pandas的应用(一)创建与读写
1. DataFrame and Series
1.1DataFrame
A DataFrame is a table. It contains an array of individual entries, each of which has a certain value. Each entry corresponds to a row (or record) and a column.
For example, consider the following simple DataFrame:
pd.DataFrame({'Yes': [50, 21], 'No': [131, 2]})
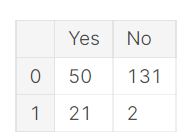
In this example, the “0, No” entry has the value of 131. The “0, Yes” entry has a value of 50, and so on.
DataFrame entries are not limited to integers. For instance, here’s a DataFrame whose values are strings:
pd.DataFrame({'Bob': ['I liked it.', 'It was awful.'], 'Sue': ['Pretty good.', 'Bland.']})
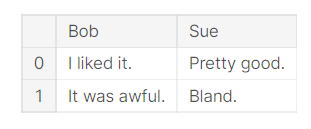
We are using the pd.DataFrame() constructor to generate these DataFrame objects. The syntax for declaring a new one is a dictionary whose keys are the column names (Bob and Sue in this example), and whose values are a list of entries. This is the standard way of constructing a new DataFrame, and the one you are most likely to encounter.
The list of row labels used in a DataFrame is known as an Index. We can assign values to it by using an index parameter in our constructor:
pd.DataFrame({'Bob': ['I liked it.', 'It was awful.'],
'Sue': ['Pretty good.', 'Bland.']},
index=['Product A', 'Product B'])

1.2 Series
A Series, by contrast, is a sequence of data values. If a DataFrame is a table, a Series is a list. And in fact you can create one with nothing more than a list:
pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
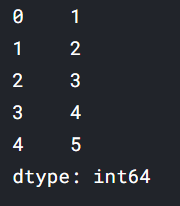
A Series is, in essence, a single column of a DataFrame. So you can assign column values to the Series the same way as before, using an index parameter. However, a Series does not have a column name, it only has one overall name:
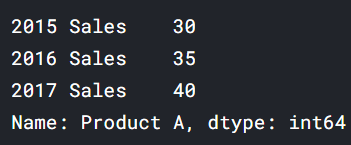
pd.Series([30, 35, 40], index=['2015 Sales', '2016 Sales', '2017 Sales'], name='Product A')
1.3 Reading data files
wine_reviews = pd.read_csv("../input/wine-reviews/winemag-data-130k-v2.csv")
We can use the shape attribute to check how large the resulting DataFrame is:
wine_reviews.shape
We can examine the contents of the resultant DataFrame using the head() command, which grabs the first five rows:
wine_reviews.head()