常用地图底图的绘制一般由Basemap或者cartopy模块完成,由于Basemap库是基于python2开发的一个模块,目前已经不开发维护。故简单介绍cartopy模块的一些基础操作。
将地球三维球体投影到二维面上,减少失真。主要方式有默认投影(PlateCarree)、兰勃脱投影(Lambert)、墨卡托投影(Mercator)、极投影。
例一:
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#plt.axes是创建一个轴(或者说是主体) projection参数可以理解为将三维的地理信息如何投影为二维的地理信息,这个时候参数的值就是投影方式,此时是常用的平面投影
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.coastlines() #这个函数是在主体上添加了海岸线
# Save the plot by calling plt.savefig() BEFORE plt.show()
plt.savefig('coastlines.pdf')
plt.savefig('coastlines.png')
plt.show() #将图像显示出来以上代码是第一个例子,例子的运行结果如下

例二:
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
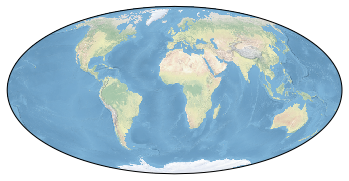
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.Mollweide()) #这里和上一个例子更换了投影方式,投影成了椭圆形
ax.stock_img() #这个方法可以认为是添加了贴纸,让海洋呈现蓝色,将陆地和海洋分开
plt.show()?以上代码的运行结果如下:
?例三:
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.stock_img()
ny_lon, ny_lat = -75, 43 #这里是伦敦的经纬度
delhi_lon, delhi_lat = 77.23, 28.61 #这里是纽约的经纬度
#接下来是要在这两个点上画线加注释文字
plt.plot([ny_lon, delhi_lon], [ny_lat, delhi_lat],
color='blue', linewidth=2, marker='o',
transform=ccrs.Geodetic(),
) #前面两个参数是线的起始点的经纬度,最后一个参数是用来指定数据的坐标系,
一般来说,数据的坐标系与这个整体轴的坐标系是相同的,我们也可以设置为不同,此时整体是平面坐标系,数据设置为了椭圆坐标系,就是在椭圆中这两个点画个直线应该是什么样的
plt.plot([ny_lon, delhi_lon], [ny_lat, delhi_lat],
color='gray', linestyle='--',
transform=ccrs.PlateCarree(),
)
plt.text(ny_lon - 3, ny_lat - 12, 'New York',
horizontalalignment='right',
transform=ccrs.Geodetic())
plt.text(delhi_lon + 3, delhi_lat - 12, 'Delhi',
horizontalalignment='left',
transform=ccrs.Geodetic())
plt.show()以上代码的结果如下所示: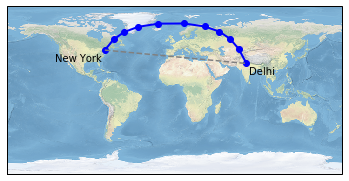
通过这三个小例子我们了解到了一些皮毛,接着往下走。
在这个例子中我们学习1.如何绘制坐标系 2.如何显示区域地图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
from cartopy.mpl.ticker import LongitudeFormatter, LatitudeFormatter
ax=plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree(central_longitude=0))
#这里设置了中心经线参数,就是说我们这个图的中心线在哪
ax.stock_img()
ax.coastlines()
#设置坐标轴标签
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(0,361,40), crs=ccrs.PlateCarree()) #设置纬度范围及其间隔,以及投影方式
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-90,90+30,30), crs=ccrs.PlateCarree())
#zero_direction_label用来设置经度的0度加不加E和W
lon_formatter = LongitudeFormatter(zero_direction_label=False)
lat_formatter = LatitudeFormatter()
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(lon_formatter)
ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(lat_formatter) #设置坐标轴标签的格式,加上N,S,E,W
ax.grid() #添加网格线
#设置坐标轴的粗细
ax.outline_patch.set_visible(False)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_visible(True)
ax.spines['left'].set_visible(True)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(True)
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(True) #设置四个边框可不可视
ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(2.5);###设置底部坐标轴的粗细
ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(2.5);####设置左边坐标轴的粗细
ax.spines['right'].set_linewidth(2.5);###设置右边坐标轴的粗细
ax.spines['top'].set_linewidth(2.5);####设置上部坐标轴的粗细
#之前都是绘制的默认的全球地图,此时绘制区域地图
ax.set_extent([40,180,0,90],crs=ccrs.PlateCarree()) #第一个参数是绘制区域,起始经度,起始纬度 第二个参数是投影类型
plt.show()接下来这个例子告诉我们在图的基础上添加一些新的元素(湖泊等)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
proj = ccrs.PlateCarree()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 7))
ax = fig.subplots(1, 1, subplot_kw={'projection': proj})
#可以看见此处设置主题轴的方式跟之前有所不同,此时是用ccrs和plt混合的方式来定义的,先用plt来设置整体大小,再来设置主轴
ax.coastlines()
#在原来图的基础上加上一些标签
ax.add_feature(cfeature.LAND) # 添加陆地
ax.add_feature(cfeature.COASTLINE,lw=0.3)# 添加海岸线
ax.add_feature(cfeature.RIVERS,lw=0.25)# 添加河流
ax.add_feature(cfeature.LAKES)# 添加湖泊
ax.add_feature(cfeature.BORDERS, linestyle='-',lw=0.25)# 不推荐,我国丢失了藏南、台湾等领土
ax.add_feature(cfeature.OCEAN)#添加海洋
#ax.add_feature(cfeature.OCEAN,color='green')#添加海洋,我们还可以设置一些参数改变默认设置,主要修改lw、linestyle、color这三个参数
#设置经纬度
gl = ax.gridlines(draw_labels=True, linewidth=0.2, color='k', alpha=0.5, linestyle='--')
# 调节字体大小
gl.xlabel_style={'size':12.5}
gl.ylabel_style={'size':12.5}
#设置高精度 会出现地图上本来没有的一些小岛
ax.add_feature(cfeature.COASTLINE.with_scale('10m'),lw=0.5)绘制中国地图:
重点是从文件中读取CN-border-La.da文件,目的是读取里面每个点的经纬度,用于给底图加上行政边界。代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
#读取CN-border-La.dat文件
with open('D:/绘制地图/CN-border-La.dat') as src:
context = src.read()
blocks = [cnt for cnt in context.split('>') if len(cnt) > 0]
borders = [np.fromstring(block, dtype=float, sep=' ') for block in blocks]
#设置画图各种参数
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[8, 8])
# 设置投影类型和经纬度
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.LambertConformal(central_latitude=90,
central_longitude=105))
# 画海,陆地,河流,湖泊
ax.add_feature(cfeature.OCEAN.with_scale('50m'))
ax.add_feature(cfeature.LAND.with_scale('50m'))
ax.add_feature(cfeature.RIVERS.with_scale('50m'))
ax.add_feature(cfeature.LAKES.with_scale('50m'))
# 画国界
for line in borders:
ax.plot(line[0::2], line[1::2], '-', color='gray',transform=ccrs.Geodetic())
# 画经纬度网格
ax.gridlines(linestyle='--')
# 框出区域
ax.set_extent([80, 140, 13, 55])
# 画南海,这一步是新建一个ax,设置投影
sub_ax = fig.add_axes([0.741, 0.11, 0.14, 0.155],
projection=ccrs.LambertConformal(central_latitude=90,
central_longitude=115))
# 画海,陆地,河流,湖泊
sub_ax.add_feature(cfeature.OCEAN.with_scale('50m'))
sub_ax.add_feature(cfeature.LAND.with_scale('50m'))
sub_ax.add_feature(cfeature.RIVERS.with_scale('50m'))
sub_ax.add_feature(cfeature.LAKES.with_scale('50m'))
# 画边界
for line in borders:
sub_ax.plot(line[0::2], line[1::2], '-', color='gray',
transform=ccrs.Geodetic())
# 框区域
sub_ax.set_extent([105, 125, 0, 25])
# 显示
plt.show()效果图如下: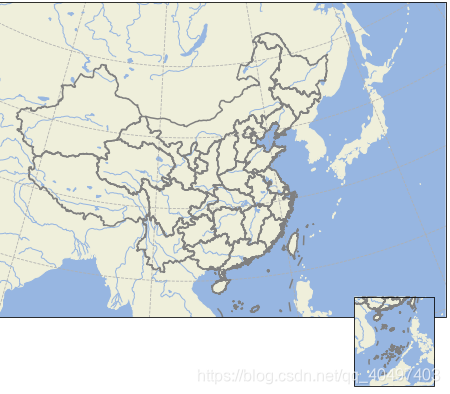
?