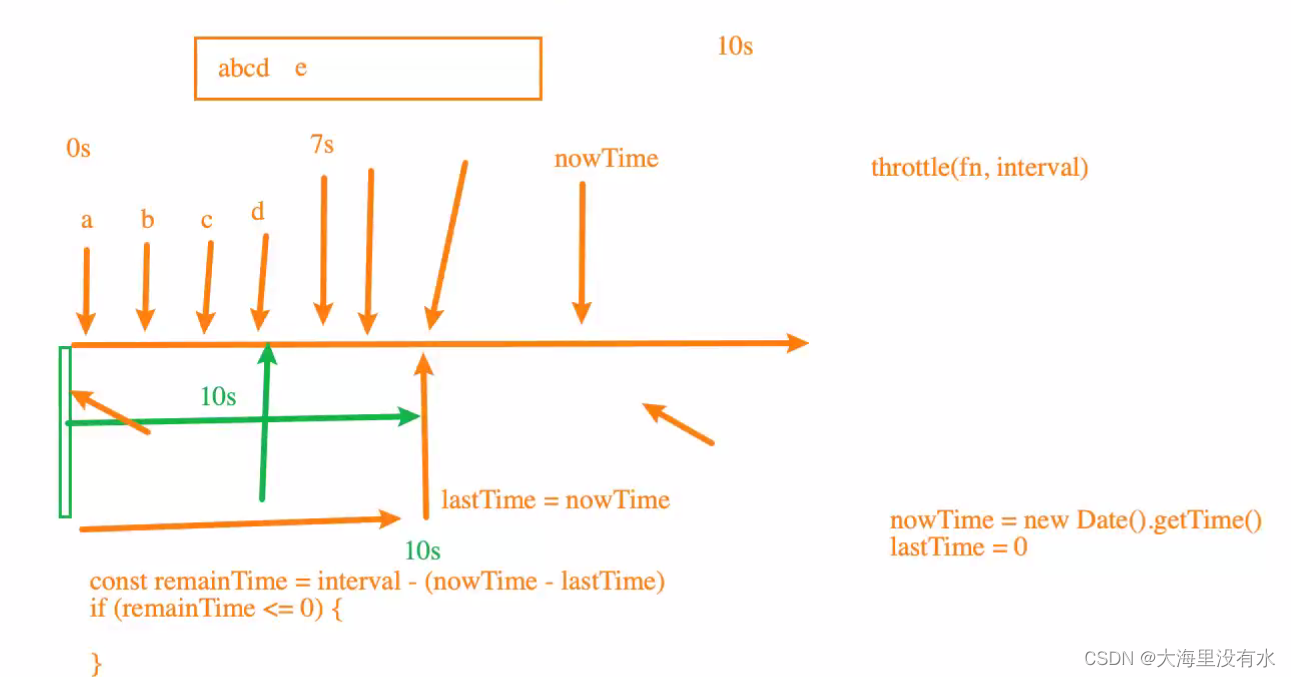
1、版本1: throttle 基本实现
function throttle(fn, interval) {
let lastTime = 0;
const _throttle = function () {
// 对这个函数进行节流
// fn();
let nowTime = new Date().getTime();
const remainTime = interval - (nowTime - lastTime);
if (remainTime <= 0) {
fn();
lastTime = nowTime;
}
};
return _throttle;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<script src="./5.throttle-基本实现.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEL = document.querySelector("input");
let counter = 0;
const inputChange = function (event) {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`, this, event);
};
// 节流: 按照一定的频率触发
inputEL.oninput = throttle(inputChange, 2000);
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、版本2: throttle - leading实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<!-- <script src="./5.throttle-基本实现.js"></script> -->
<!-- <script src="./6.throttle-leading功能实现.js"></script> -->
<script src="./7.throttle-training功能实现.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEL = document.querySelector("input");
let counter = 0;
const inputChange = function (event) {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`, this, event);
};
// 节流: 按照一定的频率触发, 第三个参数,决定第一次触不触发函数
inputEL.oninput = throttle(inputChange, 3000, {
leading: true,
training: true,
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
function throttle(
fn,
interval,
options = {
leading: true,
training: false,
}
) {
const { leading, training } = options;
// 1、记录上一次的时间
let lastTime = 0;
// 2、事件触发时,真正执行的函数
const _throttle = function () {
// 对这个函数进行节流
// fn();
// 2.1、获取当前事件触发时的时间
const nowTime = new Date().getTime();
if (!lastTime && !leading) lastTime = nowTime;
// 上面的写法等同于下面的写法
// if(lastTime == 0 && leading == false) lastTime = nowTime;
// 2.2、使用当前触发的时间和之前的时间间隔以及上一次开始的时间,计算出还剩余多次时间触发事件函数
const remainTime = interval - (nowTime - lastTime);
if (remainTime <= 0) {
// 2.3、真正触发函数
fn();
// 2.4、保留上次触发的时间
lastTime = nowTime;
}
};
return _throttle;
}
3、版本3: throttle - training实现
function throttle(
fn,
interval,
options = {
leading: true,
training: false,
}
) {
const { leading, training } = options;
// 1、记录上一次的时间
let lastTime = 0;
let timer = null;
// 2、事件触发时,真正执行的函数
const _throttle = function () {
// 对这个函数进行节流
// fn();
// 2.1、获取当前事件触发时的时间
const nowTime = new Date().getTime();
if (!lastTime && !leading) lastTime = nowTime;
// 上面的写法等同于下面的写法
// if(lastTime == 0 && leading == false) lastTime = nowTime;
// 2.2、使用当前触发的时间和之前的时间间隔以及上一次开始的时间,计算出还剩余多次时间触发事件函数
const remainTime = interval - (nowTime - lastTime);
if (remainTime <= 0) {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
}
// 2.3、真正触发函数
fn();
// 2.4、保留上次触发的时间
lastTime = nowTime;
return;
}
if (training && !timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null;
lastTime = !leading ? 0 : new Date().getTime();
fn();
}, remainTime);
}
};
return _throttle;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<!-- <script src="./5.throttle-基本实现.js"></script> -->
<!-- <script src="./6.throttle-leading功能实现.js"></script> -->
<script src="./7.throttle-training功能实现.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEL = document.querySelector("input");
let counter = 0;
const inputChange = function (event) {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`, this, event);
};
// 节流: 按照一定的频率触发, 第三个参数,决定第一次触不触发函数
inputEL.oninput = throttle(inputChange, 3000, {
leading: true,
training: true,
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
4、版本4: throttle - this, 取消实现
function throttle(
fn,
interval,
options = {
leading: true,
training: false,
}
) {
const { leading, training } = options;
// 1、记录上一次的时间
let lastTime = 0;
let timer = null;
// 2、事件触发时,真正执行的函数
const _throttle = function (...args) {
// 对这个函数进行节流
// fn();
// 2.1、获取当前事件触发时的时间
const nowTime = new Date().getTime();
if (!lastTime && !leading) lastTime = nowTime;
// 上面的写法等同于下面的写法
// if(lastTime == 0 && leading == false) lastTime = nowTime;
// 2.2、使用当前触发的时间和之前的时间间隔以及上一次开始的时间,计算出还剩余多次时间触发事件函数
const remainTime = interval - (nowTime - lastTime);
if (remainTime <= 0) {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
}
// 2.3、真正触发函数
fn.apply(this, args);
// 2.4、保留上次触发的时间
lastTime = nowTime;
return;
}
if (training && !timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null;
lastTime = !leading ? 0 : new Date().getTime();
fn.apply(this, args);
}, remainTime);
}
};
_throttle.cancel = function () {
if (timer) {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = null;
lastTime = 0;
}
};
return _throttle;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="text" />
<button id="cancel">取消</button>
<!-- <script src="./5.throttle-基本实现.js"></script> -->
<!-- <script src="./6.throttle-leading功能实现.js"></script> -->
<script src="./8.throttle-this功能实现.js"></script>
<script>
const inputEL = document.querySelector("input");
let counter = 0;
const inputChange = function (event) {
console.log(`发送了第${++counter}网络请求`, this, event);
};
// 节流: 按照一定的频率触发, 第三个参数,决定第一次触不触发函数
const _throttle = throttle(inputChange, 3000, {
leading: true,
training: true,
});
inputEL.oninput = _throttle;
// 取消功能
const cancelBtn = document.querySelector("#cancel");
cancel.onclick = () => {
_throttle.cancel();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>