生命不息,学习不止
什么是Three?
Three官网
Three.js是基于原生WebGL封装运行的三维引擎,是一款运行在浏览器中的 3D 引擎,说到数字化与可视化,就得说到数字孪生,而3D模型在浏览器展示就是其中的一环,就是数字模型设计。使用CAD工具开发出满足技术规格的产品虚拟原型,精确记录产品的各种物理参数,以可视化的方式展示出来,并通过一系列验证手段来检验设计的精准程度。
3DMAX支持转化在three展示的类型(其他软件没有了解过)
这边3D建模使用的是3DMAX,主要支持转化能在three中展示的类型有fbx、3ds、obj、stl、dae。
vue使用three安装步骤
three的使用需要安装以下内容
npm install --save three
npm install --save three-orbit-controls 轨道控件插件
npm i --save three-obj-mtl-loader 安装加载.obj和.mtl文件的插件
npm i --save three-css2drender .安装渲染器插件
创建一个简单的展示模型
<template>
<div>
<div id="container"></div>
<div class="controls-box">
<section>
<el-row>
<div v-for="(item,key) in properties" :key="key">
<div>
<el-col :span="8">
<span class="vertice-span">{{item.name}}</span>
</el-col>
<el-col :span="13">
<el-slider v-model="item.value" :min="item.min" :max="item.max" :step="item.step" :format-tooltip="formatTooltip"></el-slider>
</el-col>
<el-col :span="3">
<span class="vertice-span">{{item.value}}</span>
</el-col>
</div>
</div>
</el-row>
</section>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import * as Three from 'three'
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js'
import { SceneUtils } from 'three/examples/jsm/utils/SceneUtils.js'
export default {
name: 'ThreeTest',
data() {
return {
properties: {
width: {
name: 'width',
value: 0.5,
min: 0,
max: 1,
step: 0.01
},
height: {
name: 'height',
value: 0.5,
min: 0,
max: 1,
step: 0.01
},
depth: {
name: 'depth',
value: 0.5,
min: 0,
max: 1,
step: 0.01
},
widthSegments: {
name: 'widthments',
value: 8,
min: 0,
max: 40,
step: 1
},
heightSegments: {
name: 'heightments',
value: 8,
min: 0,
max: 40,
step: 1
},
depthSegments: {
name: 'depthments',
value: 8,
min: 0,
max: 40,
step: 1
}
},
camera: null,
scene: null,
renderer: null,
mesh: null
}
},
mounted() {
this.init();
},
methods: {
formatTooltip(val) {
return val
},
init() {
this.createScene() // 创建场景
this.createMesh() // 创建网格模型
this.createLight() // 创建光源
this.createCamera() // 创建相机
this.createRender() // 创建渲染器
this.createControls() // 创建控件对象
this.render() // 渲染
},
// 创建场景
createScene() {
this.scene = new THREE.Scene()
},
// 创建网格模型
createMesh() {
//创建图形
let geometry = new Three.BoxGeometry(
this.properties.width.value,
this.properties.height.value,
this.properties.depth.value,
Math.round(this.properties.widthSegments.value),
Math.round(this.properties.heightSegments.value),
Math.round(this.properties.depthSegments.value)
);
// 创建材质
const meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({
side: THREE.DoubleSide
})
const wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ wireframe: true })
// 添加组合材质
this.mesh = SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geometry, [
meshMaterial,
wireFrameMat
])
this.scene.add(this.mesh);
},
// 创建光源
createLight() {
},
// 创建相机
createCamera() {
let container = document.getElementById('container');
this.camera = new Three.PerspectiveCamera(70, container.clientWidth/container.clientHeight, 0.01, 10);
this.camera.position.z = 1;
},
// 创建渲染器
createRender() {
let container = document.getElementById('container');
this.renderer = new Three.WebGLRenderer({antialias: true});
//setSize 设置大小
this.renderer.setSize(container.clientWidth, container.clientHeight);
container.appendChild(this.renderer.domElement);
},
// 更新属性
updateFun() {
const tempRotationY = this.mesh.rotation.y
this.scene.remove(this.mesh)
this.createMesh()
this.mesh.rotation.y += tempRotationY + 0.01
},
render() {
this.updateFun()
this.renderer.render(this.scene, this.camera)
requestAnimationFrame(this.render)
},
// 创建控件对象
createControls() {
this.controls = new OrbitControls(this.camera, this.renderer.domElement)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#container {
height: 400px;
}
.controls-box {
position: absolute;
left: 5px;
top: 45%;
width: 300px;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid #c3c3c3;
}
.vertice-span {
line-height: 38px;
padding: 0 2px 0 10px;
}
</style>
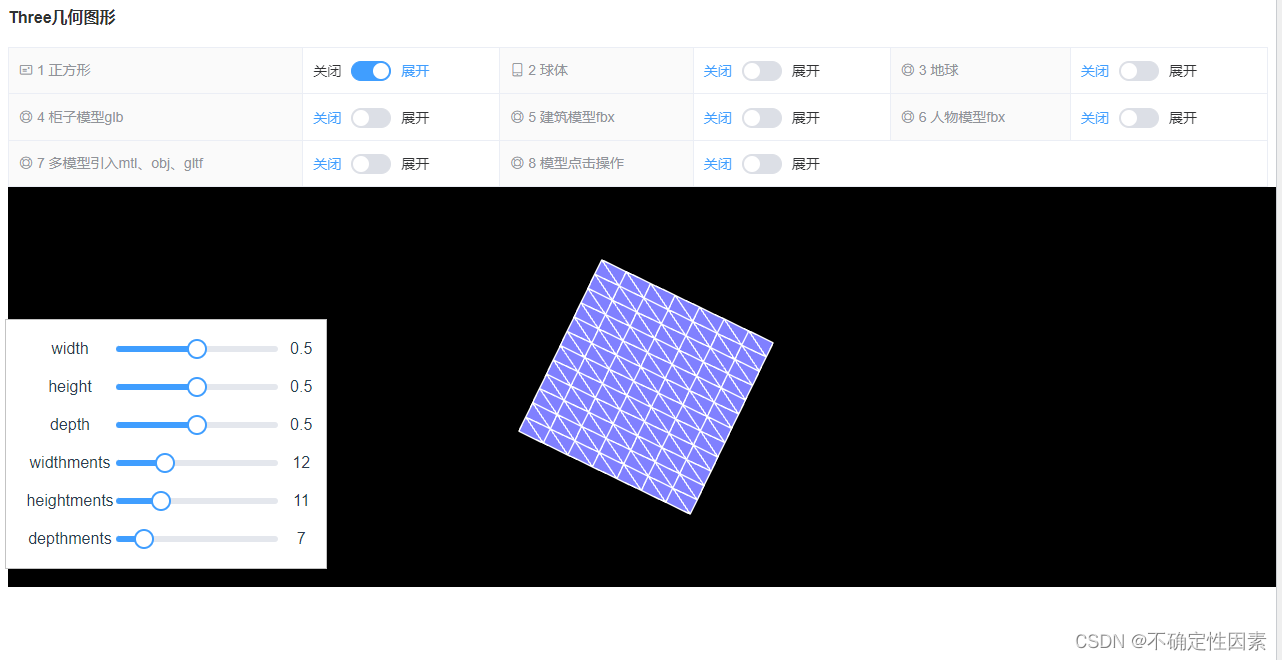
通过这个简单的模型,可以发现Three有个参数new Three.BoxGeometry()来创建图形,然后我就看了下,其他创建几何的three.js的参数,大概有那么多BoxGeometry(立方缓冲几何体)、CircleGeometry(圆形缓冲几何体)、ConeGeometry(圆锥缓冲几何体)、CylinderGeometry(圆柱缓冲几何体)、DodecahedronGeometry(十二面缓冲几何体)、EdgesGeometry(边缘几何体)、ExtrudeGeometry(挤压缓冲几何体)、IcosahedronGeometry(二十面缓冲几何体)、LatheGeometry(车削缓冲几何体)、OctahedronGeometry(八面缓冲几何体)、PlaneGeometry(平面缓冲几何体)、PolyhedronGeometry(多面缓冲几何体)、RingGeometry(圆环缓冲几何体)、ShapeGeometry(形状缓冲几何体)、SphereGeometry(球缓冲几何体)、TetrahedronGeometry(四面缓冲几何体)、TorusGeometry(圆环缓冲几何体)、TorusKnotGeometry(圆环缓冲扭结几何体)、TubeGeometry(管道缓冲几何体)、WireframeGeometry(网格几何体),
基于此,我又创建了一个关于球的例子:
<template>
<div>
<div id="container"></div>
<div class="controls-box">
<section>
<el-row>
<div v-for="(item,key) in properties" :key="key">
<div>
<el-col :span="8">
<span class="vertice-span">{{item.name}}</span>
</el-col>
<el-col :span="13">
<el-slider v-model="item.value" :min="item.min" :max="item.max" :step="item.step" :format-tooltip="formatTooltip"></el-slider>
</el-col>
<el-col :span="3">
<span class="vertice-span">{{item.value}}</span>
</el-col>
</div>
</div>
</el-row>
</section>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import * as THREE from 'three'
import { OrbitControls } from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls.js'
import { SceneUtils } from 'three/examples/jsm/utils/SceneUtils.js'
export default {
data() {
return {
properties: {
radius: {
name: 'radius',
value: 8,
min: 0,
max: 40,
step: 1
},
widthSegments: {
name: 'widthSeg',
value: 10,
min: 0,
max: 20,
step: 1
},
heightSegments: {
name: 'heightSeg',
value: 10,
min: 0,
max: 20,
step: 1
},
phiStart: {
name: 'phiStart',
value: 0,
min: 0,
max: Math.PI * 2,
step: 0.1
},
phiLength: {
name: 'phiLength',
value: Math.PI * 2,
min: 0,
max: Math.PI * 2,
step: 0.1
},
thetaStart: {
name: 'thetaStart',
value: 0,
min: 0,
max: Math.PI * 2,
step: 0.1
},
thetaLength: {
name: 'thetaLength',
value: Math.PI,
min: 0,
max: Math.PI * 2,
step: 0.1
}
},
mesh: null,
camera: null,
scene: null,
renderer: null,
controls: null
}
},
mounted() {
this.init()
},
methods: {
formatTooltip(val) {
return val
},
// 初始化
init() {
this.createScene() // 创建场景
this.createMesh() // 创建网格模型
this.createLight() // 创建光源
this.createCamera() // 创建相机
this.createRender() // 创建渲染器
this.createControls() // 创建控件对象
this.render() // 渲染
},
// 创建场景
createScene() {
this.scene = new THREE.Scene()
},
// 创建网格模型
createMesh() {
//创建三维球体
const geom = new THREE.SphereGeometry(
this.properties.radius.value,
this.properties.widthSegments.value,
this.properties.heightSegments.value,
this.properties.phiStart.value,
this.properties.phiLength.value,
this.properties.thetaStart.value,
this.properties.thetaLength.value
)
// 创建材质
const meshMaterial = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial({
side: THREE.DoubleSide
})
const wireFrameMat = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ wireframe: true })
// 添加组合材质
this.mesh = SceneUtils.createMultiMaterialObject(geom, [
meshMaterial,
wireFrameMat
])
// 网格对象添加到场景中
this.scene.add(this.mesh)
},
// 创建光源
createLight() {
// 环境光
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.1) // 创建环境光
this.scene.add(ambientLight) // 将环境光添加到场景
const spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff) // 创建聚光灯
spotLight.position.set(-40, 60, -10)
spotLight.castShadow = true
this.scene.add(spotLight)
},
// 创建相机
createCamera() {
const element = document.getElementById('container')
const width = element.clientWidth // 窗口宽度
const height = element.clientHeight // 窗口高度
const k = width / height // 窗口宽高比
// PerspectiveCamera( fov, aspect, near, far )
this.camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(35, k, 0.1, 1000)
this.camera.position.set(-80, 60, 40) // 设置相机位置
this.camera.lookAt(new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0)) // 设置相机方向
this.scene.add(this.camera)
},
// 创建渲染器
createRender() {
const element = document.getElementById('container')
this.renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true, alpha: true })
this.renderer.setSize(element.clientWidth, element.clientHeight) // 设置渲染区域尺寸
this.renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true // 显示阴影
this.renderer.shadowMap.type = THREE.PCFSoftShadowMap
this.renderer.setClearColor(0x3f3f3f, 1) // 设置背景颜色
element.appendChild(this.renderer.domElement)
},
// 更新属性
updateFun() {
const tempRotationY = this.mesh.rotation.y
this.scene.remove(this.mesh)
this.createMesh()
this.mesh.rotation.y += tempRotationY + 0.01
},
render() {
this.updateFun()
this.renderer.render(this.scene, this.camera)
requestAnimationFrame(this.render)
},
// 创建控件对象
createControls() {
this.controls = new OrbitControls(this.camera, this.renderer.domElement)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
#container {
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.controls-box {
position: absolute;
left: 5px;
top: 45%;
width: 300px;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid #c3c3c3;
}
.vertice-span {
line-height: 38px;
padding: 0 2px 0 10px;
}
</style>
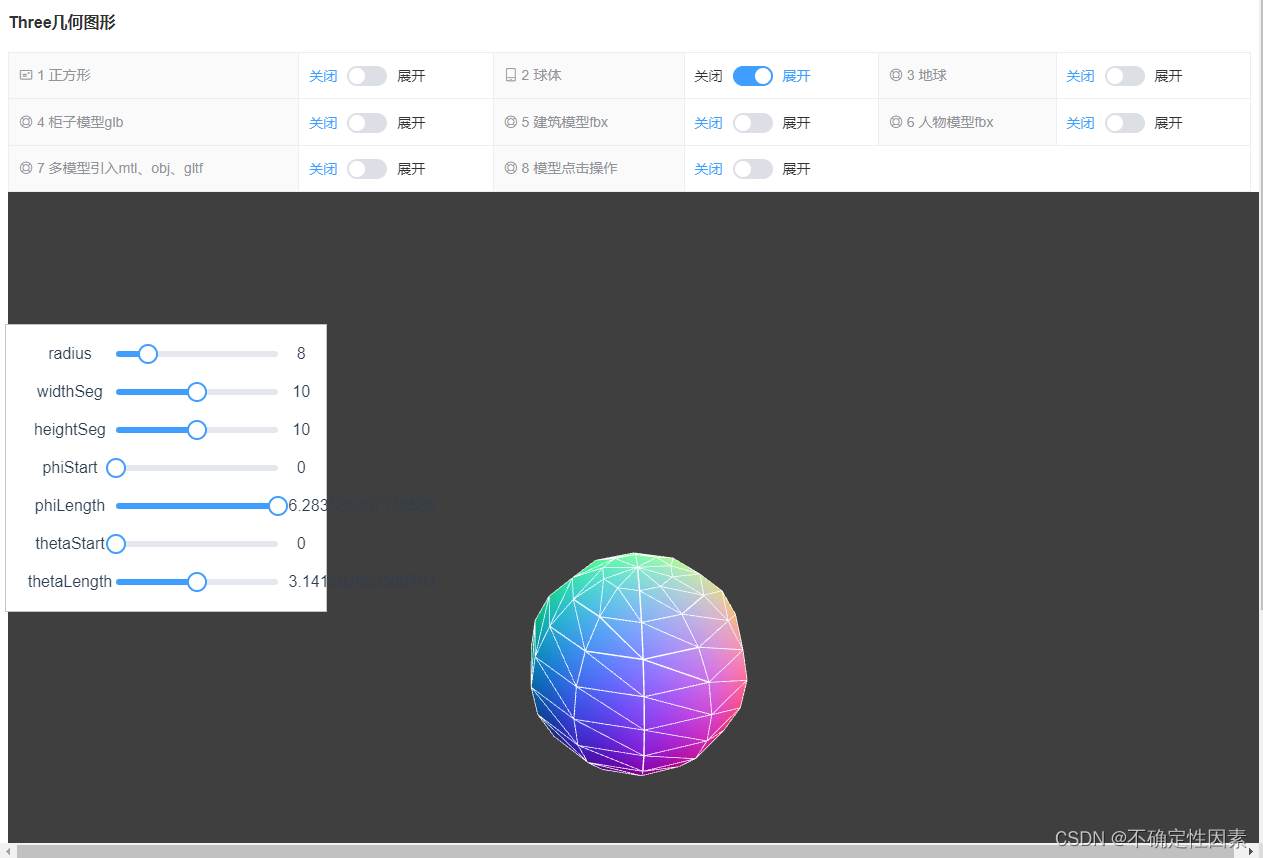
总结
本次例子使用了element ui,参考three.js添加到vue实现的3D效果,只是简单的学习手记。