python—正则表达式
官方中文文档:https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/re.html#search-vs-match
-
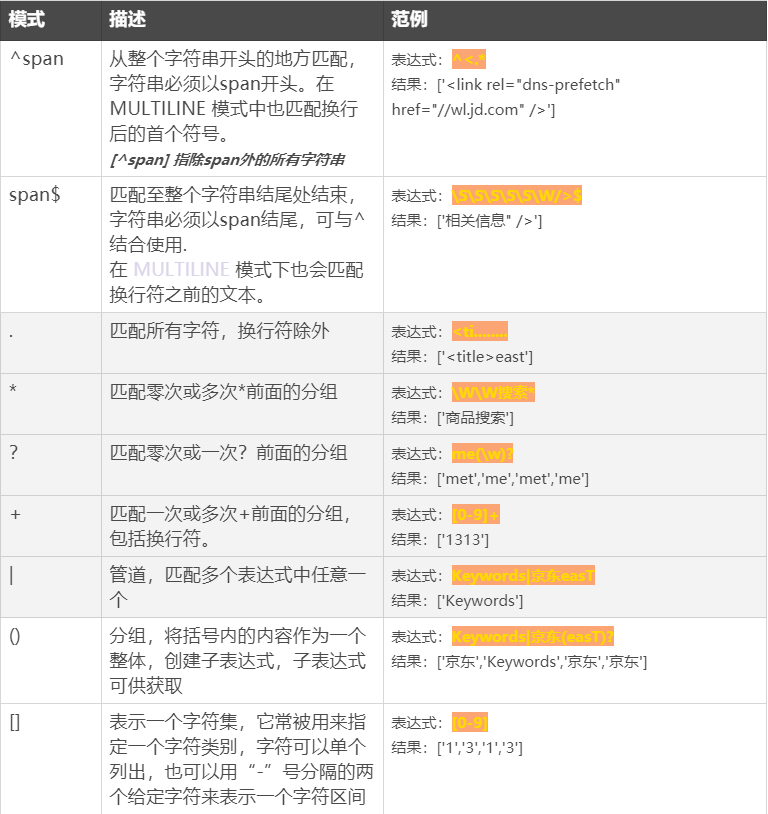
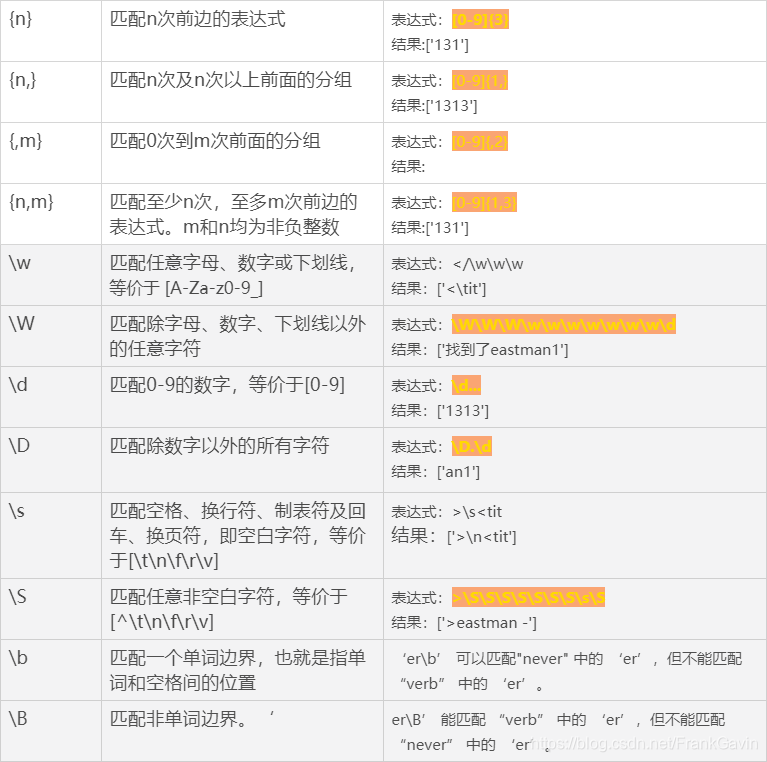
正则语法表
以下为常用语法,部分不常用语法(先行断言(lookahead)和后行断言(lookbehind) )见补充:https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/reg-lookahead-lookbehind.html
范例所用文本:
"""<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//wl.jd.com" />
<title>eastman - 商品搜索 - 京东</title>
<meta name="Keywords" content="eastman,京东eastman" />
<meta name="description" content="在京东找到了eastman1313件eastman的类似商品,其中包含了eastman价格、eastman评论、eastman导购、eastman图片等相关信息" />"""

-
贪婪模式与非贪婪模式
python默认贪婪模式。
贪婪模式:在匹配结果有二义时,尽量匹配最大长度字符串。
'’, ‘+’,和 ‘?’ 修饰符都是 贪婪的,它们在字符串进行尽可能多的匹配。有时候并不需要这种行为。如果正则式 <.> 希望找到 ’ b ',它将会匹配整个字符串,而不仅是 ‘’。
在修饰符之后添加 ? 将使样式以非贪婪`方式进行匹配,尽量少的字符将会被匹配。 使用正则式 <.*?> 将会仅仅匹配 ‘’。 -
python中常用正则函数
- re.match() 与 re.search()
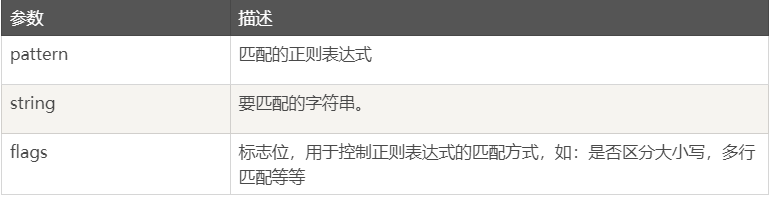
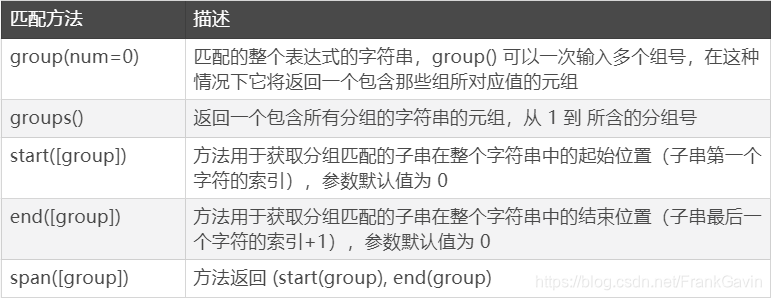
语法:re.match(pattern, string, flags=0)
尝试从字符串的起始位置匹配一个模式,如果不是起始位置匹配成功的话,match()就返回none。
即便是 MULTILINE 多行模式, re.match() 也只匹配字符串的开始位置,而不匹配每行开始。
import re
text = '''<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//wl.jd.com" />
<title>eastman - 商品搜索 - 京东</title>
'''
mo = re.match('<\w\w\w',text)
print(mo)#<re.Match object; span=(0, 4), match='<lin'>
print(mo.group())#<lin
print(mo.start())#0
print(mo.span())#(0, 4)
mo1 = re.match('rel',text)#'rel'不在该字符串起始位置,所以返回None
print(mo1)#None
'''一般常这样用 :'''
content = 'Hello 123 456 welcome to tuling'
result = re.match('^Hello(.*)ng$', content)
print(result)#<re.Match object; span=(0, 31), match='Hello 123 456 welcome to tuling'>
print(result.group())#Hello 123 456 welcome to tuling
print(result.groups())#(' 123 456 welcome to tuli',)
print(result.group(1))#123 456 welcome to tuli
print(result.span(1))#(5, 29)
语法:re.search(pattern, string, flags=0)
扫描整个字符串并返回第一个成功的匹配。如果搜索完了还没有找到,就返回 None。
匹配方法与re.match()相同
import re
text = '''<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//wl.jd.com" />
<title>eastman - 商品搜索 - 京东</title>
<meta name="Keywords" content="eastman,京东eastman" />
<meta name="description" content="在京东找到了eastman1313件eastman的类似商品,其中包含了eastman价格、eastman评论、eastman导购、eastman图片等相关信息" />
'''
mo = re.search('^<meta',text,re.MULTILINE)# MULTILINE 多行模式中函数 match() 只匹配字符串的开始,但使用 search() 和以 '^' 开始的正则表达式会匹配每行的开始。
print(mo)#<re.Match object; span=(82, 87), match='<meta'>
print(mo.group())#<meta
print(mo.span())#(82, 87)
mo1 = re.search('^meta',text,re.MULTILINE)#使用'^'限制匹配到字符串的首位
print(mo1)#None
re.match只匹配字符串的开始,如果字符串开始不符合正则表达式,则匹配失败,函数返回None;而re.search匹配整个字符串,直到找到一个匹配。
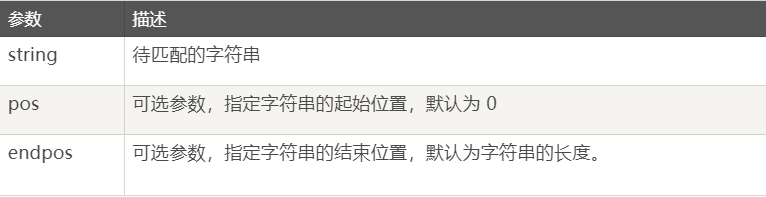
- re.findall() 与 re.finditer()
语法:findall(string[, pos[, endpos]])
在字符串中找到正则表达式所匹配的所有子串,并返回一个列表,如果没有找到匹配的,则返回空列表。
注意: match 和 search 是匹配一次 findall 匹配所有。
import re
text = '''<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//wl.jd.com" />
<title>eastman - 商品搜索 - 京东</title>
<meta name="Keywords" content="eastman,京东eastman" />
<meta name="description" content="在京东找到了eastman1313件eastman的类似商品,其中包含了eastman价格、eastman评论、eastman导购、eastman图片等相关信息" />
'''
mo = re.findall('\w\weastman',text)
print(mo)#['京东eastman', '到了eastman', '3件eastman', '含了eastman']
语法:re.finditer(pattern, string, flags=0)
re.finditer 和 re.findall 类似,在字符串中找到正则表达式所匹配的所有子串,并把它们作为一个迭代器返回。迭代器中的每一个元素都是一个Match对象
import re
text = '''<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//wl.jd.com" />
<title>eastman - 商品搜索 - 京东</title>
<meta name="Keywords" content="eastman,京东eastman" />
<meta name="description" content="在京东找到了eastman1313件eastman的类似商品,其中包含了eastman价格、eastman评论、eastman导购、eastman图片等相关信息" />
'''
mo = re.finditer('\w\weastman',text)
print(mo) #<callable_iterator object at 0x000001B47F1CD448>
for i in mo:
print(i)
print(i.group())
#输出结果:
#<re.Match object; span=(121, 130), match='京东eastman'>
#京东eastman
#<re.Match object; span=(173, 182), match='到了eastman'>
#到了eastman
#<re.Match object; span=(185, 194), match='3件eastman'>
#3件eastman
#<re.Match object; span=(203, 212), match='含了eastman'>
#含了eastman
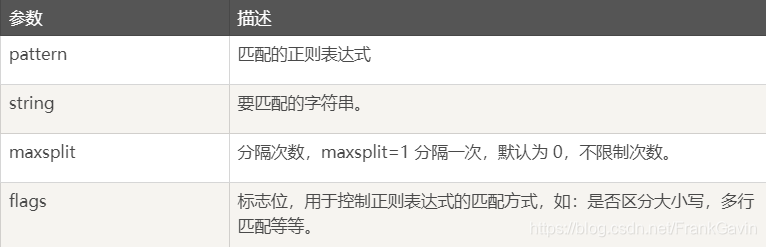
- split()
语法:re.split(pattern, string, maxsplit=0, flags=0)
按照能够匹配的子串将字符串分割后返回列表。
如果 maxsplit 非零, 最多进行 maxsplit 次分隔, 剩下的字符全部返回到列表的最后一个元素。
import re
a = re.split(r'\W+', 'Words, words, words')
print(a)#['Words', 'words', 'words']
如果在表达式中有圆括号,那么除被 圆括号中的表达式匹配掉的字符 外的字符也会作为元素被包含在列表里(含空白字符)
b = re.split(r'(\W+)', 'Words,\n,words, words')
print(b)#['Words', ',\n,', 'words', ', ', 'words']
如果分隔符里有捕获组合,并且匹配到字符串的开始或结尾,那么结果将会以一个空字符串开始或结尾
c = re.split(r'\W+', '.words, words。')
print(c)#['', 'words', 'words', '']
对于一个找不到匹配的字符串而言,split 不会对其作出分割
d = re.split('\s', 'helloworld')
print(d)#['helloworld']
样式的空匹配仅在与前一个空匹配不相邻时才会拆分字符串
e = re.split('1*','helloworld')
print(e)#['', 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd', '']
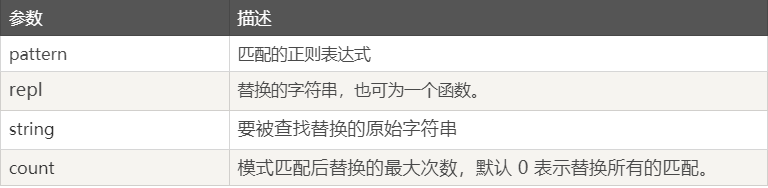
- re.sub()
语法:re.sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0)
返回通过使用 repl 替换在 string 最左边非重叠出现的 pattern 而获得的字符串。 如果样式没有找到,则不加改变地返回 string。
repl 可以是字符串或函数。如repl为字符串,则其中任何反斜杠转义序列都会被处理。 也就是说,\n 会被转换为一个换行符,\r 会被转换为一个回车附,依此类推。
import re
phone = "2004-959-559 # 这是一个国外电话号码"
# 删除字符串中的 Python注释
num = re.sub(r'#.*$', "", phone)
print("电话号码是:%s"%num) #电话号码是:2004-959-559
# 删除非数字(-)的字符串
num = re.sub(r'\D', "", phone)
print("电话号码是:%s"%num) #电话号码是:2004959559
- compile()
语法:re.compile(pattern[, flags])
用于编译正则表达式,生成一个正则表达式( Pattern )对象,供 match() 和 search() 这两个函数使用。
match() 或 search() 函数匹配成功后,返回的是一个match对象。该对象可使用如group()、start()、span()等方法。
import re
pattern = re.compile(r'\d+')
text = 'abcd 12315 .a'
mo = pattern.search(text)
print(mo)#<re.Match object; span=(5, 10), match='12315'>
print(mo.group())#12315
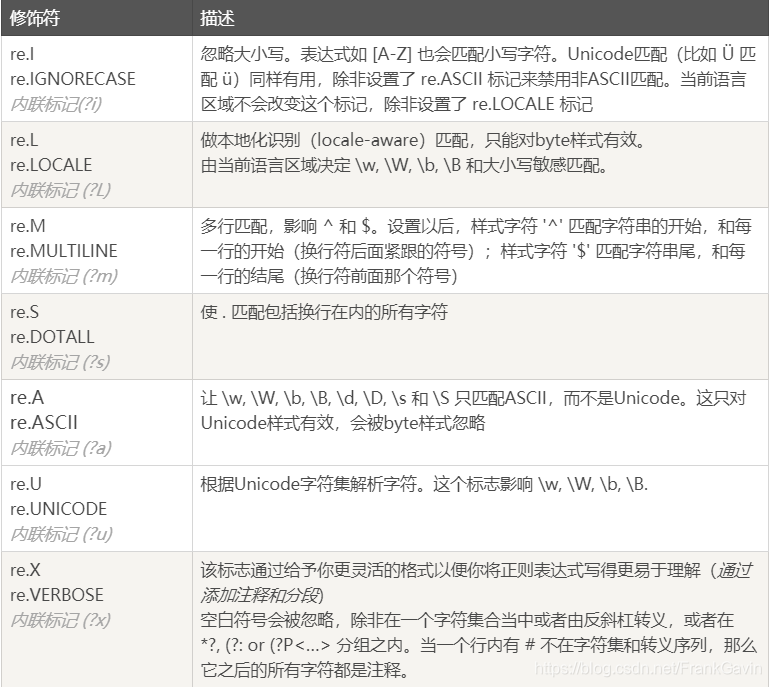
- 正则表达式修饰符(可选标志)