微前端
结合小编多年搬砖的经验,企业级的大规模集成平台普遍存在巨石项目难以维护的痛点。载最近的招聘面试中也会有面试官提及微前端的应用场景。小编拙见认为未来微前端将会成为一种趋势。目前为止,对于这种普遍的平台集成,第一种是打击熟悉的iframe,但是用过的人都知道,iframe的缺点,谁用谁知道哈。第二种的话就是基于阿里孵化的项目qiankun.js。这也是小编强力推荐的微前端解决方案。优缺点我就不再这里说了,各位可以移步qiankun.js的官网了解。
主应用框架
小编基于Vue3+typescript+vite搭建了一个主应用的项目。Github项目地址
主要实现功能点包括:
-
通过接口获取子应用列表实现动态配置微应用
作为一个集成平台,很多时候我们都希望子系统是可以动态配置的,那么我们可以通过API获取到子应用的基本信息,动态注册到qiankun.js进行挂载。载主应用登录之后,会跳转到portal.vue页面,载这个页面注册我们的子应用。这注意要确保挂载的时候挂载节点容器dom已经存在,所以小编在onMounted钩子里面加了nextTick处理。
小编接口使用的免费mock平台,你们有需要可以自己注册账号玩。
onMounted(() => {
loadingInstance = ElLoading.service({
fullscreen: true,
lock: true,
text: 'Loading',
background: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)',
})
nextTick(() => {
getAPPList();
})
})
//远程获取需要注册的微应用
const getAPPList = () => {
API.getAPPList({}).then(({ data: { models = [] } }) => {
appList = models;
initQiankun(store, models, (e:any) => {
router.push({ name: '404', params: e})
});
loadingInstance.close();
checkRouter(models,router.currentRoute.value.fullPath,router.currentRoute.value.name);
})
}-
处理路由异常及应用加载异常公用主应用错误页面
通常错误页面都是集成使用主应用的错误页面,在qiankun.js中子应用的激活挂载是通过路由来识别的,也就是所有的应用其实是公用一个URL的,子应用内报错想要使用主应用的错误页面的话,直接在子应用跳转错误路由就好。所以在注册子应用的时候,我们就需要把主应用的错误路由URL传递给子应用。qiankun.js注册子应用的时候提供了props的参数供主应用传递额外参数给子应用。如下:通过errorRouter字段将错误路由传递给子应用。子应用出现路由错误的时候直接跳这个错误路由接可以显示主应用的错误页面了。
错误一:子应用匹配路由错误
主应用将错误路由传给子应用
{
name: item.name,
entry: item.entry,
container: item.container,
props: {
mainRouterPath: item.mainRouterPath,
getGlobalState: qiankunStore.getGlobalState,
errorRouter:'/404'
},
activeRule: (e: Location) => {
return e.hash.includes(item.mainRouterPath);
},
}子应用main.js里面获取到错误路由并注册到子应用的路由守卫。
function render (props = {}) {
const { container } = props
const router = getRouter(props.mainRouterPath ? props.mainRouterPath : '')
// 校验路由
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (!to.name && to.fullPath !== '/404') {
router.push({ path: props.errorRouter })
} else {
next()
}
})
instance = new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount(container ? container.querySelector('#app') : '#app')
}
// webpack打包公共文件路径
if (window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__) {
__webpack_public_path__ = window.__INJECTED_PUBLIC_PATH_BY_QIANKUN__
}
// 独立运行
if (!window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__) {
render()
}
/**
* bootstrap 只会在微应用初始化的时候调用一次,下次微应用重新进入时会直接调用 mount 钩子,不会再重复触发 bootstrap。
* 通常我们可以在这里做一些全局变量的初始化,比如不会在 unmount 阶段被销毁的应用级别的缓存等。
*/
export async function bootstrap () {
console.log('[vue] vue app bootstraped')
}
/**
* 应用每次进入都会调用 mount 方法,通常我们在这里触发应用的渲染方法
*/
export async function mount (props) {
const param = { customer: true }
props.onGlobalStateChange((state, prev) => {
// state: 变更后的状态; prev 变更前的状态
console.log('customer son1监听', state, prev)
})
render(props)
props.setGlobalState(param)
console.log('customer son1初始化获取', props.getGlobalState())
}
错误二:子应用加载的时候由qiankun.js获取到的错误。
在qiankun/index.ts内监听qiankun.js获取到的错误,这里小编在activeRule这个函数处理,这个钩子在每次路由变化的时候都会出发,并根据返回值匹配挂载的子应用。小编利用其对每一个微应用注册一个错误监听,同时也做了loading的加载过渡期处理。如果监听到错误,这会调用error这函数。
list.forEach(item => {
item.isFirst = true;
appList.push({
name: item.name,
entry: item.entry,
container: item.container,
props: {
mainRouterPath: item.mainRouterPath,
getGlobalState: qiankunStore.getGlobalState,
errorRouter:'/404'
},
activeRule: (e: Location) => {
if ( e.hash.includes(item.mainRouterPath) && item.isFirst) {
loadingInstance = ElLoading.service({
fullscreen: true,
lock: true,
text: `${item.name}加载中`,
background: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)',
})
item.isFirst = false;
errorFunction[item.name] = (handler: any) => {
console.log(handler)
let appOrParcelName = "";
appOrParcelName = handler.reason && handler.reason.appOrParcelName
appOrParcelName=handler.error && handler.error.appOrParcelName
if (appOrParcelName==item.name) {
error({...item,message:handler.message})
if (loadingInstance) {
loadingInstance.close();
loadingInstance = null;
}
}
}
addGlobalUncaughtErrorHandler(errorFunction[item.name])
}
return e.hash.includes(item.mainRouterPath);
},
})
})
错误三:主应用内的路由错误
这个错误的话需要区分是主应用的错误还是内嵌子应用的错误,因为子应用也会挂载在主应用的动态路由之下。
首先在主应用的main.ts路由守卫做一层检查。主要检查页面是否在主应用存在。不错载着跳404
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import ElementPlus from 'element-plus'
import 'element-plus/dist/index.css'
import router from './router';
import store from './store/index';
//校验路由
router.beforeEach((to, from) => {
if (!to.name) {
return { name: '404' }
} else {
return true
}
})
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(router)
app.use(ElementPlus)
app.use(store)
app.mount('#app')
console.log(import.meta.env.BASE_URL)
console.log(import.meta.env.VITE_BASE_URL)其次在portal里面载检查下是否是子应用的路由错误。这里小编将所有的子应用都挂载/portal/:chapters*这个动态路由之下。那么匹配到这个路由的时候还需要匹配下是否是子应用的激活路由,是的话就不做错误路由拦截,因为子应用中已经可以自己处理了。
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useRouter,onBeforeRouteUpdate } from 'vue-router'
import { onMounted, nextTick, computed } from 'vue';
import { useStore } from "@/hooks/store"
import {initQiankun} from '@/qiankun'
import API from '@/API'
import { ElLoading } from 'element-plus'
const router = useRouter();
const {getters } = useStore();
const store = useStore();
const isLogin = computed(() => getters['loginModule/GettersIsLogin'])
let appList:Array<any> = [];
let loadingInstance: any = null
onBeforeRouteUpdate((to,from) => {
checkRouter(appList,to.fullPath,to.name);
})
onMounted(() => {
loadingInstance = ElLoading.service({
fullscreen: true,
lock: true,
text: 'Loading',
background: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7)',
})
nextTick(() => {
getAPPList();
})
})
//远程获取需要注册的微应用
const getAPPList = () => {
API.getAPPList({}).then(({ data: { models = [] } }) => {
appList = models;
initQiankun(store, models, (e:any) => {
router.push({ name: '404', params: e})
});
loadingInstance.close();
checkRouter(models,router.currentRoute.value.fullPath,router.currentRoute.value.name);
})
}
//校验路由
const checkRouter = (models:Array<any>,fullPath:string,name:any) => {
let result = models.some((item: any) => {
let regStr = (item.mainRouterPath+"/").replace(/\//g, '\\\/');
let reg = eval(`/^(${regStr})/`);
return reg.test(fullPath)
})
if (!result && !name) {
router.push({ path: '/404'})
}
}
const goSon = (url:any) => {
router.push({ path: url})
}
</script>-
实现主应用与子应用间双向通信
qiankun.js提供initGlobalState注册全局状态及onGlobalStateChange进行状态监听。这部分内容官网都有介绍,具体可以移步官网小编在此就不再做介绍。现在主要介绍,子应用在挂在的时候主动获取主应用的信息。针对这个业务场景我们可以通过在props注册回调的方式实现。getGlobalState这个函数就是供子应用挂载后立马获取主应用的信息。在子应用调用:
/**
* 应用每次进入都会调用 mount 方法,通常我们在这里触发应用的渲染方法
*/
export async function mount (props) {
const param = { system: true }
props.onGlobalStateChange((state, prev) => {
// state: 变更后的状态; prev 变更前的状态
console.log('system son监听', state, prev)
})
render(props)
// 在子应用更新数据,同步到主应用
props.setGlobalState(param)
console.log('system初始化获取主应用数据', props.getGlobalState())
}-
子应用页面共享
在微前端的概念里面,各个子系统子建最好是独立的存在,尽量不要涉及到各个子应用中相互嵌套耦合的情况。但是在实际开发应用场景中往往过=还是回出现A系统需要内嵌B系统的页面的业务场景。然而qiankun.js是通过路由来控制页面跳转的,同一个页面想要加载两个系统页面显然有点行不通。 所以这里小编通过组件库的方式来实现。例如A系统内需要嵌入B系统的页面,那么我们可以将B系统的页面打包成一个组件库,然后载主应用里面以js的形式引入,那么所有的子系统内都可以把B系统的页面当作一个普通组件来使用而不是路由页面。?缺点?当然这个解决方案要求A,B两个系统都是基于同一个框架构建的项目。如果一个是Vue一个是React的那么组件载各个系统间就不能通用了。
如果真的实现这种状况,那只能通过iframe内嵌解决了。
小编将需要加载组件编译成了一个组件库,在APP.vue页面通过接口的方式动态引用到主应用当中。这样各个子应用就可以使用子应用了。
<template>
<router-view> </router-view>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { onBeforeMount } from 'vue';
import API from '@/API'
onBeforeMount(()=>{
API.getLibList({}).then(({ data: { models = [] } }) => {
models.forEach((item:any)=>{
loadScript(item.js)
loadCss(item.css)
})
})
})
const loadScript=(url:string)=>{
let scriptDom = document.createElement('script')
scriptDom.type = 'text/javascript';
scriptDom.src = url;
document.body.append(scriptDom);
}
const loadCss=(url:string)=>{
let linkDom = document.createElement('link')
linkDom.rel = 'stylesheet';
linkDom.href = url;
document.body.append(linkDom);
}
</script>子应用中main.js注册组件,然后噢就可以像普通vue组件这样使用了。
Vue.use(system.default)
子应用system
子应用集成到qiankun.js里面需要做的改动比较小在main.js内基本可以处理完毕。
/* eslint-disable no-undef */
/* eslint-disable camelcase */
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import getRouter from './router/index'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
let router = null
let instance = null
// 主应用中引用,在子应用注册使用
Vue.use(system.default)
function render (props = {}) {
const { container } = props
const router = getRouter(props.mainRouterPath ? props.mainRouterPath : '')
// 校验路由
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (!to.name && to.fullPath !== '/404') {
router.push({ path: props.errorRouter })
} else {
next()
}
})
instance = new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount(container ? container.querySelector('#app') : '#app')
}
// webpack打包公共文件路径
if (window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__) {
__webpack_public_path__ = window.__INJECTED_PUBLIC_PATH_BY_QIANKUN__
}
// 独立运行
if (!window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__) {
render()
}
/**
* bootstrap 只会在微应用初始化的时候调用一次,下次微应用重新进入时会直接调用 mount 钩子,不会再重复触发 bootstrap。
* 通常我们可以在这里做一些全局变量的初始化,比如不会在 unmount 阶段被销毁的应用级别的缓存等。
*/
export async function bootstrap () {
console.log('[vue] vue app bootstraped')
}
/**
* 应用每次进入都会调用 mount 方法,通常我们在这里触发应用的渲染方法
*/
export async function mount (props) {
const param = { system: true }
props.onGlobalStateChange((state, prev) => {
// state: 变更后的状态; prev 变更前的状态
console.log('system son监听', state, prev)
})
render(props)
// 在子应用更新数据,同步到主应用
props.setGlobalState(param)
console.log('system son初始化获取', props.getGlobalState())
}
/**
* 应用每次 切出/卸载 会调用的方法,通常在这里我们会卸载微应用的应用实例
*/
export async function unmount () {
instance.$destroy()
instance.$el.innerHTML = ''
instance = null
router = null
}
将system的页面打包成组件库,如图小编将lib下的组件,编译成库文件
?index.js
import my from './my.vue'
if (typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.Vue) {
window.Vue.component('my', my)
}
// 为组件添加 install 方法
my.install = function (Vue) {
Vue.component(my.name, my)
}
export default my
vue.config.js
const path = require('path')
const { name } = require('./package')
function resolve (dir) {
return path.join(__dirname, dir)
}
const port = 7101 // dev port
module.exports = {
outputDir: 'dist',
assetsDir: 'static',
publicPath: './',
filenameHashing: true,
devServer: {
// host: '0.0.0.0',
hot: true,
disableHostCheck: true,
port,
overlay: {
warnings: false,
errors: true
},
// 跨域
headers: {
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'
}
},
// 自定义webpack配置
configureWebpack: {
resolve: {
alias: {
'@': resolve('src')
}
},
output: {
// 把子应用打包成 umd 库格式(必须)
library: `${name}`,
libraryTarget: 'umd',
jsonpFunction: `webpackJsonp_${name}`
}
}
}
package.json
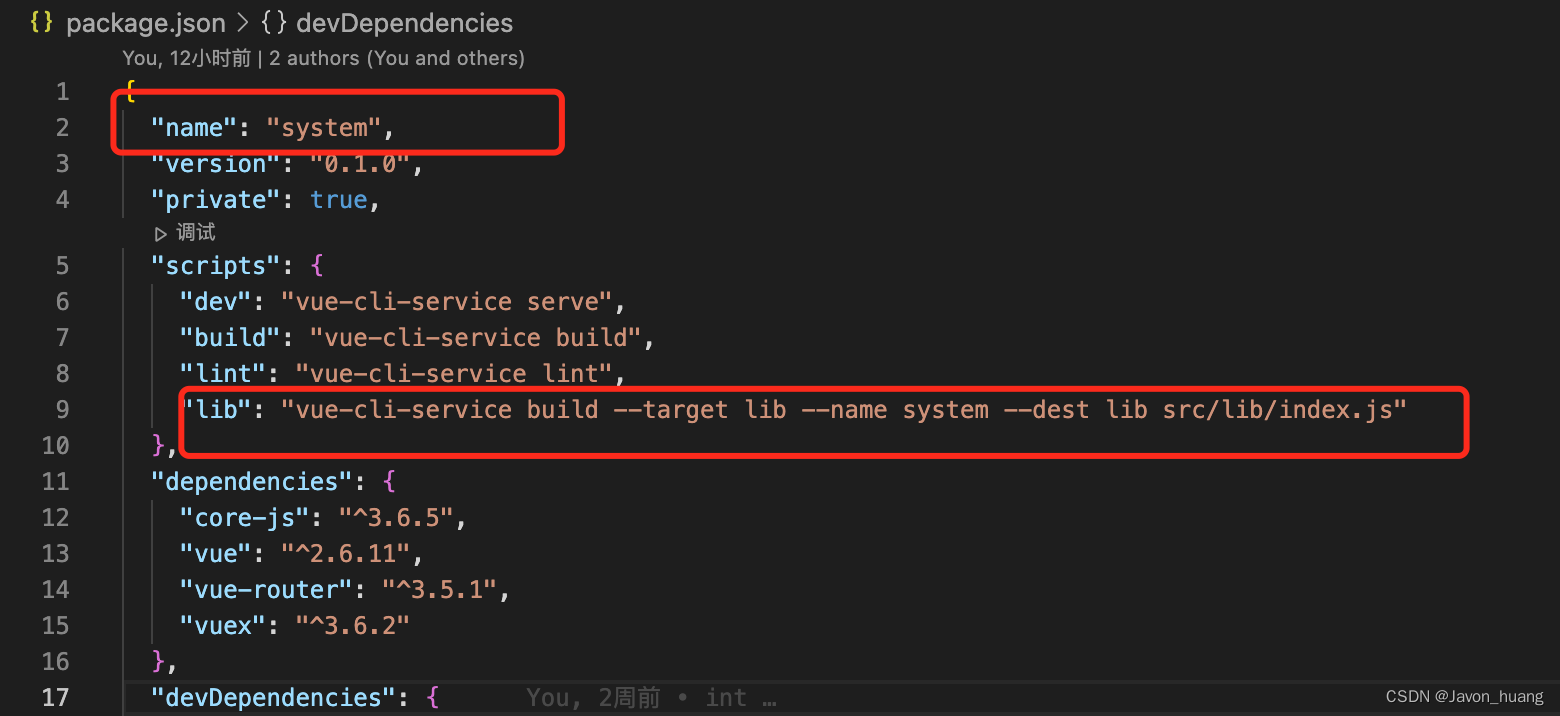
?执行npm run lib 就可以将该文件打包成库,然后将去部署供主应用引用。
npm run lib子应用customer
在这个子应用中使用system打包生成的组件。因为已经在主应用里面引用了js,所以在main.js内直接注册组件就可以了。
/* eslint-disable no-undef */
/* eslint-disable camelcase */
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import getRouter from './router/index'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 主应用中引用,在子应用注册使用
Vue.use(system.default)
let router = null
let instance = null
function render (props = {}) {
const { container } = props
const router = getRouter(props.mainRouterPath ? props.mainRouterPath : '')
// 校验路由
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (!to.name && to.fullPath !== '/404') {
router.push({ path: props.errorRouter })
} else {
next()
}
})
instance = new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount(container ? container.querySelector('#app') : '#app')
}
// webpack打包公共文件路径
if (window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__) {
__webpack_public_path__ = window.__INJECTED_PUBLIC_PATH_BY_QIANKUN__
}
// 独立运行
if (!window.__POWERED_BY_QIANKUN__) {
render()
}
/**
* bootstrap 只会在微应用初始化的时候调用一次,下次微应用重新进入时会直接调用 mount 钩子,不会再重复触发 bootstrap。
* 通常我们可以在这里做一些全局变量的初始化,比如不会在 unmount 阶段被销毁的应用级别的缓存等。
*/
export async function bootstrap () {
console.log('[vue] vue app bootstraped')
}
/**
* 应用每次进入都会调用 mount 方法,通常我们在这里触发应用的渲染方法
*/
export async function mount (props) {
const param = { customer: true }
props.onGlobalStateChange((state, prev) => {
// state: 变更后的状态; prev 变更前的状态
console.log('customer son1监听', state, prev)
})
render(props)
props.setGlobalState(param)
console.log('customer son1初始化获取', props.getGlobalState())
}
/**
* 应用每次 切出/卸载 会调用的方法,通常在这里我们会卸载微应用的应用实例
*/
export async function unmount () {
instance.$destroy()
instance.$el.innerHTML = ''
instance = null
router = null
}
在需要使用的页面
<template>
<div>
system的组件
<my></my>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
}
</script>