1、数据准备
- 数据规模:数据分组、数据采样(处理大数据时候尤为需要)
- 数据类型:数值数据、分类数据(一定要对数据结构特别清楚:连续?离散?有序吗?)
- 数据规模:取值异常、数据缺失
数据分组 groupby
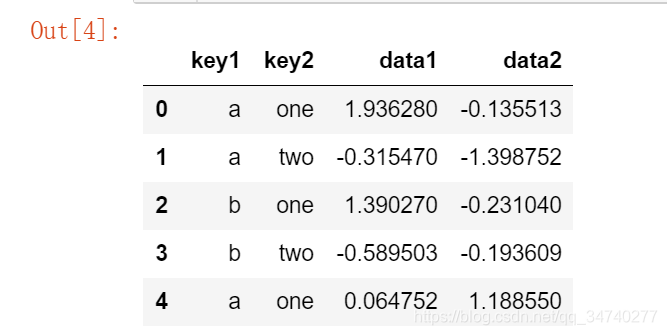
# DataFarme
df = pd.DataFrame({'key1':['a','a','b','b','a'],
'key2':['one','two','one','two','one'],
'data1':np.random.normal(size=5),
'data2':np.random.normal(size=5)})
df
df['data1'].groupby(df['key1']).mean()

数据采样 sample (处理大数据时尤为需要)
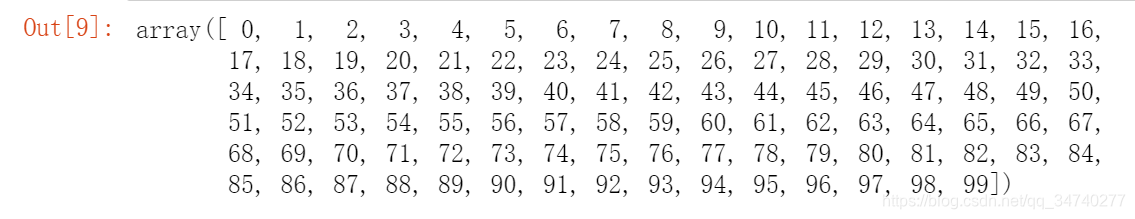
import random
x = np.arange(1,100)
y = random.sample(list(x),10)# 采样
y

取值异常、数据缺失
- 数据准备
- 确定图表
NA处理 dropna fillna
# 去掉异常
x = np.arange(0,100)
y = x[(x>90)|(x<100)]
y
# 替换异常
y = x
for i in np.arange(0,100):
if i >= 0 and i<=90:
y[i] = 0
else:
y[i] = i
y

np.array([0 if i>= 10 and i <= 90 else i for i in range(0,100)])

# NA处理
from numpy import nan
data = pd.Series([1,nan,2,nan,3,nan])
data

data.dropna() # 删除空值

data.fillna(4) # 用4替换空值

2、确定图表
数据可视化里通常面临的三类问题:
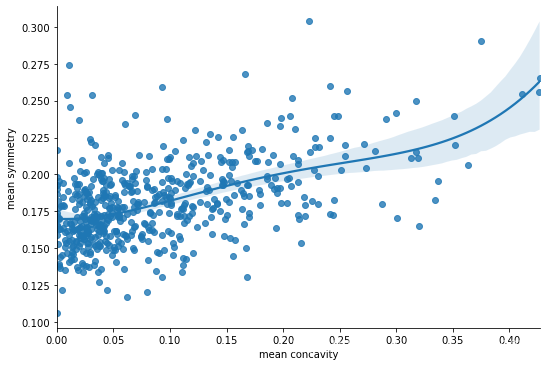
- 关联分析:散点图,曲线图(scatter,plot)
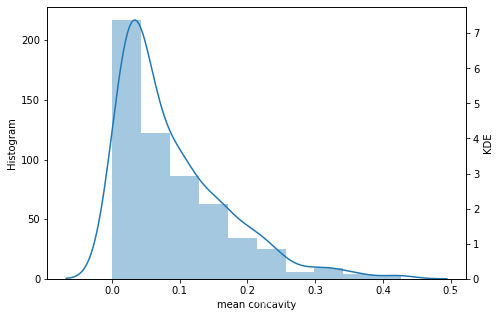
- 分布分析:灰度图,密度图(hist,gaussian_kde,plot)
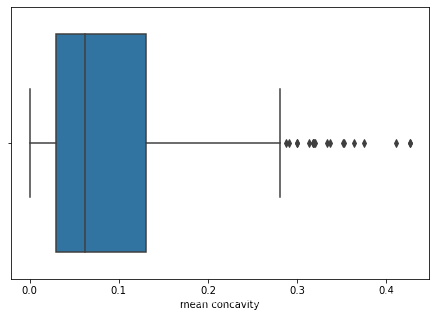
- 分类分析:柱状图,箱式图(bar,boxplot)
关联分析
from sklearn import datasets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
bc = datasets.load_breast_cancer()
df = pd.DataFrame(bc.data,columns=bc.feature_names)
sns.lmplot('mean concavity','mean symmetry',df,
height=5,aspect=1.5,fit_reg=True,order=4)
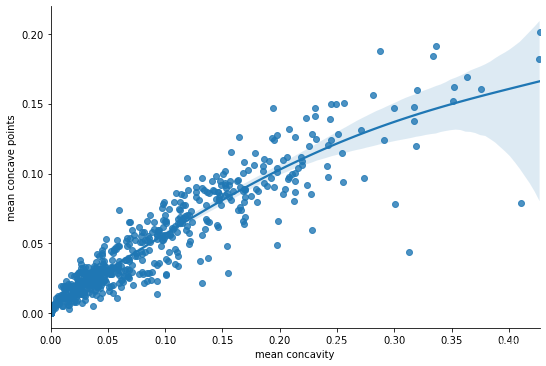
sns.lmplot('mean concavity','mean concave points',df,
height=5,aspect=1.5,fit_reg=True,order=4)
分布分析
plt.figure(figsize=(7.5,5))
sns.distplot(df['mean concavity'],bins=10,kde=False)
plt.ylabel('Histogram')
plt.twinx()
sns.kdeplot(df['mean concavity'],cumulative=False)
plt.ylabel('KDE')
分类分析
plt.figure(figsize=(7.5,5))
sns.boxplot(x='mean concavity',data=df)
df['mean concavity'].describe()

3、分析迭代
- 确定拟合模型:OLS, fit OLS = 最小二乘;fit = 拟合
- 分析拟合性能:summary_table统计学汇总
- 确定数据分布:hist
- 确定重点区间:quartile 分布的上下四分位数,以及各分位数之间的区间
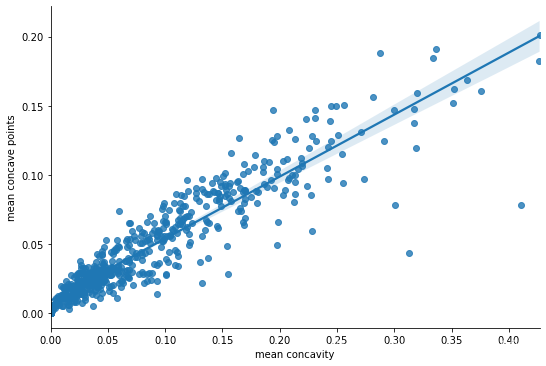
sns.lmplot('mean concavity','mean concave points',df,
height=5,aspect=1.5,fit_reg=True,order=1)
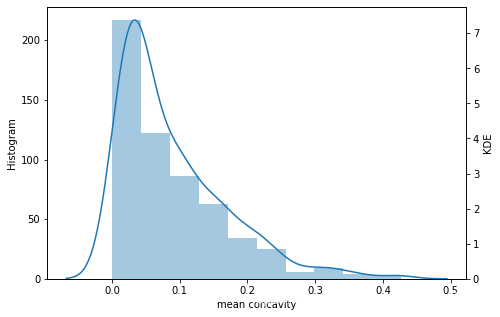
plt.figure(figsize=(7.5,5))
sns.distplot(df['mean concavity'],bins=10,kde=False)
plt.ylabel('Histogram')
plt.twinx()
sns.kdeplot(df['mean concavity'],kernel = 'gau',cumulative=False)
# sns.kdeplot(df['mean concavity'],kernel = 'gau',cumulative=False)
plt.ylabel('KDE')
plt.figure(figsize=(7.5,5))
sns.boxplot(x='mean concavity',data=df)
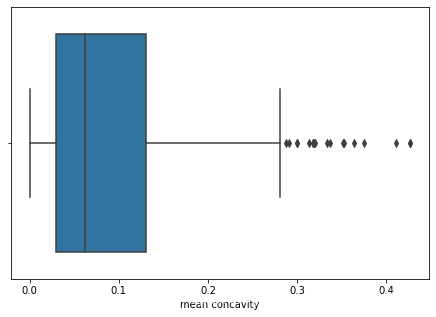
- 箱型图Boxplot
观察分布的对称性和偏性
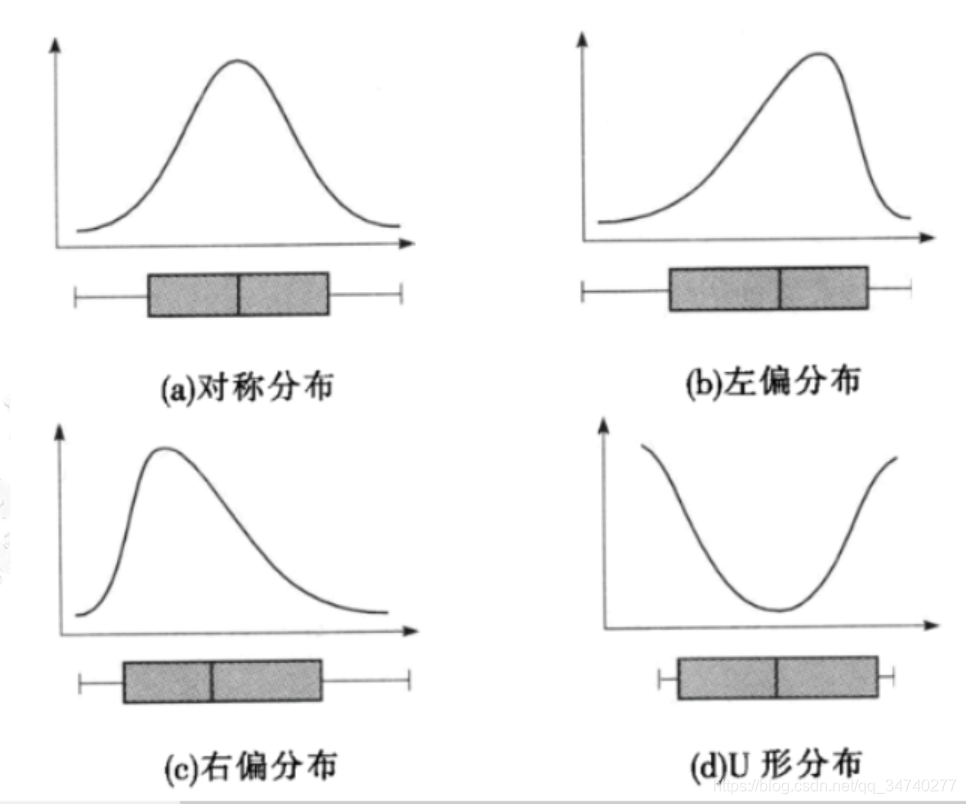
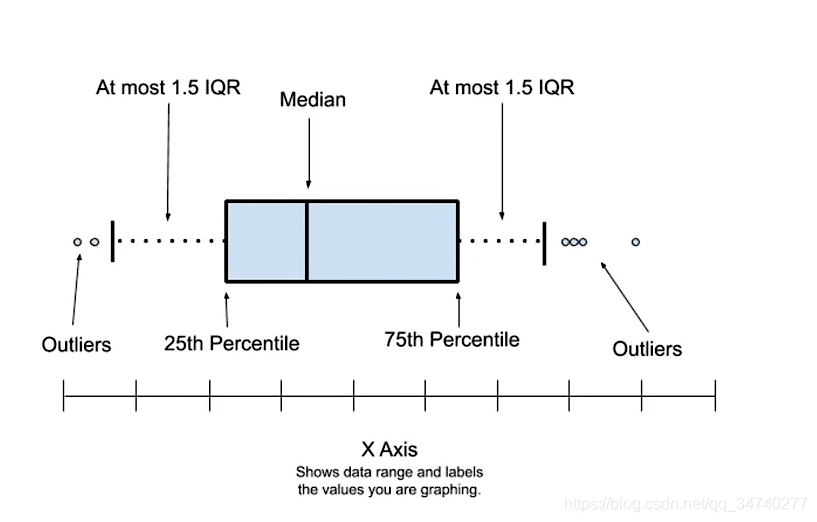
箱型图的局限性
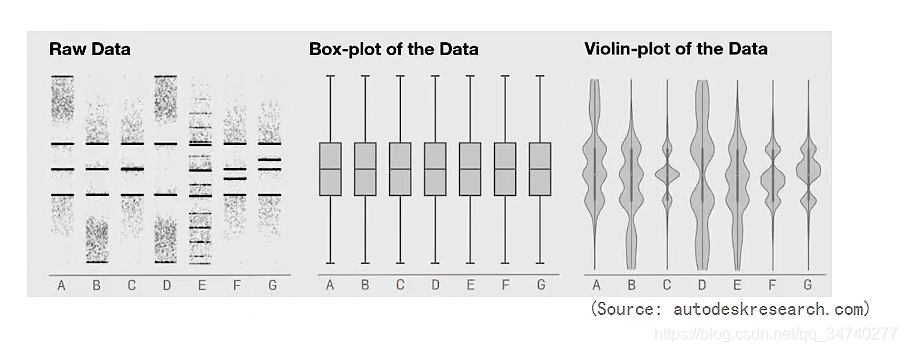
对数据的本质理解会产生偏差,不同的数据集可能得到相同的箱型图。
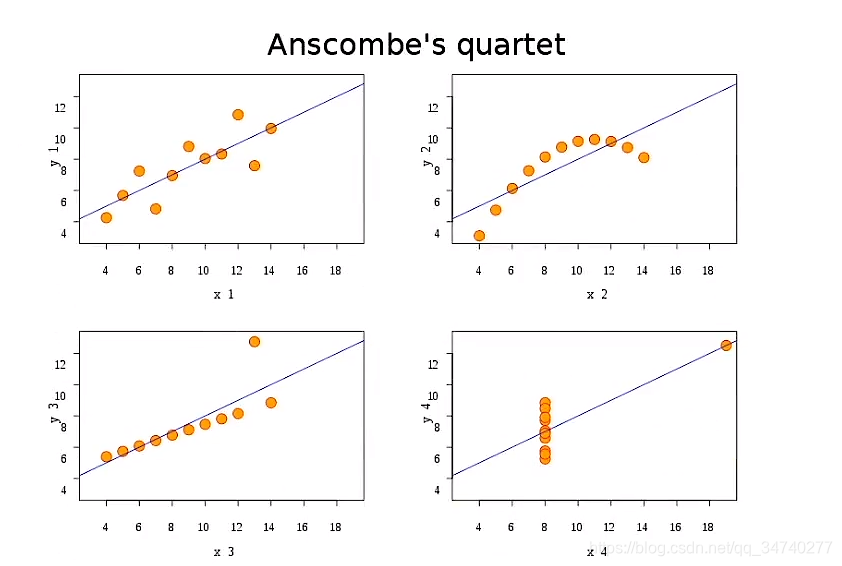
"""
Edward Tufte uses this example from Anscombe to show 4 datasets of x
and y that have the same mean, standard deviation, and regression
line, but which are qualitatively different.
"""
x=[10,8,13,9,11,14,6,4,12,7,5]
x4=[8,8,8,8,8,8,8,19,8,8,8]
y1=[8.04,6.95,7.58,8.81,8.33,9.96,7.24,4.26,10.84,4.82,5.68]
y2=[9.14,8.14,8.74,8.77,9.26,8.10,6.13,3.10,9.13,7.26,4.74]
y3=[7.46,6.77,12.74,7.11,7.81,8.84,6.08,5.39,8.15,6.42,5.73]
y4=[6.58,5.76,7.71,8.84,8.47,7.04,5.25,12.50,5.56,7.91,6.89]
df=pd.DataFrame({'x':x,'y1':y1,'y2':y2,'y3':y3,'y4':y4,})
df[['y1','y2','y3','y4']].describe().loc['mean':'std']
分析迭代的要素,不仅依赖于数据本身,也依赖人的分析角度。
4、输出结论
- 养成看图说话的习惯
- 提出一个好问题,画出一个好图像,给出一个好结论
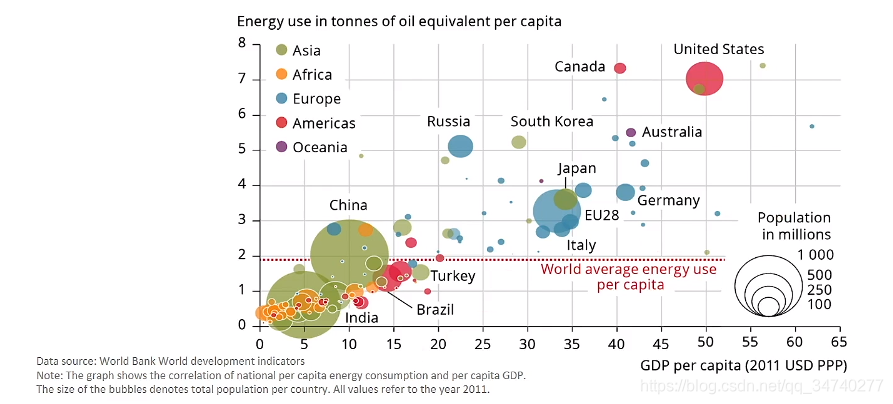
结论:
(1)人均GDP和石油消耗量成正比
(2)人均GDP和石油消耗量与国家人口数量没有关系
5、小结
6、作业
绘制出Edward Tufte的散点图和一维拟合曲线,如下所示。(答案在下一篇文章公布)