vue3的diff和vue2有一点不同,vue2有前后、后前和遍历父节点查找比较过程。vue3就直接将这几个过程改成了使用最长递增子序列算法去求最小移动步骤。接下来我们重点看涉及递增子序列算法部分,前几个过程和vue2类似就不讲解。
dom节点:
原dom
<div key="A">1</div>
<div key="B">2</div>
<div key="C">3</div>
<div key="D">4</div>
<div key="E">5</div>
<div key="F">6</div>
<div key="g">7</div>
<div key="h">8</div>
更改后
<div key="A">1</div>
<div key="D">4</div>
<div key="C">3</div>
<div key="B">2</div>
<div key="E">5</div>
<div key="g">7</div>
<div key="F">6</div>
<div key="h">8</div>
值为1和8的会在前面几个步骤先处理,所以这里只会有中间的dom,我们来具体看看是怎么处理中间部分的:
const s1 = i; // prev starting index
const s2 = i; // next starting index
// 5.1 build key:index map for newChildren
const keyToNewIndexMap = new Map();
for (i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {
const nextChild = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i])
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]));
if (nextChild.key != null) {
if (keyToNewIndexMap.has(nextChild.key)) {
warn$1(`Duplicate keys found during update:`, JSON.stringify(nextChild.key), `Make sure keys are unique.`);
}
keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i);
}
}
// 5.2 loop through old children left to be patched and try to patch
// matching nodes & remove nodes that are no longer present
let j;
let patched = 0;
const toBePatched = e2 - s2 + 1;
let moved = false;
// used to track whether any node has moved
let maxNewIndexSoFar = 0;
// works as Map<newIndex, oldIndex>
// Note that oldIndex is offset by +1
// and oldIndex = 0 is a special value indicating the new node has
// no corresponding old node.
// used for determining longest stable subsequence
const newIndexToOldIndexMap = new Array(toBePatched);
for (i = 0; i < toBePatched; i++)
newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] = 0;
for (i = s1; i <= e1; i++) {
const prevChild = c1[i];
if (patched >= toBePatched) {
// all new children have been patched so this can only be a removal
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true);
continue;
}
let newIndex;
if (prevChild.key != null) {
newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key);
}
else {
// key-less node, try to locate a key-less node of the same type
for (j = s2; j <= e2; j++) {
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[j - s2] === 0 &&
isSameVNodeType(prevChild, c2[j])) {
newIndex = j;
break;
}
}
}
if (newIndex === undefined) {
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true);
}
else {
newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex - s2] = i + 1;
if (newIndex >= maxNewIndexSoFar) {
maxNewIndexSoFar = newIndex;
}
else {
moved = true;
}
patch(prevChild, c2[newIndex], container, null, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized);
patched++;
}
}
首先遍历新节点并设置keyToNewIndexMap,这个是新节点对应的index值:
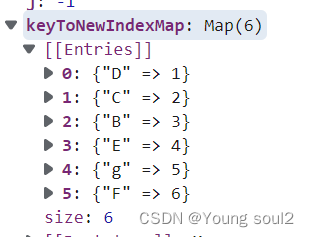
随后会去遍历老节点,并查找新节点在老节点中的索引值index,如果找到了就会设置在newIndexToOldIndexMap,如果没找到说明新的节点不需要该节点,则会删除该节点:


之所以要建立新老节点的索引列表是因为要求出最小递增子序列,通过该序列可以确定哪些节点可以不用动:
const increasingNewIndexSequence = moved
? getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap)
: EMPTY_ARR;
j = increasingNewIndexSequence.length - 1;
// looping backwards so that we can use last patched node as anchor
for (i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const nextIndex = s2 + i;
const nextChild = c2[nextIndex];
const anchor = nextIndex + 1 < l2 ? c2[nextIndex + 1].el : parentAnchor;
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] === 0) {
// mount new
patch(null, nextChild, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, slotScopeIds, optimized);
}
else if (moved) {
// move if:
// There is no stable subsequence (e.g. a reverse)
// OR current node is not among the stable sequence
if (j < 0 || i !== increasingNewIndexSequence[j]) {
move(nextChild, container, anchor, 2 /* MoveType.REORDER */);
}
else {
j--;
}
}
}
通过getSequence方法获取最长递增子序列increasingNewIndexSequence:

可以看出索引值有2、3、5是newIndexToOldIndexMap中的最长递增序列,那么这些下标对应的新节点位置不用移动。接下来带大家遍历一下,遍历顺序为倒叙:
- 第一个索引是5,key为F,然后取出increasingNewIndexSequence最后一个值5进行对比判断值是否相等,此时相等就不用移动,j–,j为1。
- 第二个索引是4,key为g,然后取出increasingNewIndexSequence倒数第二个值3进行对比判断值是否相等,此时不相等则移动真实dom把g插入到F前面。
- 第三个索引是3,key为E,然后取出increasingNewIndexSequence倒数第二个值3进行对比判断值是否相等,此时相等就不用移动,j–,j为0。
- 第四个索引是2,key为B,然后取出increasingNewIndexSequence倒数第二个值3进行对比判断值是否相等,此时相等就不用移动,j–,j为-1。
- 第五个索引是1,key为C,此时j<0直接移动,移动真实dom将C插入到B前面。
- 第六个索引是0,key为D,此时j<0直接移动,移动真实dom将D插入到C前面。

总结
先获取新节点的索引(当前位置),再求出新节点在旧节点中的索引(当前新节点在旧节点中的位置),根据新节点在旧节点中的索引去求最长递增子序列(在旧节点中哪些需要移动,哪些不用移动,这样可以使得移动步骤最少)。然后倒叙遍历新节点,并判断新节点的索引是不是和最长递增子序列的索引相对应,如果相对应则不用移动,否则需要插入。