learn from https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/
1. 第一步
pip install fastapi[all]
from fastapi import FastAPI
my_app = FastAPI() # my_app 实例, 名字对应于 终端里的
@my_app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message" : "Hello World"}
http操作:
POST:创建数据。
GET:读取数据。
PUT:更新数据。
DELETE:删除数据。
@my_app.get("/") 告诉 FastAPI 在它下方的函数负责处理如下访问请求:
- 请求路径为
/ - 使用 get 操作
函数可以返回一个 dict、list,像 str、int 一样的单个值,等等。还可以返回 Pydantic 模型
1.1 小结
- 导入
FastAPI - 创建一个 app 实例
- 编写一个路径操作装饰器(如
@app.get("/")) - 编写一个路径操作函数(如上面的
def root(): ...) - 运行开发服务器(如
uvicorn main:app --reload)
2. 路径参数
- 函数参数,与 { } 内的名字,保持一致
@my_app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id): # 要跟上面的 {} 内保持一致
return {"itemid": item_id} # 返回字符串
- 参数类型限制
: type,参数类型不匹配会报错
@my_app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: int): # 要跟上面的 {} 内保持一致
return {"itemid": item_id} # 返回 int
- 文档
http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs,http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc
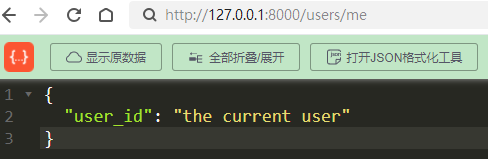
2.1 顺序很重要
@my_app.get("/users/me")
async def read_user_me():
return {"user_id": "the current user"}
@my_app.get("/users/{user_id}")
async def read_user(user_id: str):
return {"user_id": user_id}
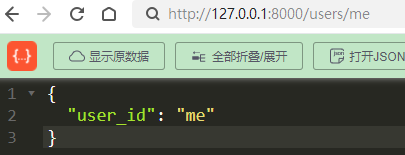
如果上面,两个函数顺序反了,如下结果
2.2 预设值
- 使用 Enum
from enum import Enum
app = FastAPI()
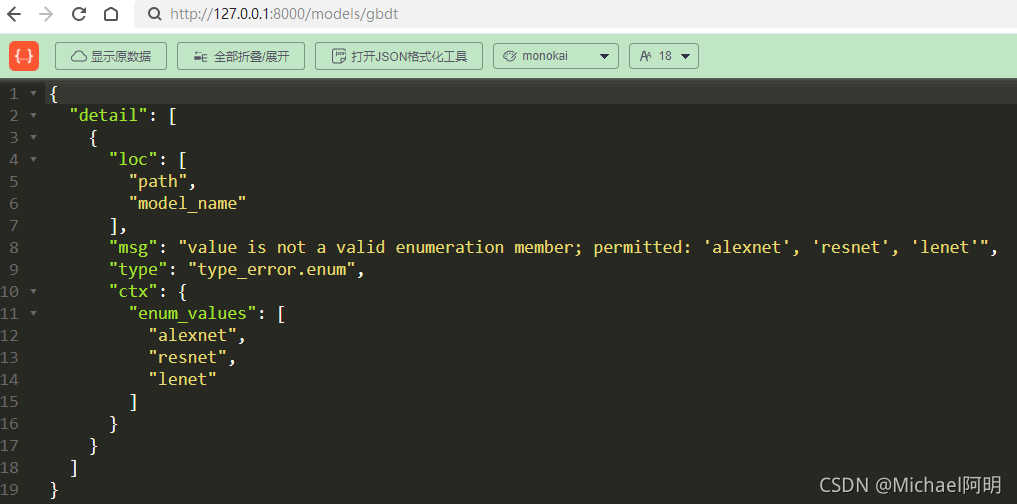
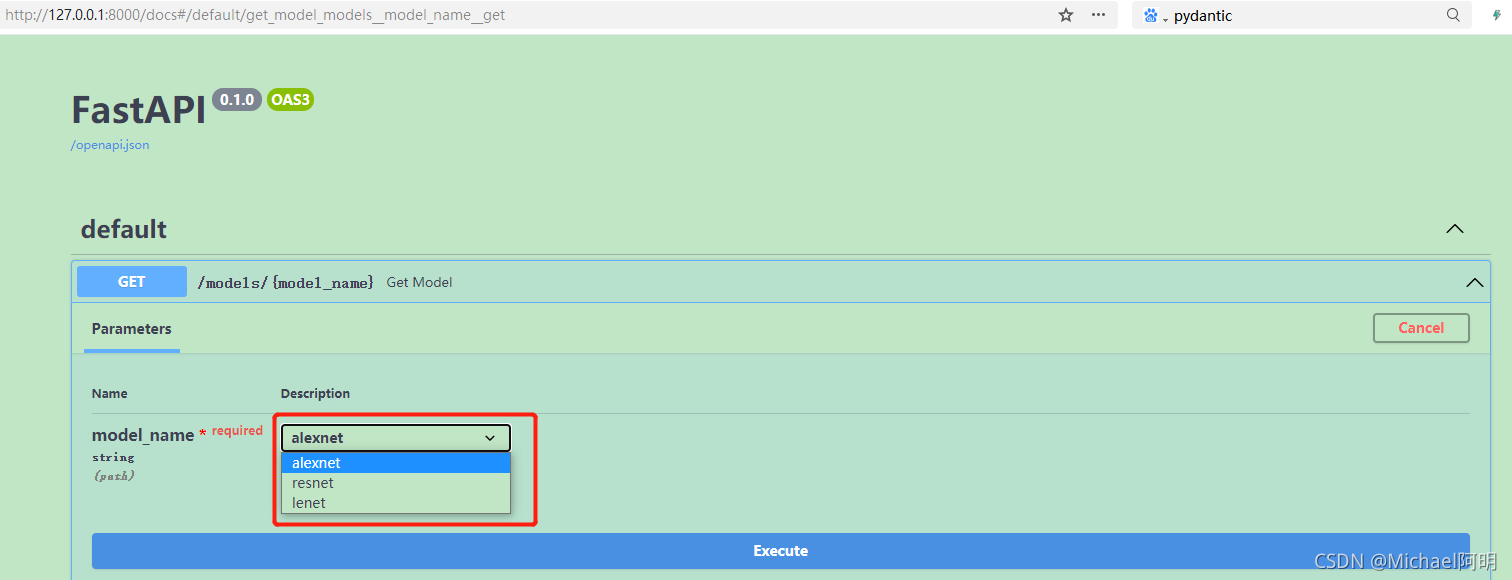
class ModelName(str, Enum): # 继承string, 枚举, 必须是字符串且是指定的枚举值
alexnet = "alexnet"
resnet = "resnet"
lenet = "lenet"
@app.get("/models/{model_name}")
async def get_model(model_name: ModelName):
if model_name == ModelName.alexnet:
return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "Deep Learning FTW!"}
if model_name.value == "lenet":
return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "LeCNN all the images"}
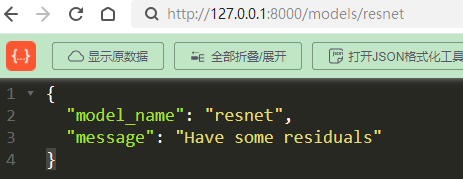
return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "Have some residuals"}
可以使用 model_name.value 或通常来说 your_enum_member.value 来获取实际的值
2.3 包含路径的路径参数
- 参数 { } 内
参数名:path:前后均没有空格,不加:path无法识别 带有/的路径参数
@app.get("/files/{file_path:path}")
async def read_file(file_path: str):
return {"file_path": file_path}
3. 查询参数
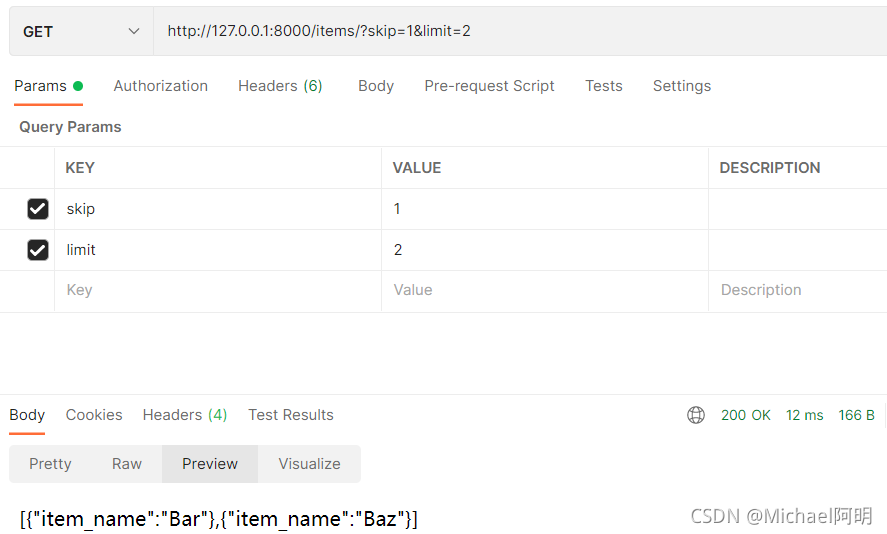
fake_items_db = [{"item_name": "Foo"}, {"item_name": "Bar"}, {"item_name": "Baz"}]
@app.get("/items")
async def read_item(skip: int = 0, limit: int = 10):
return fake_items_db[skip:skip + limit]
- 使用
?开始,参数间使用&分割
from typing import Optional
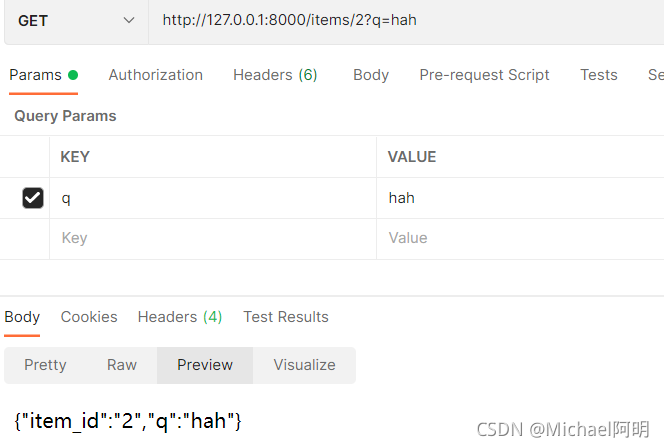
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: str, q: Optional[str] = None):
if q:
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
return {"item_id": item_id}
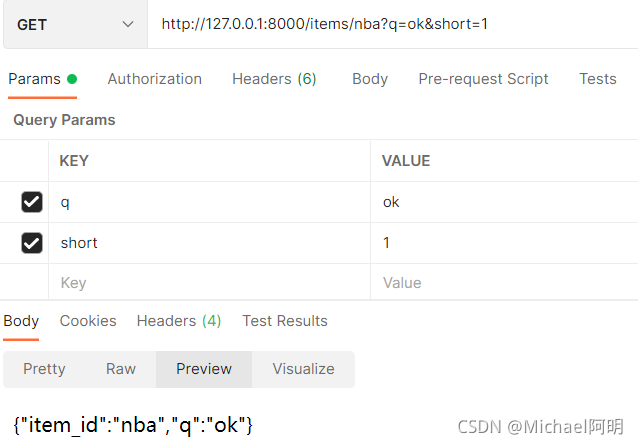
3.1 查询参数类型转换
from typing import Optional
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: str, q: Optional[str] = None, short: bool = False):
item = {"item_id" : item_id}
if q:
item.update({"q" : q})
if not short:
item.update(
{"description": "This is an amazing item that has a long description"}
)
return item
输入 short=,后面是 1,True, true, yes, on, On, YES 任意变形体都是一样的效果,都是 true
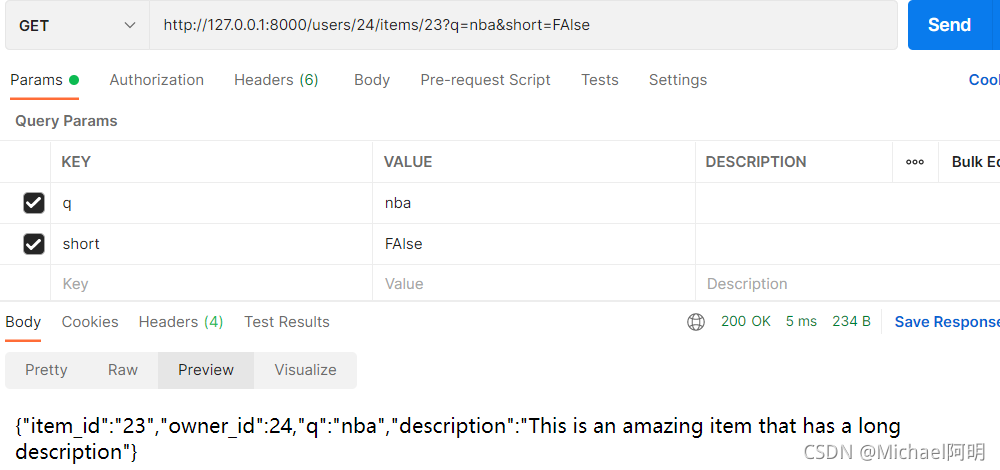
- 多个参数的顺序没影响,通过名字查找的
@app.get("/users/{user_id}/items/{item_id}")
async def read_user_item(
item_id: str, user_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None, short: bool = False
):
item = {"item_id": item_id, "owner_id": user_id}
if q:
item.update({"q": q})
if not short:
item.update(
{"description": "This is an amazing item that has a long description"}
)
return item
item_id: str, user_id: int,更换两个变量的位置,没有关系
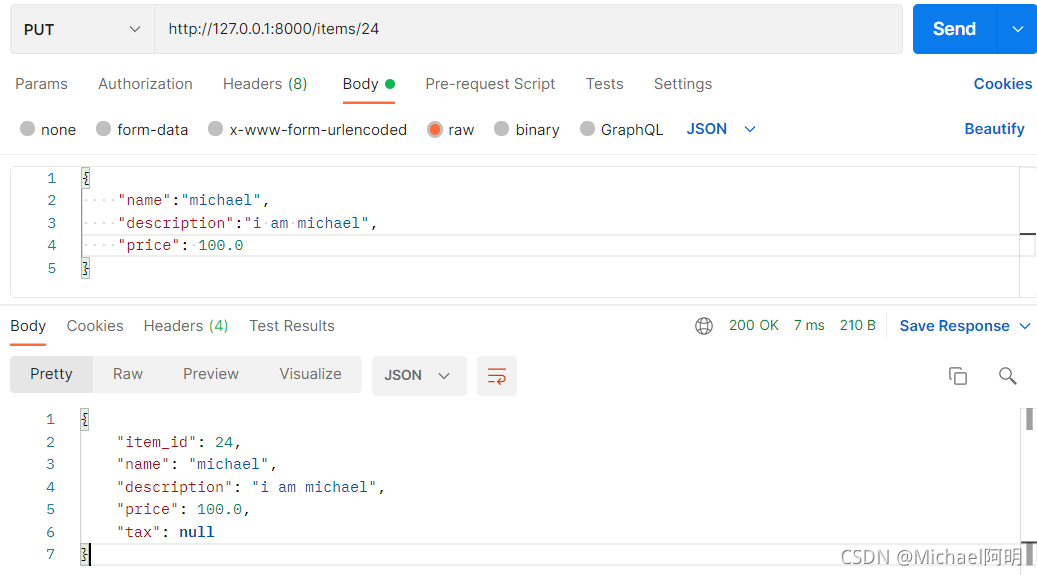
4. 请求体
请求体是客户端发送给 API 的数据
响应体是 API 发送给客户端的数据
使用 Pydantic 模型来声明请求体
from typing import Optional
from Pinyin2Hanzi import Item
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Optional[str]=None
price:float
tax:Optional[float] = None
app = FastAPI()
@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def create_item(item_id: int, item: Item, q: Optional[str] = None):
result = {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}
if q:
result.update({"q": q})
return result
- 还可以同时声明请求体、路径参数和查询参数。
函数参数将依次按如下规则进行识别:
1.如果在路径中也声明了该参数,它将被用作路径参数
2.如果参数属于单一类型(比如 int、float、str、bool 等)它将被解释为查询参数
3.如果参数的类型被声明为一个 Pydantic 模型,它将被解释为请求体