learn from 《流畅的python》
1. 序列__getitem__
如果没有
__iter__和__contains__方法,
Python 会调用__getitem__方法,
设法让 迭代 和in运算符可用
class Foo:
def __getitem__(self, pos):
return range(0, 30, 10)[pos]
f = Foo()
print(f[1]) # 10
for i in f:
print(i) # 0, 10, 20
# 如果没有 __iter__ 和 __contains__ 方法,
# Python 会调用 __getitem__ 方法,
# 设法让迭代和 in 运算符可用
2. __setitem__
import collections
Card = collections.namedtuple('Card', ['rank', 'suit'])
class FrenchDeck:
ranks = [str(n) for n in range(2, 11)] + list('JQKA')
suits = 'spades diamonds clubs hearts'.split()
def __init__(self):
self._cards = [Card(rank, suit) for suit in self.suits for rank in self.ranks]
def __len__(self):
return len(self._cards)
def __getitem__(self, position):
return self._cards[position]
def __str__(self):
return ",".join(str(i) for i in self._cards)
from random import shuffle
deck = FrenchDeck()
print(str(deck))
# Card(rank='2', suit='spades'),Card(rank='3', suit='spades'),Card(rank='4', suit='spades'),Card(rank='5', suit='spades'),Card(rank='6', suit='spades'),Card(rank='7', suit='spades'),Card(rank='8', suit='spades'),Card(rank='9', suit='spades'),Card(rank='10', suit='spades'),Card(rank='J', suit='spades'),Card(rank='Q', suit='spades'),Card(rank='K', suit='spades'),Card(rank='A', suit='spades'),Card(rank='2', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='3', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='4', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='5', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='6', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='7', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='8', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='9', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='10', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='J', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='Q', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='K', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='A', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='2', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='3', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='4', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='5', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='6', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='7', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='8', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='9', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='10', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='J', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='Q', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='K', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='A', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='2', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='3', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='4', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='5', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='6', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='7', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='8', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='9', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='10', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='J', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='Q', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='K', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='A', suit='hearts')
shuffle(deck) # TypeError: 'FrenchDeck' object does not support item assignment
- 加入
__setitem__
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
self._cards[key] = value
shuffle(deck)
print(str(deck))
# 牌被随机打乱了
# Card(rank='6', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='2', suit='spades'),Card(rank='3', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='A', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='7', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='Q', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='5', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='6', suit='spades'),Card(rank='5', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='8', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='K', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='Q', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='8', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='3', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='Q', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='A', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='9', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='7', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='A', suit='spades'),Card(rank='J', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='3', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='4', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='Q', suit='spades'),Card(rank='10', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='10', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='K', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='2', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='4', suit='spades'),Card(rank='3', suit='spades'),Card(rank='7', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='9', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='J', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='J', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='10', suit='spades'),Card(rank='4', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='7', suit='spades'),Card(rank='9', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='2', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='6', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='K', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='4', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='A', suit='hearts'),Card(rank='K', suit='spades'),Card(rank='2', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='J', suit='spades'),Card(rank='8', suit='spades'),Card(rank='5', suit='spades'),Card(rank='9', suit='spades'),Card(rank='10', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='8', suit='clubs'),Card(rank='6', suit='diamonds'),Card(rank='5', suit='clubs')
或者 在类外打补丁 FrenchDeck.__setitem__ = 函数
def set_card(deck, position, card):
deck._cards[position] = card
FrenchDeck.__setitem__ = set_card
3. 抽象基类
class Test:
def __len__(self):
return 24
from collections import abc
print(isinstance(Test(), abc.Sized)) # True
只要实现了 __len__() 方法,就可以被 abc.Sized 识别为子类
4. 不要直接子类化内置类型
class AnswerDict(dict):
def __getitem__(self, key):
return 24
ad = AnswerDict(a="good")
print(ad['a']) # 24
d = {}
d.update(ad)
print(d['a']) # good
print(ad) # {'a': 'good'}
print(d) # {'a': 'good'}
直接子类化内置类型(如 dict、list 或 str)容易出错, 因为 内置类型的方法 通常会 忽略用户覆盖的方法。
不要子类化内置 类型,用户自己定义的类 应该继承 collections 模块 中的类,例如 UserDict、UserList 和 UserString,这些类做了特殊设计,因 此易于扩展
import collections
class AnswerDict2(collections.UserDict):
def __getitem__(self, key):
return 24
ad = AnswerDict2(a="good")
print(ad['a']) # 24
d = {}
d.update(ad)
print(d['a']) # 24
print(ad) # {'a': 'good'}
print(d) # {'a': 24}
5. 继承顺序
- 多重继承的同名方法调用,根据类的
__mro__属性顺次在类中查找 - 推荐使用
super()函数
6. 重载运算符

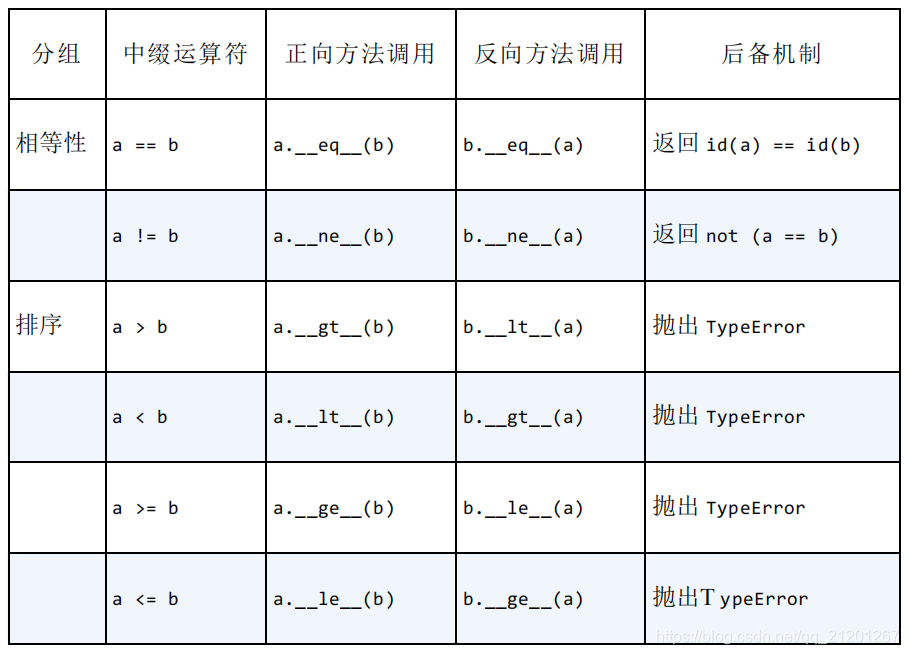
不可变类型,,一定不能实现就地特殊方法
__iadd__等增量赋值特殊方法 必须返回 self