Python II Basics [C]
- Python II Basics [C]
- Python beginner
- Variables & Data Types
- Basic Operators & Input
- Conditions
- IF/ELIF/ELSE
- Chained Conditionals & Nested Statements
- For Loops
- While Loops
- Lists and Tuples
- Iteration by Item (For Loops Continued)
- String Methods
- Slice Operator
- Functions
- File IO (Reading Files)
- File IO(Writing Files)
- List Methods (.count/in;/index)
- Introduction to Modular Programming
- Error Handling (Try/Except)
- Global vs Local
- Classes and Objects
- Python Intermediate
- OOP
- Thread
- Advanced
- Numpy
- PyQt I
- PyQt II
- Install pyqt
- PyQt Hello World
- PyQt Buttons
- PyQt QMessageBox
- PyQt grid
- QLineEdit
- PyQt QPixmap
- PyQt Combobox
- QCheckBox
- QSlider
- Progressbar
- PyQt table
- QVBoxLayout
- PyQt style
- Compile PyQt to exe
- QDial
- Pyqt-radiobutton
- Pyqt-groupbox
- Pyqt-tooltip
- PyQt toolbox
- PyQt toolbar
- PyQt menubar
- PyQt tabwidget
- PyQt auto complete
- PyQt list box
- PyQt input dialog
Python II Basics [C]

- Notes from techwithtim and pythonbasics
Python beginner
Variables & Data Types
- Integer: “int”
- Float: “float” : add .0 to make int loat
- String: “str”
- Boolean: “bool”
>>> var='hello'
>>> print(var,'!')
hello !
Basic Operators & Input
- input()
- var= input(‘ask’)
name=input('name:')
print('hello ',name)
- operators:
+ # addition
- # subtraction
/ # division
* # multiplication
** # exponential
// # integer division (removes decimal portion)
% # modulus (gives remainder of division)
-
order of operation: Brackets> Exponents> Multiplication> Division> Addition>Subtraction>Comparison Operators
-
Strings: + : concat, * : repeat
str1='hello'+ 'world'
str2='python'*3
print(str1)
print(str2)
- convert type : type(var)
num='333'
num2=int(num)
print(type(num))
print(type(num2))
Conditions
- Comparison Operators
< # less than
<= # less than or equal to
> # greater than
>= # greater than or equal to
== # equal to
!= # not equal to
- must be the same type to compare
- == can be used with string
x=4
y=5
print(x==y-1)
print(x!=y-1)
IF/ELIF/ELSE
- if , elif, else
x=int(input('enter num 1-10:'))
y=5
if x<y:
print('x<y')
elif x>y:
print('x>y')
else:
print('you win')
Chained Conditionals & Nested Statements
- and, or , not
print((True or False) and False)
print((True or False) and True)
- nested statements
ans=input('num 1-10:')
if int(ans)>=5:
ans=input('a or b or c:')
if ans== 'c':
print('cool')
else:
print('not cool')
else:
print('too low')
For Loops
- for x in range(num)
- range(start, stop, step)
- range default start with 0
for x in range(10):
print(x)
print('___________')
for x in range(3,10):
print(x)
print('___________')
for x in range(3,10,2):
print(x)
While Loops
- while condition==true: do something …condition: break…
while True:
i=input('num 1-10:')
if i=='5':
break
print('loop')
Lists and Tuples
- Lists use square brackets [list]
- add by assigning value into the index location
- append: add to the end
- remove(‘value’), remove lower index num, remove 1 item only
- del var[index]
append() Adds an element at the end of the list
clear() Removes all the elements from the list
copy() Returns a copy of the list
count() Returns the number of elements with the specified value
extend() Add the elements of a list (or any iterable), to the end of the current list
index() Returns the index of the first element with the specified value
insert() Adds an element at the specified position
pop() Removes the element at the specified position
remove() Removes the first item with the specified value
reverse() Reverses the order of the list
sort() Sorts the list
list1=['a',22,4.0,True]
print(list1)
print(list1[0])
list1[0]='new'
print(list1)
list1.append('new')
print(list1)
list1.remove('new')
print (list1)
del list1[0]
print(list1)
- Tuple : sets
- immutable: cannot change value of a tuple,
append, remove, del, index add,
tup=(1,'a',True,3.3)
print(tup)
print(tup[0])
Iteration by Item (For Loops Continued)
For item in list: loop
colletions: String, List, Tuple
l=[1,2,'hi']
count=0
for item in l:
print(item)
count+=1
print (count)
String Methods
- .strip() clear while spaces at beginning and end of string
- .split() returns list of substrings
- .lower() lower case
- .upper() upper case
- len() * function*
str1=' Hello world ! '
print(str1)
print(len(str1))
print(str1.strip())
lstr=str1.split()
print(lstr)
print(str1.lower())
print(str1.upper())
str1=str1.strip()
print(len(str1))
Slice Operator
- used for String, list
- String[start:stop:step]
- String[:stop]
- String[start:]
- String[::step]
str1='Hello world !'
print(len(str1))
print(str1[1:])
print(str1[:5])
print(str1[::2])
print(str1[1:5:2])
- use slice to insert
- strings are inserted as individual characters
list1=['a',22,4.0,True]
print(len(list1))
list1[1:1]='AB'
print(list1)
- negative index
- list, tuple, string
- [::-1] reverses
list1=['a',22,4.0,True]
print(list1)
print(list1[-1])
print(list1[-2])
print(list1[-3])
print(list1[-4])
print(list1[::-1])
print(list1[:-1])
print(list1[:-2])
print(list1[:-3])
Functions
- def functName(param): … return result
- functName(input) call
def addTwo(x):
print('x+2')
return x+2
print(addTwo(3))
addTwo(3)
File IO (Reading Files)
- file=open(‘file path’, ‘r’)
- data=f.readlines()
- data is a list of strings
f=open('file.txt','r')
data=f.readlines()
print(type(data))
print(data)
for line in data:
print(type(line))
lineStripped=line.strip()
print(lineStripped)
File IO(Writing Files)
- file=open(‘file path’, ‘w’)
- file.write(data)
- file.close()
f=open('file2.txt','w')
data=['hello','hello2','hello3']
for line in data:
f.write(line + '\n')
f.close()
List Methods (.count/in;/index)
- .count(): count elements
- in: return boolean
- index(item) : return index
list1=['a',22,4.0,True,'a',22,4.0,True]
print(list1.count('a'))
print(22 in list1)
print(list1.index(True))
Introduction to Modular Programming
- import module.py
- each function can return multiple values
# module1.py
def func(x):
return x+2
def func1(y):
return y*2
#import module1
#value=module1.func(5)
print (func(3))
print (func1(3))
Error Handling (Try/Except)
- try except
num=input('add 5, enter :')
try:
addNum=int(num)+5
print(addNum)
except:
print('that''s not a number')
Global vs Local
- global ,not good to use, hard to follow code
x=13
print(x)
def func1():
global y
y=7
print('func1',y)
global x # replaces x
x=5
print('func1',x)
y=12
print(y)
func1()
print(x)
print(y)
Classes and Objects
- type(): find type for object
print(type('aaa'))
print(type(123))
print(type(22.0))
print(type([1,3]))
print(type(True))
print(type((1,2)))
print(type({3,4}))
- class
- def _ init_(self)
class Number:
def __init__(self):
self.var=22
def display(self):
print(self.var)
new=Number()
new.display()
Python Intermediate
Optional Parameters
def myFunct(x,y=6):
print(x+y)
#myFunc()# must pass x
myFunct(12)
myFunct(10,10)
Static & Class Methods
- @staticmethod
class Music:
@staticmethod
def play(): #no self required
print( 'playing static')
def stop(self):
print('stop')
Music.play() # does not need to create object
obj=Music()
obj.stop()
- @classMethod
- classMethod()
class Fruit:
name='fruit'
def printName2(cls):
print('name:',cls.name)
@classmethod
def printName(cls): #no self declared, refers to class instead
print('name:',cls.name)
Fruit.printName() #does not need to create an object for instantiation
apple=Fruit()
apple.name='apple'
apple.printName()
Fruit.name='apple'#must declare param with class name
apple.printName()
Fruit.printAge=classmethod(Fruit.printName2)#declare in main code
Fruit.printAge()
Map() Function
- map(functionName,Parameters)
def f1(x):
return x+x
nums=[1,2,3,4,5]
newList=list(map(f1,nums))
print(newList)
Filter() Function
- Filter(functionName,Params)
- returns param if set condition is true
def isOne(x):
return x==1
nums=[1,1,2,1,2,3,1,2,3,4]
newList=list(filter(isOne,nums))
print(newList)
Lambda Functions
- anonymous function
- performs one line functions
func=lambda x,y:x+y
print(func(3,4))
- lambda with filter and map
L=[1,2,3,4,5]
newL=list(filter(lambda x: x>3,L))
newL2=list(map(lambda x:x+1,L))
print(newL)
print(newL2)
Collections/Counter()
- import collections
- Counter(param) :works like a dictionary
- counts number of occurences
import collections
from collections import Counter
c=Counter('hello')
print(c)
print(c['l'])
- .most_common(n)
- .subtract(collection)
- .update(collection)
- .clear()
import collections
from collections import Counter
c=Counter([1,2,3,4,5,4,3,2,1,2])
d=[1,2,3]
print(c)
print(c.most_common(1))
print(c.most_common(2))
c.subtract(d)
print(c)
c.update(d)
print(c)
c.clear()
print(c)
Collections/namedtuple()
- from collections import namedtuple
- give names to the elements within a tuple object
- namedtuple(‘tName’,'name1,name2…‘)
import collections
from collections import namedtuple
Point=namedtuple('name1','p1,p2,px')
p=Point(1,2,3)
print(p)
print(p.p1)
print(p.px)
Collections/Deque(deck)
- from collections import deque
- deque typically used to perform on the beginning and end of a list
- append(), appendleft()
- pop(),popleft()
import collections
from collections import deque
d=deque('hello')
print(d)
#d is now deque
d.appendleft(5)
print(d)
d.append(4)#right
print(d)
print(d.pop())#right
print(d.popleft())#left
OOP
Introduction to Objects
- instance: new obj
- method: function specific to an obj .method()
- attribute: specification for an obj
Creating Classes
- init(self)
- self
class Dog():
def __init__(self,name,age): #constructor method1, automatically called
print('dog created')
self.name=name # attribute
self.age=age
#pass (empty method)
def speak(self): #method2 # no need to pass name b/c included in obj
print(self.name)
print(self.age)
def change_age(self,age):
self.age=age
p1=Dog('puppy1',1)
p2=Dog('puppy2',2)
p1.speak()
p2.speak()
p1.age=9
p1.speak()
Inheritance
- can inherit other classes: child, subclass, derived , concrete
- allow inheritance: parent, super, abstract
- overriding methods, child class with same name attributes override attributes in parent class
class Animal():
def __init__(self,name,age): #constructor method1, automatically called
print('animal created')
self.name=name
self.age=age
#pass (empty method)
def speak(self): #method2 # no need to pass name b/c included in obj
print(self.name)
print(self.age)
def change_age(self,age):
self.age=age
class Dog(Animal): #inherit from Animal
def __init__(self, name, age):
super().__init__(name,age) #attributes from parent
self.type='dog' #specific to dog attribute
def speak(self):
print('dog created')
print(self.name)
print(self.age)
p1=Dog('puppy1',1)
p2=Dog('puppy2',2)
p1.speak()
p2.speak()
p1.age=9
p1.speak()
Overloading Methods
- overload +,-, *, //, ==, with add, sub, mul,div, eq
- overload >, >=, <,<=, with gt, ge, lt, le
- overload str is toString
- getter, setter : def getItem(self):return self.item, def setItem(self):self.item=item
class Point():
def __init__(self, x=0,y=0):
self.x=x
self.y=y
self.coords=(self.x,self.y)
def move(self, x, y):
return Point(self.x+x,self.y+y)
def __eq__(self,other): #overload default method
return self.x==other.x and self.y==other.y
def __add__(self,other):
return Point(self.x+other.x,self.y+other.y)
def __sub__(self,other):
return Point(self.x-other.x,self.y-other.y)
def __mul__(self,other):
return Point(self.x*other.x, self.y*other.y)
def __div__(a, b):
return a/b
def length(self):
import math
return math.sqrt(self.x**2+self.y**2)
def __gt__(self, other):
return self.length()>other.length()
def __ge__(self, other):
return self.length()>=other.length()
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.length()<other.length()
def __le__(self, other):
return self.length()>=other.length()
def __str__(self): #toString
return "Point("+str(self.x)+','+str(self.y)+')'
p1=Point(1,1)
p2=Point(1,2)
p3=Point(2,1)
p4=Point(1,1)
same=p1==p2 #== is __eq__
print(same)
same=p1==p4
print(same)
pMove=p1.move(1,1)
print(p1)
print(pMove)
p5=p1+p2
p6=p1-p2
p7=p1*p2
p8=Point((p2.x)/2,(p2.y)/2)
print(p5) # <__main__.Point object at 0x0000002E3ABB9040> must overload string
print(p6)
print(p7)
print(p8)
print(p1)
Less=p1<p4
print(Less)
Less=p1<=p4
print(Less)
Private and Public Classes
- no private classes in python
- _ used to simulate private
class _Private:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name=name
print(self.name+'private')
class NotPrivate:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name=name
self.priv=_Private(name) #can call private
print(self.name)
def _display(self):
print('private')
def display(self):
print('public')
x=NotPrivate('bob')
x._display()
x.display()
Thread
What is a Thread?
- process (ram memory location (CPU)) of different threads run on multiple cores (parallel), multithread allows one thread to wait while inactive while an active thread to take over the memory location for its task
Creating New Threads
- import threading
- threading.Thread
- import time
- threading.Thread.init(self)
- thread1.start()
- thread1.join()
- The thread.join() function force the program to wait for the execution of the thread to complete before it can be closed.
import threading
import time
class myThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, threadID, name, counter):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadID=threadID
self.name=name
self.counter=counter
def run(self):
print('Start:' + self.name+'\n')
print_time(self.name,self.counter, 5)
print('Exit: '+self.name+'\n')
def print_time(threadName, delay,counter):
while counter:
time.sleep(delay)
print('%s: %s %s'%(threadName, time.ctime(time.time()), counter)+'\n')
counter-=1
#create new threads
t1=myThread(1, 't1', 1)
t2=myThread(2,'t2', 1.5)
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print('exit main thread')
- ThreadPoolExecutor
- no need for start(), join()
- with cocurrent.futures
import concurrent.futures
import time
def t1():
print('t1 started')
time.sleep(1)
print('t1 ended')
def t2():
print('t2 started')
time.sleep(1)
print('t2 ended')
print ('start!')
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=2) as executor:
executor.submit(t1)
executor.submit(t2)
print('end!')
Synchronizing and Locking Threads
-
race condition:
-
2 or more threads access a set of shared data or resources, creating inconsistent results
-
both threads refer to the same resource, both performed for that thread thus one is lost to the other one ( two ppl booked the same ticket, then not enough tickets were made)
-
solve race conditions with locks
-
wait for another thread to finish before another thread start
-
examples: verify credit/debit card, sending confirmation or shipping details in emials, load automatic reply, redirecting to main website
-
locking
-
threadLock=threading.lock()
-
threadLock.acquire()
-
threadLock.release()
-
time.sleep(1) # sleep for a second
import threading
import time
class myThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, threadID, name, counter):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadID=threadID
self.name=name
self.counter=counter
def run(self):
print('Start:' + self.name+'\n')
threadLock.acquire()
print_time(self.name,self.counter, 5)
threadLock.release()
print('Exit: '+self.name+'\n')
def print_time(threadName, delay,counter):
while counter:
time.sleep(delay)
print('%s: %s %s'%(threadName, time.ctime(time.time()), counter)+'\n')
counter-=1
#create new threads
threadLock=threading.Lock()
t1=myThread(1, 't1', 1)
t2=myThread(2,'t2', 1.5)
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print('exit main thread')
Deadlock
-
Thread 1: Acquire and hold L1. (L1-lock)
-
Thread 2: Acquire and hold L2.
-
Thread 1: Try to acquire L2, but it’s in use, so wait.
-
Thread 2: Try to acquire L1, but it’s in use, so wait.
Daemon Threads
- Daemon threads runs in the backgorund, executes independently of the main thread ( non-blocking threads)
- automatically stops when main thread finishes
- usually for logging or other background tasks
Advanced
Virtualenv
- open cmd as admin
- check path
>echo %PATH%
- pip install virtual environment
>pip install virtualenv
>virtualenv myEnv
C:\Windows\System32>virtualenv myEnv
created virtual environment CPython3.9.7.final.0-64 in 9116ms
creator CPython3Windows(dest=C:\Windows\System32\myEnv, clear=False, no_vcs_ig
nore=False, global=False)
seeder FromAppData(download=False, pip=bundle, setuptools=bundle, wheel=bundle
, via=copy, app_data_dir=C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\pypa\virtualenv)
added seed packages: pip==21.2.4, setuptools==58.0.4, wheel==0.37.0
activators BashActivator,BatchActivator,FishActivator,NushellActivator,PowerSh
ellActivator,PythonActivator
C:\Windows\System32>myEnv\Scripts\activate
(myEnv) C:\Windows\System32>deactivate
C:\Windows\System32>
Enumerate
- list
#create sequence
seq1=['a1','b2','c3','d4']
#iterate using enumerate()
for i, j in enumerate(seq1):
print(i,j)
# enumerate converts seq1 to list
list1=list(enumerate(seq1))
print (list1)
- string
- tuple
#create sequence of tuples
seq1=[(9,'a1'),(8,'b2'),(7,'c3'),(6,'d4')]
#iterate using enumerate()
for i, j in enumerate(seq1):
print(i,j)
print('---------------')
#iterate using enumerate()
for i, j in enumerate(seq1,start=2):
print(i,j)
print('---------------')
# enumerate converts list
list1=list(enumerate(seq1))
print (list1)
print('---------------')
fruit='apple'
for i,j in enumerate(fruit):
print(i,j)
Pickle
- Pickling is a method to convert an object (list, dict, etc) to a file and vice versa
- serialize obj
import pickle
exampleObj={'A':1,'B':2,'C':3}
fileObj=open('data.obj','wb')
pickle.dump(exampleObj, fileObj)
fileObj.close()
- deserialize obj
import pickle
fileObj=open('data.obj','rb')
exampleObj=pickle.load(fileObj)
fileObj.close()
print(exampleObj)
Regular Expressions
Numpy
Introduction
- install in window command
> pip install numpy
- np.array([list…])
- .shape
- [0,0] index
- .size
- .ndim
- np.append(array,item)
- np.delete(array, index)
import numpy as np
arr=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) #create numpy array with a list
print(arr)
print('shape',arr.shape)#shape : num of elements in each dimension 2 x 3
print('[1,1]',arr[1,1]) #index
print('size',arr.size) #size : num of items
print('ndim',arr.ndim) # dimension : num of y
arr=np.delete(arr,0)#flattens array into 1 dim
print(arr)
print('shape',arr.shape)#shape : num of elements in each dimension
print('ndim',arr.ndim) # dimension : num of y
arr=np.append(arr,7) #flattens array into 1 dim
print (arr)
print('shape',arr.shape)#shape : num of elements in each dimension
print('ndim',arr.ndim) # dimension : num of y
Array Creation
- np.zeros(shape)
import numpy as np
arr = np.zeros((2,3))
print(arr)
- np.ones(shape)
import numpy as np
arr = np.ones((2,3))
print(arr)
- np.arrange()
import numpy as np
arr = np.arange(10)
print(arr)
arr=np.arange(2,10,3)
print(arr)
arr=np.arange(2,3,.1)
print(arr)
- .linspace(start,stop, values)
import numpy as np
arr = np.linspace(0,4,2) # step value in 0 to 4
print(arr)
arr = np.linspace(0,4,3) # step value in 0 to 4
print(arr)
arr = np.linspace(0,4,4) # step value in 0 to 4
print(arr)
arr = np.linspace(0,4,5) # step value in 0 to 4
print(arr)
arr = np.linspace(0,4,6) # step value in 0 to 4
print(arr)
- np.full(shape, value) # fill
import numpy as np
arr = np.full((2,2),8)
print(arr)
- np.eye(size) #identity matrix (sinister )
import numpy as np
arr = np.eye(3)
print(arr)
- np.random.random(size) # 0 ->1
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.random((2,3))
print(arr)
- dtype=type
import numpy as np
arr = np.ones((3,3),dtype=int)
print(arr)
print(type(arr[0,0]))
arr=np.zeros((2,2),dtype=str)
print(type(arr[0,0]))
Array Math
- addition: + or np.add()
- subtraction: - or np.subtract()
- multiplication: * or np.multiply()
- division: / or np.divide()
- square root: np.sqrt()
import numpy as np
x=np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
y=np.array([[2,3],[4,5]])
print (x+y)
print (x-y)
print (x*y)
print (x/y)
print(np.sqrt(x))
- .dot()
import numpy as np
v=np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
w=np.array([[2,3],[4,5]])
print(v.dot(w))
print(w.dot(v))
print(np.dot(v,w))
print(np.dot(w,v))
- .cross()
import numpy as np
v=np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
w=np.array([[2,3],[4,5]])
print(np.cross(v,w))
print(np.cross(w,v))
- .T # transpose
import numpy as np
v=np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
w=np.array([[2,3],[4,5]])
print(v.T)
print(w.T)
- np.sum(axis=) #column sum
import numpy as np
v=np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
print(np.sum(v))
print(np.sum(v,axis=0))
PyQt I
Basic GUI Application
- install
- pip install pyqt5
- pip install pyqt5-tools
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QMainWindow,QLabel
import sys
def main():
app=QApplication(sys.argv)
win=QMainWindow()
win.setGeometry(200,200,300,300) # x, y, width, height
win.setWindowTitle('window!') # set title
label=QLabel(win)
label.setText('label!')
label.move(50,50) #x, y
win.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
main()
Buttons and Events
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow
import sys
class MyWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super(MyWindow,self).__init__()
self.initUI()
def button_clicked(self):
print('clicked') #display when clicked
self.label.setText('pressed!')
self.update()
def initUI(self):
self.setGeometry(200,200,300,300)
self.setWindowTitle('button')
self.label=QtWidgets.QLabel(self)
self.label.setText('first label!')
self.label.move(50,50)
self.b1 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self)
self.b1.setText('click!')
self.b1.clicked.connect(self.button_clicked)
def update(self):
self.label.adjustSize()
def window():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
win = MyWindow()
win.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
window()
How to Use QtDesigner
- Qt5

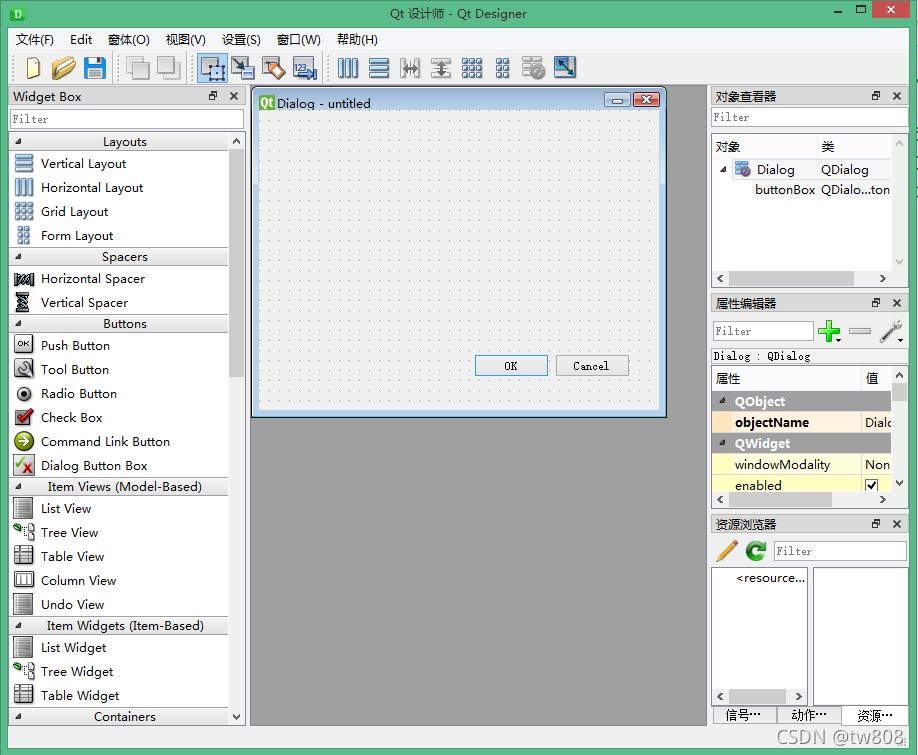
- go to file location .ui file
D:\python2021>pyuic5 -x "919testgui".ui -o "919testgui".py
- get .py code
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file '919testgui.ui'
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_Dialog(object):
def setupUi(self, Dialog):
Dialog.setObjectName("Dialog")
Dialog.resize(400, 300)
self.buttonBox = QtWidgets.QDialogButtonBox(Dialog)
self.buttonBox.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(30, 240, 341, 32))
self.buttonBox.setOrientation(QtCore.Qt.Horizontal)
self.buttonBox.setStandardButtons(QtWidgets.QDialogButtonBox.Cancel|QtWidgets.QDialogButtonBox.Ok)
self.buttonBox.setObjectName("buttonBox")
self.retranslateUi(Dialog)
self.buttonBox.accepted.connect(Dialog.accept)
self.buttonBox.rejected.connect(Dialog.reject)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(Dialog)
def retranslateUi(self, Dialog):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
Dialog.setWindowTitle(_translate("Dialog", "Dialog"))
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
Dialog = QtWidgets.QDialog()
ui = Ui_Dialog()
ui.setupUi(Dialog)
Dialog.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Menubar

- add shortcut attributes
- add statusTip attributes
- add code to setupUI
- add method clicked()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file 'gui1.ui'
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_MainWindow(object):
def setupUi(self, MainWindow):
MainWindow.setObjectName("MainWindow")
MainWindow.resize(800, 600)
self.centralwidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(MainWindow)
self.centralwidget.setObjectName("centralwidget")
self.label = QtWidgets.QLabel(self.centralwidget)
self.label.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(130, 200, 221, 56))
font = QtGui.QFont()
font.setFamily("Arial")
font.setPointSize(36)
font.setBold(True)
font.setWeight(75)
self.label.setFont(font)
self.label.setObjectName("label")
MainWindow.setCentralWidget(self.centralwidget)
self.menubar = QtWidgets.QMenuBar(MainWindow)
self.menubar.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 800, 23))
self.menubar.setObjectName("menubar")
self.menuFile = QtWidgets.QMenu(self.menubar)
self.menuFile.setObjectName("menuFile")
self.menuEdit = QtWidgets.QMenu(self.menubar)
self.menuEdit.setObjectName("menuEdit")
MainWindow.setMenuBar(self.menubar)
self.statusbar = QtWidgets.QStatusBar(MainWindow)
self.statusbar.setObjectName("statusbar")
MainWindow.setStatusBar(self.statusbar)
self.actionOpen = QtWidgets.QAction(MainWindow)
self.actionOpen.setObjectName("actionOpen")
self.actionSave = QtWidgets.QAction(MainWindow)
self.actionSave.setObjectName("actionSave")
self.actionCopy = QtWidgets.QAction(MainWindow)
self.actionCopy.setObjectName("actionCopy")
self.actionPaste = QtWidgets.QAction(MainWindow)
self.actionPaste.setObjectName("actionPaste")
self.menuFile.addAction(self.actionOpen)
self.menuFile.addAction(self.actionSave)
self.menuEdit.addAction(self.actionCopy)
self.menuEdit.addAction(self.actionPaste)
self.menubar.addAction(self.menuFile.menuAction())
self.menubar.addAction(self.menuEdit.menuAction())
self.actionOpen.triggered.connect(lambda :self.clicked('open clicked'))# added code
self.actionSave.triggered.connect(lambda :self.clicked('save clicked'))# added code
self.actionCopy.triggered.connect(lambda :self.clicked('copy clicked'))# added code
self.actionPaste.triggered.connect(lambda :self.clicked('paste clicked'))# added code
self.retranslateUi(MainWindow)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(MainWindow)
def retranslateUi(self, MainWindow):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
MainWindow.setWindowTitle(_translate("MainWindow", "MainWindow"))
self.label.setStatusTip(_translate("MainWindow", "TEXT"))
self.label.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "TEXT"))
self.menuFile.setTitle(_translate("MainWindow", "File"))
self.menuEdit.setTitle(_translate("MainWindow", "Edit"))
self.actionOpen.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "Open"))
self.actionOpen.setShortcut(_translate("MainWindow", "Ctrl+O"))
self.actionSave.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "Save"))
self.actionSave.setShortcut(_translate("MainWindow", "Ctrl+S"))
self.actionCopy.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "Copy"))
self.actionCopy.setShortcut(_translate("MainWindow", "Ctrl+C"))
self.actionPaste.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "Paste"))
self.actionPaste.setShortcut(_translate("MainWindow", "Ctrl+V"))
#added click method
def clicked(self,text):
self.label.setText(text)
self.label.adjustSize()
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
MainWindow = QtWidgets.QMainWindow()
ui = Ui_MainWindow()
ui.setupUi(MainWindow)
MainWindow.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Images/QPixmap
- use label to insert img
- set pixmap
self.img1.setPixmap(QtGui.QPixmap('bg2.jpeg')) # added

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file 'qpixmap.ui'
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_MainWindow(object):
def setupUi(self, MainWindow):
MainWindow.setObjectName("MainWindow")
MainWindow.resize(800, 600)
self.centralwidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(MainWindow)
self.centralwidget.setObjectName("centralwidget")
self.img1 = QtWidgets.QLabel(self.centralwidget)
self.img1.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 300, 300))
self.img1.setText("")
self.img1.setPixmap(QtGui.QPixmap("bg1.jpeg"))
self.img1.setObjectName("img1")
self.image1 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.centralwidget)
self.image1.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(20, 310, 75, 23))
self.image1.setObjectName("image1")
self.image2 = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.centralwidget)
self.image2.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(190, 310, 75, 23))
self.image2.setObjectName("image2")
MainWindow.setCentralWidget(self.centralwidget)
self.menubar = QtWidgets.QMenuBar(MainWindow)
self.menubar.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 800, 23))
self.menubar.setObjectName("menubar")
MainWindow.setMenuBar(self.menubar)
self.statusbar = QtWidgets.QStatusBar(MainWindow)
self.statusbar.setObjectName("statusbar")
MainWindow.setStatusBar(self.statusbar)
self.image1.clicked.connect(self.show_img1) # added
self.image2.clicked.connect(self.show_img2)# added
self.retranslateUi(MainWindow)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(MainWindow)
#added method to control image shown
def show_img1(self):
self.img1.setPixmap(QtGui.QPixmap('bg1.jpeg'))
def show_img2(self):
self.img1.setPixmap(QtGui.QPixmap('bg2.jpeg'))
def retranslateUi(self, MainWindow):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
MainWindow.setWindowTitle(_translate("MainWindow", "MainWindow"))
self.image1.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "Image1"))
self.image2.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "Image2"))
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
MainWindow = QtWidgets.QMainWindow()
ui = Ui_MainWindow()
ui.setupUi(MainWindow)
MainWindow.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
MessageBoxes & Popup Windows
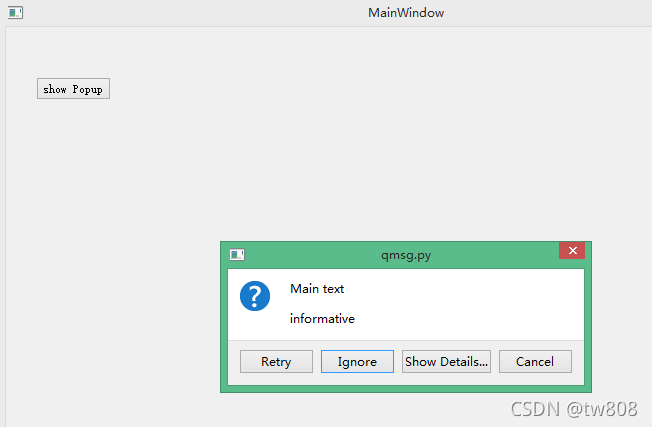
msg= QMessageBox()
- List of Icons
- QMessageBox.Critical
- QMessageBox.Warning
- QMessageBox.Information
- QMessageBox.Question
- List of Buttons
- QMessageBox.Ok
- QMessageBox.Open
- QMessageBox.Save
- QMessageBox.Cancel
- QMessageBox.Close
- QMessageBox.Yes
- QMessageBox.No
- QMessageBox.Abort
- QMessageBox.Retry
- QMessageBox.Ignore
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file 'qmsg.ui'
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBox # added
class Ui_MainWindow(object):
def setupUi(self, MainWindow):
MainWindow.setObjectName("MainWindow")
MainWindow.resize(800, 600)
self.centralwidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(MainWindow)
self.centralwidget.setObjectName("centralwidget")
self.popUp = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.centralwidget)
self.popUp.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(30, 50, 75, 23))
self.popUp.setObjectName("popUp")
MainWindow.setCentralWidget(self.centralwidget)
self.menubar = QtWidgets.QMenuBar(MainWindow)
self.menubar.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 800, 23))
self.menubar.setObjectName("menubar")
MainWindow.setMenuBar(self.menubar)
self.statusbar = QtWidgets.QStatusBar(MainWindow)
self.statusbar.setObjectName("statusbar")
MainWindow.setStatusBar(self.statusbar)
self.popUp.clicked.connect(self.show_pop) # added link
self.retranslateUi(MainWindow)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(MainWindow)
# messages for the popup
def show_pop(self):
msg=QMessageBox()
msg.setWindowTitle('qmsg.py')
msg.setText('Main text')
msg.setIcon(QMessageBox.Question)
msg.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Retry | QMessageBox.Ignore | QMessageBox.Cancel)
msg.setDefaultButton(QMessageBox.Ignore)#default
msg.setInformativeText('informative')
msg.setDetailedText('details')
#msg.buttonClicked.connect(self.popUp)# not sure why doesn't work
msg.exec_() #show msgbox
# print popup message
def pop_clicked(self,i):
print(i.text()) #print msg on the button
def retranslateUi(self, MainWindow):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
MainWindow.setWindowTitle(_translate("MainWindow", "MainWindow"))
self.popUp.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "show Popup"))
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
MainWindow = QtWidgets.QMainWindow()
ui = Ui_MainWindow()
ui.setupUi(MainWindow)
MainWindow.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
ComboBoxes
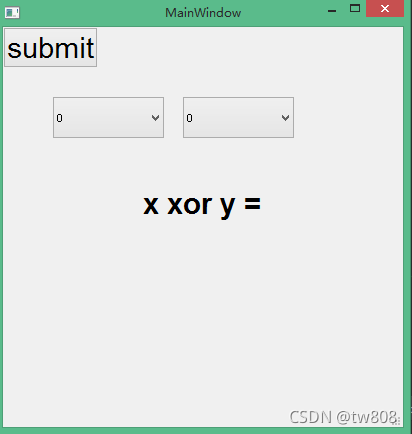
- add items to combox
self.comboX.addItem('new item')
- change default item
- index of the combobox is a list start with 0, -1 last item
index=self.comboX.findText('1',QtCore.QtMatchFixedString) #find index
self.comboX.setCurrentIndex(index)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Form implementation generated from reading ui file 'xor.ui'
from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
class Ui_MainWindow(object):
def setupUi(self, MainWindow):
MainWindow.setObjectName("MainWindow")
MainWindow.resize(400, 400)
self.centralwidget = QtWidgets.QWidget(MainWindow)
self.centralwidget.setObjectName("centralwidget")
self.comboY = QtWidgets.QComboBox(self.centralwidget)
self.comboY.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(180, 70, 111, 41))
self.comboY.setObjectName("comboY")
self.comboY.addItem("")
self.comboY.addItem("")
self.label = QtWidgets.QLabel(self.centralwidget)
self.label.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(140, 160, 121, 34))
font = QtGui.QFont()
font.setFamily("Arial")
font.setPointSize(22)
font.setBold(True)
font.setWeight(75)
self.label.setFont(font)
self.label.setObjectName("label")
self.submit = QtWidgets.QPushButton(self.centralwidget)
font = QtGui.QFont()
font.setFamily("Arial")
font.setPointSize(22)
font.setBold(False)
font.setWeight(50)
self.submit.setFont(font)
self.submit.setObjectName("submit")
self.comboX = QtWidgets.QComboBox(self.centralwidget)
self.comboX.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(50, 70, 111, 41))
self.comboX.setObjectName("comboX")
self.comboX.addItem("")
self.comboX.addItem("")
MainWindow.setCentralWidget(self.centralwidget)
self.menubar = QtWidgets.QMenuBar(MainWindow)
self.menubar.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(0, 0, 400, 23))
self.menubar.setObjectName("menubar")
MainWindow.setMenuBar(self.menubar)
self.statusbar = QtWidgets.QStatusBar(MainWindow)
self.statusbar.setObjectName("statusbar")
MainWindow.setStatusBar(self.statusbar)
self.submit.clicked.connect(self.pressed) #added
self.retranslateUi(MainWindow)
QtCore.QMetaObject.connectSlotsByName(MainWindow)
# add pressed for combobox
def pressed(self):
x = int(self.comboX.currentText())
y = int(self.comboY.currentText())
xor = (x and not y) or (not x and y)
if xor == True:
xor = 1
else:
xor = 0
self.label.setText("X XOR Y=" + str(xor))
self.label.adjustSize()
def retranslateUi(self, MainWindow):
_translate = QtCore.QCoreApplication.translate
MainWindow.setWindowTitle(_translate("MainWindow", "MainWindow"))
self.comboY.setStatusTip(_translate("MainWindow", "y"))
self.comboY.setItemText(0, _translate("MainWindow", "0"))
self.comboY.setItemText(1, _translate("MainWindow", "1"))
self.label.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "x xor y ="))
self.submit.setStatusTip(_translate("MainWindow", "submit"))
self.submit.setText(_translate("MainWindow", "submit"))
self.comboX.setStatusTip(_translate("MainWindow", "y"))
self.comboX.setItemText(0, _translate("MainWindow", "0"))
self.comboX.setItemText(1, _translate("MainWindow", "1"))
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
MainWindow = QtWidgets.QMainWindow()
ui = Ui_MainWindow()
ui.setupUi(MainWindow)
MainWindow.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Containers (GroupBoxes & Frames)
- Containter: group of widgets
- GroupBox: has a border, title
- Frame: no border or title
PyQt II
Install pyqt
- includes QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets, QtMultimedia, QtBluetooth, QtNetwork, QtPositioning, Enginio, QtWebSockets, QtWebKit, QtWebKitWidgets, QtXml, QtSvg, QtSql and QtTest.
- same as above
PyQt Hello World
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QWidget, QLabel
from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon
from PyQt5.QtCore import pyqtSlot
def window():
#initialize
app=QApplication(sys.argv)
widget=QWidget()
#label
textLabel=QLabel(widget)
textLabel.setText('Hello World')
textLabel.move(100,120)
#show window
widget.setGeometry(50,50,320,200)
widget.setWindowTitle('PyQt5 example')
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
#run
if __name__=='__main__':
window()
PyQt Buttons
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QWidget, QPushButton
from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon
from PyQt5.QtCore import pyqtSlot
def window():
#initialize
app=QApplication(sys.argv)
widget=QWidget()
#buttons
b1=QPushButton(widget)
b1.setText('B1')
b1.move(50,60)
b1.clicked.connect(b1_clicked)
#show window
widget.setGeometry(50,50,320,200)
widget.setWindowTitle('PyQt5 example')
widget.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
#click
def b1_clicked():
print('b1 clicked')
# run
if __name__=='__main__':
window()
PyQt QMessageBox
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QWidget, QPushButton,QMessageBox
from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon
from PyQt5.QtCore import pyqtSlot
def window():
#initialize
app=QApplication(sys.argv)
win=QWidget()
#buttons
b1=QPushButton(win)
b1.setText('dialog window')
b1.move(50,60)
b1.clicked.connect(showDialog)
win.setWindowTitle('click button')
win.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
#click
def showDialog():
msgBox=QMessageBox()
msgBox.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information)
msgBox.setText('message box')
msgBox.setWindowTitle('Qmessage example')
msgBox.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel)
msgBox.buttonClicked.connect(msgButtonClick)
returnValue=msgBox.exec()
if returnValue==QMessageBox.Ok:
print('Ok')
def msgButtonClick(i):
print('button:',i.text())
# run
if __name__=='__main__':
window()
PyQt grid
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QWidget, QPushButton,QGridLayout
from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon
from PyQt5.QtCore import pyqtSlot
def window():
#initialize
app=QApplication(sys.argv)
win=QWidget()
grid=QGridLayout()
for i in range(0,5):
for j in range(0,5):
grid.addWidget(QPushButton(str(i)+str(j)),i,j)
win.setLayout(grid)
win.setWindowTitle('grid')
win.setGeometry(50,50,200,200)
win.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__=='__main__':
window()
QLineEdit
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication,QMainWindow,QLabel,QLineEdit,QPushButton
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.lineEntry=QLineEdit(self)
self.lineEntry.move(15,25)
self.lineEntry.resize(200,40)
self.qlabel=QLabel(self)
self.qlabel.move(15,75)
self.lineEntry.textChanged.connect(self.onChanged)
self.setGeometry(50,50,300,200)
self.setWindowTitle('LineEdit')
self.show()
def onChanged(self,text):
self.qlabel.setText(text)
self.qlabel.adjustSize()
if __name__=='__main__':
app=QApplication(sys.argv)
ex=Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt QPixmap
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QLabel
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QGridLayout,QWidget
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPixmap
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.im=QPixmap('./image.jpg')
self.label=QLabel()
self.label.setPixmap(self.im)
self.grid=QGridLayout()
self.grid.addWidget(self.label,1,1)
self.setLayout(self.grid)
self.setGeometry(50,50,300,200)
self.setWindowTitle('show image')
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt Combobox
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QLabel
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QComboBox,QPushButton
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
c=QComboBox(self)
c.addItem('apple')
c.addItem('pear')
c.move(50,50)
self.ql=QLabel(self)
self.ql.move(50,10)
c.activated[str].connect(self.onChanged)
self.setGeometry(30,30,500,500)
self.setWindowTitle('QComboBox')
self.show()
def onChanged(self,text):
self.ql.setText(text)
self.ql.adjustSize()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
QCheckBox
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
cbutton = QCheckBox("I have a Cat")
cbutton.setChecked(True)
cbutton.animal = "Cat"
cbutton.toggled.connect(self.onClicked)
layout.addWidget(cbutton, 0, 0)
def onClicked(self):
cbutton = self.sender()
print("Animal " + (cbutton.animal) + " is " + str(cbutton.isChecked()))
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
QSlider
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QSlider
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
mySlider = QSlider(Qt.Horizontal, self)
mySlider.setGeometry(30, 40, 200, 30)
mySlider.valueChanged[int].connect(self.changeValue)
self.setGeometry(50,50,320,200)
self.setWindowTitle("Checkbox Example")
self.show()
def changeValue(self, value):
print(value)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Progressbar
import sys
from PyQt5.QtCore import QTimer
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QProgressBar
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class Example(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.pbar = QProgressBar(self)
self.pbar.setGeometry(30, 40, 200, 25)
self.pbar.setValue(50)
self.setWindowTitle("QT Progressbar Example")
self.setGeometry(32, 32, 320, 200)
self.show()
self.timer = QTimer()
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.handleTimer)
self.timer.start(1000)
def handleTimer(self):
value = self.pbar.value()
if value < 100:
value = value + 1
self.pbar.setValue(value)
else:
self.timer.stop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt table
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication, QWidget, QAction, QTableWidget, QTableWidgetItem, QVBoxLayout
from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon
from PyQt5.QtCore import pyqtSlot
import sys
data = {'col1': ['1', '2', '3', '4'],
'col2': ['1', '2', '1', '3'],
'col3': ['1', '1', '2', '1']}
class TableView(QTableWidget):
def __init__(self, data, *args):
QTableWidget.__init__(self, *args)
self.data = data
self.setData()
self.resizeColumnsToContents()
self.resizeRowsToContents()
def setData(self):
horHeaders = []
for n, key in enumerate(sorted(self.data.keys())):
horHeaders.append(key)
for m, item in enumerate(self.data[key]):
newitem = QTableWidgetItem(item)
self.setItem(m, n, newitem)
self.setHorizontalHeaderLabels(horHeaders)
def main(args):
app = QApplication(args)
table = TableView(data, 4, 3)
table.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(sys.argv)
QVBoxLayout
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout
app = QApplication([])
window = QWidget()
layout = QVBoxLayout()
layout.addWidget(QPushButton('1'))
layout.addWidget(QPushButton('2'))
layout.addWidget(QPushButton('3'))
window.setLayout(layout)
window.show()
app.exec_()
PyQt style
C:\Windows\System32>python
Python 3.9.7 (tags/v3.9.7:1016ef3, Aug 30 2021, 20:19:38) [MSC v.1929 64 bit (AM
D64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import PyQt5.QtWidgets
>>> print(PyQt5.QtWidgets.QStyleFactory.keys())
['windowsvista', 'Windows', 'Fusion']
app = QApplication([])
app.setStyle('Windows')
Compile PyQt to exe
>pip install virtualenv
>virtualenv myEnv
created virtual environment CPython3.9.7.final.0-64 in 9141ms
creator CPython3Windows(dest=C:\Windows\System32\myEnv, clear=False, no_vcs_ig
nore=False, global=False)
seeder FromAppData(download=False, pip=bundle, setuptools=bundle, wheel=bundle
, via=copy, app_data_dir=C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\pypa\virtualenv)
added seed packages: pip==21.2.4, setuptools==58.0.4, wheel==0.37.0
activators BashActivator,BatchActivator,FishActivator,NushellActivator,PowerSh
ellActivator,PythonActivator
>myEnv\Scripts\activate.bat
(myEnv) C:\Windows\System32>
- install Toolchain
(myEnv) C:\Windows\System32>pip3 install fbs PyQt5==5.12.3 PyInstaller==3.4
QDial
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
self.dial = QDial()
self.dial.setMinimum(0)
self.dial.setMaximum(100)
self.dial.setValue(40)
self.dial.valueChanged.connect(self.sliderMoved)
layout.addWidget(self.dial)
def sliderMoved(self):
print("Dial value = %i" % (self.dial.value()))
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Pyqt-radiobutton
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
radiobutton = QRadioButton("Australia")
radiobutton.setChecked(True)
radiobutton.country = "Australia"
radiobutton.toggled.connect(self.onClicked)
layout.addWidget(radiobutton, 0, 0)
radiobutton = QRadioButton("China")
radiobutton.country = "China"
radiobutton.toggled.connect(self.onClicked)
layout.addWidget(radiobutton, 0, 1)
radiobutton = QRadioButton("Japan")
radiobutton.country = "Japan"
radiobutton.toggled.connect(self.onClicked)
layout.addWidget(radiobutton, 0, 2)
def onClicked(self):
radioButton = self.sender()
if radioButton.isChecked():
print("Country is %s" % (radioButton.country))
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Pyqt-groupbox
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class GroupBox(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
self.setWindowTitle("GroupBox")
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
groupbox = QGroupBox("GroupBox Example")
groupbox.setCheckable(True)
layout.addWidget(groupbox)
vbox = QVBoxLayout()
groupbox.setLayout(vbox)
radiobutton = QRadioButton("RadioButton 1")
vbox.addWidget(radiobutton)
radiobutton = QRadioButton("RadioButton 2")
vbox.addWidget(radiobutton)
radiobutton = QRadioButton("RadioButton 3")
vbox.addWidget(radiobutton)
radiobutton = QRadioButton("RadioButton 4")
vbox.addWidget(radiobutton)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = GroupBox()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Pyqt-tooltip
- hover
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
button = QPushButton("Button")
button.setToolTip("This is a text")
layout.addWidget(button, 0, 0)
button = QPushButton("Button")
button.setToolTip("<b>HTML</b> <i>can</i> be shown too..")
layout.addWidget(button, 1, 0)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt toolbox
- tab like
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# Add toolbar and items
toolbox = QToolBox()
layout.addWidget(toolbox, 0, 0)
label = QLabel()
toolbox.addItem(label, "Students")
label = QLabel()
toolbox.addItem(label, "Teachers")
label = QLabel()
toolbox.addItem(label, "Directors")
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt toolbar
- notebox
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# Create pyqt toolbar
toolBar = QToolBar()
layout.addWidget(toolBar)
# Add buttons to toolbar
toolButton = QToolButton()
toolButton.setText("Apple")
toolButton.setCheckable(True)
toolButton.setAutoExclusive(True)
toolBar.addWidget(toolButton)
toolButton = QToolButton()
toolButton.setText("Orange")
toolButton.setCheckable(True)
toolButton.setAutoExclusive(True)
toolBar.addWidget(toolButton)
# Add textfield to window
tbox = QPlainTextEdit()
layout.addWidget(tbox)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt menubar
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# create menu
menubar = QMenuBar()
layout.addWidget(menubar, 0, 0)
actionFile = menubar.addMenu("File")
actionFile.addAction("New")
actionFile.addAction("Open")
actionFile.addAction("Save")
actionFile.addSeparator()
actionFile.addAction("Quit")
menubar.addMenu("Edit")
menubar.addMenu("View")
menubar.addMenu("Help")
# add textbox
tbox = QPlainTextEdit()
layout.addWidget(tbox, 1, 0)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt tabwidget
from PyQt5.QtCore import *
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
label1 = QLabel("Widget in Tab 1.")
label2 = QLabel("Widget in Tab 2.")
tabwidget = QTabWidget()
tabwidget.addTab(label1, "Tab 1")
tabwidget.addTab(label2, "Tab 2")
layout.addWidget(tabwidget, 0, 0)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt auto complete
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
# auto complete options
names = ["Apple", "Alps", "Berry", "Cherry" ]
completer = QCompleter(names)
# create line edit and add auto complete
self.lineedit = QLineEdit()
self.lineedit.setCompleter(completer)
layout.addWidget(self.lineedit, 0, 0)
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt list box
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
import sys
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
QWidget.__init__(self)
layout = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(layout)
self.listwidget = QListWidget()
self.listwidget.insertItem(0, "Red")
self.listwidget.insertItem(1, "Orange")
self.listwidget.insertItem(2, "Blue")
self.listwidget.insertItem(3, "White")
self.listwidget.insertItem(4, "Green")
self.listwidget.clicked.connect(self.clicked)
layout.addWidget(self.listwidget)
def clicked(self, qmodelindex):
item = self.listwidget.currentItem()
print(item.text())
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
screen = Window()
screen.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
PyQt input dialog
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QPushButton, QLineEdit, QInputDialog, QApplication, QLabel)
import sys
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
# Add button
self.btn = QPushButton('Show Input Dialog', self)
self.btn.move(30, 20)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.showDialog)
# Add label
self.le = QLabel(self)
self.le.move(30, 62)
self.le.resize(400,22)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 290, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Input dialog')
self.show()
def showDialog(self):
text, ok = QInputDialog.getText(self, 'Input Dialog', 'Enter text:')
if ok:
self.le.setText(str(text))
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
