前言
距离上一次的某乎jsvmp也过了好一段时间,现在也从2.0的版本升级到了3.0的版本
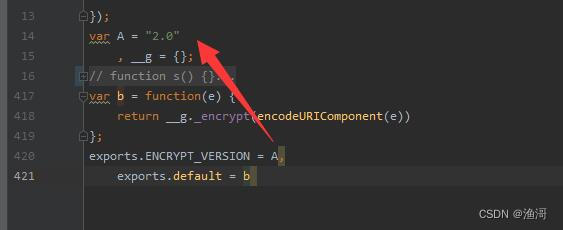
自然的,算法也就发生了一些改变。最明显最直接可见的变化就是长度边长了,并且相同的入参,输出结果并不相同。那么这篇文章就在原来2.0的基础上【JS逆向系列】某乎x96参数与jsvmp初体验,来分析一下3.0版本变难了多少,算法又要怎么还原出来。
初看js代码
至于参数如何查找这篇文章就跳过了,相关内容可以查看前一篇,这篇从【__g._encrypt】开始。两个版本的入口是相同的,都是从【__g._encrypt】进入到jsvmp内部代码,入参也都是一个md5结果的16进制字符串。
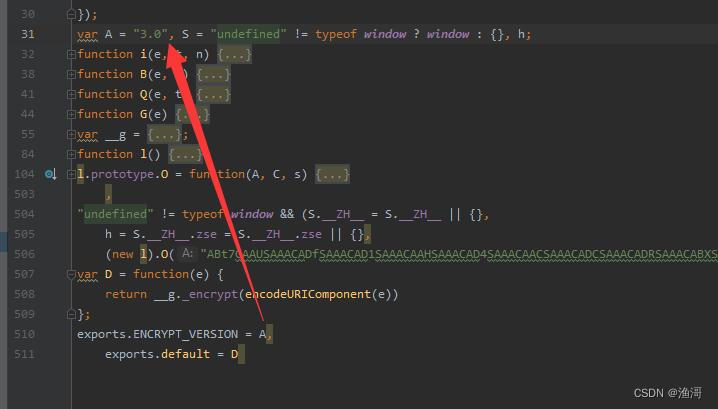
某乎的jsvmp与其他的略有不同,一般的jsvmp是堆栈式的,而某乎的这个是寄存器式的。也是也之前一样,是有vm的初始化,这次3.0的对象是【l】对象
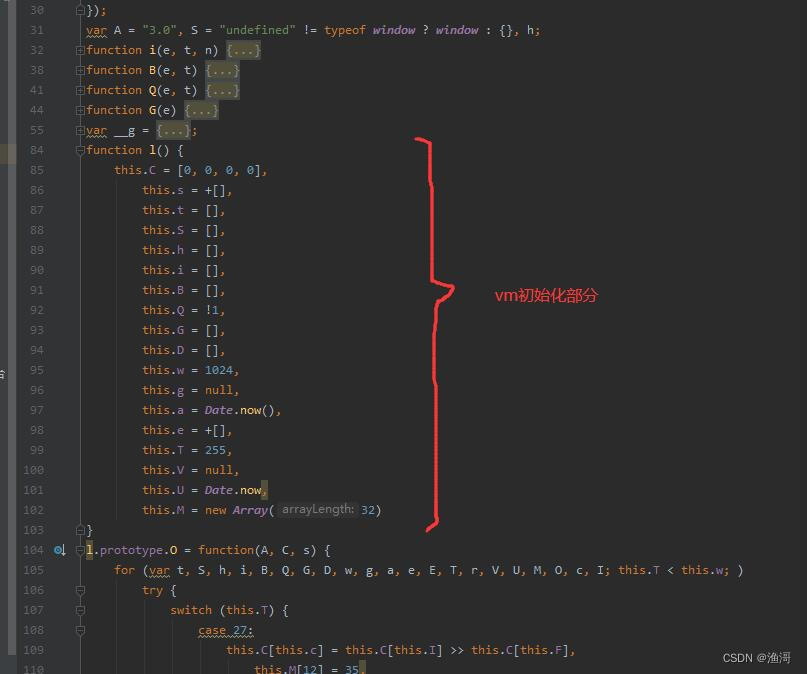
结构上和之前还是很想的,不过多了不少参数,有几个关键的参数需要注意
| 参数 | 映射含义 |
|---|---|
| this.c | 通用寄存器 |
| this.s | pc寄存器 |
| this.S | 栈帧 |
| this.i | 数组缓存 |
| this.Q | 跳转标志位 |
| this.G | 操作码数组 |
| this.D | 字符串数组 |
| this.w | 控制流出口 |
| this.g | 异常跳转 |
| this.a | 时间检测参数 |
| this.e | 3字节操作码 |
| this.T | 控制流入口 |
| this.U | 时间检测参数 |
| this.M | 常量虚假指令 |
以上的仅仅是我个人的理解,不一定正确,仅供参考。
补环境方案
还是和之前一样,首先试试能不能通过补环境得出相同的结果,首先在网页上拿一组样本。

这里入参是【a63da42088bd8d635961ede065daeb51】结果是【RiO+y9AqW9KuaS+8vShliRMUs8LvryJRSxJinhVvmy+JvR5Xel5Uv5psmxAcilNl】,按照之前的办法,就是补环境使得到相同的结果,但是对于3.0版本就会出现问题。这里发现,相同的入参,多次执行,结果是不一样的。

这就不好办了,那么即使补环境出来的结果,也不知道是不是对的。一般这种情况下,就是计算涉及到的随机数或者时间。而这里就是包含的随机数,所以需要hook随机数的返回
Math.random = function(){
return 0.50
};
输入这段代码后再执行加密函数,此时就发现结果都是一样的了
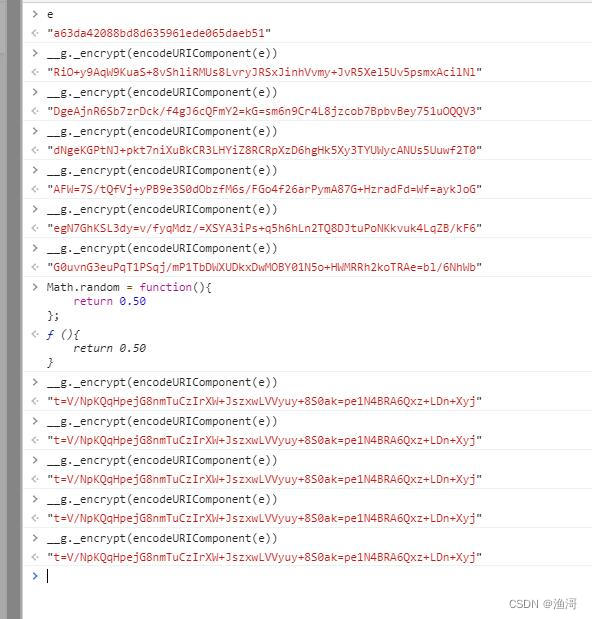
那么此时就得到了一组样本,当随机数恒定返回0.5时。入参【a63da42088bd8d635961ede065daeb51】的正确结果为【t=V/NpKQqHpejG8nmTuCzIrXW+JszxwLVVyuy+8S0ak=pe1N4BRA6Qxz+LDn+Xyj】,那么接下在就真正可以开始补环境了。
首先安装依赖库
npm install jsdom
npm install canvas
然后在头部加上jsdom的代码
const{JSDOM}=require("jsdom");
const dom=new JSDOM("<!DOCTYPE html><p>Hello world</p>");
window=dom.window;
Math.random = function(){
return 0.50
};
结尾加上测试代码
console.log(D('a63da42088bd8d635961ede065daeb51'));
console.log('t=V/NpKQqHpejG8nmTuCzIrXW+JszxwLVVyuy+8S0ak=pe1N4BRA6Qxz+LDn+Xyj');
开始测试运行
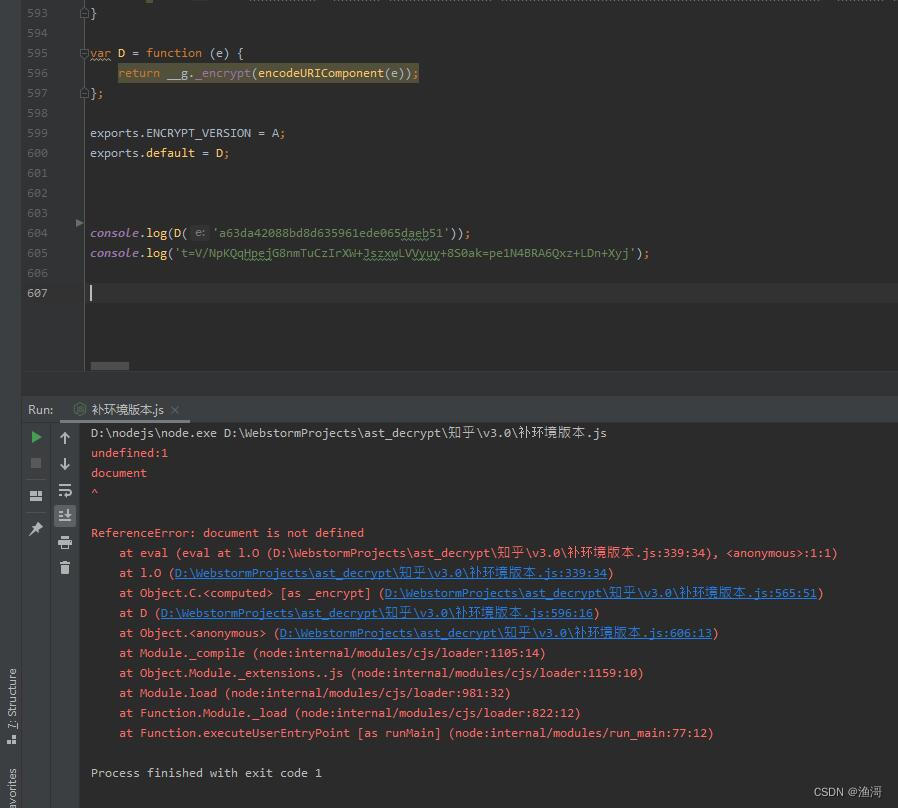
提示缺少【document】,那么就加上这个定义
document=window.document;
继续运行,后面还有类似的报错,继续补全。
最后头部为
const{JSDOM}=require("jsdom");
const dom=new JSDOM("<!DOCTYPE html><p>Hello world</p>");
window=dom.window;
document=window.document;
navigator=window.navigator;
location=window.location;
history=window.history;
screen=window.screen;
Math.random = function(){
return 0.50
};
测试可以运行出结果
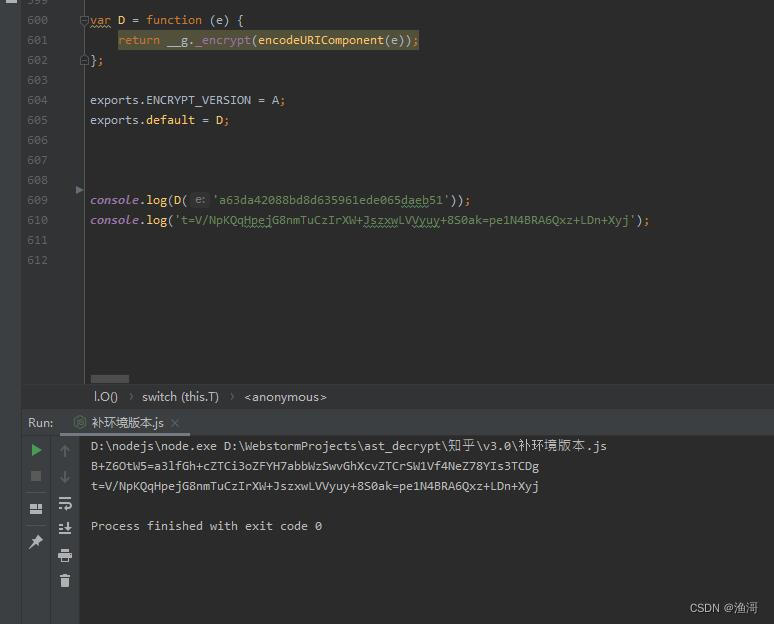
这个结果和样本明显不一样,说明还缺少了其他环境没有补到。
那么接下来就得对前面的环境变量上代理,看看还用到了什么属性和方法
window = new Proxy(window, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set window", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get window", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
document = new Proxy(document, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set document", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get document", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
navigator = new Proxy(navigator, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set navigator", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get navigator", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
location = new Proxy(location, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set location", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get location", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
history = new Proxy(history, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set history", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get history", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
screen = new Proxy(screen, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set screen", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get screen", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
同时,整个大逻辑被一个try代码块包裹着
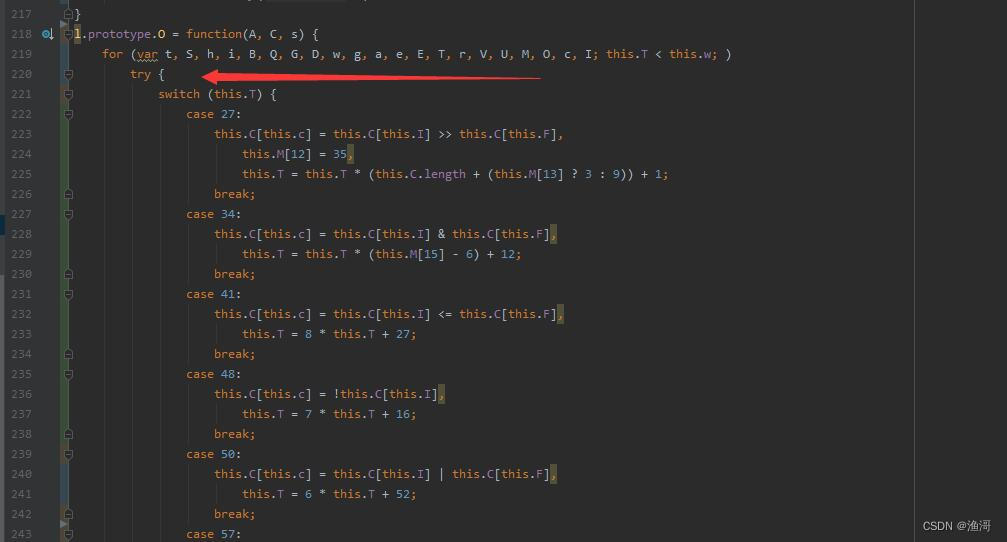
那么如果报错的话,我们也看不到,不方便补环境,所以去掉try代码块,只保留try里面的内容。
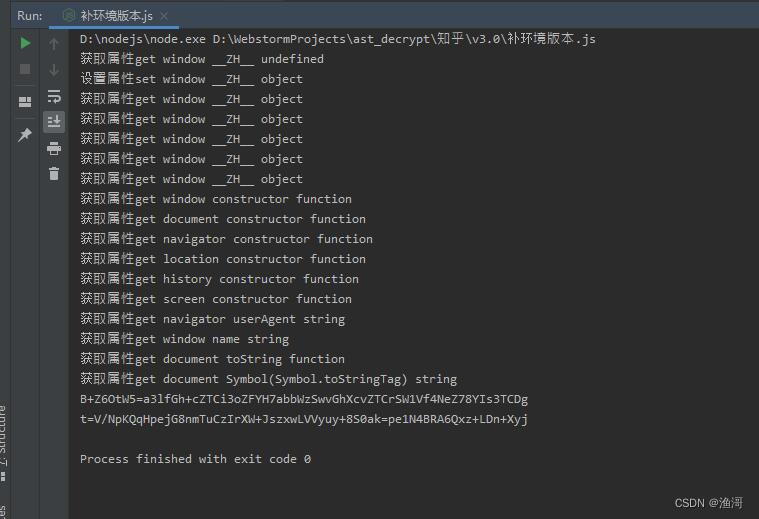
可以看到读取了不少属性,最后运行到【获取属性get document Symbol(Symbol.toStringTag) string】这一步就退出了,那么看看这一步的结果是不是和网页不一样
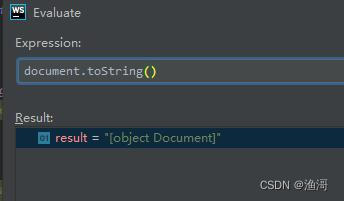
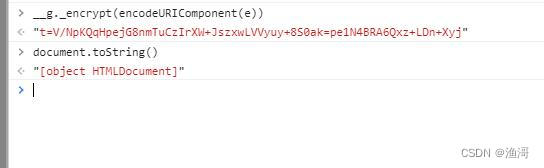
确实是不一样的结果,所以这里就需要hook掉toString方法
var Object_toString = Object.prototype.toString;
Object.prototype.toString = function () {
let _temp = Object_toString.call(this, arguments);
console.log(this);
console.log("Object.prototype.toString: " + _temp);
if(this.constructor.name === 'Document'){
return '[object HTMLDocument]';
}
return _temp;
};
再次运行后,日志内容比之前更加长了,说明补的内容有效了,同时得到的加密结果也不一样了
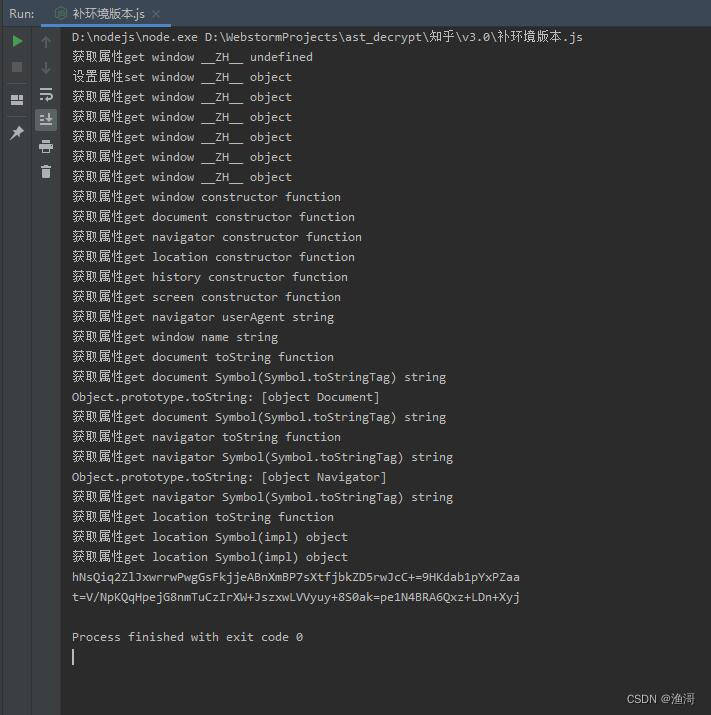
这里最后是location对象出现问题,那么在jsdom上面,就需要补上url链接,那么就会自动补全location对象,开头部分的代码就修改为
const{JSDOM}=require("jsdom");
const dom=new JSDOM("<!DOCTYPE html><p>Hello world</p>",{url:'https://www.zhihu.com/search'});
window=dom.window;
document=window.document;
navigator=window.navigator;
location=window.location;
history=window.history;
screen=window.screen;
Math.random = function(){
return 0.50
};

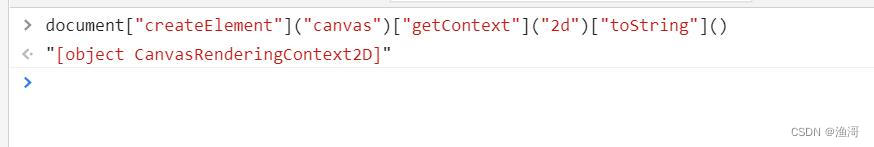
这里canvas和网页返回的不一样,继续补上
var Object_toString = Object.prototype.toString;
Object.prototype.toString = function () {
let _temp = Object_toString.call(this, arguments);
console.log(this);
console.log("Object.prototype.toString: " + _temp);
if(this.constructor.name === 'Document'){
return '[object HTMLDocument]';
}else if(this.constructor.name === 'CanvasRenderingContext2D'){
return '[object CanvasRenderingContext2D]'
}
return _temp;
};

又继续往下跑了,这次是检测了window下的_resourceLoader,浏览器上是undefined,但是node上返回对象。还有后面的_sessionHistory,一起补上。
const{JSDOM}=require("jsdom");
const dom=new JSDOM("<!DOCTYPE html><p>Hello world</p>",{url:'https://www.zhihu.com/search'});
window=dom.window;
document=window.document;
navigator=window.navigator;
location=window.location;
history=window.history;
screen=window.screen;
window._resourceLoader = undefined;
window._sessionHistory = undefined;
Math.random = function(){
return 0.50
};
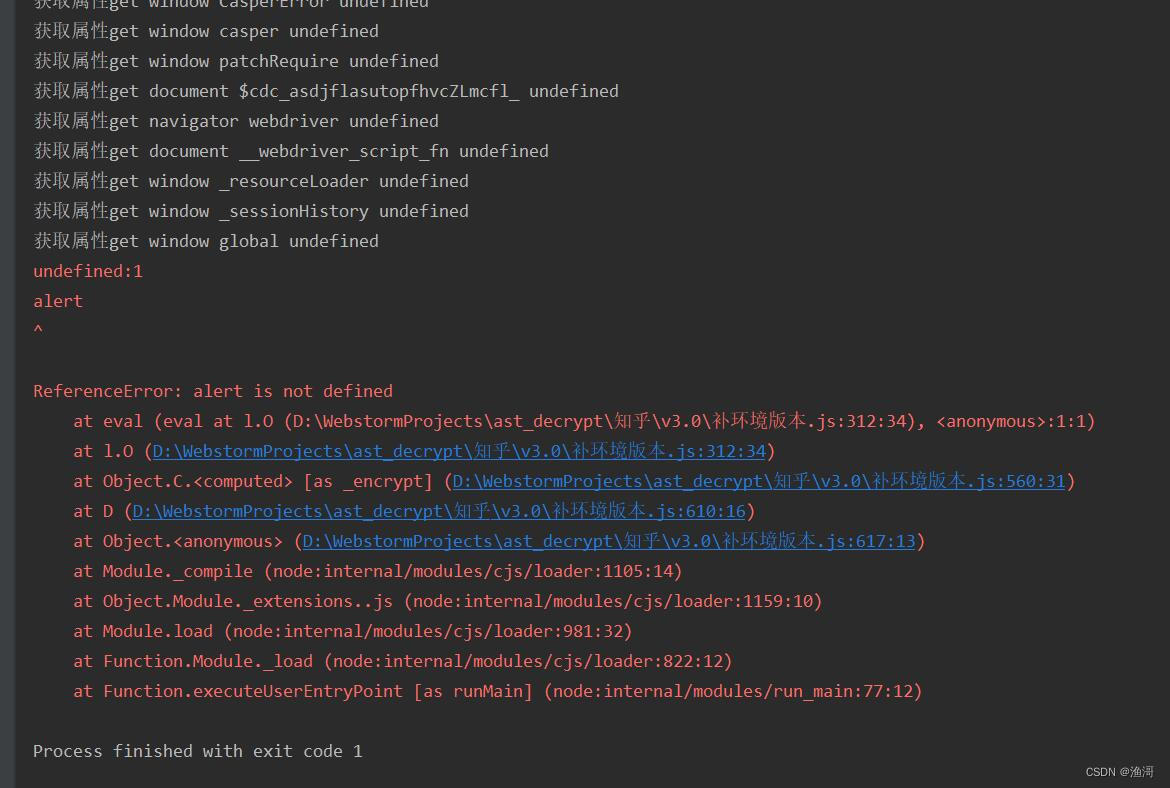
出现alert未定义,和之前一样处理
const{JSDOM}=require("jsdom");
const dom=new JSDOM("<!DOCTYPE html><p>Hello world</p>",{url:'https://www.zhihu.com/search'});
window=dom.window;
document=window.document;
navigator=window.navigator;
location=window.location;
history=window.history;
screen=window.screen;
alert=window.alert;
window._resourceLoader = undefined;
window._sessionHistory = undefined;
Math.random = function(){
return 0.50
};
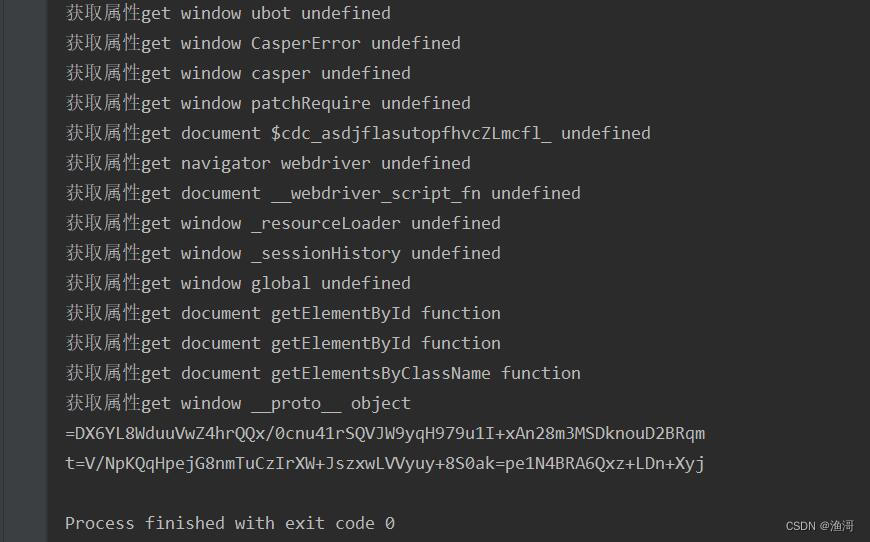
结果还是不一样,并且获取了window的原型后就没有了,那么这种情况很有可能检测了原型链和函数或者tostring,那么hook一下看看
var Function_toString = Function.prototype.toString;
Function.prototype.toString = function () {
let _temp = Function_toString.call(this, arguments);
console.log(this);
console.log("Function.prototype.toString: " + _temp);
return _temp;
};
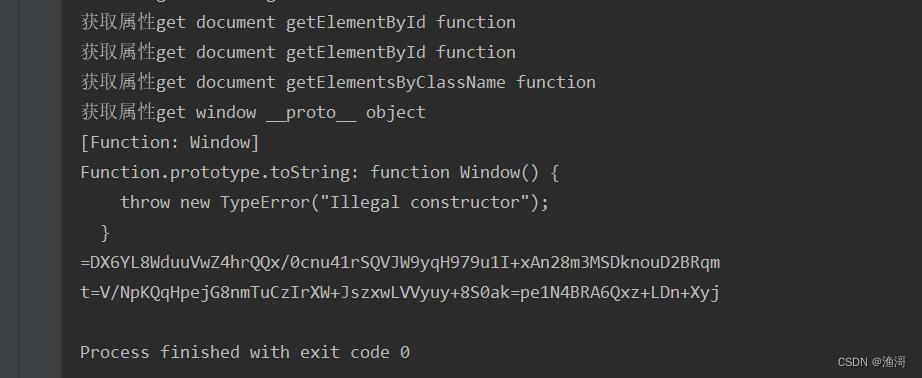
果然是,那么继续补上
var Function_toString = Function.prototype.toString;
Function.prototype.toString = function () {
let _temp = Function_toString.call(this, arguments);
console.log(this);
console.log("Function.prototype.toString: " + _temp);
if(this.name === 'Window'){
return 'function Window() { [native code] }'
}
return _temp;
};

漂亮,终于得到一样的结果,那么这里补环境就完成了,总结一下我们补了什么
const{JSDOM}=require("jsdom");
const dom=new JSDOM("<!DOCTYPE html><p>Hello world</p>",{url:'https://www.zhihu.com/search'});
window=dom.window;
document=window.document;
navigator=window.navigator;
location=window.location;
history=window.history;
screen=window.screen;
alert=window.alert;
window._resourceLoader = undefined;
window._sessionHistory = undefined;
Math.random = function(){
return 0.50
};
window = new Proxy(window, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set window", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get window", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
document = new Proxy(document, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set document", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get document", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
navigator = new Proxy(navigator, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set navigator", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get navigator", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
location = new Proxy(location, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set location", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get location", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
history = new Proxy(history, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set history", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get history", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
screen = new Proxy(screen, {
set(target, property, value, receiver) {
console.log("设置属性set screen", property, typeof value);
return Reflect.set(...arguments);
},
get(target, property, receiver) {
console.log("获取属性get screen", property, typeof target[property]);
return target[property]
}
});
var Object_toString = Object.prototype.toString;
Object.prototype.toString = function () {
let _temp = Object_toString.call(this, arguments);
console.log(this);
console.log("Object.prototype.toString: " + _temp);
if(this.constructor.name === 'Document'){
return '[object HTMLDocument]';
}else if(this.constructor.name === 'CanvasRenderingContext2D'){
return '[object CanvasRenderingContext2D]'
}
return _temp;
};
var Function_toString = Function.prototype.toString;
Function.prototype.toString = function () {
let _temp = Function_toString.call(this, arguments);
console.log(this);
console.log("Function.prototype.toString: " + _temp);
if(this.name === 'Window'){
return 'function Window() { [native code] }'
}
return _temp;
};
当需要运行的时候,可以把代码部分的代码注释掉,因为这部分只是方便我们查看以及补环境,不影响最终的结果
修改字节码方案(反混淆与反汇编)
在修改字节码之前,要么需要详细分析字节码的逻辑,又或者反汇编字节码到类似js代码的方式。再来看能不能通过修改字节码的方案来绕过环境检测。
例如之前2.0部分的代码,是先进行环境检测,检测完成后才进行真正的加密,所以才可以修改字节码,使得它跳过了环境检测的部分,直接开始核心的加密函数。如果3.0也是沿用之前的逻辑,先进行了检测再加密,那么这种方案就是可行的。
但是3.0没有办法直接进行反汇编,因为相对于2.0的代码来说,增加了控制流的代码,那么最好是先尝试还原了控制流,再做后续处理。
(首先是 按照前面说的去掉try代码块)
首先肯定是处理反调试,3.0也是有时间检测,但是时间检测被放到了jsvmp内部了,不好直接干掉,那么就把初始化里面关于时间的都干掉
// 删除时间参数
traverse(ast, {
SwitchCase(path){
if(path.node.test){
if(path.node.test.value === 300){
path.node.consequent.splice(0, 1)
}else if(path.node.test.value === 360){
path.node.consequent.splice(0, 1)
}else if(path.node.test.value === 368){
path.node.consequent[0].expression.right.test = t.booleanLiteral(false)
}
}
},
FunctionDeclaration(path){
if(path.node.id && path.node.id.name === 'l'){
for (let i = path.node.body.body.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let item = path.node.body.body[i];
if(item.expression.left.property.name === 'a' || item.expression.left.property.name === 'U'){
path.node.body.body.splice(i, 1)
}
}
}
}
});
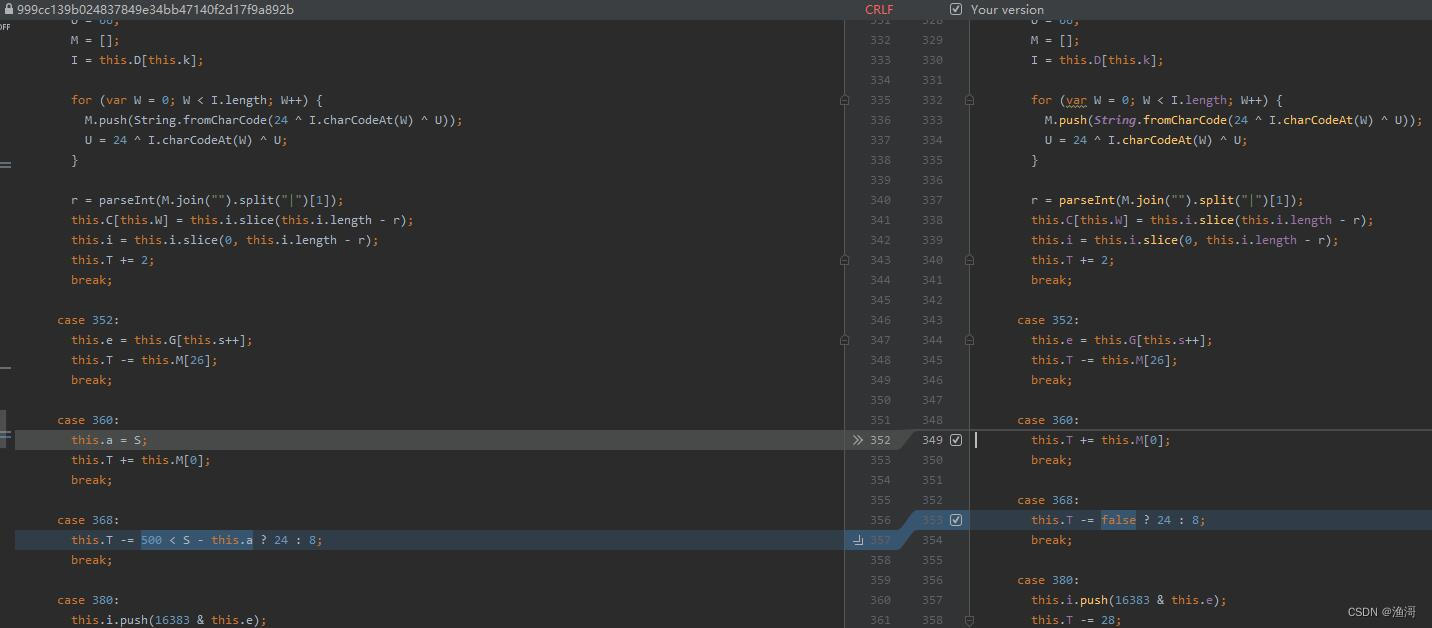
此时再运行,依然可以得到相同的结果,那么就说明这里的时间和2.0是一样,只是用来反调试,与加密逻辑无关。
接下来也不知道怎么入手,那么就来点暴力点的,这么多个case,有没有可能有一些是没有用到的呢?那么在所有的case前面都下一个断点
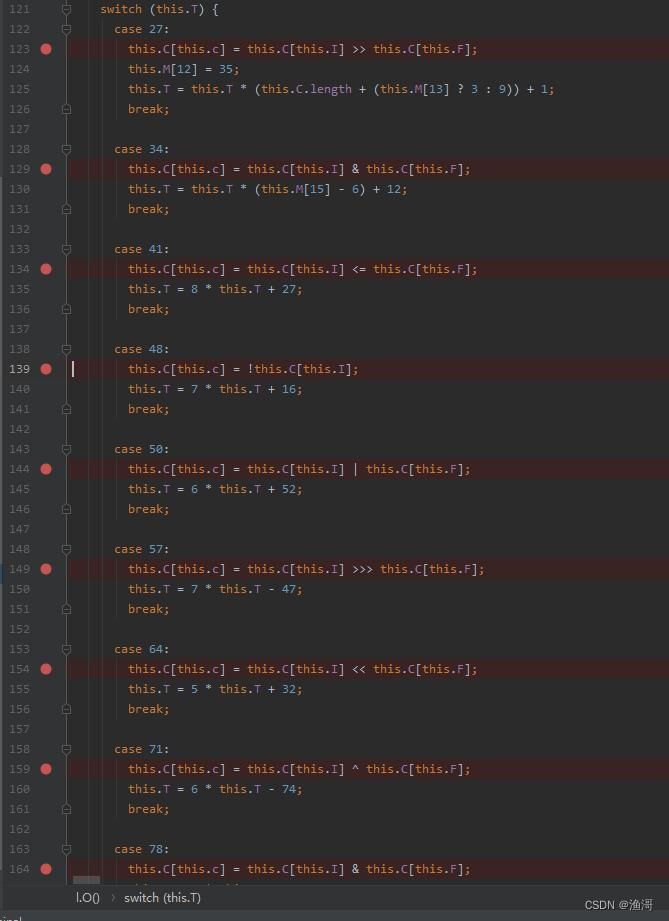
然后调试运行,当在断点停下的时候,取消断点再运行下去,直到结束。那么下载来还有断点的case,就是不会运行到的case了。
let cases_list = [27, 34, 41, 48, 101, 117, 124, 147, 258, 283, 380, 400, 449, 459, 468, 469, 473, 479, 481, 485, 491, 496, 506];
traverse(ast, {
SwitchCase(path){
if(path.node.test){
if(cases_list.includes(path.node.test.value)){
path.remove()
}
}
}
});
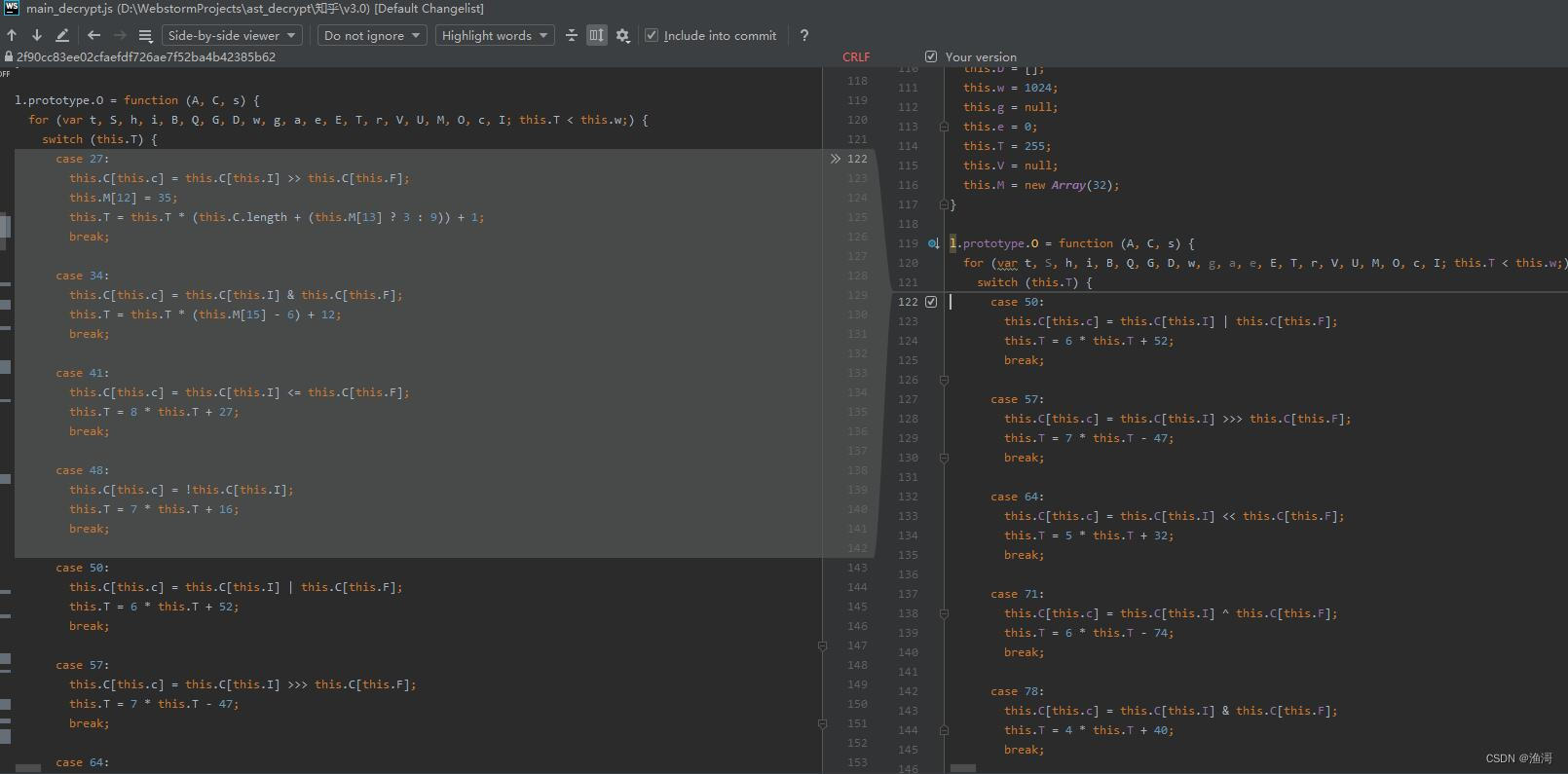
这时删除了多个case后,依然可以得到正确结果。
继续往后调试,会发现一些控制流的分支是虚假分支,也就是在运行的时候,是恒真或者恒假的分支,这种最好是可以将它还原掉,方便后面真实分支的case合并。
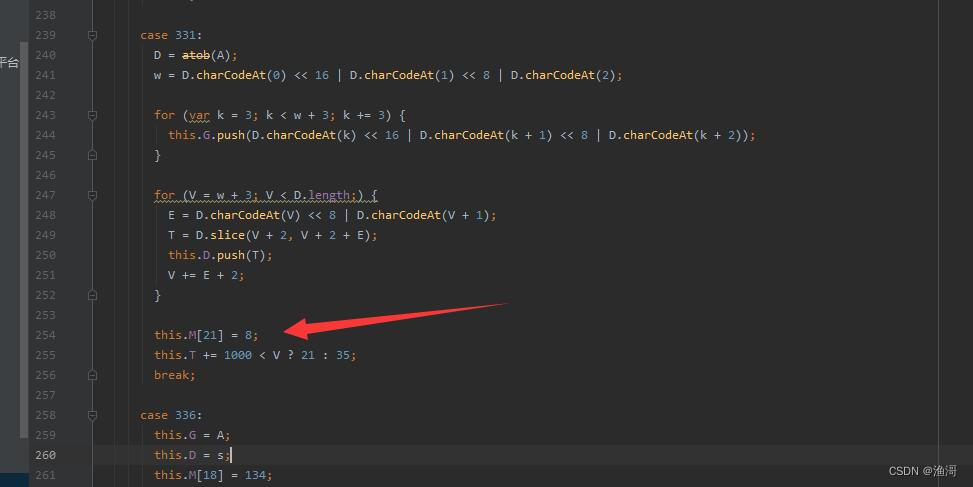
分析发现,例如在case 331中存在赋值的【this.M[21] = 8;】,这里就可以把这个值记录下来,其他任何没有出现赋值的,都是null了
let cases_dict = {};
// 数组虚假分析
traverse(ast, {
MemberExpression(path){
if(path.node.object.type === 'ThisExpression' && path.node.property.type === 'Identifier' && path.node.property.name === 'M' && path.parent.type === 'MemberExpression'){
if(path.parentPath.parent.type === 'AssignmentExpression' && path.parentPath.parent.right.type === 'NumericLiteral'){
cases_dict[path.parentPath.parent.left.property.value] = path.parentPath.parent.right.value;
path.parentPath.parentPath.parentPath.remove()
}
}
}
});
traverse(ast, {
MemberExpression(path){
if(path.node.object.type === 'ThisExpression' && path.node.property.type === 'Identifier' && path.node.property.name === 'M' && path.parent.type === 'MemberExpression'){
if(cases_dict.hasOwnProperty(path.parent.property.value)){
path.parentPath.replaceWith(t.numericLiteral(cases_dict[path.parent.property.value]))
}else{
path.parentPath.replaceWith(t.numericLiteral(0))
}
}
}
});
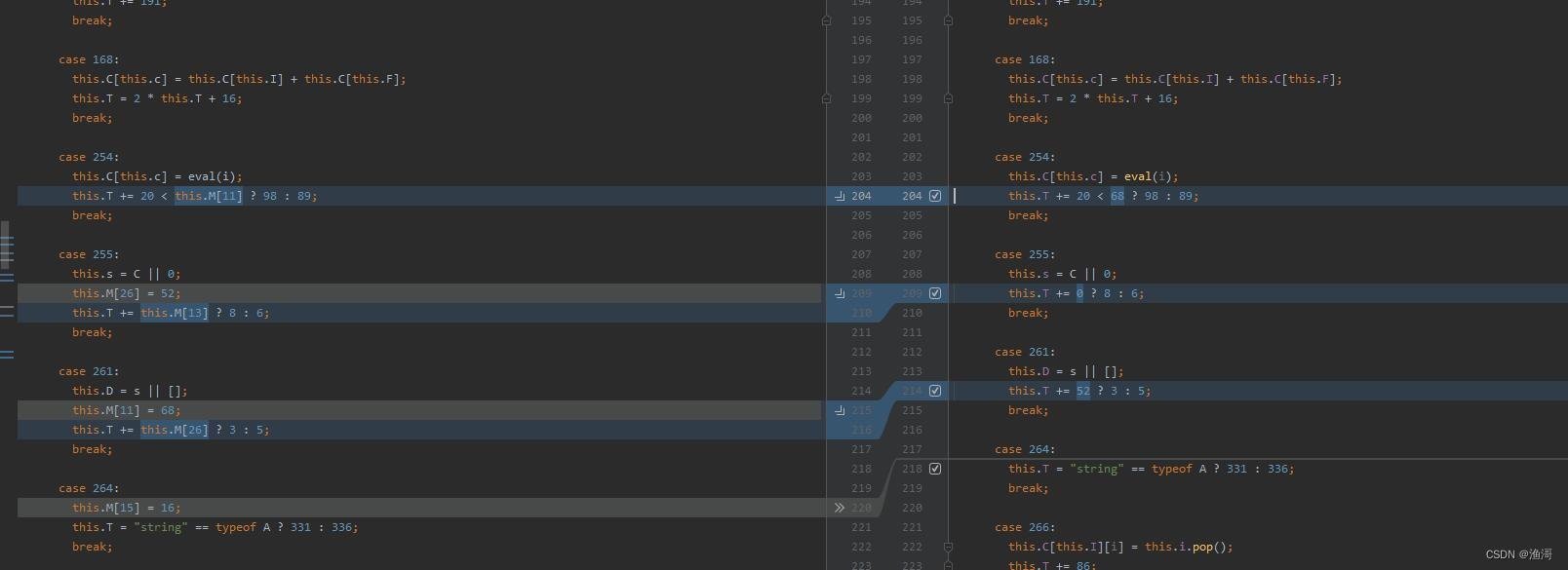
这样就转变成了字面量
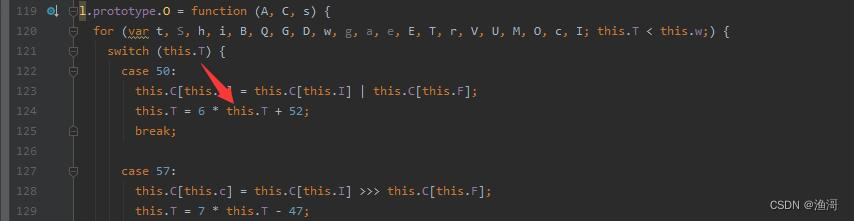
接着例如case 50,下面的this.T实际就是上面的50,像这种也可以还原为字面量
// 还原this.T
traverse(ast, {
SwitchCase(path){
if(path.node.test){
if(path.node.consequent.length > 1 && path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.right.type === 'BinaryExpression'){
let item = path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.right;
if(item.left.type === 'BinaryExpression' && item.left.right.type === 'MemberExpression' && item.left.right.property.type === 'Identifier' && item.left.right.property.name === 'T'){
item.left.right = t.numericLiteral(path.node.test.value);
}
}
}
}
});
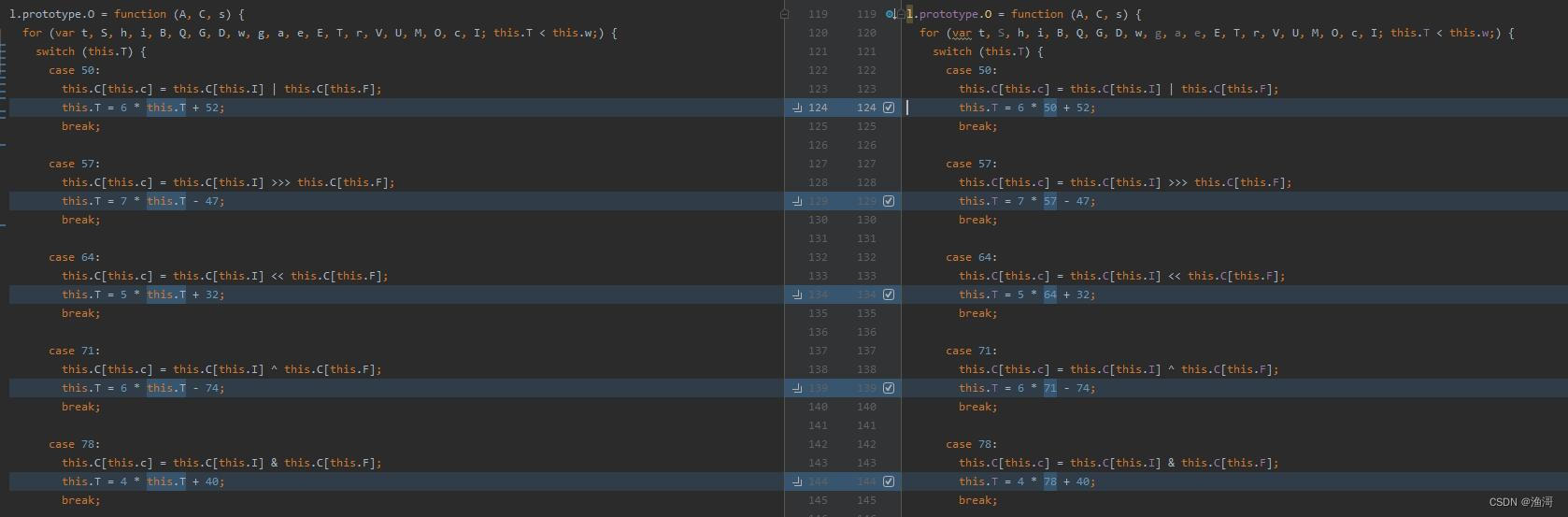
最后是case 331的地方

这里的【V】变量只出现了一次,所以可以进行手动的处理
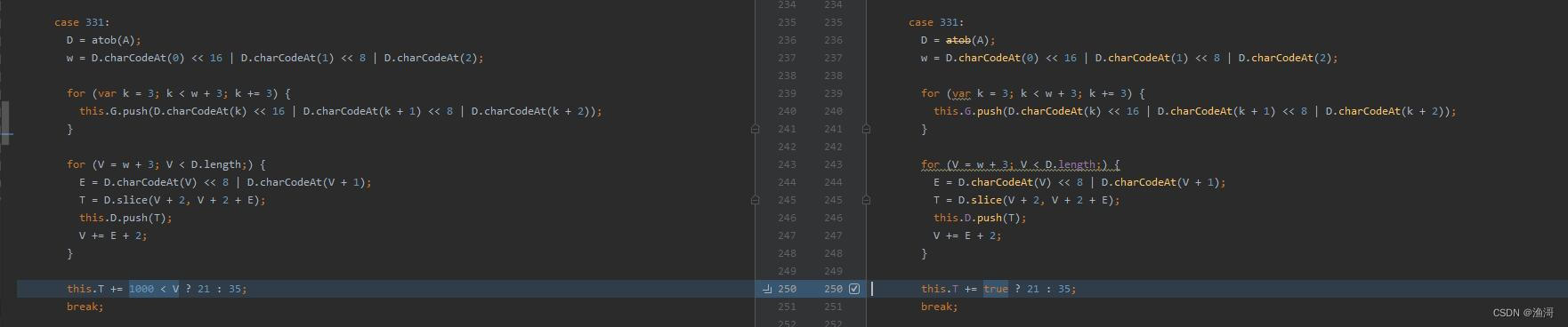
接着再将字面量的内容还原一下

前面会发现很多个都指向了352,那么这个352肯定是一个关键的地方
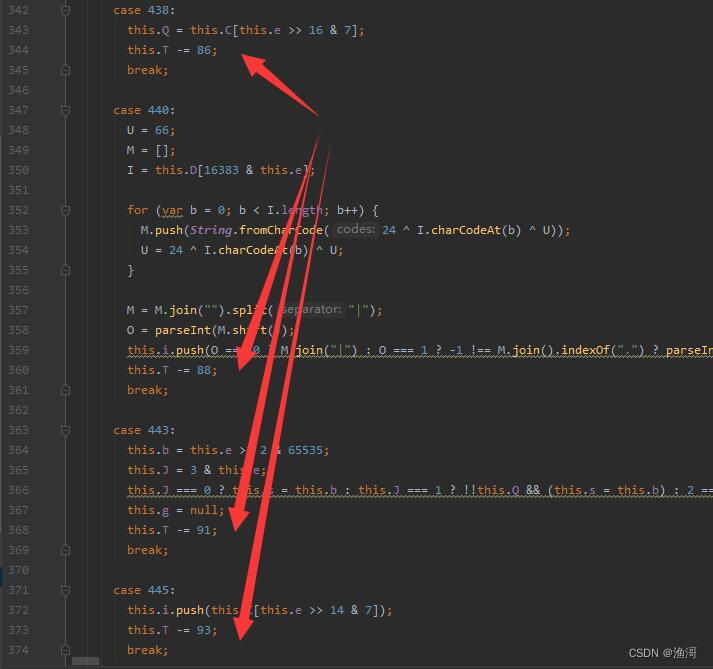
最后还有一些是有【+=】或者【-=】的,这种也可以顺带还原一下
traverse(ast, {
SwitchCase(path){
if(path.node.test){
if(path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.right.type === 'NumericLiteral'){
if(path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.operator === '+='){
path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.operator = '=';
path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.right.value = path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.right.value + path.node.test.value;
}else if(path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.operator === '-='){
path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.operator = '=';
path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.right.value = path.node.test.value - path.node.consequent[path.node.consequent.length - 2].expression.right.value;
}
}
}
}
});
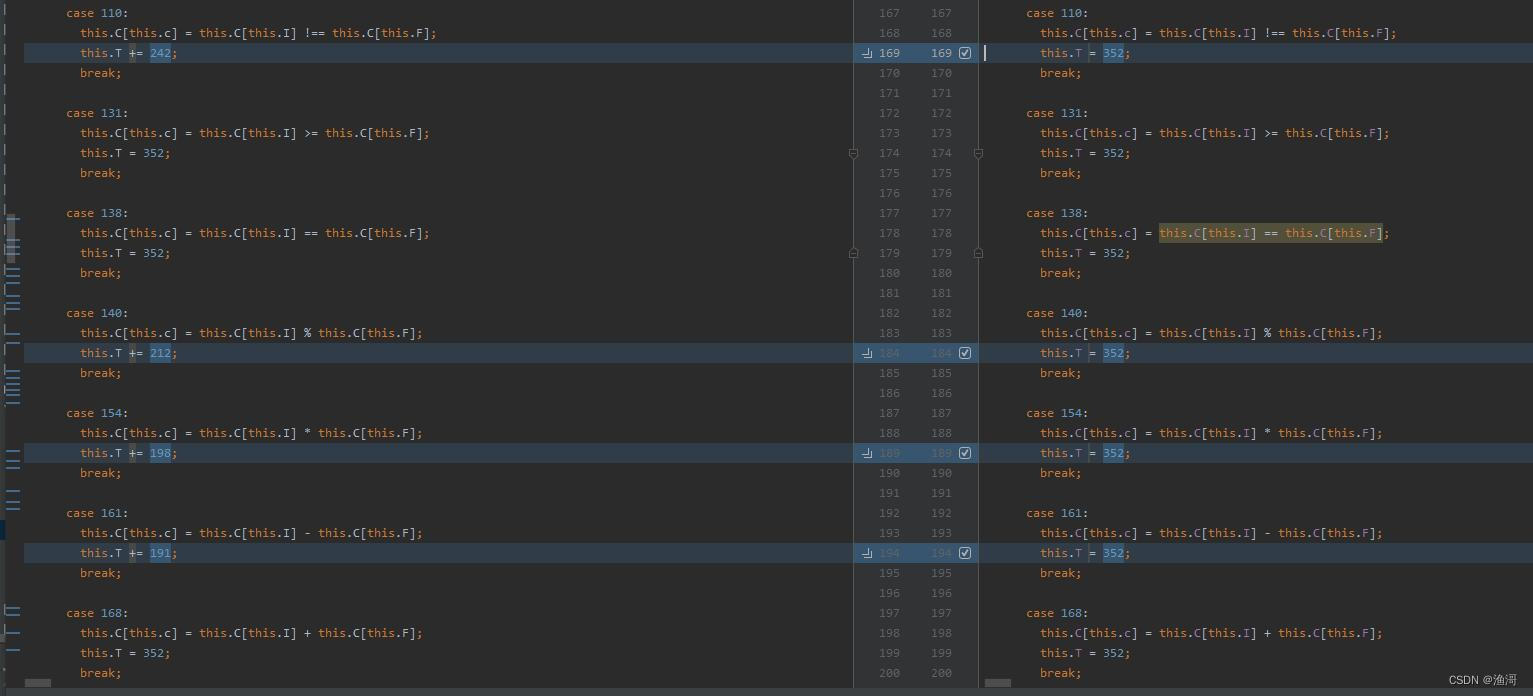
那么来到这里,ast的部分就算完成了。
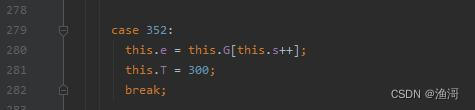
先看看这个case 352,它是指向case 300
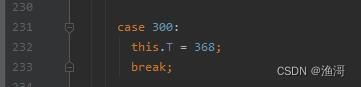
然后case 300,又指向了case 368,那么如下图
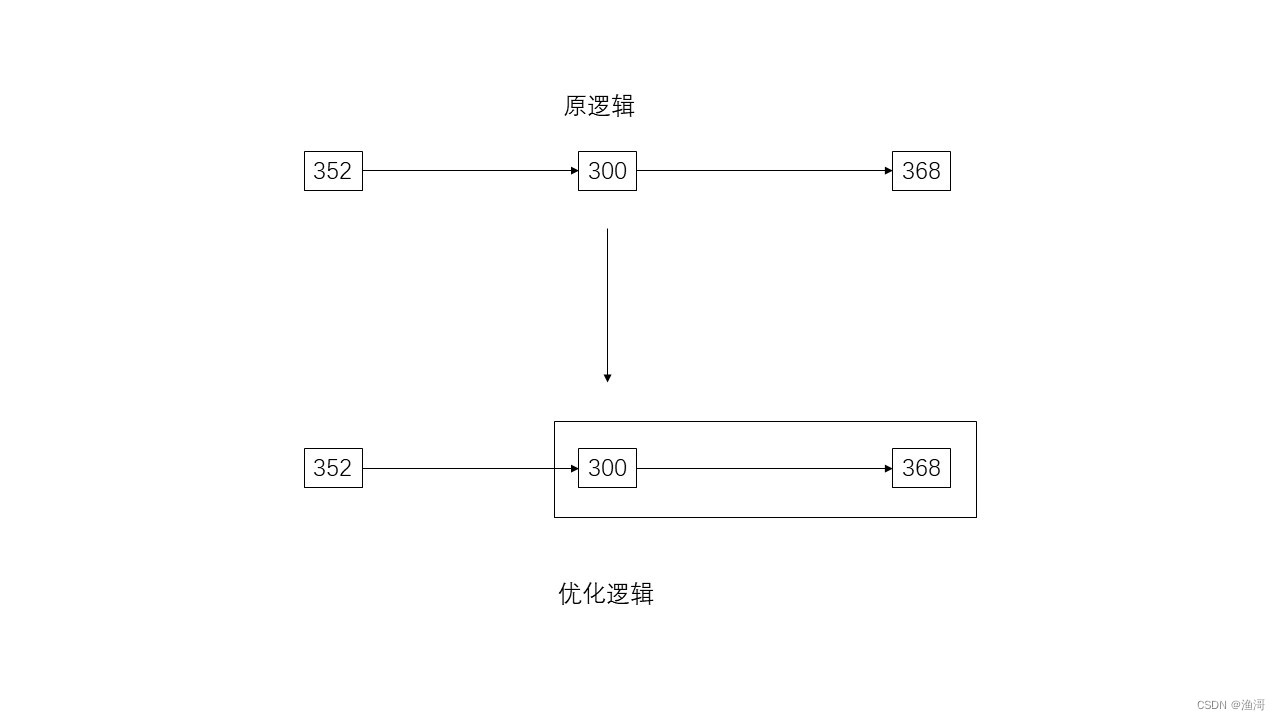
如果把后面的两个节点合并成一个,那么就少了一个节点了,其实相当于把case 368的代码全部放到case 300的下面

换完以后,再次运行一下代码,也能得到相同的结果,那就说明这么修改是没有问题的,没有影响原来的执行流程。
接着就可以开始分析vmp的代码逻辑了。根据之前2.0的经验以及分析,case 331就是解码那段base64字符串到字节码的逻辑
let b64_code = 'ABt7CAAUSAAACADfSAAACAD1SAAACAAHSAAAC......'; //内容太长省略了
let opcode_list = [];
let text_list = [];
function decrypt_text(item){
let U = 66;
let M = [];
for (let b = 0; b < item.length; b++) {
M.push(String.fromCharCode(24 ^ item.charCodeAt(b) ^ U));
U = 24 ^ item.charCodeAt(b) ^ U;
}
return M.join("")
}
(function () {
let D = atob(b64_code);
let w = D.charCodeAt(0) << 16 | D.charCodeAt(1) << 8 | D.charCodeAt(2);
for (var k = 3; k < w + 3; k += 3) {
opcode_list.push(D.charCodeAt(k) << 16 | D.charCodeAt(k + 1) << 8 | D.charCodeAt(k + 2));
}
for (let V = w + 3; V < D.length;) {
let E = D.charCodeAt(V) << 8 | D.charCodeAt(V + 1);
let T = D.slice(V + 2, V + 2 + E);
text_list.push(decrypt_text(T));
V += E + 2;
}
})();
console.log(opcode_list);
console.log(text_list);
可以看到字节码和字符串都解密出来了,接着就从case 352开始入手写代码,相对于2.0,代码逻辑基本没有变化太多,变化的都是因为控制流而影响的
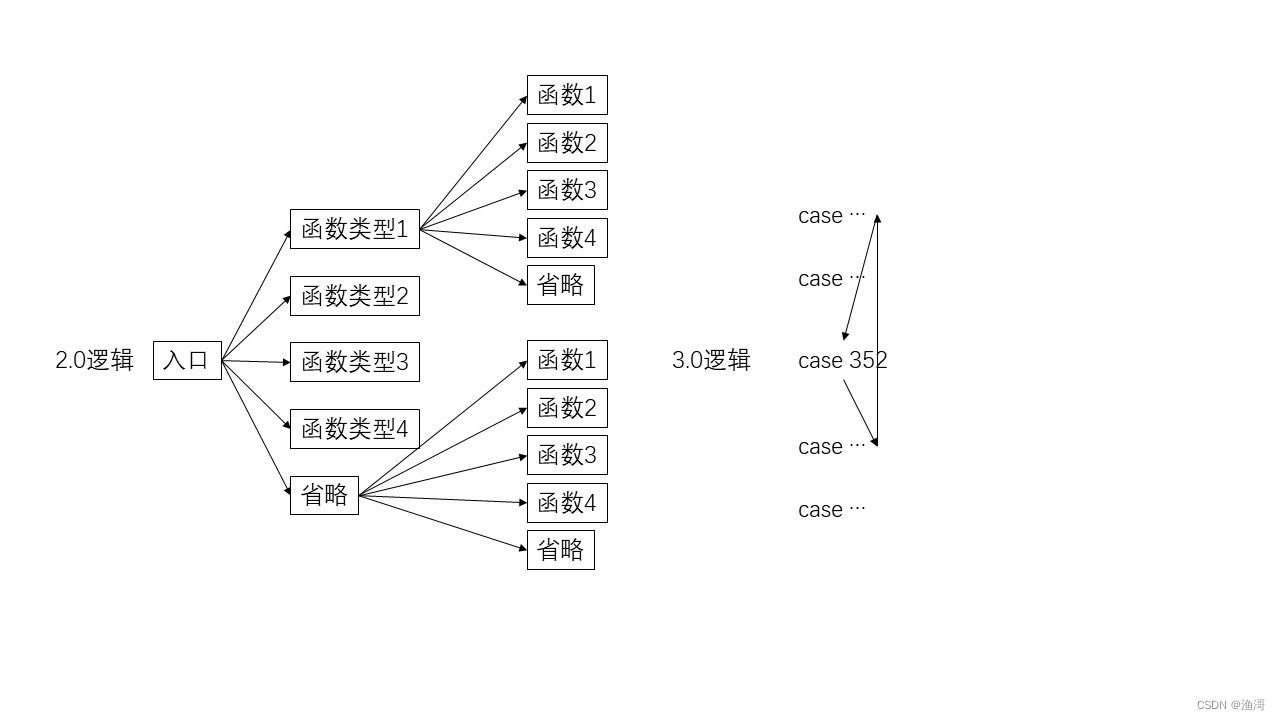
相当于把2.0逻辑的所有函数展平,然后用控制流来执行,把之前的代码改一改,又能用起来,还原了初始化的代码如下
(function () {
let local_0 = [20, 223, 245, 7, 248, 2, 194, 209, 87, 6, 227, 253, 240, 128, 222, 91, 237, 9, 125, 157, 230, 93, 252, 205, 90, 79, 144, 199, 159, 197, 186, 167, 39, 37, 156, 198, 38, 42, 43, 168, 217, 153, 15, 103, 80, 189, 71, 191, 97, 84, 247, 95, 36, 69, 14, 35, 12, 171, 28, 114, 178, 148, 86, 182, 32, 83, 158, 109, 22, 255, 94, 238, 151, 85, 77, 124, 254, 18, 4, 26, 123, 176, 232, 193, 131, 172, 143, 142, 150, 30, 10, 146, 162, 62, 224, 218, 196, 229, 1, 192, 213, 27, 110, 56, 231, 180, 138, 107, 242, 187, 54, 120, 19, 44, 117, 228, 215, 203, 53, 239, 251, 127, 81, 11, 133, 96, 204, 132, 41, 115, 73, 55, 249, 147, 102, 48, 122, 145, 106, 118, 74, 190, 29, 16, 174, 5, 177, 129, 63, 113, 99, 31, 161, 76, 246, 34, 211, 13, 60, 68, 207, 160, 65, 111, 82, 165, 67, 169, 225, 57, 112, 244, 155, 51, 236, 200, 233, 58, 61, 47, 100, 137, 185, 64, 17, 70, 234, 163, 219, 108, 170, 166, 59, 149, 52, 105, 24, 212, 78, 173, 45, 0, 116, 226, 119, 136, 206, 135, 175, 195, 25, 92, 121, 208, 126, 139, 3, 75, 141, 21, 130, 98, 241, 40, 154, 66, 184, 49, 181, 46, 243, 88, 101, 183, 8, 23, 72, 188, 104, 179, 210, 134, 250, 201, 164, 89, 216, 202, 220, 50, 221, 152, 140, 33, 235, 214];
let local_1 = [120, 50, 98, 101, 99, 98, 119, 100, 103, 107, 99, 119, 97, 99, 110, 111];
let local_2 = [100, 51, 100, 50, 101, 55, 50, 54, 102, 53, 48, 100, 52, 49, 48, 49];
let local_3 = new Array(32);
let local_23 = [462357, 472066609, 943670861, 1415275113, 1886879365, 2358483617, 2830087869, 3301692121, 3773296373, 4228057617, 404694573, 876298825, 1347903077, 1819507329, 2291111581, 2762715833, 3234320085, 3705924337, 4177462797, 337322537, 808926789, 1280531041, 1752135293, 2223739545, 2695343797, 3166948049, 3638552301, 4110090761, 269950501, 741554753, 1213159005, 1684763257];
let local_24 = [2746333894, 1453994832, 1736282519, 2993693404];
let local_25 = new Array(4);
let local_26 = new Array(36);
let local_6 = (local_2[0] & 255) << 24;
let local_7 = (local_2[0 + 1] & 255) << 16;
let local_8 = (local_2[0 + 2] & 255) << 8;
let local_9 = local_2[0 + 3] & 255;
local_25[0] = local_6 | local_7 | local_8 | local_9;
local_6 = (local_2[4] & 255) << 24;
local_7 = (local_2[4 + 1] & 255) << 16;
local_8 = (local_2[4 + 2] & 255) << 8;
local_9 = local_2[4 + 3] & 255;
local_25[1] = local_6 | local_7 | local_8 | local_9;
local_6 = (local_2[8] & 255) << 24;
local_7 = (local_2[8 + 1] & 255) << 16;
local_8 = (local_2[8 + 2] & 255) << 8;
local_9 = local_2[8 + 3] & 255;
local_25[2] = local_6 | local_7 | local_8 | local_9;
local_6 = (local_2[12] & 255) << 24;
local_7 = (local_2[12 + 1] & 255) << 16;
local_8 = (local_2[12 + 2] & 255) << 8;
local_9 = local_2[12 + 3] & 255;
local_25[3] = local_6 | local_7 | local_8 | local_9;
local_26[0] = local_25[0] ^ local_24[0];
local_26[1] = local_25[1] ^ local_24[1];
local_26[2] = local_25[2] ^ local_24[2];
local_26[3] = local_25[3] ^ local_24[3];
local_9 = 0;
while (local_9 < 32) {
let local_27 = local_26[local_9 + 1];
let local_28 = local_26[local_9 + 2];
let local_29 = local_26[local_9 + 3];
let local_30 = local_27 ^ local_28 ^ local_29 ^ local_23[local_9];
let local_16 = new Array(4);
let local_5 = new Array(4);
local_16[0] = 255 & local_30 >>> 24;
local_16[0 + 1] = 255 & local_30 >>> 16;
local_16[0 + 2] = 255 & local_30 >>> 8;
local_16[0 + 3] = 255 & local_30;
local_5[0] = local_0[local_16[0] & 255];
local_5[1] = local_0[local_16[1] & 255];
local_5[2] = local_0[local_16[2] & 255];
local_5[3] = local_0[local_16[3] & 255];
local_6 = (local_5[0] & 255) << 24;
local_7 = (local_5[0 + 1] & 255) << 16;
local_8 = (local_5[0 + 2] & 255) << 8;
local_9 = local_5[0 + 3] & 255;
let local_17 = local_6 | local_7 | local_8 | local_9;
let local_13 = 32 - 13;
let local_14 = (local_17 & 4294967295) << 13;
let local_15 = local_14 | local_17 >>> local_13;
let local_18 = local_15;
local_13 = 32 - 23;
local_14 = (local_17 & 4294967295) << 23;
local_15 = local_14 | local_17 >>> local_13;
let local_19 = local_15;
let local_20 = local_17 ^ local_18 ^ local_19;
let local_31 = local_20;
local_26[local_9 + 4] = local_26[local_9] ^ local_31;
local_3[local_9] = local_26[local_9 + 4];
local_9 = local_9 + 1;
}
window["__ZH__"]["zse"]["zk"] = local_3;
window["__ZH__"]["zse"]["zb"] = local_0;
window["__ZH__"]["zse"]["zm"] = local_1;
function _0x2068(parameter) {}
__g["_encrypt"] = _0x2068;
})();
可以看到这里是初始化了一大堆固定值,然后复制给了【zk】、【zb】、【zm】这三个对象,那么它前面的一大堆计算其实也不用管,因为也没有涉及到时间和随机数,也就是说计算前是定值,那么计算后,也一定是一个定值,那么我们直接用计算后的定值就可以了。最后两句是定义了一个函数,赋值给了【__g】的【_encrypt】属性,这一点和2.0是一模一样的。
那么接着还原一下【_0x2068】内部的逻辑
function _0x2068(parameter) {
let local_47 = Date["now"]();
let local_48 = [48, 53, 57, 48, 53, 51, 102, 55, 100, 49, 53, 101, 48, 49, 100, 55];
let local_44 = Date["now"]();
if (typeof window == "undefined") {
local_44 = 1;
}
if (!(typeof window == "undefined")) {
if (typeof document == "undefined") {
local_44 = 2;
}
if (!(typeof document == "undefined")) {
if (typeof navigator == "undefined") {
local_44 = 3;
}
if (!(typeof navigator == "undefined")) {
if (typeof location == "undefined") {
local_44 = 4;
}
if (!(typeof location == "undefined")) {
if (typeof history == "undefined") {
local_44 = 5;
}
if (!(typeof history == "undefined")) {
if (typeof screen == "undefined") {
local_44 = 6;
}
if (!(typeof screen == "undefined")) {
if (typeof navigator["userAgent"] == "undefined") {
local_44 = 7;
}
if (!(typeof navigator["userAgent"] == "undefined")) {
if (window["name"] == "nodejs") {
local_44 = 8;
}
if (!(window["name"] == "nodejs")) {
if (document["toString"]()["indexOf"]("HTMLDocument") == -1) {
local_44 = 10;
}
if (!(document["toString"]()["indexOf"]("HTMLDocument") == -1)) {
if (navigator["toString"]()["indexOf"]("Navigator") == -1) {
local_44 = 11;
}
if (!(navigator["toString"]()["indexOf"]("Navigator") == -1)) {
if (location["toString"]()["indexOf"]("http") == -1) {
local_44 = 12;
}
if (!(location["toString"]()["indexOf"]("http") == -1)) {
if (history["toString"]()["indexOf"]("History") == -1) {
local_44 = 13;
}
if (!(history["toString"]()["indexOf"]("History") == -1)) {
if (screen["toString"]()["indexOf"]("Screen") == -1) {
local_44 = 14;
}
if (!(screen["toString"]()["indexOf"]("Screen") == -1)) {
if (navigator["userAgent"]["toLowerCase"]()["indexOf"]("headless") !== -1) {
local_44 = 15;
}
if (!(navigator["userAgent"]["toLowerCase"]()["indexOf"]("headless") !== -1)) {
let local_45 = Object["getOwnPropertyDescriptor"];
if (local_45["toString"]()["indexOf"]("native code") == -1) {
local_44 = 16;
}
if (!(local_45["toString"]()["indexOf"]("native code") == -1)) {
if (typeof document["createElement"] == "undefined") {
local_44 = 17;
}
if (!(typeof document["createElement"] == "undefined")) {
if (document["createElement"]("canvas")["getContext"]("2d")["toString"]()["indexOf"]("Canvas") == -1) {
local_44 = 22;
}
if (!(document["createElement"]("canvas")["getContext"]("2d")["toString"]()["indexOf"]("Canvas") == -1)) {
if (typeof window["buffer"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 24;
}
if (!(typeof window["buffer"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["emit"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 25;
}
if (!(typeof window["emit"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["callPhantom"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 26;
}
if (!(typeof window["callPhantom"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["__phantomas"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 27;
}
if (!(typeof window["__phantomas"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["_phantom"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 28;
}
if (!(typeof window["_phantom"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["WebPage"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 29;
}
if (!(typeof window["WebPage"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["fxdriver_id"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 30;
}
if (!(typeof window["fxdriver_id"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["__fxdriver_unwrapped"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 31;
}
if (!(typeof window["__fxdriver_unwrapped"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["domAutomation"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 32;
}
if (!(typeof window["domAutomation"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["ubot"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 33;
}
if (!(typeof window["ubot"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["CasperError"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 34;
}
if (!(typeof window["CasperError"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["casper"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 35;
}
if (!(typeof window["casper"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["patchRequire"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 36;
}
if (!(typeof window["patchRequire"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof document["$cdc_asdjflasutopfhvcZLmcfl_"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 37;
}
if (!(typeof document["$cdc_asdjflasutopfhvcZLmcfl_"] !== "undefined")) {
if (navigator["webdriver"] == true) {
local_44 = 38;
}
if (!(navigator["webdriver"] == true)) {
if (typeof document["__webdriver_script_fn"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 39;
}
if (!(typeof document["__webdriver_script_fn"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["_resourceLoader"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 40;
}
if (!(typeof window["_resourceLoader"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["_sessionHistory"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 41;
}
if (!(typeof window["_sessionHistory"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["global"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 42;
}
if (!(typeof window["global"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof Object["getPrototypeOf"](alert) !== "function") {
local_44 = 43;
}
if (!(typeof Object["getPrototypeOf"](alert) !== "function")) {
if (typeof document["getElementById"] == "undefined") {
local_44 = 44;
}
if (!(typeof document["getElementById"] == "undefined")) {
if (typeof Object["getPrototypeOf"](document["getElementById"]) !== "function") {
local_44 = 45;
}
if (!(typeof Object["getPrototypeOf"](document["getElementById"]) !== "function")) {
if (typeof document["getElementsByClassName"] == "undefined") {
local_44 = 46;
}
if (!(typeof document["getElementsByClassName"] == "undefined")) {
if (window["__proto__"]["constructor"]["toString"]()["indexOf"]("[native code]") == -1) {
local_44 = 48;
}
if (!(window["__proto__"]["constructor"]["toString"]()["indexOf"]("[native code]") == -1)) {
if (typeof window["__nightmare"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 49;
}
if (!(typeof window["__nightmare"] !== "undefined")) {
if (new Error()["stack"]["indexOf"]("localhost") !== -1) {
local_44 = 50;
}
if (!(new Error()["stack"]["indexOf"]("localhost") !== -1)) {
if (new Error()["stack"]["indexOf"]("puppeteer") !== -1) {
local_44 = 51;
}
if (!(new Error()["stack"]["indexOf"]("puppeteer") !== -1)) {
if (navigator["userAgent"]["toLowerCase"]()["indexOf"]("phantomjs") !== -1) {
local_44 = 52;
}
if (!(navigator["userAgent"]["toLowerCase"]()["indexOf"]("phantomjs") !== -1)) {
if (navigator["userAgent"]["toLowerCase"]()["indexOf"]("electron") !== -1) {
local_44 = 53;
}
if (!(navigator["userAgent"]["toLowerCase"]()["indexOf"]("electron") !== -1)) {
if (location["href"]["indexOf"]("localhost") !== -1) {
local_44 = 54;
}
if (!(location["href"]["indexOf"]("localhost") !== -1)) {
if (window["spawn"]) {
local_44 = 56;
}
if (!window["spawn"]) {
if (typeof window["_Selenium_IDE_Recorder"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 57;
}
if (!(typeof window["_Selenium_IDE_Recorder"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["_selenium"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 58;
}
if (!(typeof window["_selenium"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["__webdriver_evaluate"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 59;
}
if (!(typeof window["__webdriver_evaluate"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["__selenium_evaluate"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 60;
}
if (!(typeof window["__selenium_evaluate"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["__webdriver_script_function"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 61;
}
if (!(typeof window["__webdriver_script_function"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["__fxdriver_evaluate"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 62;
}
if (!(typeof window["__fxdriver_evaluate"] !== "undefined")) {
if (typeof window["__driver_unwrapped"] !== "undefined") {
local_44 = 63;
}
if (!(typeof window["__driver_unwrapped"] !== "undefined")) {
local_44 = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
let local_49 = local_44;
let local_41 = [];
let local_42 = parameter["length"];
let local_12 = 0;
while (local_12 < local_42) {
let local_43 = parameter["charCodeAt"](local_12);
local_41["push"](local_43 & 255);
local_12 = local_12 + 1;
}
let local_50 = local_41;
let local_51 = Date["now"]() - local_47;
if (local_51 > 10000) {
local_49 = 126;
}
if (!(local_51 > 10000)) {}
let local_52 = Math["floor"](Math["random"]() * 127);
local_50["unshift"](local_49);
local_50["unshift"](local_52);
let local_21 = local_50["length"] % 16;
let local_10 = 16 - local_21;
let local_33 = 0;
while (local_33 < local_10) {
local_50["push"](local_10);
local_33 = local_33 + 1;
}
let local_34 = local_50["slice"](0, 16);
let local_35 = new Array(16);
let local_11 = 0;
while (local_11 < 16) {
local_35[local_11] = local_34[local_11] ^ local_48[local_11] ^ 42;
local_11 = local_11 + 1;
}
let local_36 = __g["r"](local_35);
let local_37 = local_36["slice"]();
let local_38 = local_50["slice"](16, local_50["length"]);
let local_39 = __g["x"](local_38, local_36);
local_37 = local_37["concat"](local_39);
let local_53 = local_37;
let local_54 = local_53["length"] % 3;
if (local_54 == 1) {
local_53["push"]("\0");
local_53["push"]("\0");
}
if (!(local_54 == 1)) {}
if (local_54 == 2) {
local_53["push"]("\0");
}
if (!(local_54 == 2)) {}
let local_55 = "6fpLR" + "qJO8M/c3j" + "nYxFkUV" + "C4ZIG12SiH=5v0mXDazWB" + "Tsuw7QetbKdoPyAl+hN9rgE";
let local_56 = 0;
let local_57 = "";
let local_13 = local_53["length"] - 1;
while (local_13 >= 0) {
let local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4);
local_56 = local_56 + 1;
let local_59 = local_53[local_13] ^ 58 >>> local_58 & 255;
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4);
local_56 = local_56 + 1;
local_59 = local_59 | (local_53[local_13 - 1] ^ 58 >>> local_58 & 255) << 8;
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4);
local_56 = local_56 + 1;
local_59 = local_59 | (local_53[local_13 - 2] ^ 58 >>> local_58 & 255) << 16;
local_57 = local_57 + local_55["charAt"](local_59 & 63);
local_57 = local_57 + local_55["charAt"](local_59 >>> 6 & 63);
local_57 = local_57 + local_55["charAt"](local_59 >>> 12 & 63);
local_57 = local_57 + local_55["charAt"](local_59 >>> 18 & 63);
local_13 = local_13 - 3;
}
return local_57;
}
环境检测部分有点长,但是却发现,3.0的逻辑也是先进行环境检测,再进行加密函数的,那么到这里就可以确定,之前说的修改字节码的方法是可以实现的。
修改的核心思路那之前的基本相似,就是当第一次出现跳转指令的时候,把pc寄存器的值修改到第二次跳转的后面
3.0的跳转代码在case 443,第一次出现跳转时,pc寄存器的值为【1284】,这里的this.b就是要转跳的值,在第一次跳转的时候暂时不用管。
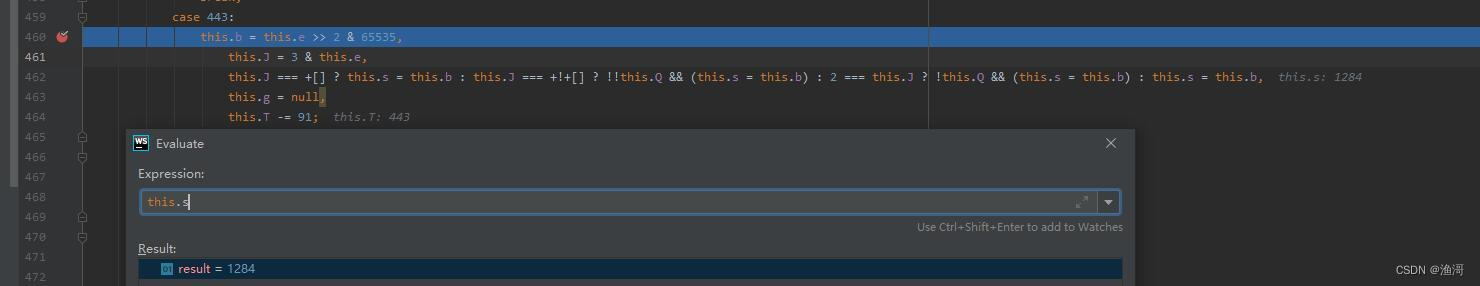
接着进入到第二次跳转,此时的pc寄存器位【1288】,并且记录一下this.b为【2066】。这时就可以尝试修改。但是这里有一个逗号表达式,不方便我们修改,那么手动把它搞成一个一个语句。
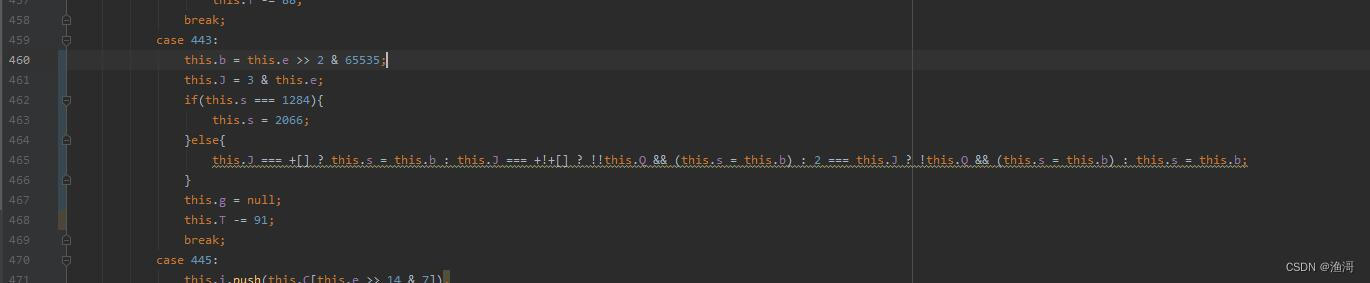
但是这样还不对,因为环境检测还不是一个正确的值,那么直接设置为检验通过的值
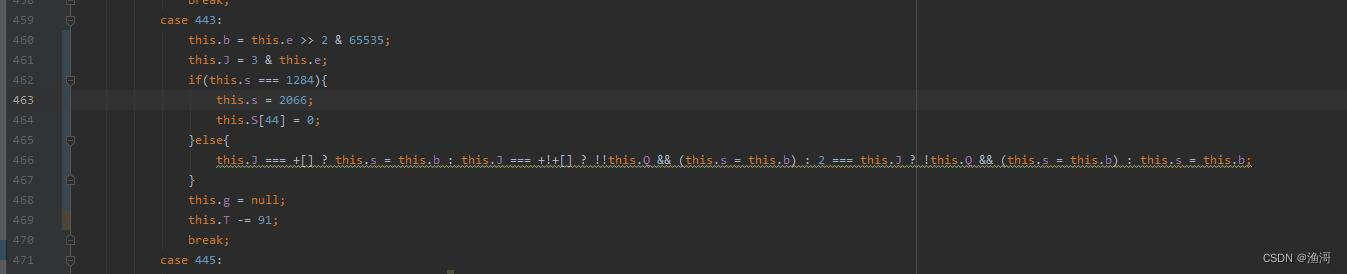
那么加上检测校验正确的值,那么就应该可以了,前面仅仅保留一些必要的代码
window=global;
Math.random = function(){
return 0.50
};
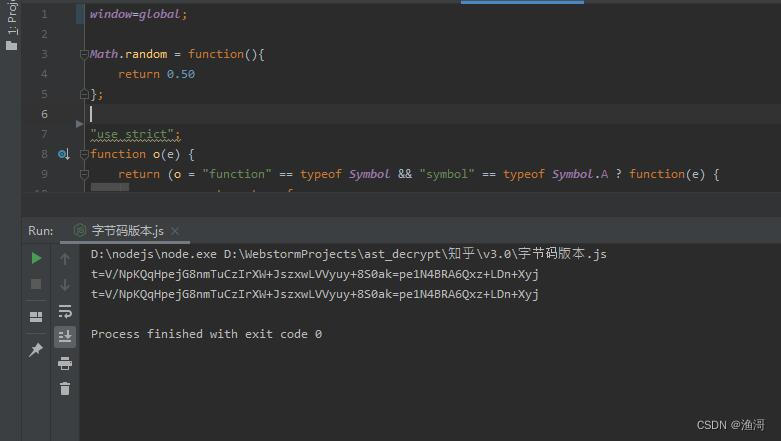
这时运行发现,结果也是一模一样的,那么说明修改字节码的方案完成。
算法还原
那么把vmp反汇编出来了,那么算法还原的难度也就基本没有了,相当于就是把js的逻辑写成其他语言的逻辑
def x_zse_96_b64encode(md5_bytes: bytes):
h = {
"zk": [1170614578, 1024848638, 1413669199, -343334464, -766094290, -1373058082, -143119608, -297228157, 1933479194, -971186181, -406453910, 460404854, -547427574, -1891326262, -1679095901, 2119585428, -2029270069, 2035090028, -1521520070, -5587175, -77751101, -2094365853, -1243052806, 1579901135, 1321810770, 456816404, -1391643889, -229302305, 330002838, -788960546, 363569021, -1947871109],
"zb": [20, 223, 245, 7, 248, 2, 194, 209, 87, 6, 227, 253, 240, 128, 222, 91, 237, 9, 125, 157, 230, 93, 252, 205, 90, 79, 144, 199, 159, 197, 186, 167, 39, 37, 156, 198, 38, 42, 43, 168, 217, 153, 15, 103, 80, 189, 71, 191, 97, 84, 247, 95, 36, 69, 14, 35, 12, 171, 28, 114, 178, 148, 86, 182, 32, 83, 158, 109, 22, 255, 94, 238, 151, 85, 77, 124, 254, 18, 4, 26, 123, 176, 232, 193, 131, 172, 143, 142, 150, 30, 10, 146, 162, 62, 224, 218, 196, 229, 1, 192, 213, 27, 110, 56, 231, 180, 138, 107, 242, 187, 54, 120, 19, 44, 117, 228, 215, 203, 53, 239, 251, 127, 81, 11, 133, 96, 204, 132, 41, 115, 73, 55, 249, 147, 102, 48, 122, 145, 106, 118, 74, 190, 29, 16, 174, 5, 177, 129, 63, 113, 99, 31, 161, 76, 246, 34, 211, 13, 60, 68, 207, 160, 65, 111, 82, 165, 67, 169, 225, 57, 112, 244, 155, 51, 236, 200, 233, 58, 61, 47, 100, 137, 185, 64, 17, 70, 234, 163, 219, 108, 170, 166, 59, 149, 52, 105, 24, 212, 78, 173, 45, 0, 116, 226, 119, 136, 206, 135, 175, 195, 25, 92, 121, 208, 126, 139, 3, 75, 141, 21, 130, 98, 241, 40, 154, 66, 184, 49, 181, 46, 243, 88, 101, 183, 8, 23, 72, 188, 104, 179, 210, 134, 250, 201, 164, 89, 216, 202, 220, 50, 221, 152, 140, 33, 235, 214],
"zm": [120, 50, 98, 101, 99, 98, 119, 100, 103, 107, 99, 119, 97, 99, 110, 111]
}
def left_shift(x, y):
x, y = ctypes.c_int32(x).value, y % 32
return ctypes.c_int32(x << y).value
def Unsigned_right_shift(x, y):
x, y = ctypes.c_uint32(x).value, y % 32
return ctypes.c_uint32(x >> y).value
def Q(e, t):
return left_shift((4294967295 & e), t) | Unsigned_right_shift(e, 32 - t)
def G(e):
t = list(struct.pack(">i", e))
n = [h['zb'][255 & t[0]], h['zb'][255 & t[1]], h['zb'][255 & t[2]], h['zb'][255 & t[3]]]
r = struct.unpack(">i", bytes(n))[0]
return r ^ Q(r, 2) ^ Q(r, 10) ^ Q(r, 18) ^ Q(r, 24)
def g_r(e):
n = list(struct.unpack(">iiii", bytes(e)))
[n.append(n[r] ^ G(n[r + 1] ^ n[r + 2] ^ n[r + 3] ^ h['zk'][r])) for r in range(32)]
return list(struct.pack(">i", n[35]) + struct.pack(">i", n[34]) + struct.pack(">i", n[33]) + struct.pack(">i", n[32]))
def g_x(e, t):
n = []
i = 0
for _ in range(len(e), 0, -16):
o = e[16 * i: 16 * (i + 1)]
a = [o[c] ^ t[c] for c in range(16)]
t = g_r(a)
n += t
i += 1
return n
local_48 = [48, 53, 57, 48, 53, 51, 102, 55, 100, 49, 53, 101, 48, 49, 100, 55]
local_50 = bytes([63, 0]) + md5_bytes # 随机数 0 是环境检测通过
local_50 = x_zse_96_V3.pad(bytes(local_50))
local_34 = local_50[:16]
local_35 = [local_34[local_11] ^ local_48[local_11] ^ 42 for local_11 in range(16)]
local_36 = g_r(local_35)
local_38 = local_50[16:]
local_39 = g_x(local_38, local_36)
local_53 = local_36 + local_39
local_55 = "6fpLRqJO8M/c3jnYxFkUVC4ZIG12SiH=5v0mXDazWBTsuw7QetbKdoPyAl+hN9rgE"
local_56 = 0
local_57 = ""
for local_13 in range(len(local_53) - 1, 0, -3):
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4)
local_56 = local_56 + 1
local_59 = local_53[local_13] ^ Unsigned_right_shift(58, local_58) & 255
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4)
local_56 = local_56 + 1
local_59 = local_59 | (local_53[local_13 - 1] ^ Unsigned_right_shift(58, local_58) & 255) << 8
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4)
local_56 = local_56 + 1
local_59 = local_59 | (local_53[local_13 - 2] ^ Unsigned_right_shift(58, local_58) & 255) << 16
local_57 = local_57 + local_55[local_59 & 63]
local_57 = local_57 + local_55[Unsigned_right_shift(local_59, 6) & 63]
local_57 = local_57 + local_55[Unsigned_right_shift(local_59, 12) & 63]
local_57 = local_57 + local_55[Unsigned_right_shift(local_59, 18) & 63]
return local_57
运行一下测试代码

结果也是完全正确的,那么算法还原的方案也完成了。
那么有了编码,会不会也有解码的方法呢?那肯定是有的,因为如果没有,服务器又怎么验证传上来的结果对不对呢。解码方法其实就是编码方法的逆运算。
例如加法和减法互为逆运算,因为一个数字我加上一个数,再减去这个数,还是得到原来的数字。
乘法和除法互为逆运算、异或和自身互为逆运算等等。那么如果要得到解码方法,相当于就是自己写一个逆运算的方法,按照前面的逻辑可以尝试编写
class x_zse_96_V3(object):
local_48 = [48, 53, 57, 48, 53, 51, 102, 55, 100, 49, 53, 101, 48, 49, 100, 55]
local_55 = "6fpLRqJO8M/c3jnYxFkUVC4ZIG12SiH=5v0mXDazWBTsuw7QetbKdoPyAl+hN9rgE"
h = {
"zk": [1170614578, 1024848638, 1413669199, -343334464, -766094290, -1373058082, -143119608, -297228157, 1933479194, -971186181, -406453910, 460404854, -547427574, -1891326262, -1679095901, 2119585428, -2029270069, 2035090028, -1521520070, -5587175, -77751101, -2094365853, -1243052806, 1579901135, 1321810770, 456816404, -1391643889, -229302305, 330002838, -788960546, 363569021, -1947871109],
"zb": [20, 223, 245, 7, 248, 2, 194, 209, 87, 6, 227, 253, 240, 128, 222, 91, 237, 9, 125, 157, 230, 93, 252, 205, 90, 79, 144, 199, 159, 197, 186, 167, 39, 37, 156, 198, 38, 42, 43, 168, 217, 153, 15, 103, 80, 189, 71, 191, 97, 84, 247, 95, 36, 69, 14, 35, 12, 171, 28, 114, 178, 148, 86, 182, 32, 83, 158, 109, 22, 255, 94, 238, 151, 85, 77, 124, 254, 18, 4, 26, 123, 176, 232, 193, 131, 172, 143, 142, 150, 30, 10, 146, 162, 62, 224, 218, 196, 229, 1, 192, 213, 27, 110, 56, 231, 180, 138, 107, 242, 187, 54, 120, 19, 44, 117, 228, 215, 203, 53, 239, 251, 127, 81, 11, 133, 96, 204, 132, 41, 115, 73, 55, 249, 147, 102, 48, 122, 145, 106, 118, 74, 190, 29, 16, 174, 5, 177, 129, 63, 113, 99, 31, 161, 76, 246, 34, 211, 13, 60, 68, 207, 160, 65, 111, 82, 165, 67, 169, 225, 57, 112, 244, 155, 51, 236, 200, 233, 58, 61, 47, 100, 137, 185, 64, 17, 70, 234, 163, 219, 108, 170, 166, 59, 149, 52, 105, 24, 212, 78, 173, 45, 0, 116, 226, 119, 136, 206, 135, 175, 195, 25, 92, 121, 208, 126, 139, 3, 75, 141, 21, 130, 98, 241, 40, 154, 66, 184, 49, 181, 46, 243, 88, 101, 183, 8, 23, 72, 188, 104, 179, 210, 134, 250, 201, 164, 89, 216, 202, 220, 50, 221, 152, 140, 33, 235, 214],
"zm": [120, 50, 98, 101, 99, 98, 119, 100, 103, 107, 99, 119, 97, 99, 110, 111]
}
@staticmethod
def pad(data_to_pad):
padding_len = 16 - len(data_to_pad) % 16
padding = chr(padding_len).encode() * padding_len
return data_to_pad + padding
@staticmethod
def unpad(padded_data):
padding_len = padded_data[-1]
return padded_data[:-padding_len]
@staticmethod
def left_shift(x, y):
x, y = ctypes.c_int32(x).value, y % 32
return ctypes.c_int32(x << y).value
@staticmethod
def Unsigned_right_shift(x, y):
x, y = ctypes.c_uint32(x).value, y % 32
return ctypes.c_uint32(x >> y).value
@classmethod
def Q(cls, e, t):
return cls.left_shift((4294967295 & e), t) | cls.Unsigned_right_shift(e, 32 - t)
@classmethod
def G(cls, e):
t = list(struct.pack(">i", e))
n = [cls.h['zb'][255 & t[0]], cls.h['zb'][255 & t[1]], cls.h['zb'][255 & t[2]], cls.h['zb'][255 & t[3]]]
r = struct.unpack(">i", bytes(n))[0]
return r ^ cls.Q(r, 2) ^ cls.Q(r, 10) ^ cls.Q(r, 18) ^ cls.Q(r, 24)
@classmethod
def g_r(cls, e):
n = list(struct.unpack(">iiii", bytes(e)))
[n.append(n[r] ^ cls.G(n[r + 1] ^ n[r + 2] ^ n[r + 3] ^ cls.h['zk'][r])) for r in range(32)]
return list(struct.pack(">i", n[35]) + struct.pack(">i", n[34]) + struct.pack(">i", n[33]) + struct.pack(">i", n[32]))
@classmethod
def re_g_r(cls, e):
n = [0] * 32 + list(struct.unpack(">iiii", bytes(e)))[::-1]
for r in range(31, -1, -1):
n[r] = cls.G(n[r + 1] ^ n[r + 2] ^ n[r + 3] ^ cls.h['zk'][r]) ^ n[r + 4]
return list(struct.pack(">i", n[0]) + struct.pack(">i", n[1]) + struct.pack(">i", n[2]) + struct.pack(">i", n[3]))
@classmethod
def g_x(cls, e, t):
n = []
i = 0
for _ in range(len(e), 0, -16):
o = e[16 * i: 16 * (i + 1)]
a = [o[c] ^ t[c] for c in range(16)]
t = cls.g_r(a)
n += t
i += 1
return n
@classmethod
def re_g_x(cls, e, t):
n = []
i = 0
for _ in range(len(e), 0, -16):
o = e[16 * i: 16 * (i + 1)]
a = cls.re_g_r(o)
t = [a[c] ^ t[c] for c in range(16)]
n += t
t = o
i += 1
return n
@classmethod
def b64encode(cls, md5_bytes: bytes, device: int = 0, seed: int = 63) -> str:
local_50 = bytes([seed, device]) + md5_bytes # 随机数 0 是环境检测通过
local_50 = cls.pad(bytes(local_50))
local_34 = local_50[:16]
local_35 = [local_34[local_11] ^ cls.local_48[local_11] ^ 42 for local_11 in range(16)]
local_36 = cls.g_r(local_35)
local_38 = local_50[16:]
local_39 = cls.g_x(local_38, local_36)
local_53 = local_36 + local_39
local_56 = 0
local_57 = ""
for local_13 in range(len(local_53) - 1, 0, -3):
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4)
local_56 = local_56 + 1
local_59 = local_53[local_13] ^ cls.Unsigned_right_shift(58, local_58) & 255
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4)
local_56 = local_56 + 1
local_59 = local_59 | (local_53[local_13 - 1] ^ cls.Unsigned_right_shift(58, local_58) & 255) << 8
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4)
local_56 = local_56 + 1
local_59 = local_59 | (local_53[local_13 - 2] ^ cls.Unsigned_right_shift(58, local_58) & 255) << 16
local_57 = local_57 + cls.local_55[local_59 & 63]
local_57 = local_57 + cls.local_55[cls.Unsigned_right_shift(local_59, 6) & 63]
local_57 = local_57 + cls.local_55[cls.Unsigned_right_shift(local_59, 12) & 63]
local_57 = local_57 + cls.local_55[cls.Unsigned_right_shift(local_59, 18) & 63]
return local_57
@classmethod
def b64decode(cls, x_zse_96: str) -> dict:
local_56 = 0
local_57 = []
for local_13 in range(0, len(x_zse_96), 4):
local_59 = (cls.local_55.index(x_zse_96[local_13 + 3]) << 18) + (cls.local_55.index(x_zse_96[local_13 + 2]) << 12) + (cls.local_55.index(x_zse_96[local_13 + 1]) << 6) + cls.local_55.index(x_zse_96[local_13])
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4)
local_56 = local_56 + 1
local_57.append((local_59 & 255) ^ cls.Unsigned_right_shift(58, local_58))
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4)
local_56 = local_56 + 1
local_57.append(((local_59 >> 8) & 255) ^ cls.Unsigned_right_shift(58, local_58))
local_58 = 8 * (local_56 % 4)
local_56 = local_56 + 1
local_57.append(((local_59 >> 16) & 255) ^ cls.Unsigned_right_shift(58, local_58))
local_36, local_39 = local_57[-16:][::-1], local_57[:-16][::-1]
local_38 = cls.re_g_x(local_39, local_36)
local_35 = cls.re_g_r(local_36)
local_34 = [local_35[local_11] ^ cls.local_48[local_11] ^ 42 for local_11 in range(16)]
local_50 = cls.unpad(bytes(local_34 + local_38))
return {
'seed': local_50[0],
'device': local_50[1],
'md5_bytes': local_50[2:]
}
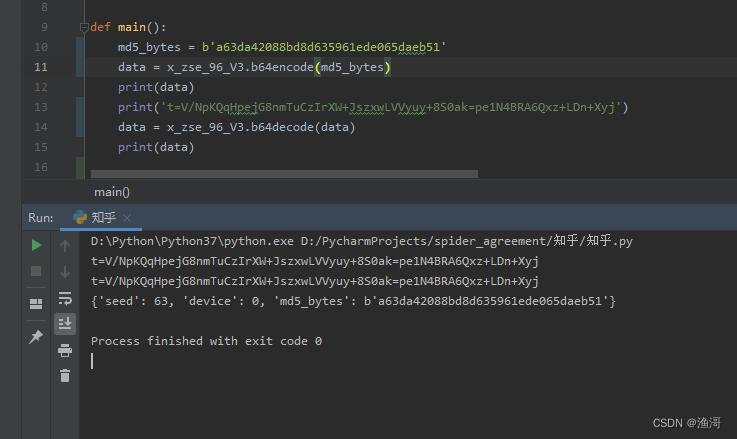
非常好的,得到了相同的结果,说明解码函数没有问题了。
后记
这次的分析比2.0的更加详细,其中是因为3.0来说确实是难了一些
1.结果不是完全固定的
2.存在控制流
3.存在两个时间控制的反调试
4.从编码方法中推导出解码方法
更多内容欢迎加入我的星球学习
