文章目录
附上这节的练习代码:
django_study_03
下班了。。。
接着上篇文章继续写
来聊一下响应response
Http响应报文是由3部分组成:响应行、响应头和响应体
来看下HttpRsponse,它是一个类
接来下来看下它的底层代码咋写的
def __init__(self, content=b'', *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
# Content is a bytestring. See the `content` property methods.
self.content = content
除了这个响应还有一个页面渲染响应render
举个例子
新建一个视图类
def show_goods1(request):
return render(request, 'goods.html')

在templates下新建一个HTML文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid indianred;
font-size: 25px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
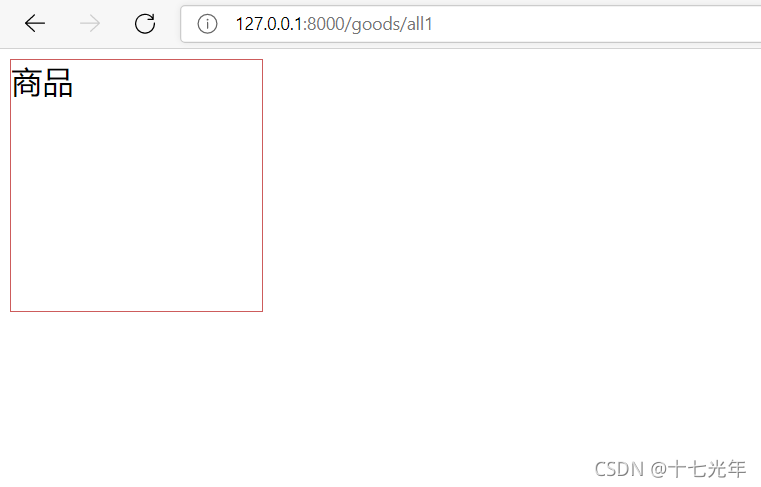
<div>商品</div>
</body>
</html>

然后关联上它的路由
path('all1', show_goods1),
最后展示效果:

好了,例子就先到这里
接下来看下render的底层
def render(request, template_name, context=None, content_type=None, status=None, using=None):
"""
Return a HttpResponse whose content is filled with the result of calling
django.template.loader.render_to_string() with the passed arguments.
"""
content = loader.render_to_string(template_name, context, request, using=using)
return HttpResponse(content, content_type, status)
结果我发现这货最终返回的竟然是HttpResponse
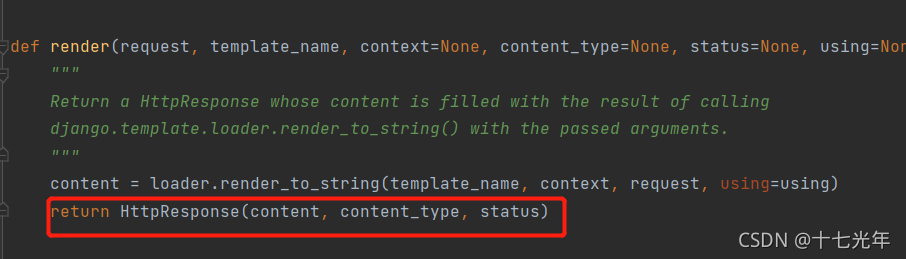
发现我调render,最后render的底层还是response的对象
除了它还有一个需要注意的是它上面那行的content里的loader,他在这里主要是把模板加载过来
这里可以简单的通过loader的底层看下
def render_to_string(template_name, context=None, request=None, using=None):
"""
Load a template and render it with a context. Return a string.
template_name may be a string or a list of strings.
"""
if isinstance(template_name, (list, tuple)):
template = select_template(template_name, using=using)
else:
template = get_template(template_name, using=using)
return template.render(context, request)
渲染就是通过loader加载器把模板找到,找到之后把模板里的东西转成一个字符串的形式,然后返回到content
render函数的特点:
通过模板引擎Django去加载模板,奖模板加载完成之后装成字符串(str类型),再将这个str交给HttpResponse作为参数
接下来看第二个函数:redirect
还是来看下底层代码
def redirect(to, *args, permanent=False, **kwargs):
"""
Return an HttpResponseRedirect to the appropriate URL for the arguments
passed.
The arguments could be:
* A model: the model's `get_absolute_url()` function will be called.
* A view name, possibly with arguments: `urls.reverse()` will be used
to reverse-resolve the name.
* A URL, which will be used as-is for the redirect location.
Issues a temporary redirect by default; pass permanent=True to issue a
permanent redirect.
"""
redirect_class = HttpResponsePermanentRedirect if permanent else HttpResponseRedirect
return redirect_class(resolve_url(to, *args, **kwargs))
来看下这里
Return an HttpResponseRedirect to the appropriate URL for the arguments
大概意思是说它返回了一个HttpResponseRedirect
然后再来看下这个所谓的HttpResponseRedirect又是个什么玩意
再来进入HttpResponseRedirect的底层瞅一眼
class HttpResponseRedirect(HttpResponseRedirectBase):
status_code = 302
再进一层看HttpResponseRedirectBase
class HttpResponseRedirectBase(HttpResponse):
allowed_schemes = ['http', 'https', 'ftp']
就这么个玩意。。。
发现最终还是HttpResponse,所以发现找回来找回去最终还是一个HttpResponse对象
接下来就再回来看下这个redirect的讲解是啥样的
The arguments could be:
#一个模型:获取URL路径
* A model: the model's `get_absolute_url()` function will be called.
#一个视图名,用urls.reverse()可以得到一个视图名(反向解析)
* A view name, possibly with arguments: `urls.reverse()` will be used
to reverse-resolve the name.
#直接传URL就可以了
* A URL, which will be used as-is for the redirect location.
这里讲的是说我的参数可以是什么
看下怎么使用reverse

上代码:
goods/views.py
def show_goods1(request):
return render(request, 'goods.html')
def my_redirect(request):
url = reverse('goods:all1')
print(url)
return redirect(url)
主路由urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
from users import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('users/', include('users.urls', namespace='users')),
path('goods/', include('goods.urls', namespace='goods')),
]
goods/urls.py
from django.urls import path
from goods.views import index, show_goods, show_goods1, my_redirect
app_name = 'goods'
urlpatterns = [
path('', index),
path('all', show_goods, name='all'),
path('all1', show_goods1, name='all1'),
path('myreverse', my_redirect, name='myreverse'),
]
输入http://127.0.0.1:8000/goods/myreverse回车后会自动指向all1
运行结果: