文章目录
3 Matplotlib
3.1 figure、axes、axis
ax1 = plt.subplot(221)
ax2 = plt.subplot(222)
ax3 = plt.subplot(223)
ax4 = plt.subplot(224)
plt.show()
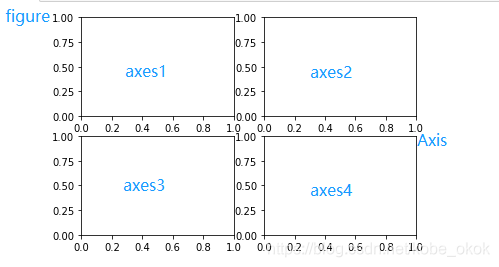
由上图可以看出,figure是一个画布,一个画布上可以画多个坐标系(axes),每个(二维)坐标系有两个轴(axis),相信大家看到上图就能够知道画布,坐标系和坐标轴三者之间的关系。
3.2 图像布局
3.2.1 plt.subplot()
上例中使用的也是一种图像布局的方法,将一个画布分成四个部分,将四个坐标系分别命名成ax1,ax2,ax3,ax4
3.2.2 plt.subplots()
fig,ax=plt.subplots(2,2)
ax[0,0].plot([1,2,3],[1,2,3])
ax[0,1].scatter([1,2,3],[1,2,3])
ax[1,0].bar([1,2,3],[1,2,3])
ax[1,1].pie([10,20,30])
plt.show()
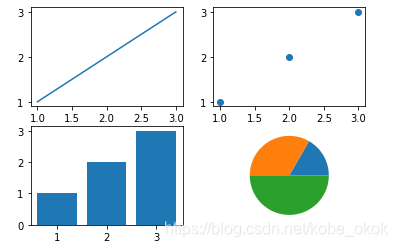
3.3 折线图-plt.plot()
面向对象制图
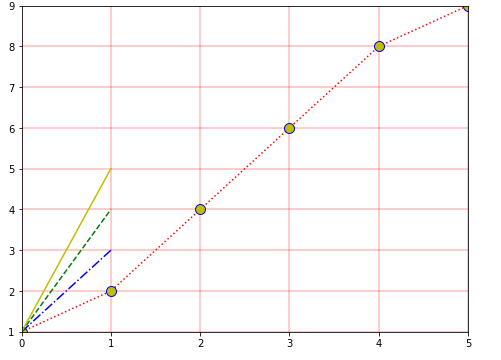
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,6)) # 创建一个画布
axes = fig.add_subplot() # 新建一个子坐标系
axes.plot([0,1,2,3,4,5], [1,2,4,6,8,9],c='r',ls=':',marker='o',markersize='10',mec='b',mfc='y') # 画折线图
axes.plot([1,3],c='b',ls='-.')
axes.plot([1,4],c='g',ls='--')
axes.plot([1,5],c='y',ls='-')
axes.grid(True,color='r', linestyle='-', linewidth=2, alpha=0.2) # 添加背景方格
axes.set_xmargin(0) #图形到底边的距离
axes.set_ymargin(0) #图形到左边的距离
plt.show()
使用循环画多个图
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,6)) # 新建画布
config = {
'c':['r','g','b','y'],
'ls':['-','-.','--',':'],
'lw':[1,2,3,4],
} # 配置项
ax = fig.add_subplot() # 添加坐标系
for i in range(4):
ax.plot([1,i+2],c=config['c'].pop(),ls=config['ls'].pop(),lw=config['lw'].pop())
# 循环画四个折线图
plt.show()
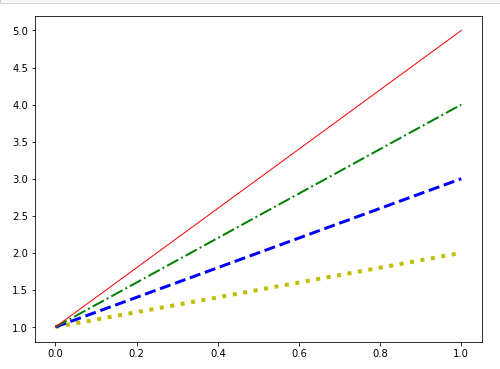 > 常用参数说明
> 常用参数说明
xdata,ydata : # 具有相同维度的数据
c or color : # 颜色
# 常用颜色列表:
============= ===============================
character color
============= ===============================
``'b'`` blue
``'g'`` green
``'r'`` red
``'c'`` cyan
``'m'`` magenta
``'y'`` yellow
``'k'`` black
``'w'`` white
============= ===============================
linestyle or ls : # 线型
# 支持的线型:
============= ===============================
character description
============= ===============================
``'-'`` solid line style
``'--'`` dashed line style
``'-.'`` dash-dot line style
``':'`` dotted line style
============= ===============================
linewidth or lw : # 线宽 float
marker : # 数据点的类型
# 常用的marker:
============= ===============================
character description
============= ===============================
``'.'`` point marker
``','`` pixel marker
``'o'`` circle marker
``'v'`` triangle_down marker
``'^'`` triangle_up marker
``'<'`` triangle_left marker
``'>'`` triangle_right marker
``'1'`` tri_down marker
``'2'`` tri_up marker
``'3'`` tri_left marker
``'4'`` tri_right marker
``'8'`` octagon marker
``'s'`` square marker
``'p'`` pentagon marker
``'P'`` plus (filled) marker
``'*'`` star marker
``'h'`` hexagon1 marker
``'H'`` hexagon2 marker
``'+'`` plus marker
``'x'`` x marker
``'X'`` x (filled) marker
``'D'`` diamond marker
``'d'`` thin_diamond marker
``'|'`` vline marker
``'_'`` hline marker
============= ===============================
markeredgecolor or mfc : #数据点的边框颜色
markeredgewidth or mew: float #数据点的边框粗细
markerfacecolor or mfc: color #数据点前景色
markersize or ms: float #数据点的大小
markevery: None or int or (int, int) or slice or list[int] or float or (float, float) or list[bool] #每个点是不是应该有数据
# 对于上面的第一个例子
# 设置:markevery=[False,True,True,False,False,False]
# 则那么只有(1,2),(2,4)这两个点显示
fmt = '[marker][line][color]'
# 可以将marker=’o‘,line=':',color='r' 简写成 ‘o:r’
3.4 散点图-plt.scatter()
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.scatter(x=np.random.randn(50),y=np.random.randn(50),s=np.random.randint(0,100,50),c=np.random.randn(50),marker='*')
plt.show()
# s : size
# c : color
# 其余参数和plot都差不多
3.5 柱状图-plt.bar()
垂直柱状图
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = "SimHei"
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot()
x = ['裤子','上衣','袜子']
y1 = [14,20,23]
y2 = [17,19,32]
ax.bar(
x=x, # x坐标
height=y1, # 柱状图高度
width=0.2, # 柱状图高度
align='center', # 对齐方式'center' or ‘edge’
bottom=0, # 底部坐标
color = 'b', # 颜色 字符或者字符列表
edgecolor = 'y', # 边框颜色
linewidth = 5, # 边框宽度
# tick_label = [], 修改x轴的标注
)
ax.set_label('男生')
ax.bar(
x=x,
height=y2,
width=0.2,
align='center',
bottom=y1,
color = 'r',
edgecolor = 'y',
linewidth = 5,
# tick_label = [], 修改x轴的标注
)
ax.set_label("女生")
ax.legend(["男","女"]) # 设置图例
plt.show()
横向柱状图
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = "SimHei"
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot()
x = ['裤子','上衣','袜子']
y1 = [14,20,23]
ax.barh(y=x,width=y1,height=0.8,left=[0,0,5])
ax.legend("销量")
plt.show(
直方图
hz,bins = np.histogram(np.random.randint(1,100,5000),bins=np.linspace(0,100,100))
hz,bins
plt.bar(x=bins[:-1],height=hz)
3.6 饼状图-plt.pie()
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = "SimHei"
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.pie(x=[12,45,23],explode=np.array([0,0,0.2]),labels=list("中美日"),colors=list('rgb'),autopct='%1.1f%%',shadow=True)
plt.show()
#参数说明:
3.7 fontdict
# 默认设置
{'fontsize': rcParams['axes.titlesize'],
'fontweight': rcParams['axes.titleweight'],
'color': rcParams['axes.titlecolor'],
'verticalalignment': 'baseline',
'horizontalalignment': loc}
附件0 综合练习
x = np.arange(-5,6,1) # X轴测试数据
y = 2*x + 5 # Y轴测试数据
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1) # 新建一个画布,一个坐标系
ax.set_title("Test Axes",fontdict={'size':16,'color':'b'}) # 设置一个标题
ax.spines['right'].set_color(None) # 设置坐标系右边的轴不显示
ax.spines['top'].set_color(None) # 设置坐标系上面的轴不显示
ax.set_xlim(-5,+5) # 显示X轴的范围是-5 ~ +5
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(-5,6,1)) # 显示X轴的标记点是[-5,6)左闭右开区间,间隔为1
ax.set_ylim(-20,+20) # 设置y轴的范围是-20 ~ +20
ax.set_xlabel('X',loc='right') # 设置x轴的标记为X,位置靠右
ax.set_ylabel('y',loc='top') # 设置Y轴的标记为Y,位置靠上
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data',0)) # 设置底部的轴在左侧数值轴为0的位置
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data',0)) # 设置左侧的轴在底部数值轴为0的位置
ax.annotate('$y=2x+5$',xy=(3,16)) # 设置标记
ax.scatter(x=(-5/2),y=0,c='b') # scatter是画一个点,x表示x轴的位置,y表示y轴的位置,c表示颜色
ax.scatter(x=0,y=5,c='b') # scatter是画一个点,x表示x轴的位置,y表示y轴的位置
ax.scatter(x=2,y=9,c='b')
plt.scatter(x=(2,)*10,y=np.linspace(0,9,10),s=1,c='b') # 使用点线画一条虚线
plt.scatter(x=np.linspace(0,2,10),y=(9,)*10,s=1,c='b')
ax.plot(x,y) # plot画一条直线
plt.show() # 显示图像
如下图所示

附件1 所有配置项
plt.rcParams.keys()
附件2 常用配置项
# 显示中文
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei'
#设置正常显示字符(负号)
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.rcParams['savefig.dpi'] = 300 #图片像素
plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 300 #分辨率
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8.0, 4.0) # 图像显示大小
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest' # 最近邻差值: 像素为正方形
#Interpolation/resampling即插值,是一种图像处理方法,它可以为数码图像增加或减少象素的数目。
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray' # 使用灰度输出而不是彩色输出