1. TypeScript简介
- TS是以JavaScript为基础构建的语言,是一个JavaScript的超集
- TS扩展了JavaScript,并添加了类型
- TS可以在任何支持JavaScript的平台中执行
注意:
TS不能被JS解析器直接执行。需要将TS编写的代码编译成为JS代码,最终执行的时候还是JS代码。
2. 开发环境搭建
- 下载并安装Node.js
- 全局安装typescript
npm i -g typescript - 创建一个ts文件
- 使用tsc对ts文件进行编译
- 进入ts文件所在目录
- 执行命令:tsc xxx.ts
![![[Pasted image 20220612191337.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/78b4c4d6a0af42a6a66612b11c04dc46.png)
3. 基本类型
3.1 类型声明
通过类型声明可以指定TS变量(参数、形参)的类型。
指定类型后,为变量赋值时,TS编辑器会自动检查值是否符合类型声明,不符合时报错,使得变量只能存储某种类型的值。
语法:
let 变量: 类型;
let 变量: 类型 = 值;
function fn(参数: 类型, 参数: 类型): 类型 {
...
}
![![[Pasted image 20220612192348.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8b6659e7125249d3849785ac466b68cf.png)
![![[Pasted image 20220612192407.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/26546fe382f749a292581e4ed0ddd349.png)
虽然执行ts代码时会报错误提示,但还是能成功编译,因为这种写法符合JS的写法。
可以通过配置编译工具,实现出现错误时不生成js文件。
TS可以编译成任意版本的JS,默认编译成ES3。
![![[Pasted image 20220612202559.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8120157f4f07468792f6c33dbacbf442.png)
如果声明变量时不指定类型就进行赋值,TS可以自动对变量进行类型检测。
![![[Pasted image 20220612202703.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3173dd314f374e78a5b9cc3b5d5ba188.png)
JS中的函数中不考虑参数的类型和个数。
![![[Pasted image 20220612203329.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e54ec8ae185548a18930e536ae573465.png)
![![[Pasted image 20220612203614.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e8e5f0b62b2945e88b99cd7303a1bb40.png)
![![[Pasted image 20220612203659.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/71dc0eb2a7b248d290eabfff1a2d6495.png)
- 使用 | 运算符连接多个类型(联合类型):
![![[Pasted image 20220612214745.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1221e7d0fa7643b9b672673a1ec4bcd2.png)

- & 运算符表示同时

3.2 类型
| 类型 | 例子 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| number | 1,-1,1.2 | 任意数字 |
| string | ‘hello’, ‘’ | 任意字符串 |
| boolean | true,false | 布尔值 |
| 字面量 | 其本身 | 限制变量的值就是该字面量的值 |
| any | * | 任意类型 |
| unknown | * | 类型安全的any |
| void | 空值(undefined) | 没有值或undefined |
| never | 没有值 | 不能是任何值 |
| object | {name: ‘张三’} | 任意JS对象 |
| array | [1,2,3] | 任意JS数组 |
| tuple | [4,5] | 元素,TS新增类型,固定长度数组 |
| enum | enum{A, b} | 枚举,TS中新增类型 |
1. 字面量
直接使用字面量进行类型声明:
![![[Pasted image 20220612214432.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d9cceb15ed8f4aeb8791671fd788cc24.png)
2. any
any 用于设置任意类型。
- 一个变量设置了 any 相当于对该变量关闭了TS的类型检测(显式的 any):
![![[Pasted image 20220612215240.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/74752098ca614d8093b880558cdedd2e.png)
- 如果不对变量设置类型,TS解析器会自动判断变量的类型为 any(隐式的 any):
![![[Pasted image 20220612215454.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e167e117d83c4f05acfe812132835046.png)
使用 TS 时,不建议使用 any 类型,更要避免使用隐式的 any。
3. unknown
unknown 表示未知类型的值。
- 变量类型设置为 unknown 和 any 效果一样:
![![[Pasted image 20220612220108.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fb4fffd0aacf4d34b03c38e144c4d66d.png)
- 和 any 的区别:
unknown实际就是一个类型安全的any,unknown类型的变量不能直接赋值给其他变量。
![![[Pasted image 20220612220447.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f23173e41b0642f793fe5f4d631155fb.png)
如果非要将 b 赋值给 s:
![![[Pasted image 20220612220647.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/99980e840f3e4cd2a1fcf8ad7a6f2936.png)
类型断言:告诉编译器 b 的实际类型就是字符串。
// 语法
变量 as 类型
// 或
<类型>变量

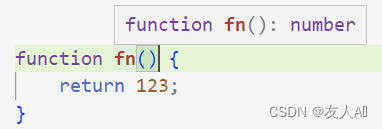
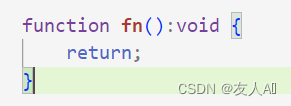
4. void
void 用来表示空。
以函数为例,表示没有返回值的函数。
![![[Pasted image 20220612221546.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/78819bb0df1046548f1ad5dc634d8420.png)
![![[Pasted image 20220612221623.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ed854d34751a47a1b2e2457a3cfa4894.png)
![![[Pasted image 20220612221703.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/eba1ffc2660140779479eb181c548a24.png)
![![[Pasted image 20220612221811.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2fb10991facd47069278f5e26a228afb.png)
5. never
never 表示永远不会返回结果。
![![[Pasted image 20220612221958.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2eb94b9a46504c24aa39b904bba43d40.png)
可用于报错:一旦报错程序就立即结束了,就不会返回值。
![![[Pasted image 20220612222108.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/dea33d6e505a4bf1a2aa8a9c545f1d6a.png)
6. object
object 表示一个js对象。
![![[Pasted image 20220612222810.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/00d120210cff41c98a0edfff9f4702f7.png)
- {} 用来指定对象中可以包含哪些属性:
- 语法:
{属性名: 属性值, 属性名: 属性值}
- 语法:
![![[Pasted image 20220612223129.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1d2efccea53d4844863899ab65f2136b.png)
![![[Pasted image 20220612223328.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b5ca4ac8b67a41838f9bcee0fb6c7f98.png)
- 可选属性:

[propName: string]: any表示任意类型的属性(propName自己命名的):
![![[Pasted image 20220612223633.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a7ebfe7ed7c64fcc9ccc2df6ab1511b6.png)
- 限制函数的结构:
设置函数结构的类型说明:
语法:(形参: 类型, 形参: 类型) => 返回值
![![[Pasted image 20220612224120.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e891522afc1b4ed1a3d74955422b38c6.png)
![![[Pasted image 20220612224211.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b9cf6903730b4d33928138d74f1496e2.png)
![![[Pasted image 20220612224240.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/de8086b83c264894b4beac4ade0deed2.png)
7. array
array 表示一个数组。
语法:
类型[]
Array<类型>
![![[Pasted image 20220612224852.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/af3b2c4161d54f149a734816c3f644cc.png)
8. tuple
元组,表示固定长度的数组。
语法:[类型, 类型, 类型]

9. enum
枚举。结果是在多个值之间进行选择时可以设置枚举。
![![[Pasted image 20220612225809.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5f4cffff771349178e700e223082d3dd.png)
10. 类型的别名

4. 编译选项
1. 自动编译文件
当想要一个文件自动编译时:
问题:每次tsc文件发生变化后都要执行tsc xxx.ts来重新编译。
解决:通过tsc xxx.ts -w让编译器自动监视文件变化,并应用到最新的文件。
当想要所有文件都自动编译时:
- 在文件夹中创建
tsconfig.js文件:输入命令行tsc --init
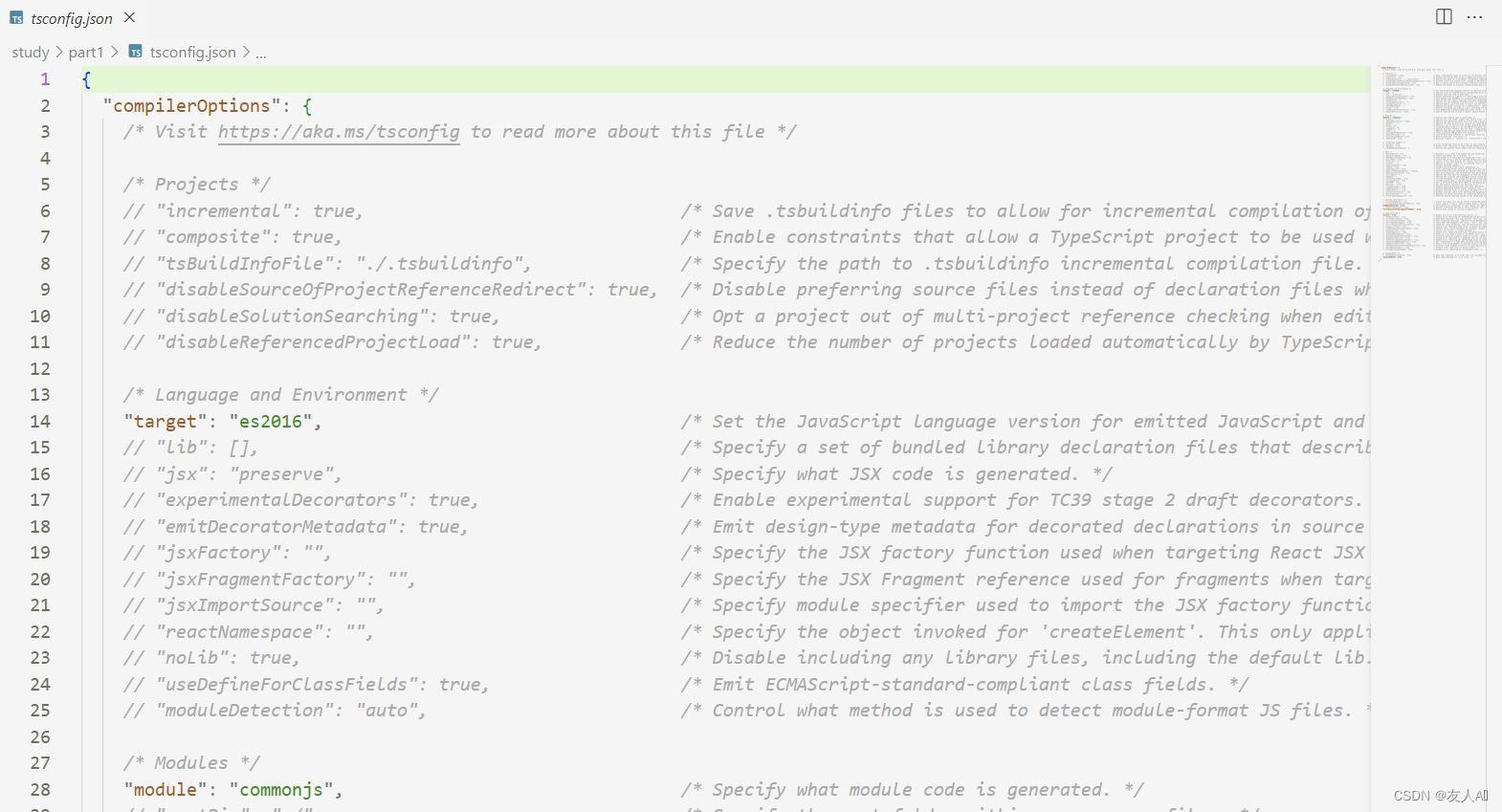
- 直接在目标文件夹路径下输入命令行
tsc即可编译该文件夹下的所有文件 - 输入
tsc -w可以监视所有 .ts 文件的变化
2. tsconfig.json
tsconfig.json 文件是一个JSON文件,添加配置文件后,只需tsc命令即可完成对整个项目的编译。
一些常用的配置项:
{
// 用来指定哪些 ts 文件需要被编译
"include": [
// **:表示任意目录
// *:表示任意文件
"./src/**/*"
],
// 不需要被编译的文件目录
"exclude": [
"./src/hello/**/*",
// 默认值:["node_modules", "bower_components", "jspm_packsges"]
"node_module"
],
// 定义被继承的配置文件
"extends": "./config/base", // 表示当前配置文件中会自动包含config目录下base.json中的所有配置信息
// 指被编译文件的列表,只有需要编译的文件少时才用到
"files": [
"core.ts",
"sys.ts",
"xxx.ts"
],
// 编译器的选项
"compilerOptions": {
// 用来指定ts被编译的ES的版本
// 'es3', 'es5', 'es6', 'es2015', 'es2016', 'es2017', 'es2018', 'es2019', 'es2020', 'es2021', 'es2022', 'esnext'
"target": "ES6", // ESNext表示最新版本的ES
// 指定要使用的模块化的规范
// 'none', 'commonjs', 'amd', 'system', 'umd', 'es6', 'es2015', 'es2020', 'es2022', 'esnext', 'node16', 'nodenext'
"module": "es2015",
// 用来指定项目中要使用的库,一般不管
"lib": [
"es6",
"dom"
],
// 指定编译后文件所在的目录
"outDir": "./dist",
// 将代码合并为一个文件
// 设置outFile后,所有的全局作用域中的代码会合并到同一个文件中
"outFile": "./dist/app.js",
// 是否对JS文件进行编译,默认false
"allowJs": false,
// 是否检查JS代码是否符合语法规范,默认false
"checkJs": false,
// 是否移除注释
"removeComments": false,
// 不生成编译后的文件
"noEmit": false,
// 当有错误时不生成编译后的文件
"noEmitOnError": false,
// 所有严格检查的总开关
"strict": true,
// 设置编译后的文件是否使用严格模式,默认false
"alwaysStrict": false,
// 不允许隐式的any类型
"noImplicitAny": true,
// 不允许不明确类型的this
"noImplicitThis": true,
// 严格地检查空值
"strictNullChecks": true,
}
}
5. 用webpack打包ts代码
1. 结合webpack和ts完成最基本的开发环境
- 要使用webpack,需要先运行
npm init -y生成package.json文件来管理项目依赖 - 安装使用webpack所需要的开发依赖
npm i -D webpack webpack-cli typescript ts-loader - 编写webpack配置文件 webpack.config.js
// 引入一个包
const path = require('path');
// 这里写webpack中所有的配置信息
module.exports = {
// 指定入口文件
entry: './src/index.ts',
// 指定打包文件所在目录
output: {
// 指定打包文件的目录
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
// 打包后文件的文件
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
// 指定webpack打包时要使用的模块
module: {
// 指定要加载的规则
rules: [
{
// 指定规则生效的文件
test: /\.ts$/,
// 要使用的loader
use: 'ts-loader',
// 要排除的文件
exclude: /node_modules/
}
]
}
}
- 配置tsconfig.json文件
- 在package.json文件中添加配置,可以通过build命令来执行webpack
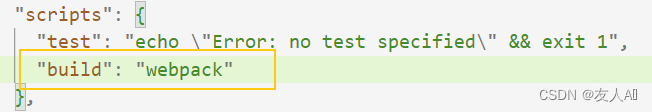
- 执行
npm run build对项目进行打包
2. 进阶
2.1 实现webpack自动创建.html文件,并可以根据项目的实际情况来调整该网页引入的资源。
- 执行
npm i -D html-webpack-plugin命令 - 在webpack.config.js文件中进行配置
// 引入html插件
const HTMLWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
// 配置webpack插件
plugins: [
new HTMLWebpackPlugin()
]
}
- 执行
npm run build
- 对index.html文件进行配置


或者直接在项目中写一个网页模板,配置之后可以根据模板生成html文件

2.2 实现热更新
- 安装插件
npm i -D webpack-dev-server@3.11.0 - 在package.json文件中添加配置
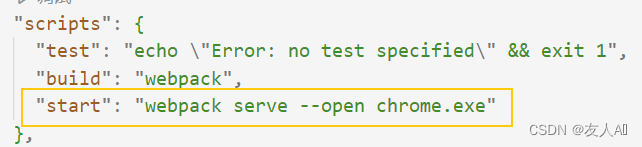
- 执行
npm start
2.3 让dist文件保持当前最新
- 安装插件
cnpm i -D clean-webpack-plugin用来清除dist目录 - 在webpack.config.js文件中引入插件
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require('clean-webpack-plugin'); - 在plugins数组中进行配置
new CleanWebpackPlugin()
2.4 模块配置
问题:webpack不知道哪些ts文件被作为模块引入,所以打包时会报错
解决:在webpack的resolve中设置引用模块
module.exports = {
// 用来设置引用模块
resolve: {
extensions: ['.ts', '.js']
}
}
2.5 配置Babel
- 安装插件
cnpm i -D @babel/core @babel/preset-env babel-loader core-js - 修改配置文件

6. 面向对象
1. 类(class)
定义类:
class 类名 {
属性名: 类型;
constructor(参数: 类型) {
this.属性名 = 参数;
}
方法名() {
...
}
}
- 实例属性和静态属性:
// 用class关键字定义一个类
class Person {
// 定义实例属性,实例属性需要在new了实例之后,通过对象的实例去访问
name: string = '张三';
// 在属性前使用static关键字可以定义类属性(静态属性),不需要创建对象就可以使用
static age: number = 12
// 定义方法
sayHello() {
console.log('hello');
}
// 类方法
static sayHi() {
console.log('Hi');
}
}
const person = new Person();
// console.log(person); // Person {name: '张三', age: 12}
console.log(Person.age); // 12
person.sayHello();
Person.sayHi();
- 构造函数:
class Dog {
name: string;
age: number;
// constructor是构造函数,构造函数会在对象创建时调用
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
fn() {
// this指向当前调用方法的对象
console.log(this);
}
}
const dog1 = new Dog('dog1', 12);
const dog2 = new Dog('dog2', 34);
- 继承
(function () {
// 定义一个Animal类
class Animal {
name: string;
age: number;
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
sayHello() {
console.log('hello');
}
}
/**
* 使用继承后,子类将拥有父类的所有方法和属性
* 通过继承可以将多个类中共有的代码写在一个父类中,即可让所有子类同时都拥有父类的属性和方法
*/
// 定义一个狗的类,并继承Animal类
class Dog extends Animal { }
// 定义一个猫的类,并继承Animal类
// 如果希望在子类中添加父类中没有的属性或方法,直接加就行
class Cat extends Animal {
run() {
console.log(`${this.name}在跑`);
}
// 方法重写:如果在子类中添加和父类相同的方法,则子类方法会覆盖父类方法
sayHello() {
console.log('hello');
}
}
const dog = new Dog('dog', 1); // Dog {name: 'dog', age: 1}
const cat = new Cat('cat', 3); // Cat {name: 'cat', age: 1}
dog.sayHello(); // hello
cat.sayHello(); // hello
cat.run(); // cat在跑
})()
- super关键字
(function () {
class Animal {
name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
sayHello() {
console.log('动物在叫');
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
age: number;
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
/**
* 如果在子类中写了构造函数,在子类中必须对父类构造函数进行调用
*/
super(name); // 调用父类的构造函数
this.age = age;
}
sayHello() {
// 在类的方法中,super表示当前类的父类
super.sayHello();
}
}
const dog = new Dog('dog', 1);
dog.sayHello(); // 动物在叫
})();
- 抽象类
(function () {
/**
* 以abstract开头的类是抽象类
* 抽象类和其他类区别不大,只是不能用来创建对象
* 抽象类是专门用来被继承的类
*
* 抽象类中可以添加抽象方法
*/
abstract class Animal {
name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* 定义一个抽象方法
* 抽象方法只能使用abstract开头,没有方法体
* 抽象方法只能定义在抽象类中,子类必须对抽象方法进行重写
*/
abstract sayHello(): void;
}
class Dog extends Animal {
sayHello() {
console.log('汪汪汪');
}
}
const dog = new Dog('dog');
dog.sayHello(); // 汪汪汪
class Cat extends Animal {
// 报错
}
})();
- 接口
(function () {
// 描述一个对象类型
type myType = {
name: string,
age: number
};
// type myType = {}; // 重复声明会报错
/**
* 接口用来定义一个类结构,用来定义一个类中应该包含哪些属性和方法
* 同时接口也可以当成类型声明去使用
*/
interface myInterface {
name: string;
age: number;
}
interface myInterface {
gender: string;
}
const obj: myInterface = {
name: '张三',
age: 12,
gender: '男'
}
/**
* 接口可以在定义类的时候限制类的结构
* 接口中所有的属性和方法都不能有实际的值
* 接口只定义对象的结构,而不考虑实际值
*/
interface myInter {
name: string;
// 接口中的所有方法都是抽象方法
sayHello(): void;
}
// 定义类时,可以使类去实现一个接口,实现接口就是使类满足接口的要求
class MyClass implements myInter {
name: string;
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name;
}
sayHello() {
console.log('hello');
}
}
})();
- 属性的封装
(function () {
// 定义一个表示人的类
class Person {
// TS可以在属性前添加属性的修饰符
/**
* public 默认值,修饰的属性可以在任意位置访问(修改)
* private 私有属性,只能在类内部进行访问(修改)
* - 通过在类中添加方法使得私有属性可以被外部访问
* protected 受保护的属性,只能在当前类和当前类的子类中访问(修改)
*/
private name: string;
public age: number;
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 属性的存取器:
* getter 方法用来读取属性
* setter 方法用来设置属性
*/
// TS中设置getter方法的方式
get name() {
return this.name;
}
// TS中设置setter方法的方式
set name(value: string) {
this.name = value;
}
// 定义方法,用来获取name属性
// getAge() {
// return this.age;
// }
// 定义方法,用来设置name属性
// setAge(value: number) {
// if (value >= 0) {
// this.age = value;
// }
// }
}
/**
* 现在属性是直接在对象中设置,属性可以被任意修改
* 属性可以任意被修改将会导致对象中的数据变得非常不安全
*/
const per = new Person('张三', 12);
// console.log(per); // Person {name: '张三', age: 12}
// per.name = '李四'; // 报错
per.age = 34;
console.log(per); // Person {name: '李四', age: 34}
// per.setAge(-1);
// console.log(per.age); // 12
})();
- 泛型
/**
* 在定义函数或类时,如果遇到类型不明确就可以使用泛型
* 可以任意定义泛型,如下面的T
* T表示任意类型,调用的时候才确定是什么类型
*/
function fn<T>(a: T): T {
return a;
}
// 可以直接调用具有泛型的函数
fn(a: 10); // 不指定泛型,TS可以自动对类型进行判断
fn<string>(a: 'hello'); // 指定泛型
// 泛型可以同时指定多个
function fn2<T, K>(a: T, b: K): T {
console.log(b);
return a;
}
fn2<number, string>(a: 123, 'hello');
interface Inter {
length: number;
}
// T extends Inter 表示泛型T必须是Inter实现类(子类)
function fn3<T extends Inter>(a: T) {
return a.length;
}