一.使用vue-cli创建工程
Vue3简介
github上的tags地址:https://github.com/vuejs/vue-next/releases/tag/v3.0.0
1 源码的升级
- 使用Proxy代替 defineProperty实现响应式
- 重写虚拟DOM的实现和Tree-Shaking
2 新的特性
2.1Composition API(组合API): - setup配置
- ref与reactive
- watch与watchEffect
- provide与inject
2.2新的内置组件 - Fragment
- Teleport
- Suspense
2.3 其他改变 - 新的周期钩子
- data选项应始终被声明为一个函数
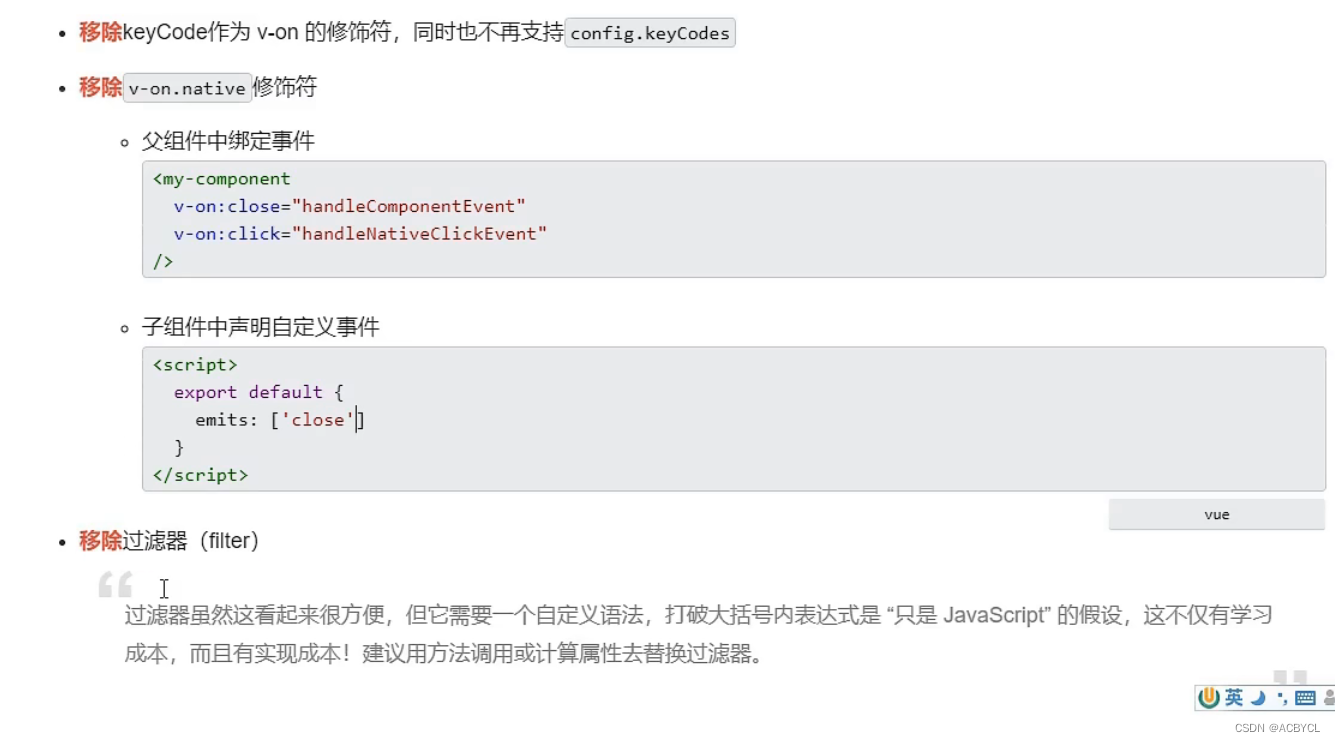
- 移除keyCode支持作为v-on的修饰符
查看版本必须大于4.3
vue -v
//vue --version
创建vue项目
C:\Users\tianyu>cd Desktop
C:\Users\tianyu\Desktop>vue create vue3_test
cd vue3_test
yarn serve
使用vite创建
官方文档:https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/guide/installation.html#vite
vite官网:https://vitejs.cn
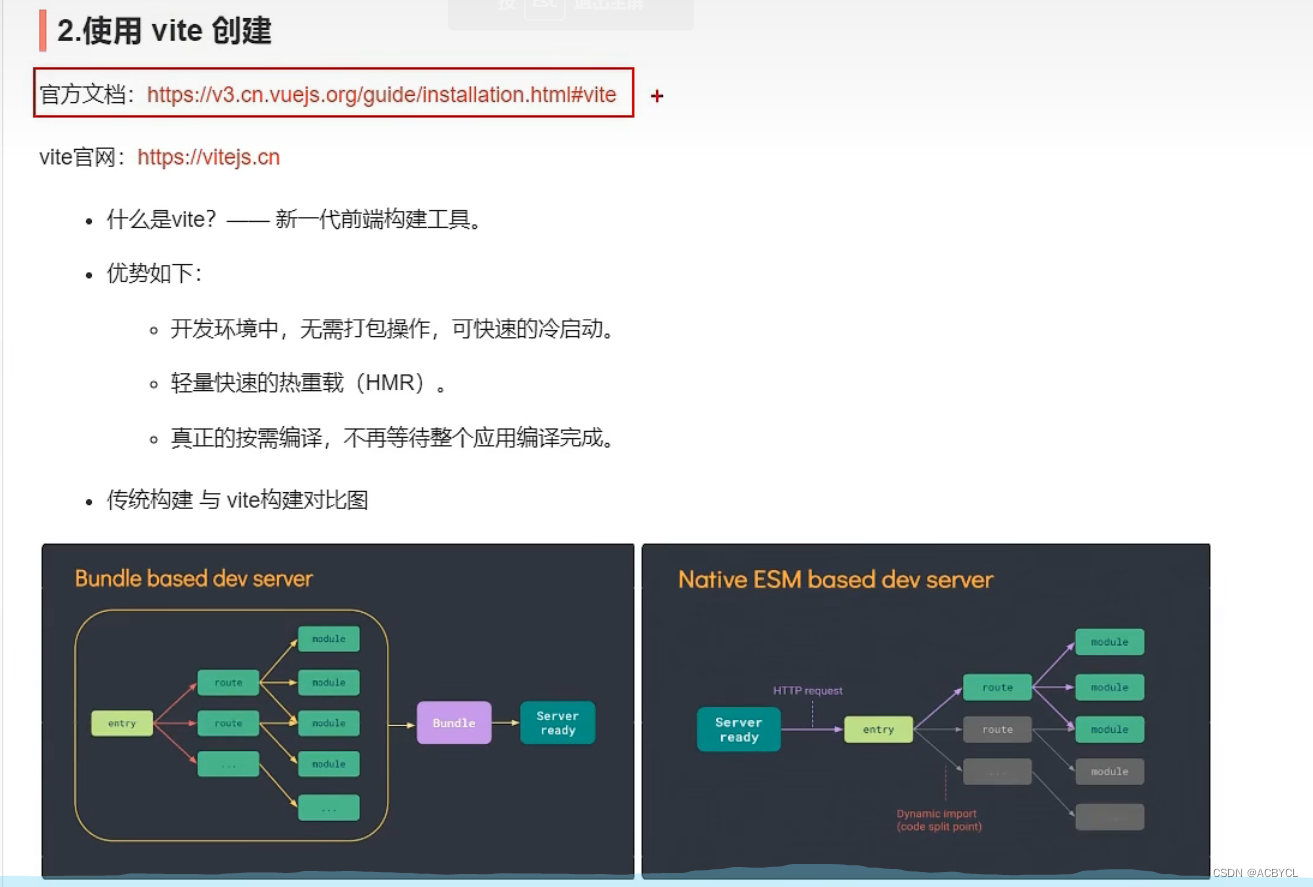
优势
- 启动速度快,因为没有依赖包
## 创建工程
npm init vite-app <project-name>
## 进入工程目录
cd <project-name>
## 安装依赖
npm install
## 运行
npm run dev
二.分析工程结构
脚手架安装失败原因
-
- npm原因:建议清理缓存
-
- 重装node.js
-
- 网络问题:配置淘宝镜像
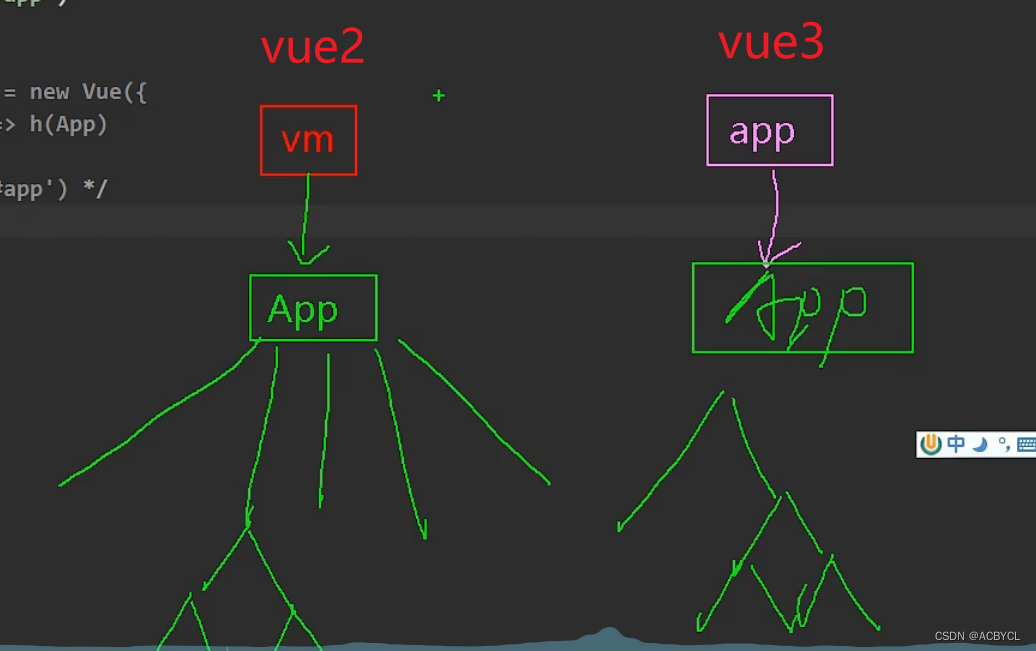
vue2和vue3的结构区别
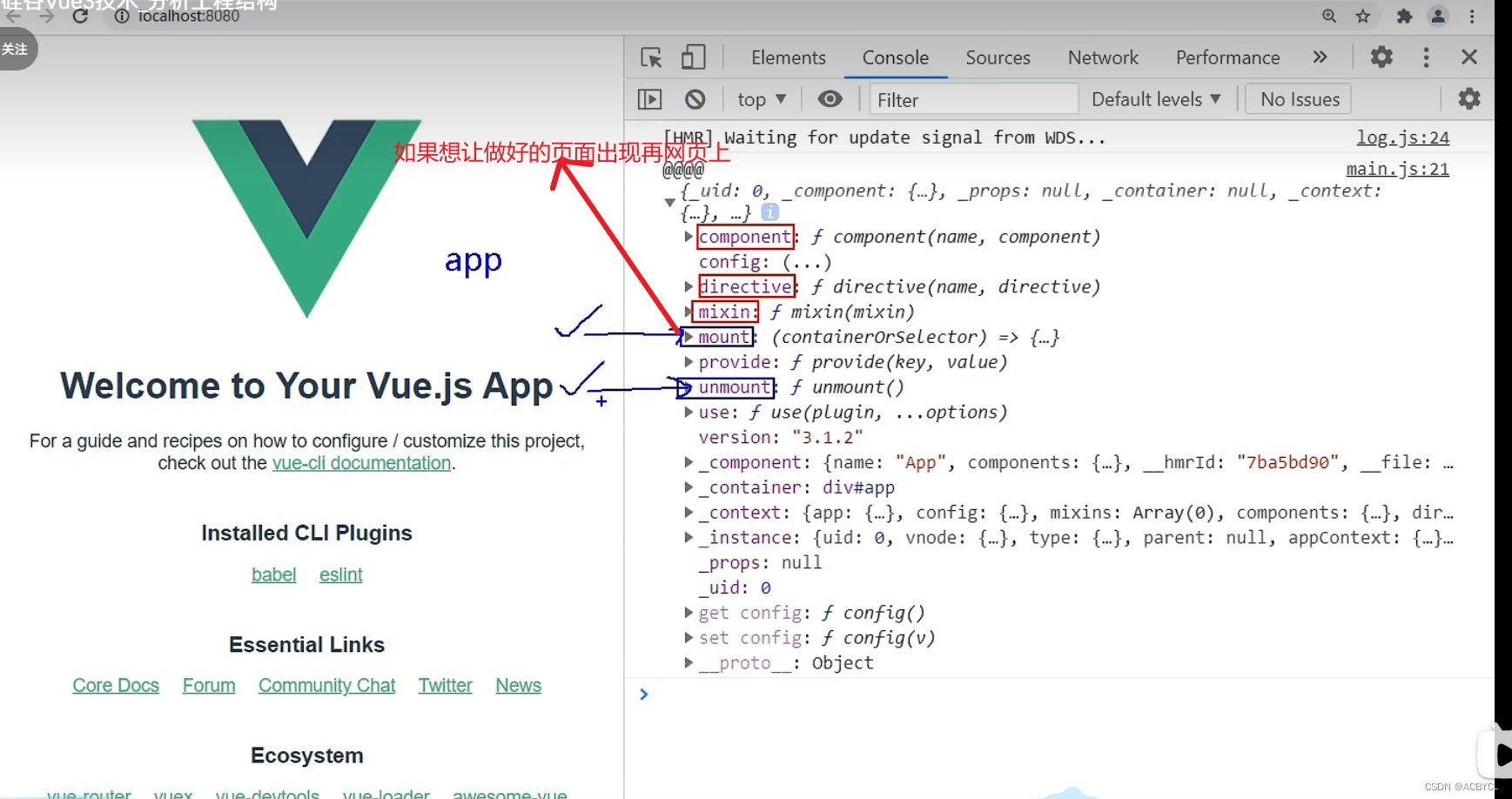
查看vue3里createApp里面的东西
关闭语法检查
vue.config.js
const { defineConfig } = require('@vue/cli-service')
module.exports = defineConfig({
transpileDependencies: true,
lintOnSave:false //关闭语法检查
})
vue3特殊之处
vue里面可以没有跟组件
//vue里面可以没有跟组件
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/>
</template>
main.js
// createApp:引入的不在是Vue的构造函数,引入的是一个名为createApp的工厂函数(无需new,里面的方法直接调用,首字母小写)
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 创建应用实例对象--app(类似于之前vue2中的vm,但app比vm"轻",因为去掉了一些不用的函数)
const app=createApp(App)
// 产看app里面的内容
console.log('@@@@',app)
// 挂载
app.mount('#app')
// 1秒后卸载 app
setTimeout(()=>{
app.unmount('#app')
},1000)
// Vue2:
// const vm=new VueElement({
// render:h=>h(App)
// })
// vm.$mount('#app')
三.常用Composition API
1.拉开序幕的setup
是什么?
相当于一个演员表演的舞台(station),所有的**函数,变量**都要在其体内

代码展示
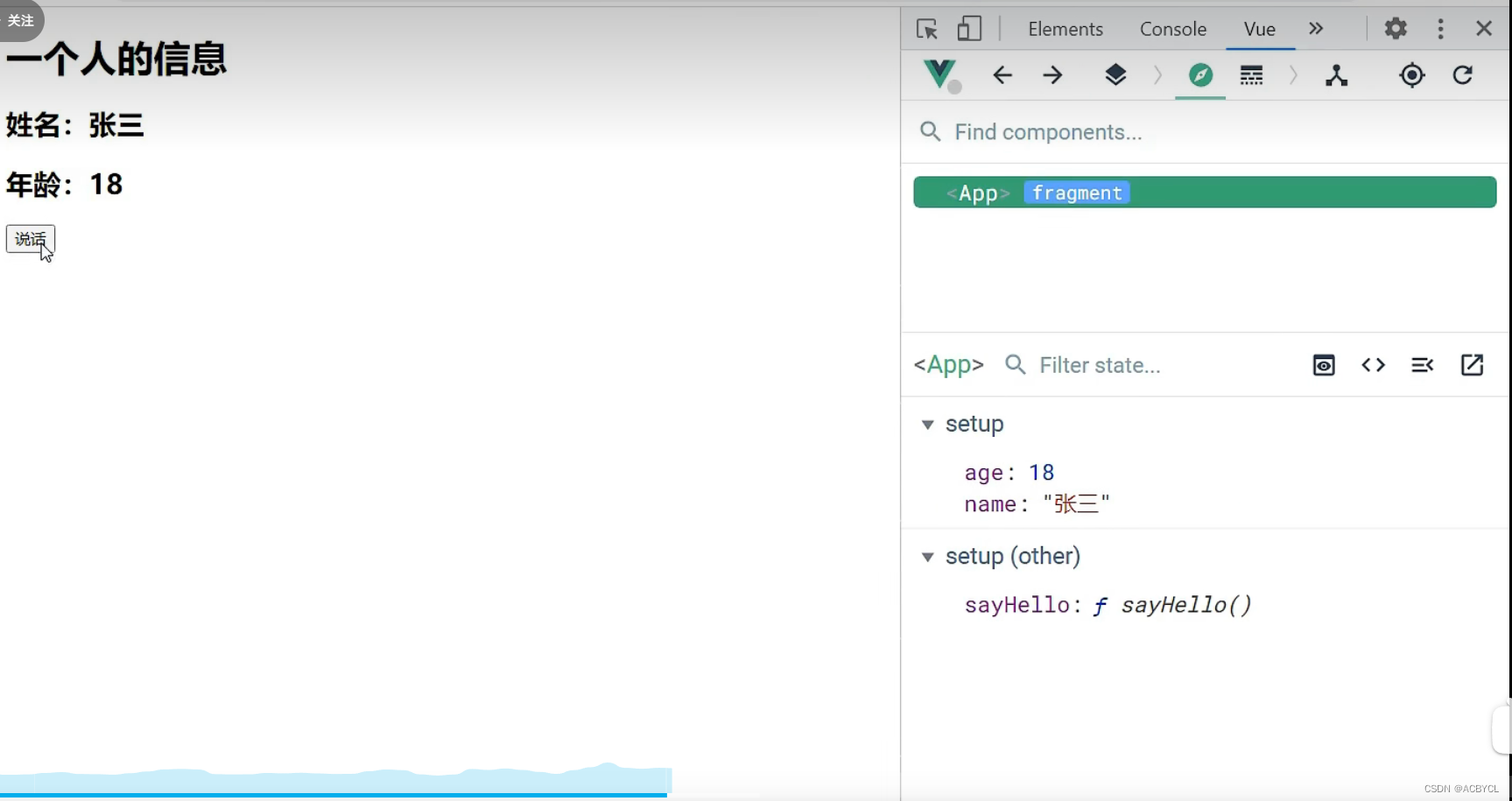
App.vue
<template>
<h1>一个人的信息</h1>
<h2>姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<button @click="sayHello">说话</button>
</template>
<script>
// import { h } from '@vue/runtime-core'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup(){
// 数据
let name='张三'
let age=18
// 方法
function sayHello(){
alert(`我叫${name},我${age}岁了,你好啊!`)
}
// 返回一个对象(常用)
return{
name,
age,
sayHello
}
// 返回一个函数(渲染函数) h函数只渲染h1--尚硅谷 不常用
// return ()=>h('h1','尚硅谷')
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
执行结果
2.ref
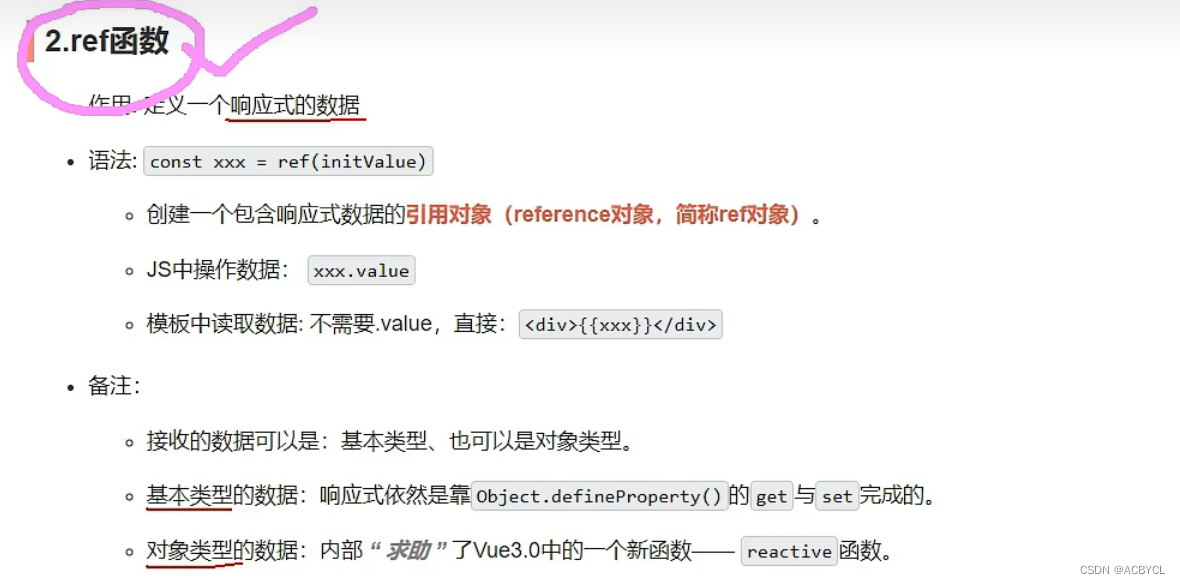
是什么?
用来打标识,是数据变为响应式的
ref的基本使用
App.vue
<template>
<h1>一个人的信息</h1>
<!-- 这里可以写name.value,但是模板自动识别了 -->
<h2>姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<button @click="changeInfo">修改人的信息</button>
</template>
<script>
import {ref} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup(){
// 数据
let name=ref('张三')
let age=ref(18)
// 方法
function changeInfo(){
// 因为repl上有引用对象value,所以可以用它来修改值
name.value='李四'
age.value=48
}
// 返回一个对象(常用)
return{
name,
age,
changeInfo
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
展示结果
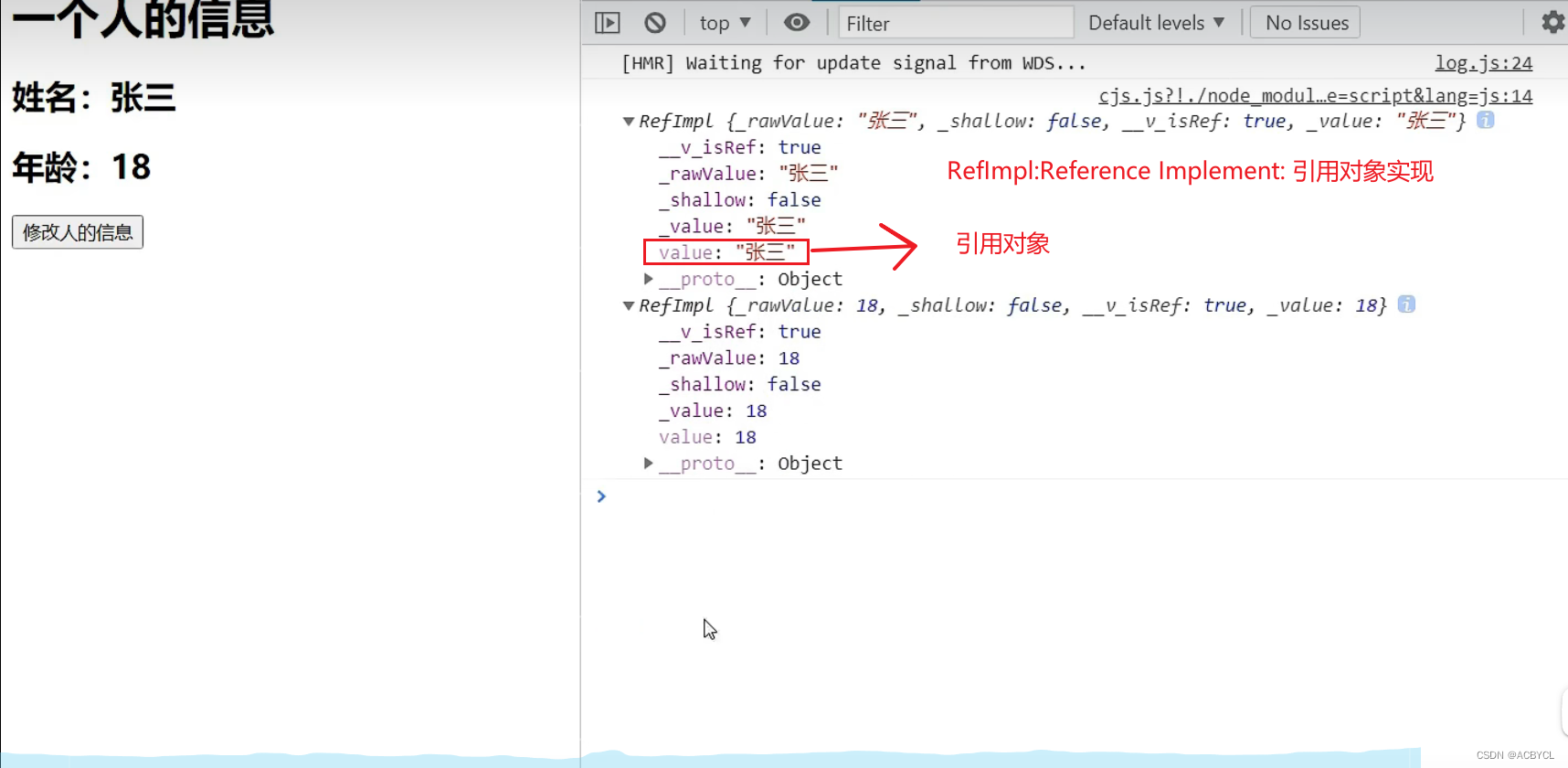
ref处理对象类型
3 . reactive函数

proxy
作用:遵循响应式原理,用来响应数据
只有reactive才能把对象数据变为proxy
ref偷偷求助了reactive
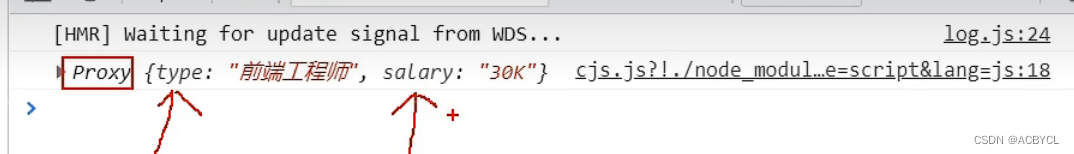
代码展示
app.vue
<template>
<h1>一个人的信息</h1>
<h2>姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<h3>工作种类:{{job.type}}</h3>
<h3>工作薪水:{{job.salary}}</h3>
<h3>爱好:{{hobby}}</h3>
<h3>测试的数据c:{{job.a.b.c}}</h3>
<button @click="changeInfo">修改人的信息</button>
</template>
<script>
import { ref,reactive } from '@vue/reactivity'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup(){
let name=ref('张三')
let age=ref(18)
let job=reactive({
type:"前端工程师",
salary:'30k',
a:{
b:{
c:666
}
}
})
let hobby=(['抽烟','喝酒','烫头'])
function changeInfo(){
// ref响应的数据
name.value='李四'
age.value=48
// reactive响应的数据
job.type='UI设计师'
job.salary='60k'
job.a.b.c=999
hobby[0]='学习'
}
return{
name,
job,
age,
hobby,
changeInfo
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
结果展示

总结
ref:改变数据必须得通过value
reactive:是一个函数,里面必须是一个对象reactive({}),不比通过value来访问数据
4.vue3.0中得响应式原理
1.vue2得响应式
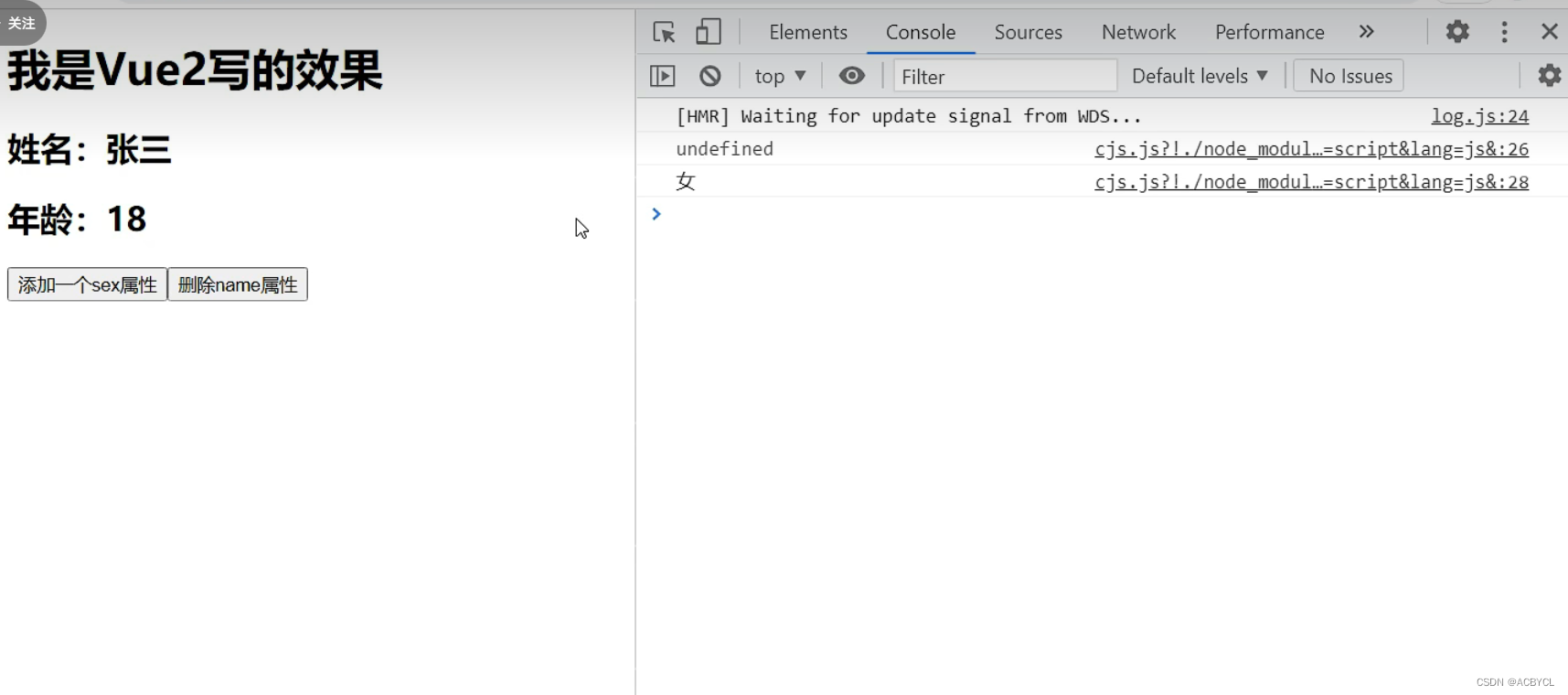
这样写数据不会发生变化
app.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>我是Vue2写得效果</h1>
<h2 v-show="person.name">姓名:{{person.name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2>
<h2 v-show="person.sex">性别:{{person.sex}}</h2>
<h2>爱好:{{person.hobby}}</h2>
<button @click="addSex">添加一个sex属性</button>
<button @click="deleteName">删除name属性</button>
<button @click="updateHobby">修改第一个爱好的名字</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import Vue from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
person:{
name:'张三',
sex:'男',
age:18,
hobby:['学习','吃饭']
}
}
},
methods:{
addSex(){
// // 这样写数据不会发生改变
// console.log(this.person.sex) //undefined
// this.person.sex='女'
// console.log(this.person.sex) //女
// 解决方案二 用$set
this.$set(this.person,'sex','女')
// // 解决方案一 用vue.set
// Vue.set(this.person,'sex','女')
},
deleteName(){
// // 数据不会更新
// console.log(this.person.name) //张三
// delete this.person.name
// console.log(this.person.name) //undefined
// // 解决方案二
// this.$delete(this.person,'name')
// // 解决方案二
// Vue.delete(this.person,'name','女')
},
updateHobby(){
// 问题:数据不会改变
this.person.hobby[0]='逛街' //不会更改
// 解决方案一:
this.$set(this.person.hobby,0,'逛街')
// 解决方案二:
this.person.hobby.splice(0,1,'逛街')
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
点击后数据不会发生改变
在这里插入代码片
2.vue3中得响应式
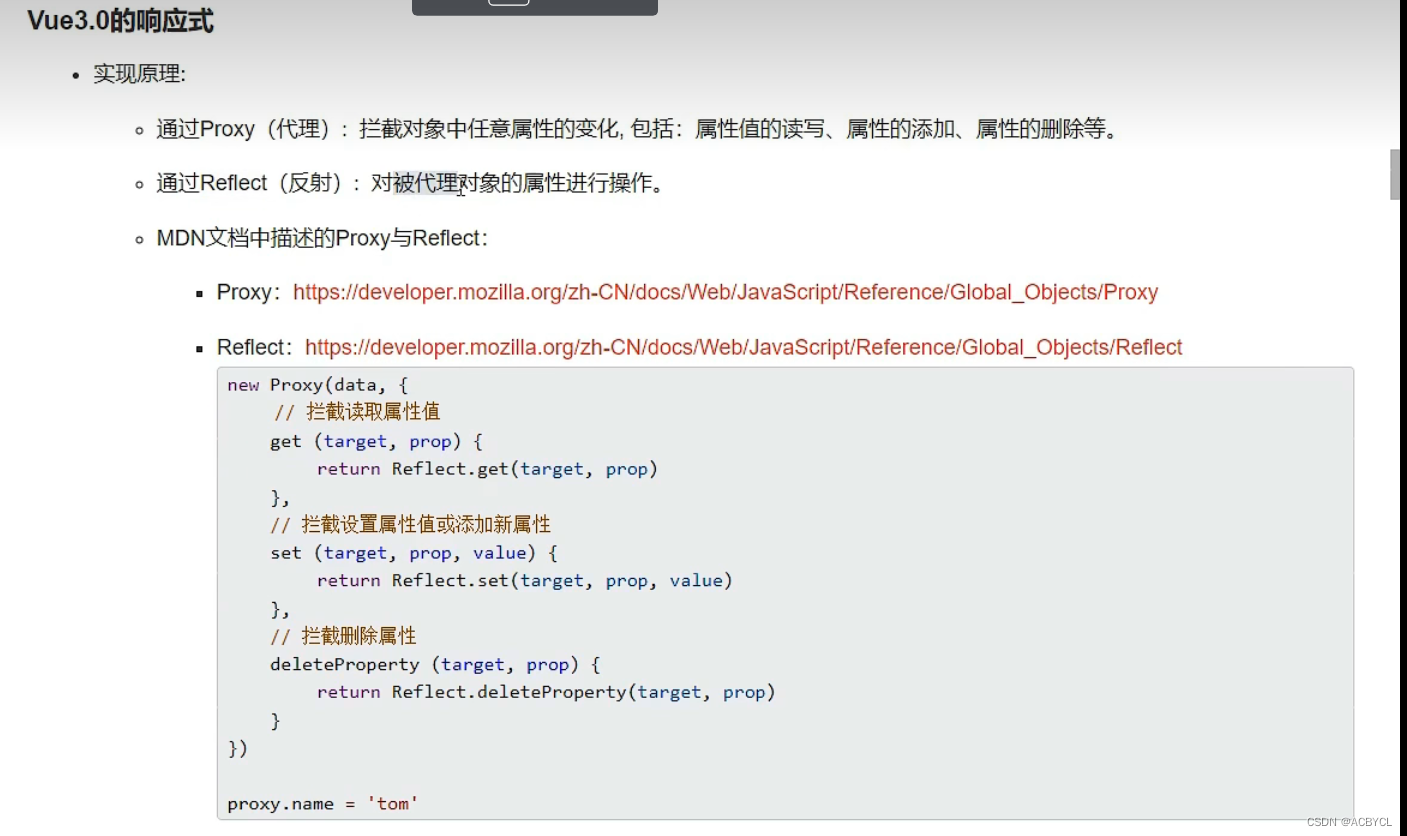
MDN文档中描述的Proxy与Reflect:
- Proxy:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Proxy
- Reflect:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Reflect
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let person={
name:'张三',
age:18
}
let obj={a:1,b:2}
// 1.错误的响应式
// Object.defineProperty('obj','c',{
// get(){
// return 3
// }
// })
// Object.defineProperty('obj','c',{
// get(){
// return 3
// }
// })//会报错,因为重复定义了
// Object与Reflect(映射)方法的区别:
// 前者会报错,且没有返回值true/false,不能捕获错误
// 如果想继续走,就需要try ... catch()
// // 2.正确的响应式
// const x1=Reflect.defineProperty('obj','c',{
// get(){
// return 3
// }
// })
// console.log(x1)//true
// const x2=Reflect.defineProperty('obj','c',{
// get(){
// return 3
// }
// })
// console.log(x1)//false
// if(x2){
// console.log('某某操作成功了!')
// }else{
// console.log('某某操作失败了')
// }
// 3.vue的底层响应式原理
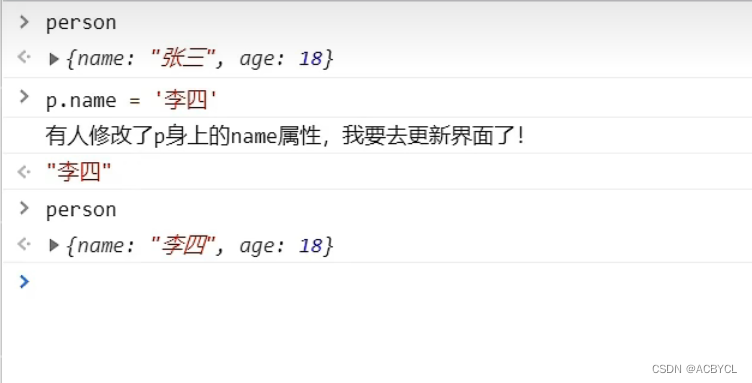
const p=new Proxy(person,{
// 有人读取p的某个属性时调用
get(target,proName){
console.log(`有人读取了p身上的${propName}属性`)
return Reflect.get(target,propName)
},
// 有人修改了p的某个属性,或给p追加某个属性时调用
set(target,propName,value){
console.log(`有人修改了p身上的${propName}属性,我要去更新界面了`)
Reflect.set(target,propName,value)//修改值
},
// 有人删除p的某个属性时调用
deleteProperty(target,proName){
console.log(`有人删除了p身上的${propName}属性,我要去更新界面了`)
return Reflect.deleteProperty(target,propName)//删除值
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
5.reactive对比ref

6.setup的两个注意点
笔记:
- vue2中 props:[‘msg’,‘school’]接受的数据传到vc上去了,如果没有声明接受只能通过 a t t r s 获取,声明接受了 attrs获取 ,声明接受了 attrs获取,声明接受了attr里的数据没有。好像一个捡漏的东西
- 插槽:父组件留坑位,子组件填坑
- VNODE:虚拟的节点

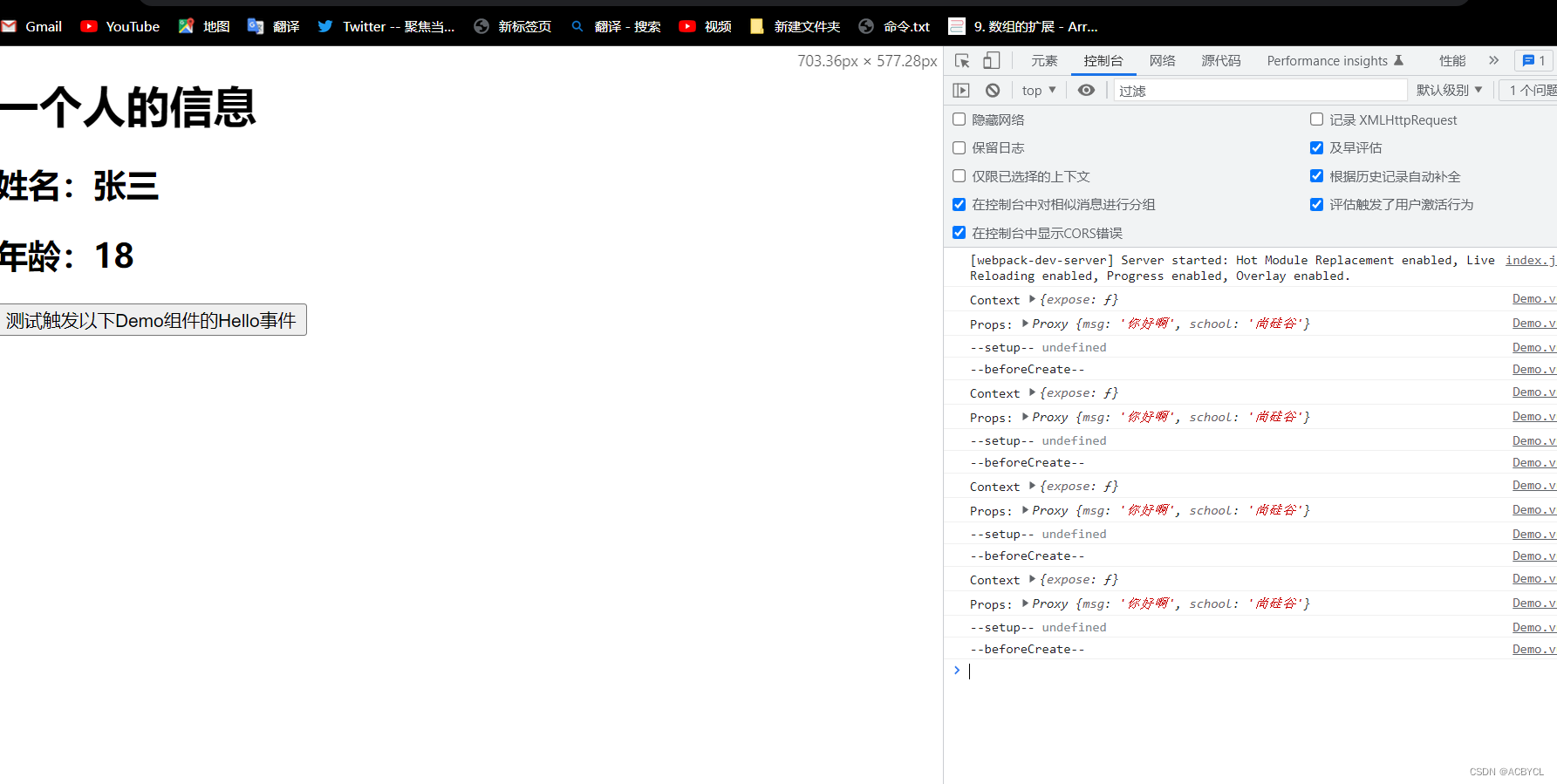
Demo.vue
<template>
<h1>一个人的信息</h1>
<h2>姓名:{{person.name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2>
<button @click="test">测试触发以下Demo组件的Hello事件</button>
</template>
<script>
import {reactive} from 'vue'
export default {
name:'Demo',
beforeCreate(){
console.log('--beforeCreate--')
},
props:['msg','school'],// proxy:代理对象
emits:['hello'], //用来给app组件发射一个hello函数
// context里面装的是{expose}
setup(props,context){
console.log('Context',context)
console.log('Props:',props)
console.log('--setup--',this)//输出结果比beforecreated早 --setup-- undefined
// 数据
let person=reactive({
name:'张三',
age:18
})
function test(){
context.emit('hello',666)
}
// 返回一个对象(常用)
return {
person,
test
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
app.vue
<template>
<!-- 用来给props传数据,插槽是再里面传东西 -->
<!-- 如果想用原生组件,后加.native....如:@click.native -->
<Demo msg="你好啊" school="尚硅谷"></Demo>
</template>
<script>
import Demo from './components/Demo.vue'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{Demo},
setup(){
function showHelloMsg(value){
alert(`你好啊,你触发了hello事件,我收到的参数是${value}`)
}
return{
showHelloMsg
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
7.计算属性与监视
app.vue
<template>
<demo></demo>
</template>
<script>
import Demo from './components/Demo.vue'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{Demo},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
Demo.vue
<template>
<h1>一个人的信息</h1>
姓:<input type="text" v-model="person.firstName">
<br>
名:<input type="text" v-model="person.lastName">
<br>
全名:<input type="text" v-model="person.fullName">
</template>
<script>
import { reactive } from '@vue/reactivity'
import { computed } from '@vue/runtime-core'
export default {
name:'Demo',
setup(){
let person=reactive({
firstName:'张',
lastName:'三'
})
// 计算属性-简写(没有考虑计算属性被修改的情况)
// person.fullName=computed(()=>{
// return person.firstName+'-'+person.lastName
// })
person.fullName=computed({
get(){
return person.firstName+'-'+person.lastName
},
set(value){
const nameArr=value.split('-')
person.firstName=nameArr[0]
person.lastName=nameArr[1]
}
})
// 返回一个对象(常用)
return{
person
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
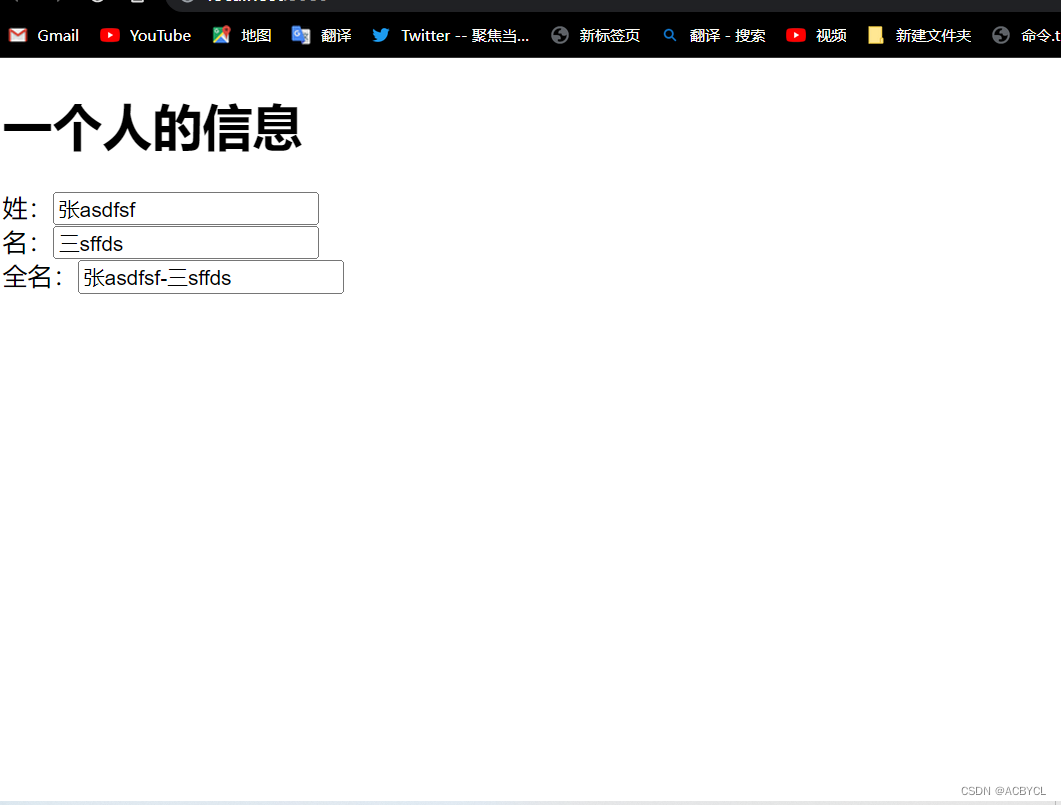
总结:
computed变为一个方法,可以写computed(()=>{})
也可以写成对象且无需返回:computed({})
8.watch属性
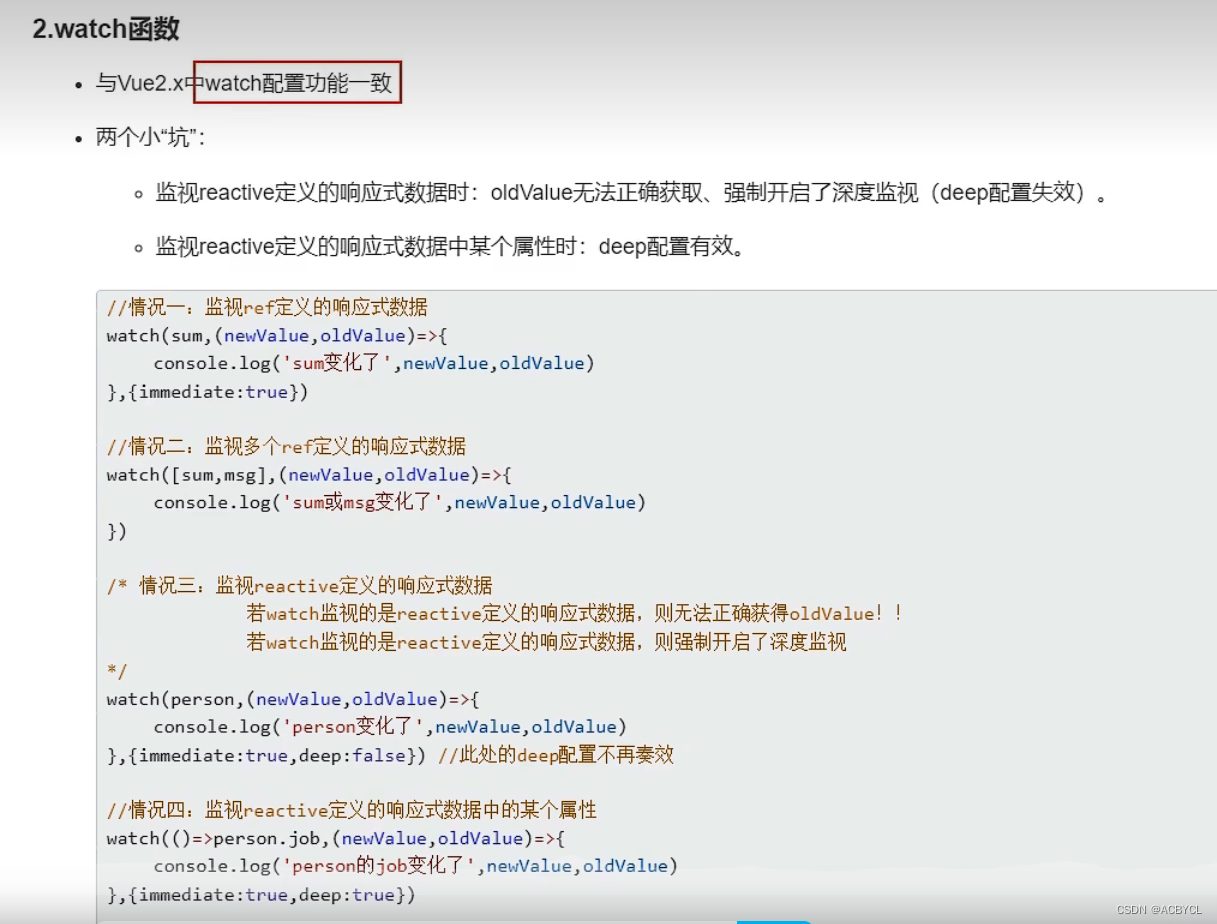
Demo.vue
<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
<button @click="sum++">点我+1</button>
<br>
<h2>当前的信息为:{{msg}}</h2>
<button @click="msg+='!'">修改信息</button>
<br>
<h2>姓名:{{person.name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2>
<h2>薪资:{{person.job.j1.salary}}</h2>
<button @click="person.name+='~'">修改姓名</button>
<button @click="person.age++">增长年龄</button>
<button @click="person.job.j1.salary++">涨薪</button>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, ref } from '@vue/reactivity'
import { watch } from '@vue/runtime-core'
export default {
name:'Demo',
setup(){
let sum=ref(0)
let msg=ref('你好啊')
let person=reactive({
name:'张三',
age:18,
job:{
j1:{
salary:20
}
}
})
// // 情况一:监视ref所定义的一个响应式数据
// watch(sum,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
// console.log('sum变化了',newValue,oldValue)
// },{immediate:true,deep:true})
// 情况二:监视ref所定义的多个响应式数据
// watch([sum,msg],(newValue,oldValue)=>{
// console.log('sum或msg变化了',newValue,oldValue)
// },{immediate:true,deep:true})
// 情况三:监视的reactive所定义的一个响应式数据的全部属性
// 1.注意:此处无法正确的获取oldValue
// 2.注意:强制开启了深度监视(deep配置无效)
watch(person,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的job变化了',newValue,oldValue)
},{deep:false})//此处的deep配置无效
// 情况四:监视reactive所定的一个响应式数据中的某个属性
watch(()=>person.name,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的name变化了',newValue,oldValue)
})
// 情况五:监视reactive所定义的一个响应式数据中的某些属性
watch([()=>person.name,()=>person.age],(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的name或age变化了',newValue,oldValue)
})
// 特殊情况
watch(()=>person.job,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的job变化了',newValue,oldValue)
},{deep:true})//此处由于监视的是reactive素定义的对象中的某个属性,所以deep配置有效
return {
sum,
msg,
person
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
app.vue
<template>
<demo></demo>
</template>
<script>
import Demo from './components/Demo.vue'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{Demo},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
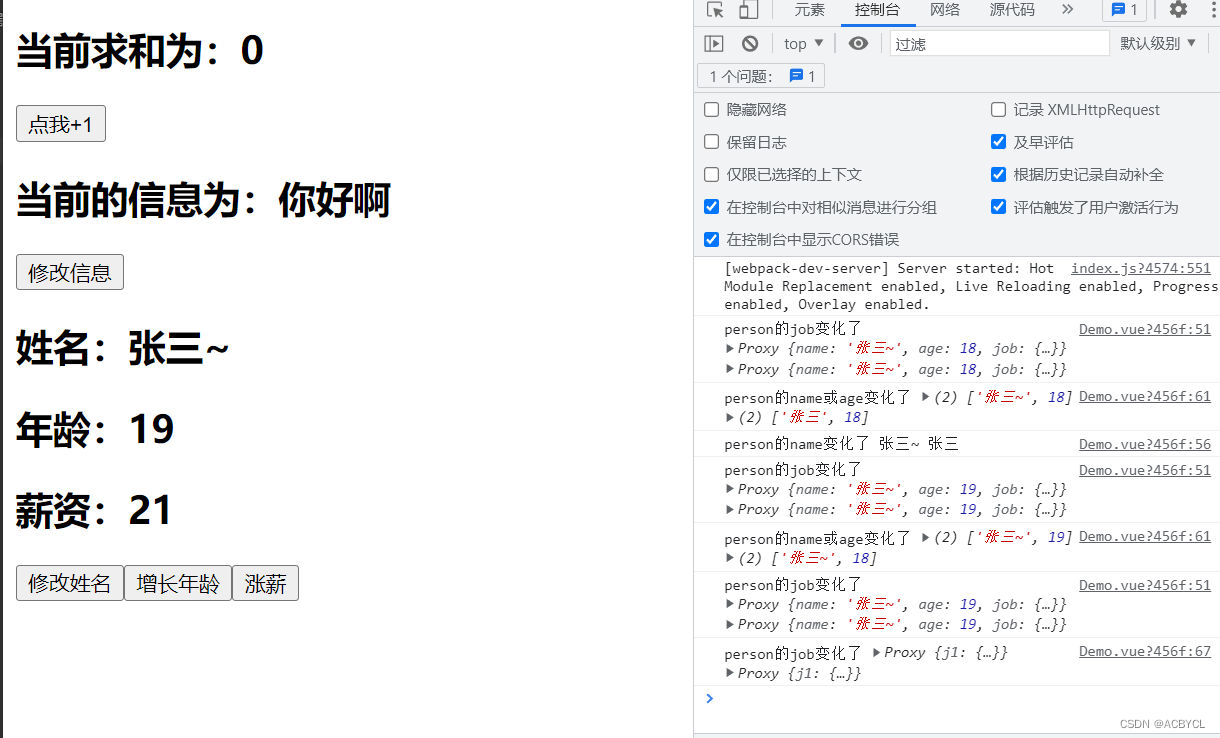
总结:
1.newValue变成一个数组,不再仅仅是一个数
2.reactive里面的对象,自动有深度监视功能。watch不用开启深度deep监视
3.当ref({})里面是个对象时,会走reactive(内部会生成一个proxy代理对象)路线,且必须通过.value来取值
watch时value的值
Demo.vue
<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
<button @click="sum++">点我+1</button>
<br>
<h2>当前的信息为:{{msg}}</h2>
<button @click="msg+='!'">修改信息</button>
<br>
<h2>姓名:{{person.name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2>
<h2>薪资:{{person.job.j1.salary}}</h2>
<button @click="person.name+='~'">修改姓名</button>
<button @click="person.age++">增长年龄</button>
<button @click="person.job.j1.salary++">涨薪</button>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, ref } from '@vue/reactivity'
import { watch } from '@vue/runtime-core'
export default {
name:'Demo',
setup(){
let sum=ref(0)
let msg=ref('你好啊')
let person=reactive({
name:'张三',
age:18,
job:{
j1:{
salary:20
}
}
})
console.log(person)
//不要用.value监视一个具体的值 如0,会报错
//也不要监视一个具体的值
watch(sum,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('sum的值变化了',newValue,oldValue)
})
// 问题访问不到,因为ref走的是reactive的路线需要开起深度监视
// 解决方案一: 通过访问.value
watch(person.value,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的值变化了',newValue,oldValue)
})
// 方案二:开启deep
watch(person,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log('person的值变化了',newValue,oldValue)
},{deep:true})
return {
sum,
msg,
person
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
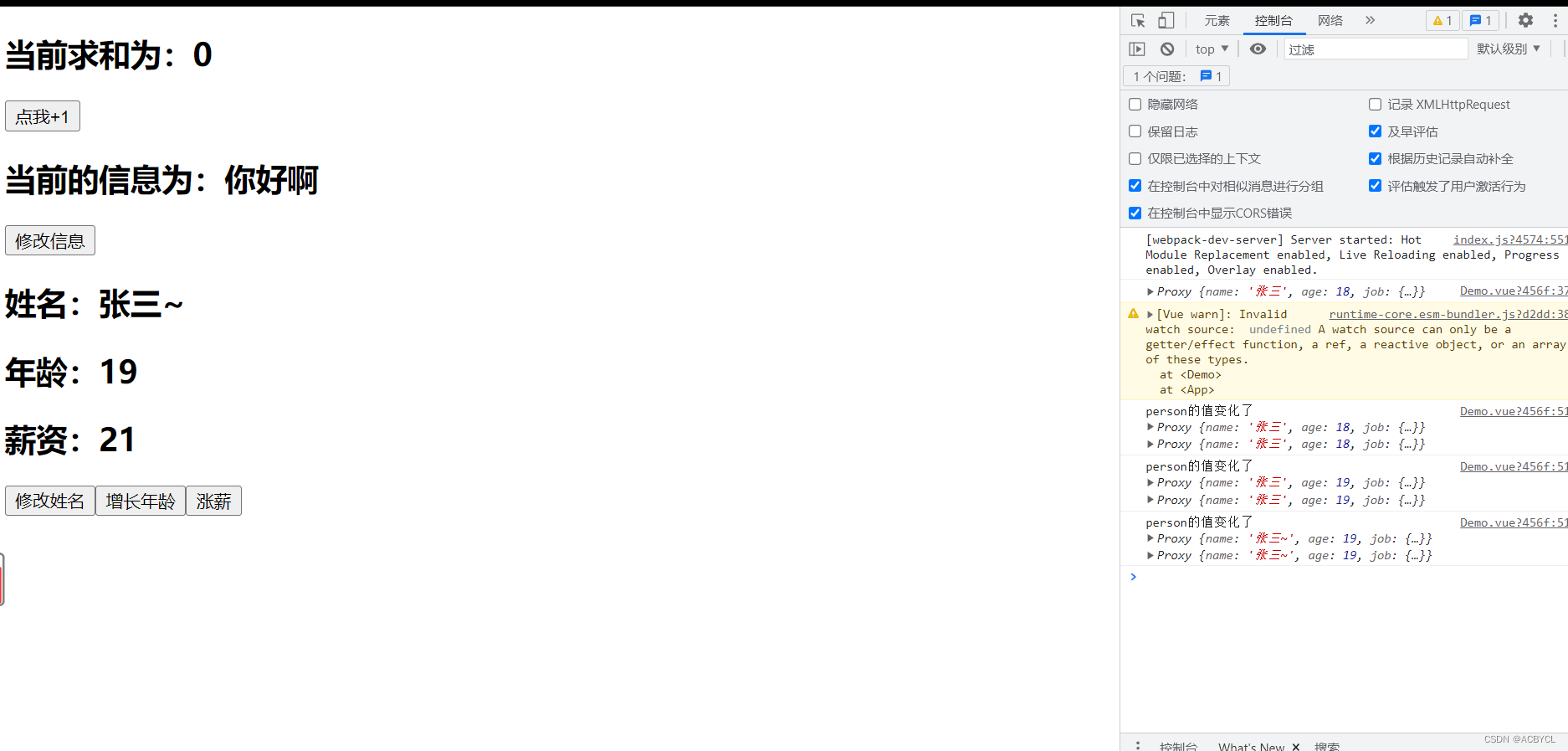
总结:
1.当sum=ref(0),不能用watch(sum.value)的.value来访问,因为是具体的值
2.proxy相当于地址,地址不变引用不变
watchEffec函数
Demo.vue
<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
<button @click="sum++">点我+1</button>
<br>
<h2>当前的信息为:{{msg}}</h2>
<button @click="msg+='!'">修改信息</button>
<br>
<h2>姓名:{{person.name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{person.age}}</h2>
<h2>薪资:{{person.job.j1.salary}}</h2>
<button @click="person.name+='~'">修改姓名</button>
<button @click="person.age++">增长年龄</button>
<button @click="person.job.j1.salary++">涨薪</button>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, ref } from '@vue/reactivity'
import { watch, watchEffect } from '@vue/runtime-core'
export default {
name:'Demo',
setup(){
let sum=ref(0)
let msg=ref('你好啊')
let person=reactive({
name:'张三',
age:18,
job:{
j1:{
salary:20
}
}
})
watchEffect(()=>{
const x1=sum.value
const x2=person.job.j1.salary
console.log('watchEffect所指定的回调执行了')
})
return {
sum,
msg,
person
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
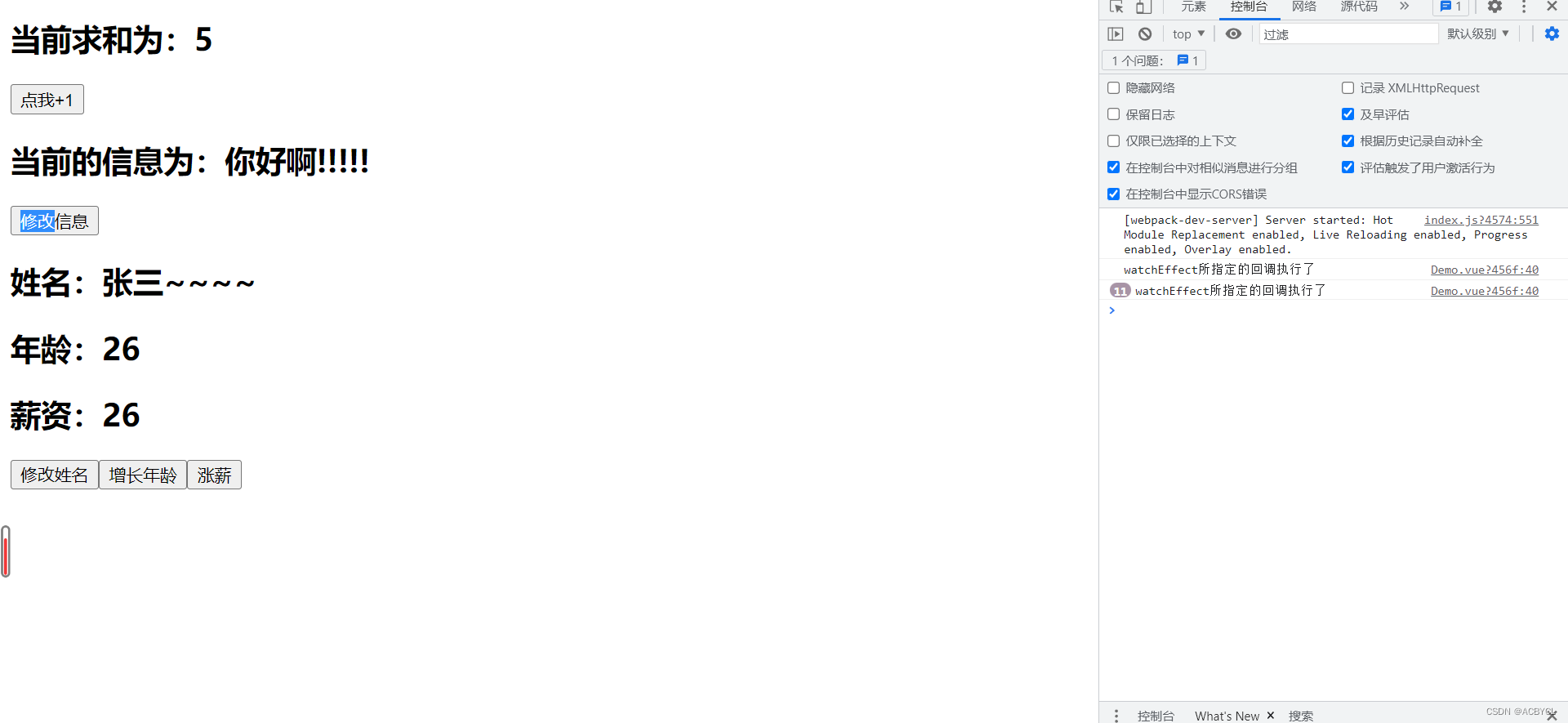
总结:
1.watchEffect不说它监视谁
2.computed函数初始化时执行一次,依赖的数据发生变化时执行一次
3.watchEffect有点像,谁用了,监视谁
4.watchEffect注重过程,computed注重值
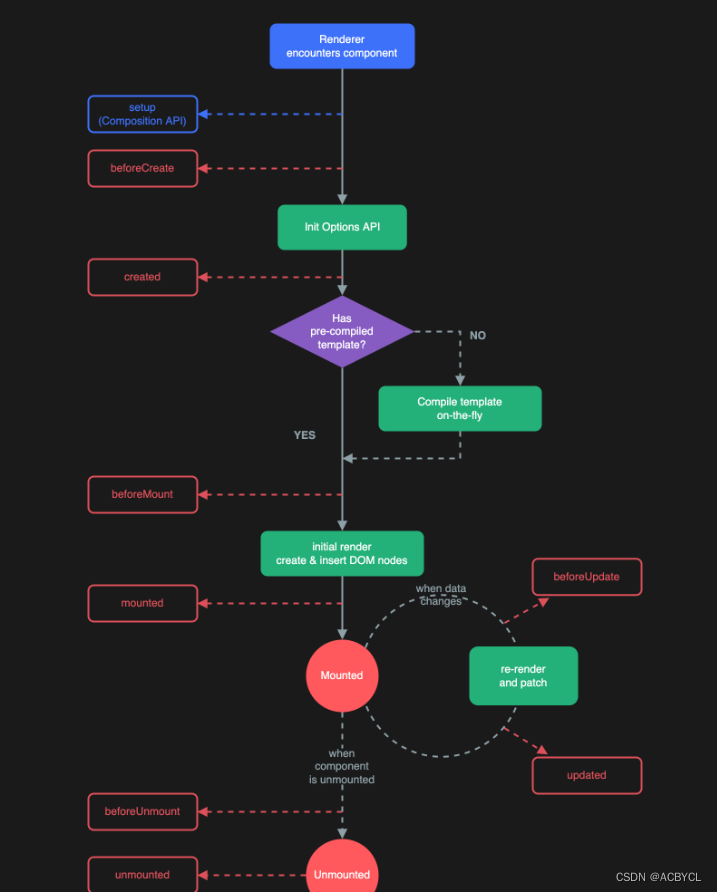
9.Vue3生命周期
生命周期钩子两种写法:
- 配置项式:与setup平级
- 组合式API式:写在setup里面
Demo.vue
<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
<button @click="sum++">点我+1</button>
</template>
<script>
import { onBeforeMount, onBeforeUnmount, onBeforeUpdate, onMounted, onUnmounted, onUpdated } from '@vue/runtime-core'
import { ref } from 'vue'
export default {
name:'Demo',
setup(){
console.log('----setup---')
let sum=ref(0)
onBeforeMount(()=>{
console.log('---onBeforeMount---')
})
onMounted(()=>{
console.log('---onMounted---')
})
onBeforeUpdate(()=>{
console.log('---onBeforeUpdate---')
})
onUpdated(()=>{
console.log('---onUpdated---')
})
onBeforeUnmount(()=>{
console.log('---onBeforeUnmount---')
})
onUnmounted(()=>{
console.log('---onUnmounted---')
})
return{
sum
}
},
// 2.通过配置项形式使用生命周期钩子
beforeCreate(){
console.log('---beforeCreate---')
},
created(){
console.log('---created---')
},
beforeMount(){
console.log('---beforeMount---')
},
mounted(){
console.log('---mounted---')
},
beforeUpdate(){
console.log('---beforeUpdate---')
},
updated(){
console.log('---updated---')
},
beforeUnmount(){
console.log('---beforeUpdate---')
},
unmounted(){
console.log('---updated---')
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
app.vue
<template>
<button @click="isShowDemo=!isShowDemo">切换隐藏/显示</button>
<demo v-if="isShowDemo"></demo>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from '@vue/reactivity'
import Demo from './components/Demo.vue'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{Demo},
setup(){
let isShowDemo=ref(true)
return{
isShowDemo
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
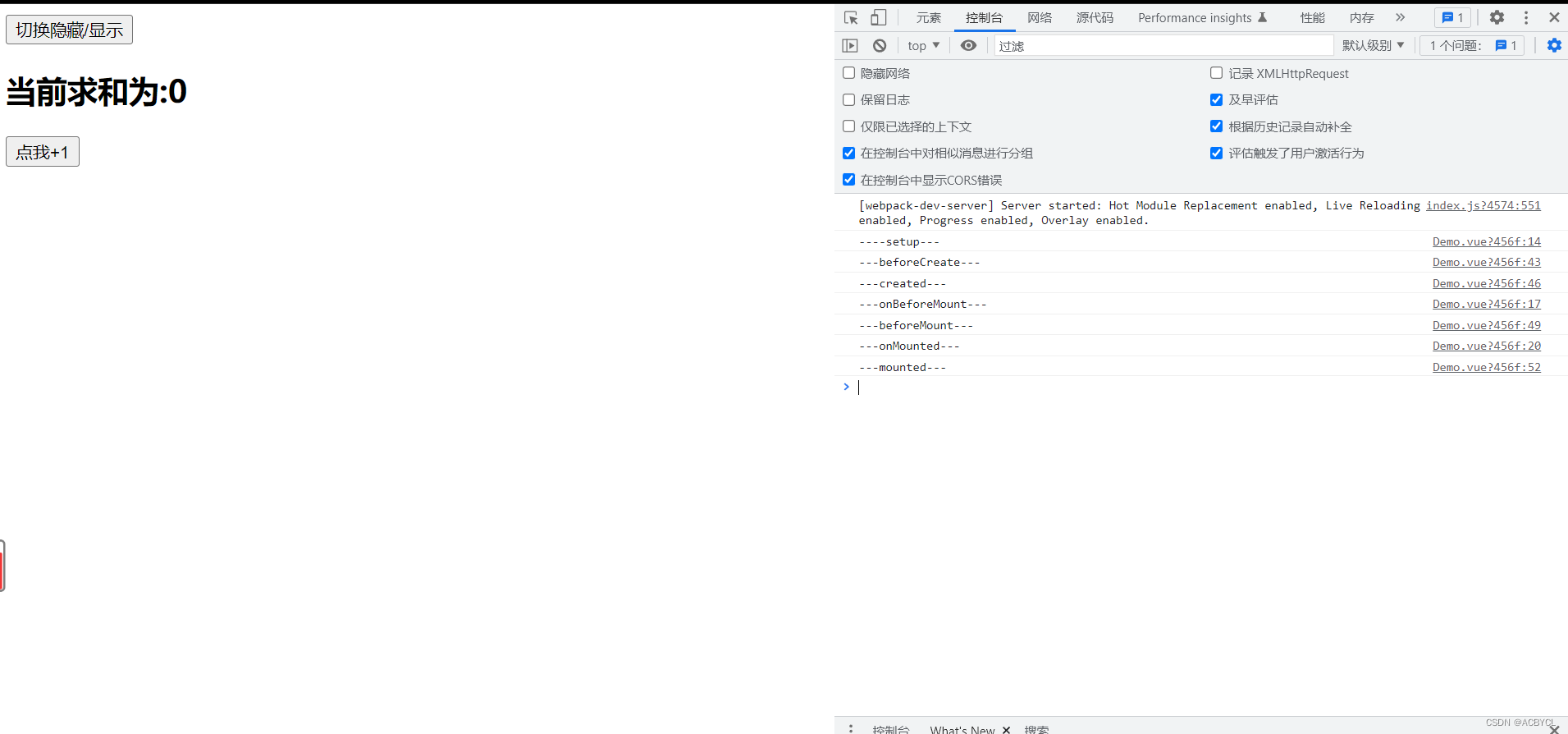
总结:
1.vue3可以继续使用vue2的生命周期钩子但有两个改名
- beforeDestroy---->beforeUnmount
- destroyed----> unmounted
2.setup执行在beforeCreate之前
3.setup与beforeCreate是平级的关系,可以写在同一个层级
4.vue2在挂载之前可以执行beforeCreate(),created().但vue3必须先挂载,再执行
5.折叠#region-----#endregion
6.钩子对应关系vue2vue3
beforeCreate=>setup()
created=====>setup()
beforeMount()=>onBeforeMount
mounted=====>onMounted
beforeUpdate====>onBeforeUpdate
update=========>onUpdated
beforeUnmounted====>onBeforeUnmount
unmounted=======>onUnmounted
9.自定义hook函数

app.vue
<template>
<button @click="isShowDemo=!isShowDemo">切换隐藏/显示</button>
<demo v-if="isShowDemo"></demo>
<hr>
<test></test>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from '@vue/reactivity'
import Demo from './components/Demo.vue'
import Test from './components/test.vue'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{Demo, Test},
setup(){
let isShowDemo=ref(true)
return{
isShowDemo
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
Demo.vue
<template>
<h2>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h2>
<button @click="sum++">点我+1</button>
<br>
<h2>当前点击鼠标的坐标为:x:{{point.x}},y:{{point.y}}</h2>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from '@vue/reactivity'
import usePoint from '../hooks/usePoint'
export default {
name:'Demo',
setup(){
let sum=ref(0)
let point=usePoint()
return{
sum,
point
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
test.vue
<template>
<h2>我是Test组件</h2>
<h2>当前点击鼠标的坐标为:{{point.x}},y:{{point.y}}</h2>
</template>
<script>
import usePoint from '../hooks/usePoint';
export default {
name:'Test',
setup(){
const point = usePoint()
return{
point
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
hooks / usePoint.js
<template>
<h2>我是Test组件</h2>
<h2>当前点击鼠标的坐标为:{{point.x}},y:{{point.y}}</h2>
</template>
<script>
import usePoint from '../hooks/usePoint';
export default {
name:'Test',
setup(){
const point = usePoint()
return{
point
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
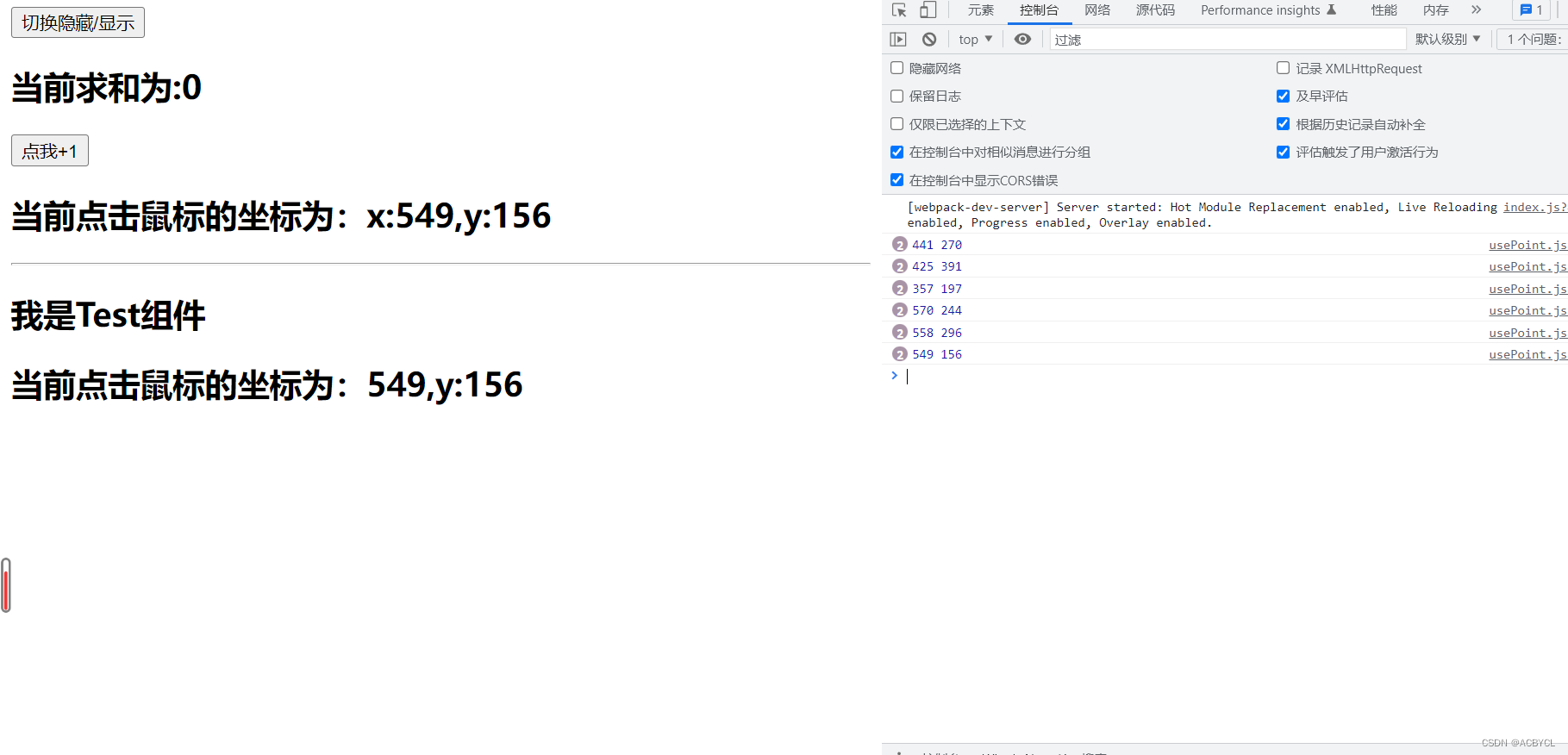
总结:
- 1.hook只是一个普普通通的js,可以提高功能的复用
- 2.组件和hook功能都一样
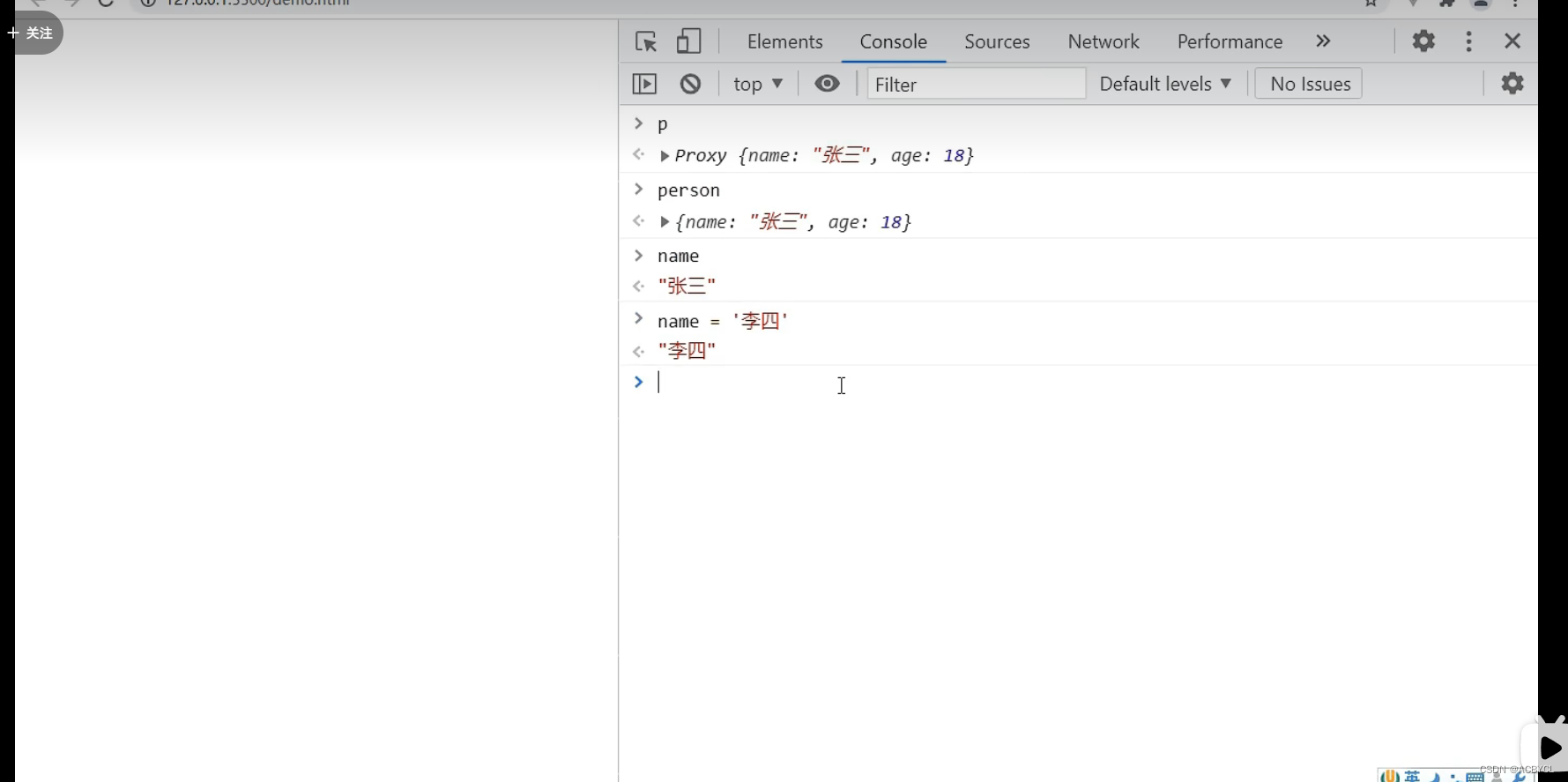
10.toRef(把什么变成ref)

问题:复制的数据非响应式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
let person={
name:'张三',
age:18
}
let p=new Proxy(person,{
set(target,propName,value){
console.log(`${propName}被修改了,我要去更新页面`)
// target[propName]=value
Reflect.set(target,propName,value)
}
})
// 问题:
// 这里是数据而非响应式
let name=p.name
</script>
</body>
</html>
Demo.vue
<template>
<h4>{{person}}</h4>
<h2>姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<h2>薪资:{{job.j1.salary}}</h2>
<button @click="name+='~'">修改姓名</button>
<button @click="age++">增长年龄</button>
<button @click="person.job.j1.salary++">涨薪</button>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, toRef,toRefs } from '@vue/reactivity'
export default {
name:'Demo',
setup(){
let person=reactive({
name:'张三',
age:18,
job:{
j1:{
salary:20
}
}
})
// // 1.toref()处理响应式引用关系
// const name1=person.name
// console.log('%%%',name1)
// const name2=toRef(person,'name')
// console.log('####',name2)
// 2.toRefs()处理多个数据
const x=toRefs(person)
console.log('******',x)
return{
person,
// 解决方案一:ref
// name:toRef(person,'name'),
// age:toRef(person,'age'),
// salary:toRef(person.job.j1,'salary'),
// 解决方案二:toRefs()处理多个数据
...toRefs(person)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
app.vue
<template>
<demo></demo>
<hr>
</template>
<script>
import Demo from './components/Demo.vue'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{Demo},
setup(){
return{
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
执行结果
总结:
1.ref是复制的数据,原数据不变,toRef是引用关系(通过getter,setter指向)
2.toRefs()只能处理第一层,不能深层次响应
三.其他Composition API
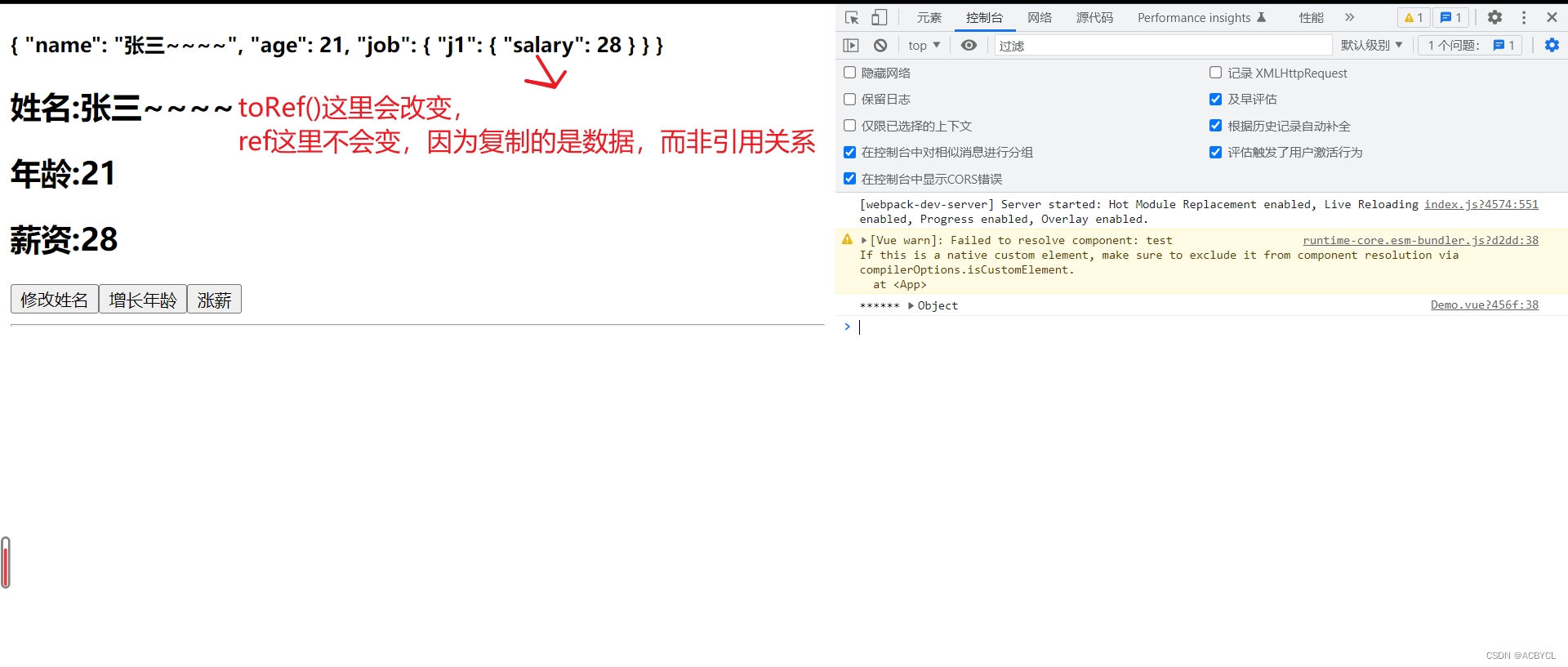
1.shallowReactive与shallowRef

Demo.vue
<template>
<h4>当前的x值是:{{x}}</h4>
<button @click="x={y:888}">点我x+1</button>
<button @click="x.y++">点我x.y++</button>
<br>
<h4>{{person}}</h4>
<h2>姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<h2>薪资:{{job.j1.salary}}</h2>
<button @click="name+='~'">修改姓名</button>
<button @click="age++">增长年龄</button>
<button @click="person.job.j1.salary++">涨薪</button>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive,toRefs,shallowRef} from '@vue/reactivity'
export default {
name:'Demo',
setup(){
//1.shallowReactive:只处理第一层数据的响应式
// let person.shallowReactive({
let person=reactive({
name:'张三',
age:18,
job:{
j1:{
salary:20
}
}
})
let x=shallowRef({
y:0
})
console.log('*****',x)
return{
x,
person,
...toRefs(person)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
app.vue
<template>
<demo></demo>
<hr>
</template>
<script>
import Demo from './components/Demo.vue'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{Demo},
setup(){
return{
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
总结:
1.reactive会把对象里所有的东西变为响应式
2.ref的value:proxy, shallowRed的value:Object,拿来就用
2.readonly与shallowReadonly
页面不变得两种情况:
- 1.页面不是响应式得
- 2.页面不让改

总结:
起到保护作用,不许修改
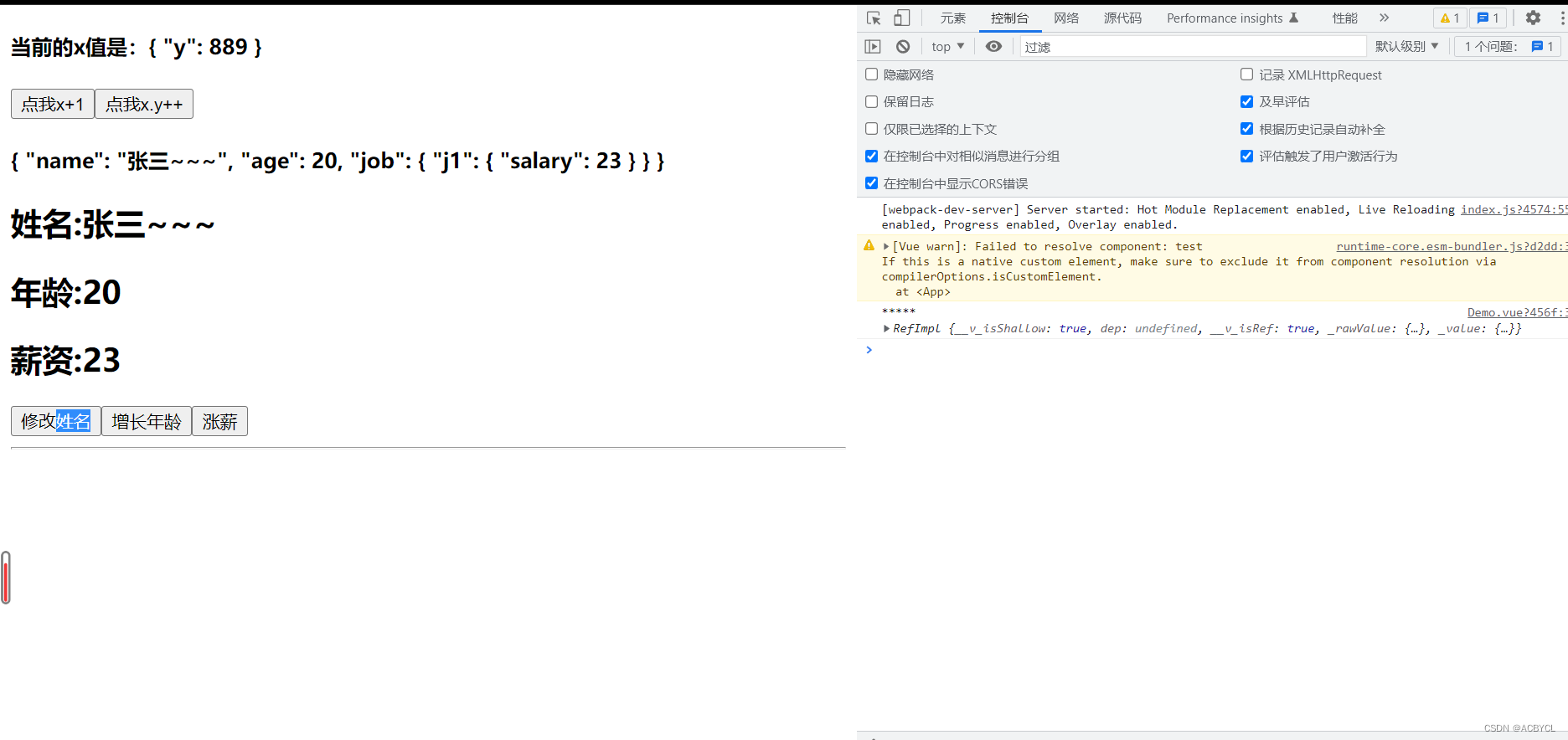
3.toRaw与markRaw

demo.vue
<template>
<h4>当前求和为:{{sum}}</h4>
<button @click="sum++">点我++</button>
<br>
<h2>姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<h2>薪资:{{job.j1.salary}}</h2>
<h3 v-show="person.car">座驾信息:{{person.car}}</h3>
<button @click="name+='~'">修改姓名</button>
<button @click="age++">增长年龄</button>
<button @click="job.j1.salary++">涨薪</button>
<button @click="showRawPerson">输出最原始得person</button>
<button @click="addCar">给人添加一台车</button>
<button @click="person.car.name+='!'">换车名</button>
<button @click="person.car.price++">换价格</button>
<button @click="changePrice">换价格</button>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive,toRefs,ref, toRaw, markRaw} from '@vue/reactivity'
export default {
name:'Demo',
setup(){
let sum=ref(0)
let person=reactive({
name:'张三',
age:18,
job:{
j1:{
salary:20
}
}
})
function showRawPerson(){
const p=toRaw(person)
p.age++
console.log(p)
}
function addCar(){
let car={name:'奔驰',price:40}
person.car=markRaw(car)
}
function changePrice(){
person.car.price++
console.log(person.car.price)
}
return{
sum,
person,
...toRefs(person),
showRawPerson,
addCar,
changePrice
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
app.vue
<template>
<demo></demo>
<hr>
</template>
<script>
import Demo from './components/Demo.vue'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{Demo},
setup(){
return{
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
执行结果
总结:
1.toRaw()只能处理reactive
2.setup只会调用一次,
3.值是undefined,不展示
4.customRef
custom:自定义
- 作用:创建一个自定义的ref,并对其依赖项跟踪和更新触发进行显示控制
trigger():让vue重新去读取模板
track():追踪数据。有追踪,get才会重新解析
实现防抖效果:
app.vue
<template>
<input type="text" v-model="keyWord">
<h3>{{keyWord}}</h3>
</template>
<script>
import { trigger } from '@vue/reactivity'
import { customRef } from 'vue'
export default {
name: "App",
components:{},
setup(){
// 自定义一个ref----名为:myRef
function myRef(value,delay){
let timer
return customRef((track,trigger)=>{
return{
get(){
console.log(`有人从myRef这个容器中读取数据了,我把${value}给他了`)
track()//通知vue追踪value的变化(提前和get商量一下,让它认为这个value是有用的)
return value
},
set(newValue){
console.log(`有人把myRef这个容器中数据改了:${newValue}`)
clearTimeout(timer)
timer=setTimeout(()=>{
value=newValue
trigger()//通知vue去重新解析模板
},delay)
}
}
})
}
// let keyWord=ref('hello') //使用vue提供的ref
let keyWord=myRef('hello',500)//使用程序自定义的ref
return{
keyWord
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
执行结果
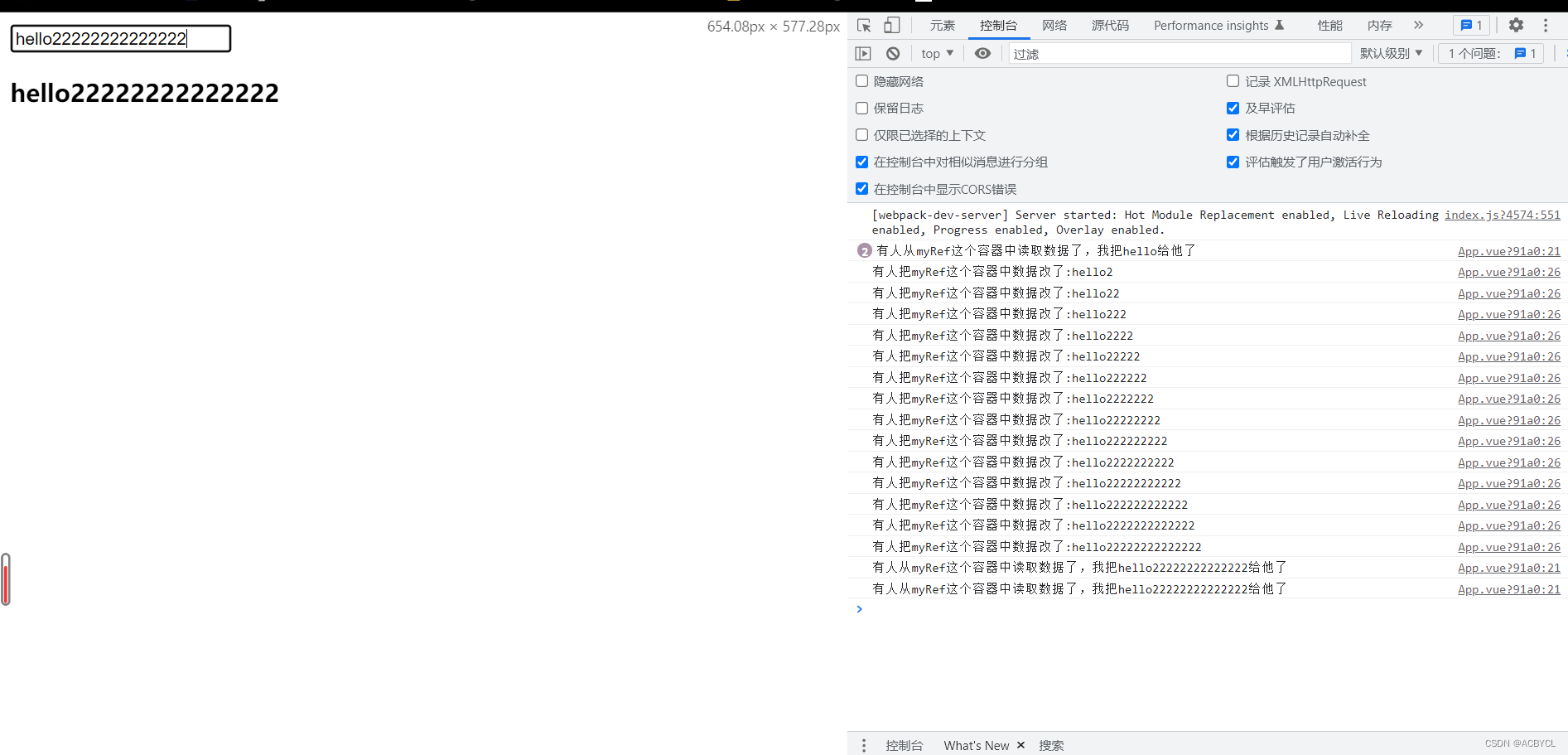
总结:
1.customRef()是一个自定义的ref函数
2.有人读,运行get()。有人改,使用set()
3.cls—快速打出console
5.provide与inject
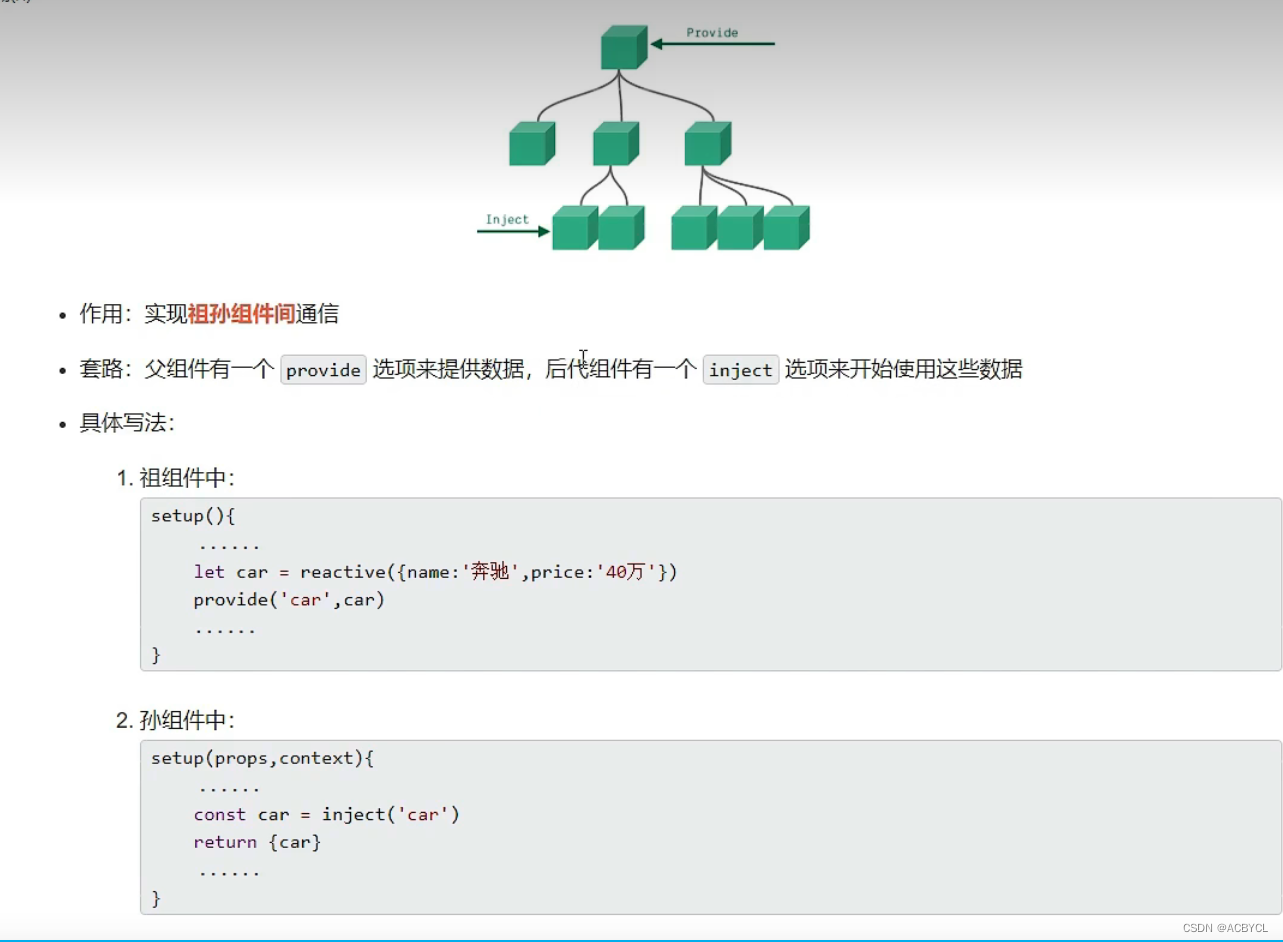
app.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>我是App组件(组),{{name}}----{{price}}</h3>
<Child></Child>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, toRefs } from '@vue/reactivity';
import Child from './components/Child.vue';
import { provide } from '@vue/runtime-core';
export default {
components: { Child },
setup(){
let car=reactive({name:'奔驰',price:'40w'})
provide('car',car)//给自己的后代组件传递数据
return{
...toRefs(car)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.app{
background-color: gray;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
Child.vue
<template>
<div class="child">
<h3>我是Child组件(子)</h3>
<Son></Son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { inject } from '@vue/runtime-core';
import Son from './Son.vue';
export default {
components: { Son },
setup(){
let x=inject('car')
console.log(x,'Chold-----')
}
}
</script>
<style>
.child{
background-color: skyblue;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
Son.vue
<template>
<div class="son">
<h3>我是SOn组件(孙)----{{car.name}}---{{car.price}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { inject } from '@vue/runtime-core'
export default {
setup(){
let car=inject('car')
return{
car
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.son{
background-color: orange;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
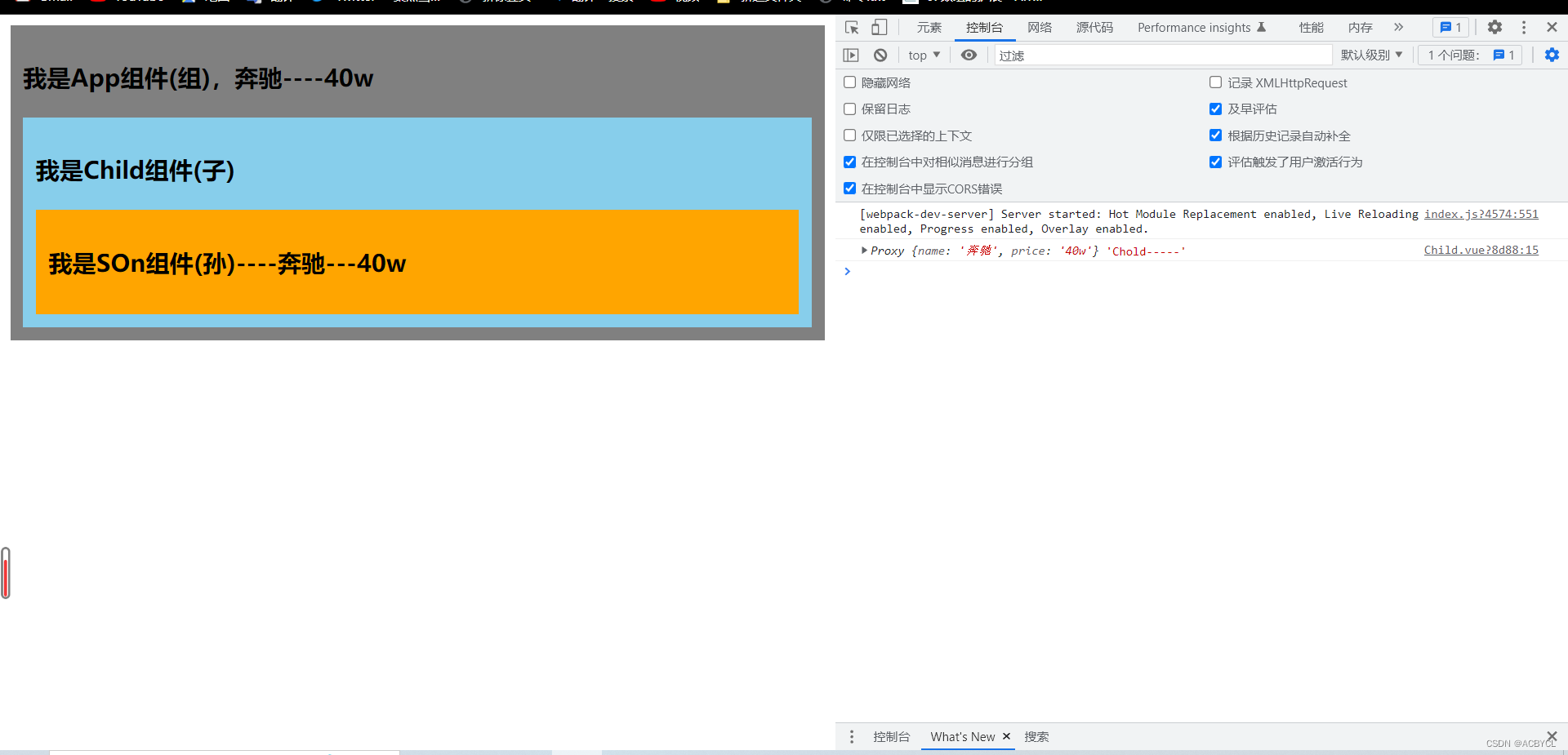
总结:
1.只要app.vue 通过provided一下,他的任意子组件都可以用,哪怕是跨级
2.inject:注入
3.用于组件间通信
6.响应式数据的判断

app.vue
<template>
<h3>我是App组件(祖)</h3>
</template>
<script>
import { isProxy, isReactive, isReadonly, isRef, reactive, readonly, toRefs ,ref} from '@vue/reactivity'
export default {
components: {},
setup(){
let car=reactive({name:'奔驰',price:'40w'})
let sum=ref(0)
let car2=readonly(car)
console.log(isRef(sum))
console.log(isReactive(car))
console.log(isReadonly(car2))
console.log(isProxy(car))
console.log(isProxy(sum)) //false
return{
...toRefs(car)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
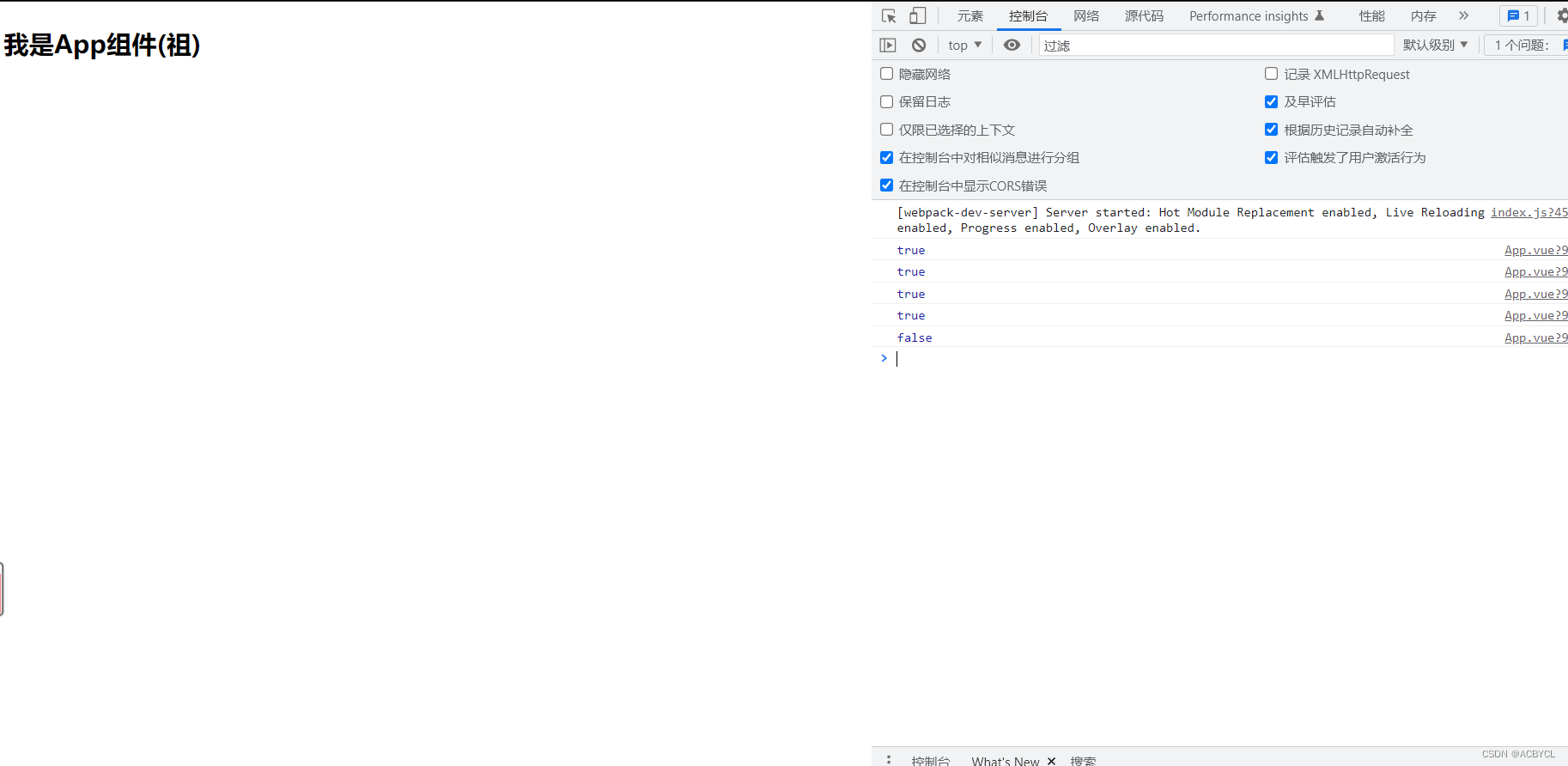
总结:
1.ref底层用的是底层Object.defined
2.readonly处理了响应式数据,但返回的还是proxy,而不是Object
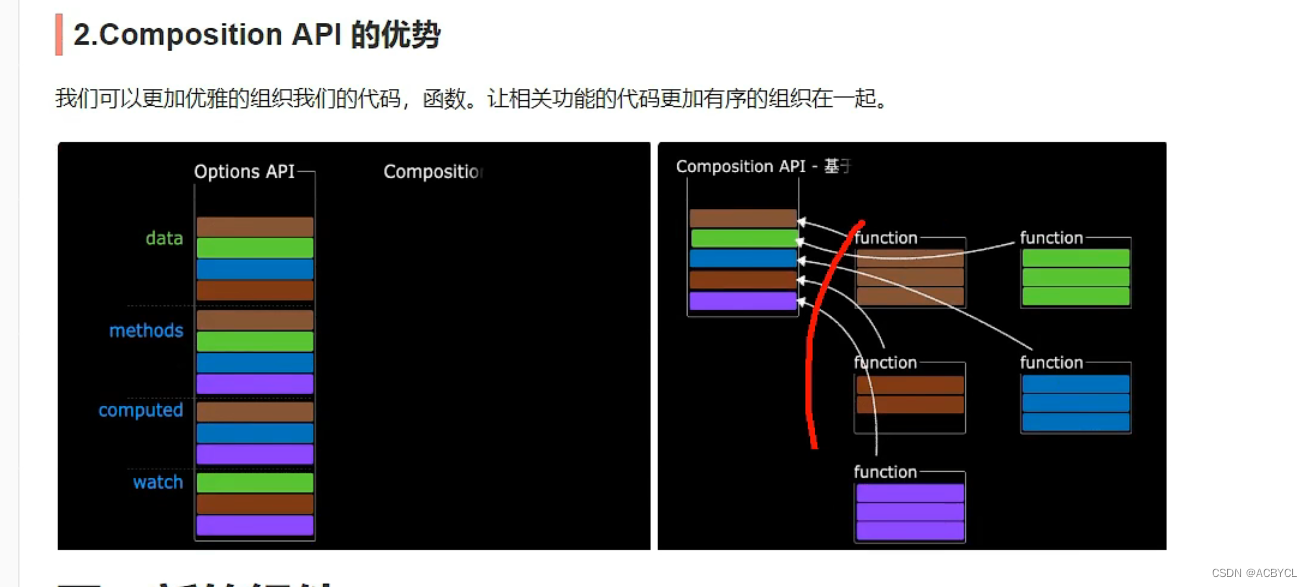
四.Composition API的优势

五.新组件
1.Fragment
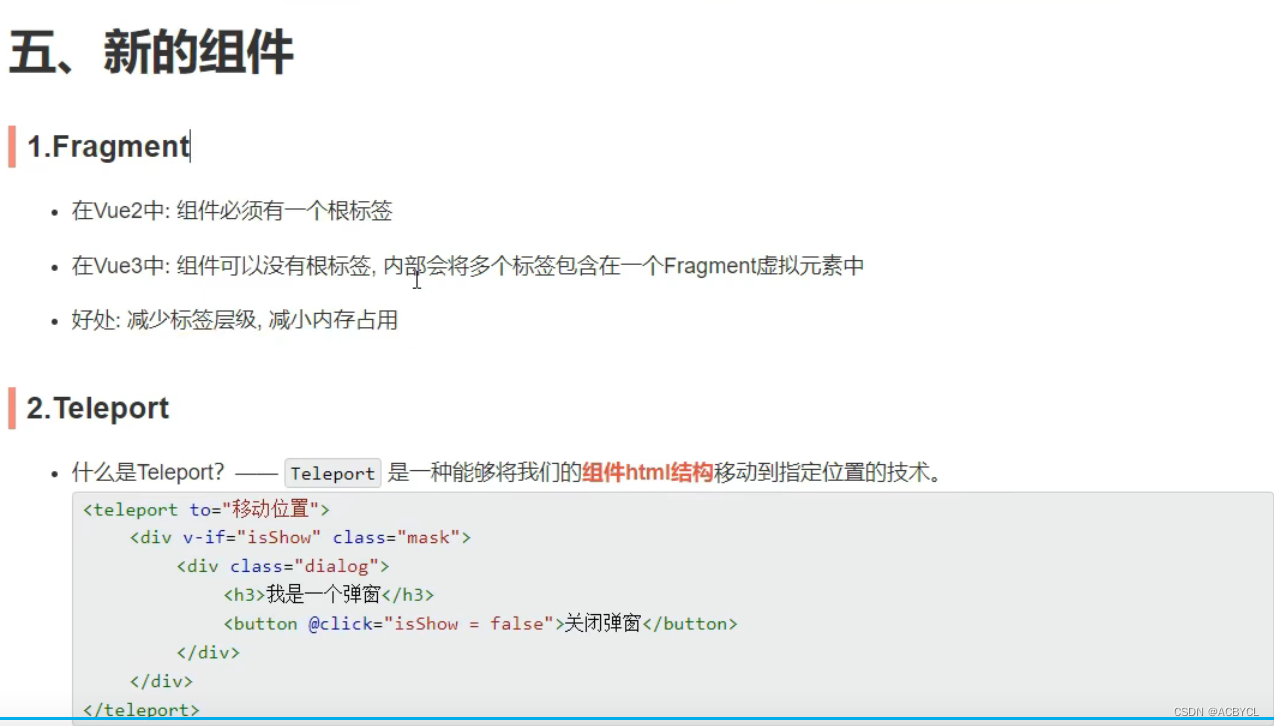
2.Teleport
app.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>我是App组件</h3>
<Child></Child>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child from "./components/Child.vue";
export default {
components: { Child },
setup(){
}
}
</script>
<style>
.app{
background-color: gray;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
Child.vue
<template>
<div class="child">
<h3>我是Child组件</h3>
<Son></Son>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Son from "./Son.vue";
export default {
components: { Son }
}
</script>
<style>
.child{
background-color: skyblue;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
Son.vue
<template>
<div class="son">
<h3>我是Son组件</h3>
<Dialong></Dialong>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Dialong from './Dialong.vue';
export default {
components: { Dialong }
}
</script>
<style>
.son{
background-color: orange;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
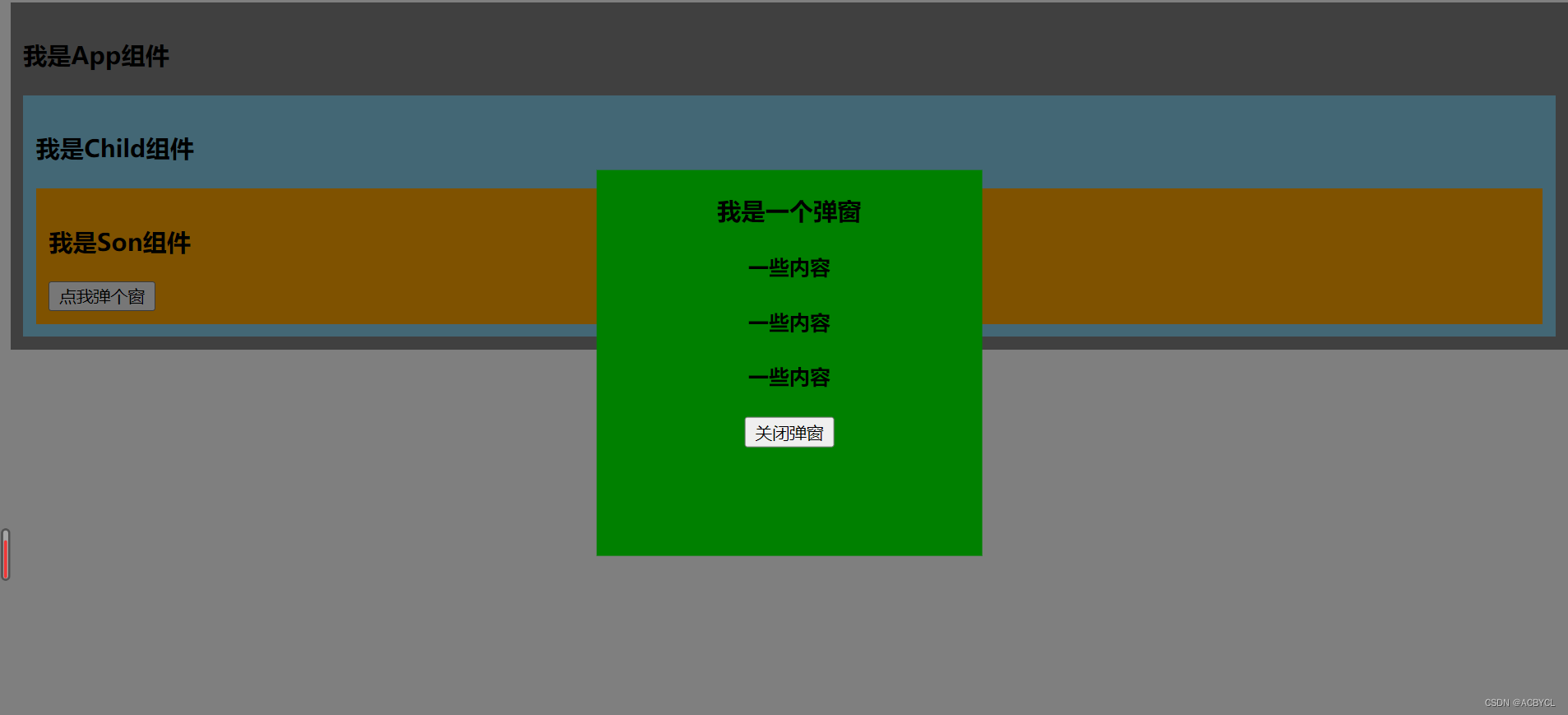
Dialong.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow=true">点我弹个窗</button>
<teleport to="body">
<div class="mask" v-if="isShow">
<div class="dialog">
<h3>我是一个弹窗</h3>
<h4>一些内容</h4>
<h4>一些内容</h4>
<h4>一些内容</h4>
<button @click="isShow=false">关闭弹窗</button>
</div>
</div>
</teleport>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref} from 'vue'
export default {
setup(){
let isShow=ref(false)
return {
isShow
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.mask{
position: absolute;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
}
.dialog{
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
text-align: center;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: green;
}
</style>
执行结果
3.Suspense–异步
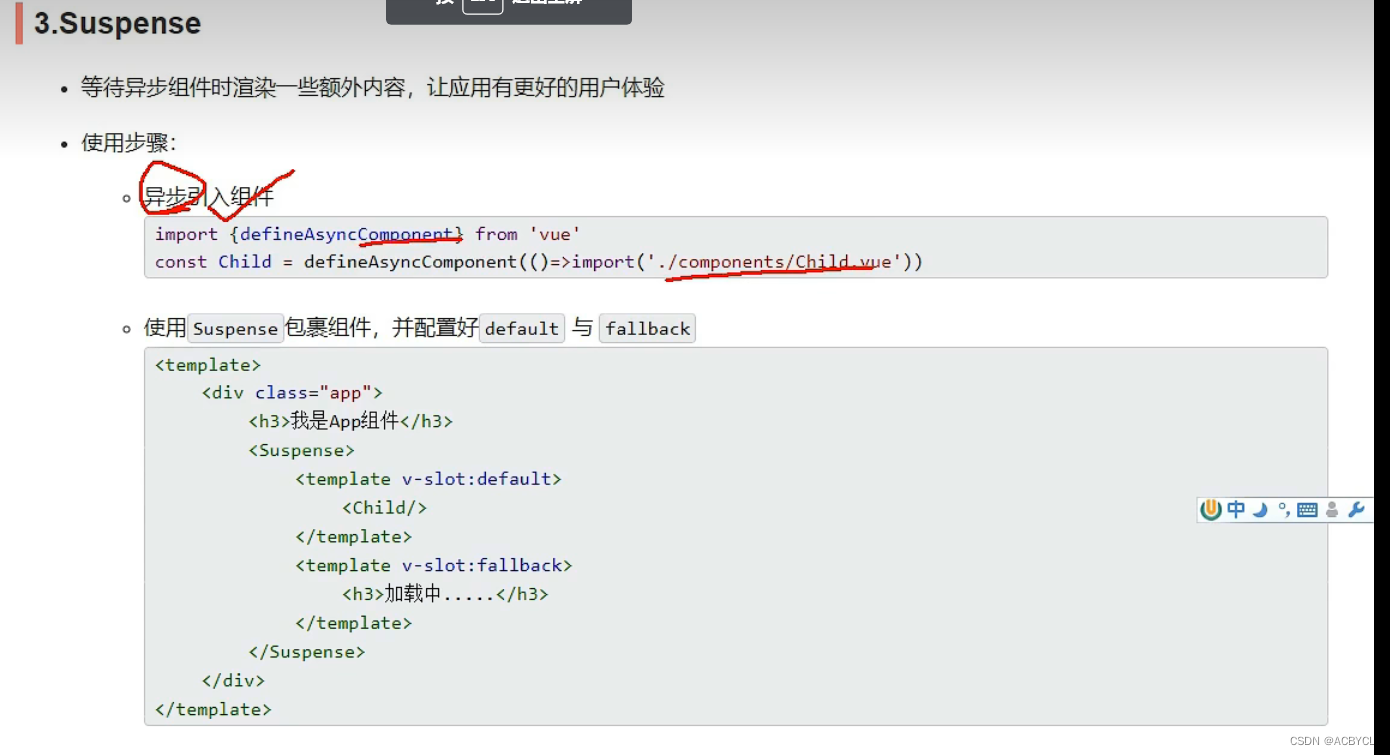
app.vue
<template>
<div class="app">
<h3>我是App组件</h3>
<Suspense>
<template v-slot:default>
<Child></Child>
</template>
<template v-slot:fallback>
<h3>稍等,加载中...</h3>
</template>
</Suspense>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import Child from "./components/Child.vue";//静态引入
import { defineAsyncComponent } from "vue";
const Child=defineAsyncComponent(()=>import('./components/Child'))//异步引入
export default {
components: { Child },
setup(){
}
}
</script>
<style>
.app{
background-color: gray;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
Child.vue
<template>
<div class="child">
<h3>我是Child组件</h3>
{{sum}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
export default {
components: {},
async setup(){
let sum=ref(0)
let p=new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve({sum})
},3000)
})
return await p
}
}
</script>
<style>
.child{
background-color: skyblue;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
执行结果
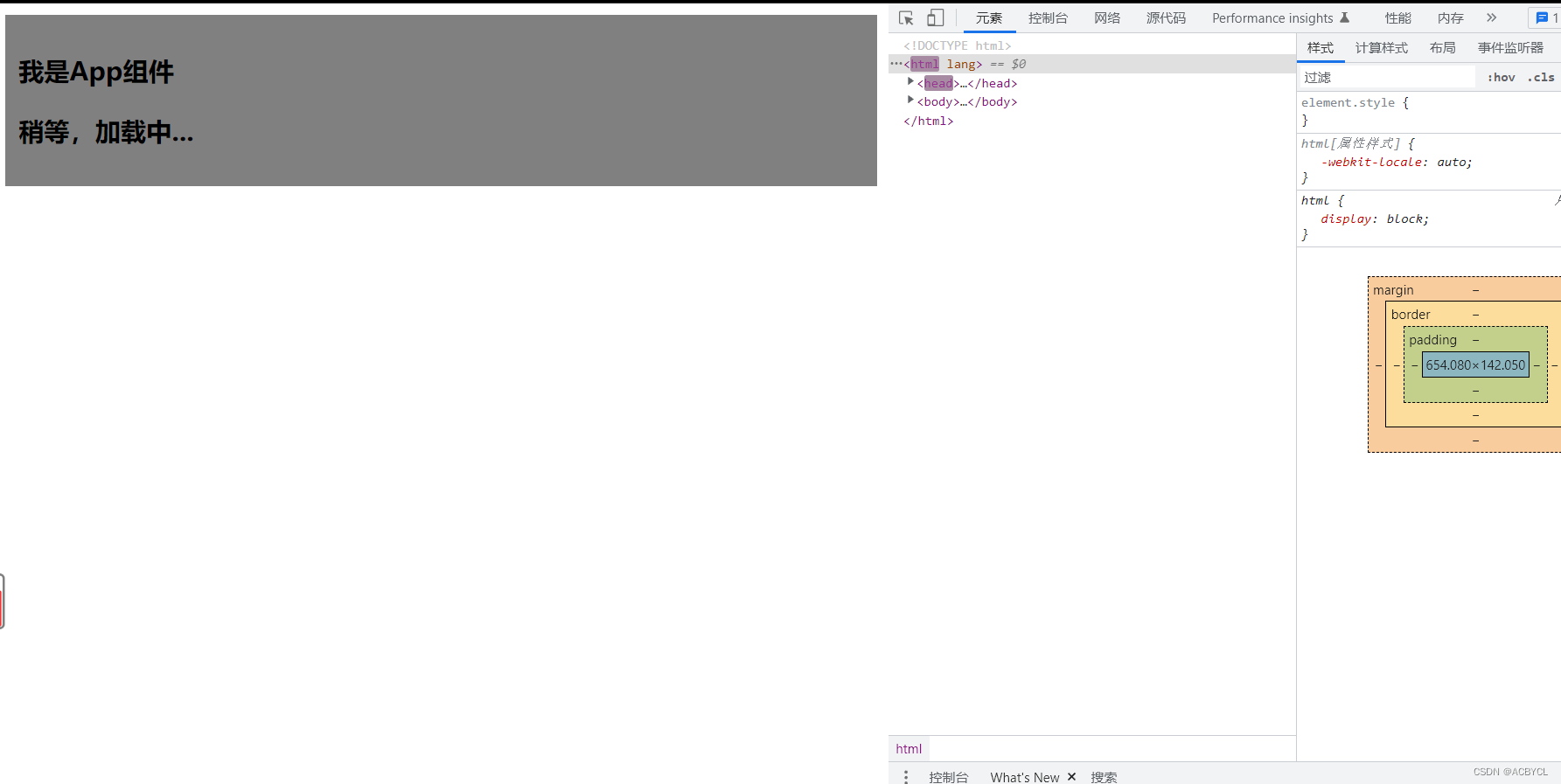
总结:
1.Suspense里面有两个插槽,第一个:要放置加载慢的插槽。第二个:应急插槽-先加载快的
2.子组件的setup不返回数,主页面就不加载更新
六.其他
1.全局API的转移


2.其他改变