第二模块 函数 & 模块
概述
主要包含两大部分:
-
函数,一个专门用于实现某个功能的代码块(可重用)。
-
内置函数
len,bin,oct,hex,sum 等
-
-
自定义函数
def send_email(): # 写了10行代码,实现了发送邮件 pass # 调用 sed_email()# 定义一个函数,功能代码块 def send_email(): # 假设写10了代码,实现了发邮件 pass goods = [ {"name": "电脑", "price": 1999}, {"name": "鼠标", "price": 10}, {"name": "游艇", "price": 20}, {"name": "美女", "price": 998} ] for index in range(len(goods)): item = goods[index] print(index + 1, item['name'], item['price']) # 调用并执行函数 send_email() while True: num = input("请输入要选择的商品序号(Q/q):") if num.upper() == "Q": break if not num.isdecimal(): print("用户输入格式错误:") break num = int(num) send_email() if num > 4 or num < 0: print("范围选择错误") break target_index = num - 1 choice_item = goods[target_index] print(choice_item["name"], choice_item['price']) send_email() -
模块,集成了很多功能的函数集合
-
内置模块,python内部帮助我们提供好的模块
import random num = random.randint(0,19) # random.randint() 在一个区间内随机抽取一个值 # random.choice() 随机抽取 import random list = [1,2,3,4,5] num = random.choice(list) print(num)import decimal v1 = decimal.Decimal("0.1") v2 = decimal.Decimal("0.2") v3 = v1 + v2 print(v3) # 输出0.3
-
-
第三方模块,网上下载别人写好的模块,(功能的集合)
-
自定义模块
day09 文件操作相关
目标:掌握基于python对文件的相关操作
- 文件操作
- 文件夹和路径
- CVS格式文件
- ini格式文件
- xml格文件
- Excel文件
- 压缩文件
注意:每种格式包含很多相关操作,主要掌握知识点的用法。
1.文件操作
-
字符串类型(str),在程序中用于表示文字信息,本质上是Unicode编码中的二进制。
name = "熊二" -
字节类型(bytes)
-
可表示文字信息,本质上是是utf-8/gbk等编码的二进制(对Unicode进行压缩,方便文件存储和网络传输)
name = "熊大" data = name.encode('utf-8') print(data) # b'\xe7\x86\x8a\xe5\xa4\xa7' result = data.decode('utf-8') print(result) # 熊大
-
1.1 读文件
-
文本文件
# 打开文件 # - 路径: # 相对路径:'info.txt' # 绝对路径:'/Users/xxx/PycharmProjects/luffyCourse/day09/info.txt' # - 模式: # rb,表示读取文件原始的二进制(r, 读 read; b, 二进制 binary) # 1.打开文件 file_object = open(r'D:\dw\python\day09-16\files\info.txt', mode='rb') # 2.读取文件内容,并赋值给data data = file_object.read() # 3.关闭文件 file_object.close() print(data) # b'root-123123\ndave-88888888\n' # 注:文本原始的二进制信息实际上是一种字节类型 text = data.decode("utf-8") print(text) #输出: D:\Python\python.exe D:/dw/python/day09-16/读文本文件.py b'root-123123\ndave-88888888\n' root-123123 dave-88888888 # 每次还得把字节类型转换成字符串类型# 1.打开文件,使用python内部方法,open就不需要每次再转换 file_object = open(r'D:\dw\python\day09-16\files\info.txt', mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') 参数解释:rt读文本文件,通过encoding='utf-8'转换为文本类型,所以就能直接读到字符串类型了 # 2.读取文件内容,并赋值给data data = file_object.read() # 3.关闭文件 file_object.close() print(data) # 输出: D:\Python\python.exe D:/dw/python/day09-16/读文本文件.py root-123123 dave-88888888注意事项:
-
路径
-
相对路径,从当前路径开始的路径
-
绝对路径,从盘符开始的路径
Windows系统中写绝对路径容易出问题: # file_object = open('D:\\dw\python\\day09-16\\files\\info.txt, mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') file_object = open(r'D:\dw\python\day09-16\files\info.txt', mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') data = file_object.read() file_object.close() print(data) # 可以通过加r 或 反斜杠 \ 的方式解决
-
-
-
读文件时,文件不存在程序会报错
D:\Python\python.exe D:/dw/python/day09-16/读文本文件.py Traceback (most recent call last): File "D:\dw\python\day09-16\读文本文件.py", line 16, in <module> file_object = open(r'C:\new\info.txt', mode='rt', encoding='utf-8') FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'C:\\new\\info.txt'# 可以通过判断路径是否存在 import os file_path = "D:\\dw\\python\\day09-16\\files\\info.txt" exists = os.path.exists(file_path) if exists: # 打开文件 file_object = open('D:\\dw\\python\\day09-16\\files\\info.txt', mode='rt', encoding='utf=8') # 读取文件内容,并赋值给data data = file_object.read() # 关闭文件 file_object.close() print(data) else: print("文件不存在")
1.2写文件
-
写文本文件
# 1.打开文件 # 路径:t1.txt # 模式:wb(要求写入的内容需要是字节类型),以utf-8写入的必须使用utf-8打开,否则会出现乱码 file_object = open("t1.txt", mode='wb') # 2.写入内容 file_object.write( "佩奇".encode("utf-8") ) # 3.文件关闭 file_object.close() # 运行后生成了一个t1.txt 文件,内容为佩奇# python提供了更方便的方式,在打开时通过如下方法直接写入: file_object = open('t2.txt', mode='wt', encoding='utf-8') file_object.write("喜羊羊与灰太狼") file_object.close() -
写图片等文件
# 运行后又生成了一张美女1.png的图片,对图片的操作都是二进制的操作, 不存在带编码的 f1 = open('美女.png',mode='rb') content = f1.read() f1.close() f2 = open('美女1.png',mode='wb') f2.write(content) f2.close()
案例基础
# 案例1:用户注册,没有则自动生成这个文件
user = input("请输入用户名:").strip()
pwd = input("请输入密码:").strip()
data = "{}-{}".format(user, pwd)
file_object = open("files/info.txt", mode='wt', encoding='utf-8')
file_object.write(data)
file_object.close()
# 运行结果,在files下生成了一个info.txt文件,内容为输入的用户名-密码
# 案例2 多用户注册
# w模式的特点: 写入文件时候,先清空文件;再在文件中写入内容,因此可以放到循环以为
file_object= open("files/info.txt", mode='wt', encoding='utf-8')
while True:
user = input("请输入用户名:").strip()
if user.upper() == "Q":
break
pwd = input("请输入密码:").strip()
data = "{}-{}\n".format(user,pwd)
file_object.write(data)
file_object.close()
小高级案例:
利用Python想某个网址发送请求并获取结果(利用第三方的模块)
- 1.下载第三方模块,pip是python自带的一个包管理工具,Windows默认安装目录D:\Python\Scripts
D:\dw\python>cd D:\Python D:\Python>pip install requests
- 使用第三方模块
import requests res = requests.get(url='网站') print(res)
# 案例1 去网上下载一点文本,文本信息写入文件。
import requests
res = requests.get(
url="https://movie.douban.com/j/search_subjects?type=movie&tag=%E7%83%AD%E9%97%A8&sort=recommend&page_limit=20&page_start=20",
headers={
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/94.0.4606.61 Safari/537.36"
}
)
# 网络传输的原始二进制信息(bytes)
# res.content
file_object = open('files/log1.txt', mode='wb')
file_object.write(res.content)
file_object.close()
# 请求头:f12-network-点击name-Headers
# 案例2
import requests
res = requests.get(
url="https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/c7e1461e4b15735fbe625c4dc85bd19904d96daf6de9fb-tosv1r_fw1200",
headers={
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/94.0.4606.61 Safari/537.36"
}
)
# res.content 获取到的是网络传输的原始二进制信息(bytes)
# 写成格式xxx.MP4也可以下载视频,在防爬机制比较低的情况下
file_object = open('files/MM.png', mode='wb')
file_object.write(res.content) # 返还的内容:res.contebt,还有很多其他信息
file_object.close()
注意事项:
- 路径
- 绝对路径
- 相对路径
- 对于文件不存在时,w模式会新建然后再写入内容,文件存在时,w模式会清空文件再写入内容。
1.3 文件打开模式
上面基于文件操作基本实现了读,写的功能,其中涉及的文件操作模式:rt,rb,wt,wb,其实在文件操作中还有其他的很多模式。
========= ===============================================================
Character Meaning
--------- ---------------------------------------------------------------
'r' open for reading (default)
'w' open for writing, truncating the file first
'x' create a new file and open it for writing
'a' open for writing, appending to the end of the file if it exists
# 不能独立存在,必须制定文本模式,b二进制,t文本模式
'b' binary mode
't' text mode (default) # 默认文本
# 每种模式带上加号就变成了读写模式。每个模式带上+变成读写模式后有光标位置的区别
'+' open a disk file for updating (reading and writing)
The default mode is 'rt' (open for reading text)
关于文件的打开模式常见应用有:
-
只读:r,rt,rb (常用)
- 存在,读
- 不存在,报错
-
只写:w,wt,wb(常用)
- 存在,清空再写
- 不存在,创建再写
-
只写:x,xt,xb
- 存在,报错
- 不存在,创建再写
-
只写,a ,at,ab [尾部追加] (常用)
- 存在,尾部追加
- 不存在,创建再写
-
读写
-
r+,rt+,rb+,默认光标位置:起始位置
# rt+案例 file_object = open('info.txt', mode='rt+') # 既可读又可写 # 读取内容 data = file_object.read() print(data) # 写入内容 file_object.write("你好呀") file_object.close() # 程序执行之前,info文件内容如下: root-123123 dave-88888888 #执行之后内容如下: root-123123 dave-88888888你好呀 总结:打开文件时,光标默认还是在起始位置,通过file_object.read()读取到所有内容,光标随着读取到了最后的位置,再写时光标到了文件最后的位置,所以再写入时,内容追加在文件光标最后位置。# 如果读写调换了位置,结果可能会变成不一样 file_object = open('info.txt', mode='rt+') # 写入内容 file_object.write('tomcat') # 读取内容 data = file_object.read() print(data) # 输出:23 file_object.close() # 程序执行之前,info文件内容如下: root-123 #执行之后,info文件内容如下: tomcat23 # 总结:先写后读时,通过rt+模式打开一个文件时,光标默认在起始位置,当写入的时候会把原有位置的值覆盖掉,所以 root-123 成了tomcat23。使用rt+时,注意读写顺序,光标位置
-
-
w+,wt+,wb+,默认光标位置:起始位置(清空文件)
file_object = open('info.txt', mode='wt+') # 读取内容 data = file_object.read() print(data) # 写入内容 file_object.write("爽歪歪") # 注:写入后光标,移动至文本最后,注:读动作是从光标位置开始往后的读。所以读不到内容,通过.seek()调整光标位置,便可以读取到内容了。 # 将光标位置充值起始 file_object.seek(0) # 读取内容 data = file_object.read() print(data) file_object.close() # 使用wt模式时,光标永远在起始位置,因为w每次都会清空文件,所以光标永远在最前。 # 执行前文件内容为:123 # 执行后内容为:爽歪歪 -
x+,xt+,xb+,默认光标位置(新文件,,老文件存在则报错)
-
a+,at+,ab+,默认光标位置:末尾
file_object = open('info.txt', mode='at+')
# 写入内容
file_object.write("佩奇")
# 将光标位置重置起始,读到所有内容,所以下面打印全部内容
file_object.seek(0)
# 读取内容
data = file_object.read()
print(data)
file_object.close()
# 执行前内容为:爽歪歪
# 执行后内容为:歪歪爽佩奇
# 默认光标位置在末尾,所写入的内容是追加在末尾
# a模式,多用户注册案例,追加模式。虽然能实现,但是每次追加内容时都打开文件,效率不高
while True:
user = input("用户名:").strip()
if user.upper() == "Q":
break
pwd = input("请输入密码:").strip()
data = "{}-{}\n".format(user, pwd)
file_object = open('files/account.txt', mode='a') # 用a模式打开,追加写入内容
file_object.write(data)
file_object.close()
# 比每次都打开文件的效率更高
file_object = open('files/account.txt', mode='a')
while True:
user = input("用户名:").strip()
if user.upper() == "Q":
break
pwd = input("密码:")
data = "{}-{}\n".format(user,pwd)
file_object.write(data)
file_object.close()
1.4 常见功能
在上述对文件的操作中,只使用了write 和 read 来对文件进行读写,其实在文件操作中还有很多其他功能来辅助实现更好的读写文件的内容。
不同的字符所占的字节是不同的。
ASCII码:
一个英文字母(不分大小写)占一个字节的空间,一个中文汉字占两个字节的空间。一个二进制数字序列,在计算机中作为一个数字单元,一般为8位二进制数,换算为十进制。最小值0,最大值255。如一个ASCII码就是一个字节。
UTF-8编码:
一个英文字符等于一个字节,一个中文(含繁体)等于三个字节。
Unicode编码:
一个英文等于两个字节,一个中文(含繁体)等于两个字节。
-
read 读
-
读所有(常用)
f = open('info.txt', mode='r',encoding='utf-8') data = f.read() f.close() print(f)f = open('info.txt', mode='rb') data = f.read() f.close() print(data) print(f)
-
-
读 n 个 字符(字节) (会用到)
f = open('info.txt', mode='r', encoding='utf-8') # 读一个字符 data = f.read(1) f.close() print(data) # info内容为:tomcatrt,输出了一个t,输出第一个字符,类型是strf = open('info.txt', mode='rb') # 读一个字节 data = f.read(3) f.close() print(data, type(data)) # 输出 b'tom' <class 'bytes'># 冲用于文件上传,断点续传,网络传输文件等,使用这种读字节的模式更多,几个字节几个字节的读,如: f = open('info.txt', mode='rb') # 读1个字节 chunk1 = f.read(3) chunk2 = f.read(3) chunk3 = f.read(1) print(chunk1, chunk2, chunk3) f.close() # 输出 b'tom' b'cat' b'r'# 也可以几个字符几个字符的读取 f = open('info.txt', mode='r', encoding='utf-8') # 读一个字符,,二进制,指的是字节,根据模式不同,读取内容就不一样 chunk1 = f.read(1) chunk2 = f.read(2) print(chunk1, chunk2) f.close() # info文本内容为:tomcatrt,当第一次读完后光标位置已经移到到了t后面,所有再读两个字符,打印出om -
readline 读一行
f = open('info.txt', mode='r', encoding='utf-8') # 读一行,不管是r还是rb模式都是读取一行 v1 = f.readline() print(v1) v2 = f.readline() print(v2) f.close()f = open('info.txt', mode='r', encoding='utf-8') v1 = f.readline() print(v1) f.close() f = open('info.txt', mode='r', encoding='utf-8') v2 = f.readline() print(v2) f.close() # 如果文件很大,可以使用readline来一行一行读取处理 -
readlines,读取所有行,每行作为列表的一个元素
f = open('info.txt', mode='rb') data_list = f.readlines() f.close() print(data_list) -
循环,读大文件(readline加强版)[常见]
f = open('info.txt', mode='r', encoding='utf-8') for line in f: print(line.strip()) f.close() # 输出每一行
1.4.1 写和光标的相关功能
-
write ,写
f = open('info.txt', mode='a', encoding='utf-8') f.write("佩奇") f.closef = open('info.txt', mode='ab') f.write("佩奇".encode('utf-8')) f.close() -
flush,刷到硬盘
f = open('info.txt', mode='a',encoding='utf-8') while True: # 执行write时,不是写到了硬盘,而是写在缓冲区,系统会将缓冲区的内容刷到硬盘,利用flush刷到硬盘中。 f.write("武沛齐") f.flush() f.close()# 优化前面多用户注册的案例 file_object = open('files/account.txt', mode='a') while True: user = input('用户名:') if user.upper() == "Q": break pwd = input("密码:") data = "{}-{}\n".format(user, pwd) file_object.write(data) file_object.flush() file_object.close() -
移动光标位置(字节)
f = open('info.txt', mode='r+', encoding='utf-8') # 移动到指定字节的位置 f.seek(3) f.write("佩奇") f.close()注意:在a模式下,调用write在文件中写入内容时,调整光标位置是没用的,永远只能将内容写入到尾部,不会写到光标的位置。
注意乱码: f = open('info.txt', mode='r+', encoding='utf-8') # 一定到指定字节的位置 f.seek(2) f.write("佩奇") f.close() # info文件的内容:你好啊中国,运行代码后info内容变成了:你浣╁国 原因:是seek(2)是光标移动到了 “你” (每个中文一个字符等于三个字节) 的里边去了,所有拼凑出来的是乱码的字符 -
获取当前光标位置
f = open('info.txt', mode='r', encoding='utf-8') p1 = f.tell() print(p1) # 0 f.read(3) # 读3个字符 3*3=9字节 p2 = f.tell() print(p2) # 9 f.close() # 文件内容:你好啊 # r模式 读的是三个字节f = open('info.txt', mode='rb') p1 = f.tell() print(p1) # 0 f.read(3) # 读3个字节 p2 = f.tell() print(p2) # 3 f.close()
1.5 上下文管理
之前对文件进行操作时,每次都要打开和关闭文件,比较繁琐且容易忘记关闭文件。
以后再进行文件操作时,推荐使用with上下文件管理,它可以自动实现关闭文件。
with open('xxx.txt', mode='rb') as file_object:
data = file_object.read()
print(data)
在python2.7后,with又支持同时对多个文件的上下文进行管理,即:
with open('xxx.txt', mode='rb') as f1, open('xxx'.txt, mode='rb') as f2:
pass
2. CSV格式文件
逗号分隔值Comma-Separated Values,CSV,有时也称为字符分隔值,因为分隔字符也可以部署逗号),其文件以纯文本形式存储表格数据(数字和文本)。
对于这种格式的数据,我们需要利用open函数读取文件并根据逗号分隔的特点来进行处理。
股票代码,股票名称,当前价,涨跌额,涨跌幅,年初至今
SH601778,N晶科,6.29,+1.92,-43.94%,+43.94%
SH688566,吉贝尔,52.66,+6.96,+15.23%,+122.29%
...
案例:下载文档中的所有图片且以用户名为图片名称存储。
ID,用户名,头像
26044585,Hush,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/51d46dc32abe7ac7f83b94c67bb88cacc46869954f478-aP4Q3V
19318369,柒十一,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/703fdb063bdc37b11033ef794f9b3a7adfa01fd21a6d1-wTFbnO
15529690,Law344,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/b438d8c61ed2abf50ca94e00f257ca7a223e3b364b471-xrzoQd
18311394,Jennah·,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/4edba1ed6a71797f52355aa1de5af961b85bf824cb71-px1nZz
18009711,可洛爱画画,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/03331ef39b5c7687f5cc47dbcbafd974403c962ae88ce-Co8AUI
30574436,花姑凉~,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/2f5b657edb9497ff8c41132e18000edb082d158c2404-8rYHbw
17740339,小巫師,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/dbc6fd49f1915545cc42c1a1492a418dbaebd2c21bb9-9aDqgl
18741964,桐末tonmo,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/b60cee303f62aaa592292f45a1ed8d5be9873b2ed5c-gAJehO
30535005,TANGZHIQI,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/bbd08ee168d54665bf9b07899a5c4a4d6bc1eb8af77a4-8Gz3K1
31078743,你的老杨,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/c46fbc3c9a01db37b8e786cbd7174bbd475e4cda220f4-F1u7MX
25519376,尺尺寸,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/ee29ee198efb98f970e3dc2b24c40d89bfb6f911126b6-KGvKes
21113978,C-CLong,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/7fa6b2a0d570e67246b34840a87d57c16a875dba9100-SXsSeY
24674102,szaa,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/0716687b0df93e8c3a8e0925b6d2e4135449cd27597c4-gWdv24
30508507,爱起床的小灰灰,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/4eafdbfa21b2f300a7becd8863f948e5e92ef789b5a5-1ozTKq
12593664,yokozen,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/cd07bbaf052b752ed5c287602404ea719d7dd8161321b-cJtHss
16899164,一阵疯,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/0940b557b28892658c3bcaf52f5ba8dc8402100e130b2-G966Uz
847937,卩丬My月伴er彎,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/e2d6bb5bc8498c6f607492a8f96164aa2366b104e7a-kWaH68
31010628,慢慢即漫漫,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/c4fb6718907a22f202e8dd14d52f0c369685e59cfea7-82FdsK
13438168,海贼玩跑跑,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/1edae3ce6fe0f6e95b67b4f8b57c4cebf19c501b397e-BXwiW6
28593155,源稚生,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/626cfd89ca4c10e6f875f3dfe1005331e4c0fd7fd429-9SeJeQ
28201821,合伙哼哼,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/f59d4780531aa1892b80e0ec94d4ec78dcba08ff18c416-769X6a
28255146,漫步AAA,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/3c034c520594e38353a039d7e7a5fd5e74fb53eb1086-KnpLaL
30537613,配?,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/efd81d22c1b1a2de77a0e0d8e853282b83b6bbc590fd-y3d4GJ
22665880,日后必火,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/69f0f959979a4fada9e9e55f565989544be88164d2b-INWbaF
16748980,keer521521,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/654953460733026a7ef6e101404055627ad51784a95c-B6OFs4
30536510,“西辞”,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/61cfffca6b2507bf51a507e8319d68a8b8c3a96968f-6IvMSk
30986577,艺成背锅王,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/c381ecc43d6c69758a86a30ebf72976906ae6c53291f9-9zroHF
26409800,CsysADk7,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/bf1d22092c2070d68ade012c588f2e410caaab1f58051-ahlgLm
30469116,18啊全阿,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/654953460733026a7ef6e101404055627ad51784a95c-B6OFs4
15514336,W/小哥,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/a30f5967fc0acf81421dd49650397de63c105b9ead1c-nVRrNl
17473505,椿の花,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/0e38d810e5a24f91ebb251fd3aaaed8bb37655b14844c-pgNJBP
19165177,っ思忆゜?,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/4815ea0e4905d0f3bb82a654b481811dadbfe5ce2673-vMVr0B
16059616,格林熊丶,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/8760a2b08d87e6ed4b7a9715b1a668176dbf84fec5b-jx14tZ
30734152,sCWVkJDG,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/f31a5305d1b8717bbfb897723f267d316e58e7b7dc40-GD3e22
24019677,虚无本心,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/6fdfa9834abe362e978b517275b06e7f0d5926aa650-N1xCXE
16670283,Y-雨后天空,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/a3bbb0045b536fc27a6d2effa64a0d43f9f5193c177f-I2vHaI
21512483,汤姆2,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/98cc50a61a7cc9b49a8af754ffb26bd15764a82f1133-AkiU7D
16441049,笑潇啸逍小鱼,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/ae8a70cd85aff3a8587ff6578d5cf7620f3691df13e46-lmrIi9
24795603,?????v,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/a7183cc3a933aa129d7b3230bf1378fd8f5857846cc5-3tDtx3
29819152,妮玛士珍多,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/ca4ecb573bf1ff0415c7a873d64470dedc465ea1213c6-RAkArS
19101282,陈勇敢?,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/ab6d04ebaff3176e3570139a65155856871241b58bc6-Qklj2E
28337572,爱意随风散,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/117ad8b6eeda57a562ac6ab2861111a793ca3d1d5543-SjWlk2
17342758,幸运instant,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/72b5f9042ec297ae57b83431123bc1c066cca90fa23-3MoJNj
18483372,Beau染,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/077115cb622b1ff3907ec6932e1b575393d5aae720487-d1cdT9
22127102,栽花的小蜻蜓,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/6c3cbf9f27e17898083186fc51985e43269018cc1e1df-QfOIBG
13802024,LoveHsu,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/f720a15f8b49b86a7c1ee4951263a8dbecfe3e43d2d-GPEauV
22558931,白驹过隙丶梨花泪う,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/e49e1341dfe5144da5c71bd15f1052ef07ba7a0e1296b-jfyfDJ
11762339,cojoy,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/5b27f876d5d391e7c4889bc5e8ba214419eb72b56822-83gYmB
30711623,雪碧学长呀,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/2c288a1535048b05537ba523b3fc9eacc1e81273212d1-nr8M4t
18906718,西霸王,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/7b02ad5e01bd8c0a29817e362814666a7800831c154a6-AvBDaG
31037856,邵阳的小哥哥,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/654953460733026a7ef6e101404055627ad51784a95c-B6OFs4
26830711,稳健谭,https://hbimg.huabanimg.com/51547ade3f0aef134e8d268cfd4ad61110925aefec8a-NKPEYX
3.ini格式
ini文件是Initialization Flie的缩写,平时用于存放软件的配置文件,例如MySQL的数据库的配置文件。[mysqld]称之为节点,#开头称之为注释。
[mysqld]
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
log-bin=py-mysql-bin
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_general_ci
log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks
symbolic-links=0
[mysqld_safe]
log-error=/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log
pid-file=/var/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid
[client]
default-character-set=utf8
这种格式可以直接open来处理,考虑到自己处理比较麻烦,python为我们提供了更为方便的方式。
import configparser # 引入模块
config = configparser.ConfigParser() # 固定搭配,名字可以自定义
config.read('my.ini', encoding='utf-8') # 读取这个文件
# 1.获取所有的节点
result = config.sections()
print(result) # ['mysqld', 'mysqld_safe', 'client']
# 2.获取节点下的键值
result = config.items("mysqld_safe")
print(result)
# 输出: [('log-error', '/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log'), ('pid-file', '/var/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid')]
for key,value in config.items("mysqld_safe"):
print(key, value)
#输出:
#log-error /var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log
#pid-file /var/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid
# 3.获取某个节点下的键值对应的值
result = config.get("mysqld", "collation-server")
print(result)
# 4.其他
# 4.1 是否存在节点
v1 = config.has_section("client")
print(v1)
# 4.2 添加一个节点
config.add_section("group") # 添加节点,仅添加到内存
config.set('group', 'name', 'peiqi') # 添加节点下的键值
config.set('client', 'name', 'peiqi')
config.write(open('new.ini', mode='w', encoding='utf-8')) # 写入到文件,一个文件对象,open打开,w模式
# 4.3 删除
config.remove_section('client') # 删除节点
config.remove_option("mysqld", "datadir") # 删除节点下的某个键值
config.write(open('new.ini', mode='w', encoding='utf-8'))
-
读取所有节点
import configparser # 引入模块 config = configparser.ConfigParser() # 固定搭配写法,config名字可以自定义 config.read('my.ini', encoding='utf-8') ret = config.sections() print(ret) -
读取节点下的键值
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read('my.ini', encoding='utf-8') item_list = config.item("mysqld_safe") print(items_list) # 以元组的方式输出: [('log-error', '/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log'), ('pid-file', '/var/run/mariadb/mariadb.pid')] -
读取节点下的值(根据 节点 + 值)
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read('my.ini', encoding='utf-8') value = config.get('mysqld', 'log-bin') print(value) # 输出:py-mysql-bin -
检查,删除,添加节点
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read('my.ini', encoding='utf-8') # 检查节点是否存在 has_sec = config.has_section('mysqld') print(has_sec) # 添加节点,仅添加到内存,还需配合write写入文件 config.add_section('SEC_1') config.write(open('my.ini', 'w')) # 在节点中设置键值 config.set('SEC_1', 'k10', "123") config.set('SEC_1', 'name', "哈哈哈哈哈") config.add_section("SEC_2") config.set('SEC_2', 'k10', "123") # 内容写入到新文件 config.write(open('xxoo.conf', 'w')) # 删除节点 config.remove_section("SEC_2") # 删除节点中的键值 config.remove_option('SEC_1', 'k10') cofig.write(open('new.conf', 'w'))4.XML格式文件
可扩展标记语言,是一种简单的数据存储语言,XML被设计用来传输和存储数据。
- 存储,可以用来存放配置文件,例如:Java的配置文件
- 传输,网络传世时以这种格式存在,如:早期Ajax传输的数据,soap(简单对象访问协议)协议等。
<data> <country name="Liechtenstein"> <rank updated="yes">2</rank> <year>2023</year> <gdppc>141100</gdppc> <neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" /> <neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" /> </country> <country name="Singapore"> <rank updated="yes">5</rank> <year>2026</year> <gdppc>59900</gdppc> <neighbor direction="N" name="Malaysia" /> </country> <country name="Panama"> <rank updated="yes">69</rank> <year>2026</year> <gdppc>13600</gdppc> <neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" /> <neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" /> </country> </data>注:在在Python开发中用的相对来比较少,了解即可(后期课程在讲解微信支付、微信公众号消息处理 时会用到基于xml传输数据)。
例如:https://developers.weixin.qq.com/doc/offiaccount/Message_Management/Receiving_standard_messages.html
4.1 读取文件和内容
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET # as 后接别名
# ET去打开xml文件
tree = ET.parse("xxx.xml")
# 获取根标签
root = tree.getroot() # 固定写法
print(root) # 输出:<Element 'data' at 0x0000028175B26180>
# 通过网络方式获取到xml文本,直接调用 ET.XML(content)把xml的内容放进去处理
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
content = """
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank updated="yes">2</rank>
<year>2023</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" />
<neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" />
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank updated="yes">69</rank>
<year>2026</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" />
<neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" />
</country>
</data>
"""
root = ET.XML(content)
print(root) # <Element 'data' at 0x000002345AC56A90>
4.2 读取节点数据
# 获取某一个标签的,然后读取他的名字,属性,以及标签中间的文本
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
content = """
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein" id="999" >
<rank>2</rank>
<year>2023</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" />
<neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" />
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>69</rank>
<year>2026</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" />
<neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" />
</country>
</data>
"""
# 获取根标签 data
root = ET.XML(content)
country_object = root.find("country")
print(country_object.tag, country_object.attrib)
# 输出标签的名字,属性:country {'name': 'Liechtenstein', 'id': '999'}
gdppc_object = country_object.find("gdppc")
print(gdppc_object.tag,gdppc_object.attrib,gdppc_object.text)
#输出标签的名字,熟悉,以及文本内容 gdppc {} 141100
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
content = """
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein" id="999" >
<rank>2</rank>
<year>2023</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" />
<neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" />
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>69</rank>
<year>2026</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" />
<neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" />
</country>
</data>
"""
# 获取根标签 data
root = ET.XML(content)
# print(root)
# 获取data的标签的子标签
for child in root:
# child.tag 其实就等于 country(子标签)
# 第一次循环:child.attrib = {"name":"Liechtenstein"} 获取到标签所有的属性
print(child.tag, child.attrib)
for node in child: # child代指的是country,这次循环获取到子标签的名字,属性,以及标签中间的文本
print(node.tag, node.attrib, node.text)
# 译文:attrib 改变或显示文件的属性
# root.iter('year')在root中 找到所有的"year"标签,获取某一个或某些标签
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
content = """
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein" id="999" >
<rank>2</rank>
<year>2023</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" />
<neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" />
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>69</rank>
<year>2026</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" />
<neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" />
</country>
</data>
"""
root = ET.XML(content)
for child in root.iter('year'):
print(child.tag, child.text)
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
content = """
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank>2</rank>
<year>2023</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" />
<neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" />
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>69</rank>
<year>2026</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" />
<neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" />
</country>
</data>
"""
root = ET.XML(content)
v1 = root.findall('country')
print(v1)
v2 = root.find('country').find('rank')
print(v2.text)
# findall() 找到所有的country标签
# find()找到第一个的标签
4.3 修改和删除节点
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
content = """
<data>
<country name="Liechtenstein">
<rank>2</rank>
<year>2023</year>
<gdppc>141100</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="E" name="Austria" />
<neighbor direction="W" name="Switzerland" />
</country>
<country name="Panama">
<rank>69</rank>
<year>2026</year>
<gdppc>13600</gdppc>
<neighbor direction="W" name="Costa Rica" />
<neighbor direction="E" name="Colombia" />
</country>
</data>
"""
root = ET.XML(content)
# 修改节点内容和属性
rank = root.find('country').find('rank') # 找到第一个标签country,再找到rank,并打印文本
print(rank.text)
rank.text = "999"
rank.set('update', '2020-11-11') # 在rank标签上再加上一个属性叫 update = 2020-11-11
print(rank.text, rank.attrib)
##########保存文件############
tree = ET.ElementTree(root) # 上面的操作,仅仅修改了内存中的数据,还需要写入 【ET.ElementTree(root)没太明白此行代码】
tree.write("new.xml", encoding='utf-8')
# 删除节点
root.remove(root.find('country'))
print(root.findall('country'))
#########保存文件###########
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write("newnew.xml", encoding='utf-8')
4.4 构建文档
方式一
<home>
<son name="儿1">
<grandson name="儿11"></grandson>
<grandson name="儿12"></grandson>
</son>
<son name="儿2"></son>
</home>
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
# 创建标签
root = ET.Element('home')
# 创建节点第一个子标签,简称大儿子
son1 = ET.Element('son', {'name': '儿1'})
# 创建第二个子标签,二儿子
son2 = ET.Element('son', {"name": '儿2'})
# 在大儿子中创建两个孙子
grandson1 = ET.Element('grandson', {'name': '儿11'})
grandson2 = ET.Element('grandson', {'name': '儿12'})
son1.append(grandson1)
son2.append(grandson2)
# 把儿子添加到跟节点
root.append(son1)
root.append(son2)
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write('oooo.xml', encoding='utf-8', short_empty_elements=False)
# 先创建,后加入
# 短标签与长标签
short_empty_elements=False # True是否用短标签
<home>
<son name="儿1">
<grandson name="儿11"></grandson> # 如果中间没有值可以不用使用 </grandson> 结束如:
<grandson name="儿111"/>
<grandson name="儿12"></grandson>
</son>
<son name="儿2"></son>
</home>
##################
True
<home><son name="儿1"><grandson name="儿11" /></son><son name="儿2"><grandson name="儿12" /></son></home>
#########################
对比False
<home><son name="儿1"><grandson name="儿11"></grandson></son><son name="儿2"><grandson name="儿12"></grandson></son></home>
# 推荐使用短标签
方法二:
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
# 创建根节点
root = ET.Element("famliy")
# 创建大儿子
son1 = root.makeelement('son', {'name': '儿1'})
# 创建小儿子
son2 = root.makeelement('son', {"name": '儿2'})
# 在大儿子中创建两个孙子
grandson1 = son1.makeelement('grandson', {'name': '儿11'})
grandson2 = son1.makeelement('grandson', {'name': '儿12'})
son1.append(grandson1)
son1.append(grandson2)
# 把儿子添加到根节点中
root.append(son1)
root.append(son2)
# 写入文件
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write('oooo.xml', encoding='utf-8')
<famliy>
</famliy>
<son name="儿1"></son>
<son name="儿2"></son>
<grandson name="儿11"></grandson>
<grandson name="儿12"></grandson>
# 先创建,再追加进去
<famliy>
<son name="儿1">
<grandson name="儿11"></grandson>
<grandson name="儿12"></grandson>
</son>
<son name="儿2"></son>
</famliy>
方式三
<famliy>
<son name="儿1">
<age name="儿11">孙子</age>
</son>
<son name="儿2"></son>
</famliy>
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
# 创建根节点
root = ET.Element("famliy")
# 创建节点大儿子
son1 = ET.SubElement(root, "son", attrib={'name': '儿1'})
# 创建小儿子
son2 = ET.SubElement(root, "son", attrib={'name': '儿2'})
# 在大儿子中创建一个孙子
grandson1 = ET.SubElement(son1, "age", attrib={'name': "儿11"})
grandson1.text = '孙子'
et = ET.ElementTree(root) #生成文档对象
et.write("test.xml", encoding="utf-8")
<user><![CDATA[你好呀]]</user>
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
# 创建根据节点
root = ET.Element('user')
root.text = "<![CDATA[你好呀]]>"
et = ET.ElementTree(root)
et.write("test1.xml", encoding="utf-8")
案例
content = """<xml>
<ToUserName><![CDATA[gh_7f083739789a]]></ToUserName>
<FromUserName><![CDATA[oia2TjuEGTNoeX76QEjQNrcURxG8]]></FromUserName>
<CreateTime>1395658920</CreateTime>
<MsgType><![CDATA[event]]></MsgType>
<Event><![CDATA[TEMPLATESENDJOBFINISH]]></Event>
<MsgID>200163836</MsgID>
<Status><![CDATA[success]]></Status>
</xml>"""
# 要求以键值的方式取出:tag与文本内容
from xml.etree import ElementTree as ET
info = {}
root = ET.XML(content) # 固定写法
for node in root:
# print(node.tag,node.text)
info[node.tag] = node.text #字典,键等与值
print(info)
5.Excel 格式文件
Python内部未提供处理Excel文件的功能,想要在Python中操作Excel需要按照第三方的模块,此模块中集成了Python操作Excel的相关功能。
pip install openpyxl
5.1 读Excel
-
读sheet
from openpyxl import load_workbook wb = load_workbook("files/p1.xlsx") # 打开Excel文件 # sheet 相关操作 # 1.获取Excel文件中的所有sheet名称 print(wb.sheetnames) # 输出:['数据导出', '用户列表', 'Sheet1', 'Sheet2'] # 2.选择sheet,基于sheet名称 sheet = wb["数据导出"] cell = sheet.cell(1, 2) # 单元格第一行,第二列 print(cell.value) # 3.选择sheet,基于索引位置 sheet = wb.worksheets[0] # 索引位置0 cell = sheet.cell(1, 2) # 索引位置0的这个sheet的第一行第二列 print(cell.value) # 4.循环所有的sheet # 循环打印每个sheet的第一行第一列 for name in wb.sheetnames: sheet = wb[name] cell = sheet.cell(1,1) print(cell.value) # 方式二 for sheet in wb.worksheets: cell = sheet.cell(1,1) print(cell.value) # 方式三 for sheet in wb: cell = sheet.cell(1, 1) print(cell.value) -
读sheet中单元格的数据
from openpyxl import load_workbook wb = load_workbook("p1.xlsx") sheet = wb.worksheets[0] # 1.获取第N行第N列单元格(位置是从1开始) cell = sheet.cell(1, 1) print(cell.value) #单元格的文本信息 print(cell.style) # 单元格的格式,样式 print(cell.font) # 单元格的字体 print(cell.alignment) # 单元格对齐, # 2.获取某个单元格 c1 = sheet["A2"] print(c1.value) c2 = sheet["D4"] print(c2.value) # 3.第N行所有的单元的内容 for cell in sheet[1]: print(cell.value) """ print(sheet2[1]) 输出一个数组:(<Cell '数据导出'.A1>, <Cell '数据导出'.B1>, <Cell '数据导出'.C1>, <Cell '数据导出'.D1>, <Cell '数据导出'.E1>, <Cell '数据导出'.F1>, <Cell '数据导出'.G1>, <Cell '数据导出'.H1>, <Cell '数据导出'.I1>, <Cell '数据导出'.J1>, <Cell '数据导出'.K1>) """ # 4.所有行的数据(获取某一列数据),sheet.rows获取到每一行的信息 for row in sheet.rows: print(row[0].value, row[1].value) # 取元组的值 .value固定写法 #row 输出的是一个元组:每一行的每个单元格都是一个元组 (<Cell '数据导出'.A1>, <Cell '数据导出'.B1>,...) # 5.获取所有列(某一行的)的数据 for col in sheet.columns: print(col[1].value) # 取出每一列的第一个单元格,即某一行 -
读取合并的单元格
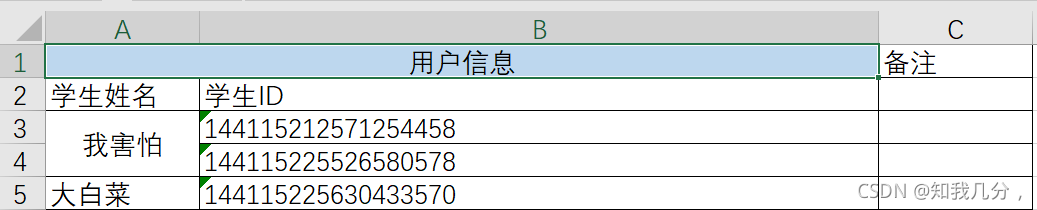
# 获取横向的合并单元格 from openpyxl import load_workbook wb = load_workbook("files/p1.xlsx") # 打开Excel文件 sheet = wb.worksheets[2] # 获取到第第二个sheet # 获取第N行第N列的单元格(位置都是从1 开始) c1 = sheet.cell(1, 1) # 取sheets的第一行,第一列 print(c1) # <Cell 'Sheet1'.A1> # 类型与mergedcell不一样 print(c1.value) # 用户信息 # 被合并的单元格没有值,所以打印出None c2 = sheet.cell(1,2) print(c2) # MergedCell 'Sheet1'.B1> MergedCell 合并的单元格 print(c2.value) # None# 垂直方向的获取合并的单元格 from openpyxl import load_workbook wb = load_workbook('files/p1.xlsx') sheet = wb.worksheets[2] for row in sheet.rows: print(row) # 被合并的单元格类型为MergeCell,值为None # 输出: (<Cell 'Sheet1'.A1>, <MergedCell 'Sheet1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C1>) (<Cell 'Sheet1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C2>) (<Cell 'Sheet1'.A3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C3>) (<MergedCell 'Sheet1'.A4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C4>) (<Cell 'Sheet1'.A5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C5>)
5.2写Excel
在Excel中想要写入文件,大致要分为在:
-
在原Excel文件基础上写内容:
# 将修改后的Excel保存为一个新的Excel文件 from openpyxl import load_workbook wb = load_workbook('files/p1.xlsx') sheet = wb.worksheets[0] # 找到单元格,并修改单元格的内容 cell = sheet.cell(1, 1) cell.value = "新的开始" # 将Excel文件保存p2.xlsx文件中 wb.save("files/p2.xlsx") -
新创建Excel文件写内容
# 创建一个新的Excel,如果已经存在这个名称则会覆盖 from openpyxl import workbook # 创建Excel 且默认会创建一个sheet(名称为Sheet) wb = workbook.Workbook() sheet = wb.worksheets[0] # 或 sheet = wb["sheet"] # 找到单元格,并修改单元格的内容 cell = sheet.cell(1, 1) cell.value = "新的开始" # 将Excel文件保存到p2.xlsx文件中 wb.save("files/p2.xlsx")
在了解如何读取Excel和创建Excel之后,后续对于Excel中的sheet和cell的操作基本上都相同。
from openpyxl import workbook
wb = workbook.Workbook() # 创建有一个默认为Sheet
# 1.修改sheet名称,
sheet = wb.worksheets[0]
sheet.title = "数据集"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 2.创建sheet并设置sheet颜色
sheet = wb.create_sheet("工作计划", 0)
sheet.sheet_properties.tabColor = "1072BA"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 网上所搜RDB颜色即可找到其他颜色,复制过来不加#即可
http://www.360doc.com/content/12/0115/10/7695942_179488602.shtml
https://www.sojson.com/rgb.html
# 3.默认打开的sheet
wb.active = 0
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 4.拷贝sheet
# 新创建一个sheet
sheet = wb.create_sheet("工作计划")
sheet.sheet_properties.tabColor = "1072BA"
# 然后将它拷贝
new_sheet = wb.copy_worksheet(wb["Sheet"])
new_sheet.title = "新的计划"
wb.save("p5.xlsx")
# 把原来的某一个sheet给它拷贝
sheet = wb['数据集']
new_sheet = wb.copy_worksheet(wb["sheet"])
new_sheet.title = "新的计划1" # 拷贝后叫新的计划1
wb.save("p2.xlsx") # 保存到文件
# 5.删除sheet,【怎么写指定要删除的个文件】
from openpyxl import workbook
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('p2.xlsx') # 打开Excel文件
# 删除
del wb["用户列表"]
wb.save('p2.xlsx')
操作Excel单元格
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Alignment, Border, Side, Font, PatternFill, GradientFill
wb = load_workbook('files/p1.xlsx') #打开Excel
sheet = wb.worksheets[1] # 选择要操作的sheet
# 1.获取某个单元格,修改值
cell = sheet.cell(1, 1) # 修改第一行第一列
cell.value = "开始"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 2.获取某个单元格,修改值
sheet["B3"] = "linux" # 直接赋值给指定的单元格
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 3.获取某些单元格,修改值
cell_list = sheet["B2":"D3"] # 选择B2到C3
for row in cell_list:
for cell in row:
cell.value = "新的值"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
B2到D3所包含的值
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-1mcdpSyn-1633099606323)(images/image-20211001124902823.png)]
# 4.对齐方式,各自参数解释:
# horizontal /?h??r??zɑ?ntl/ ,水平方向对齐方式:"general"一般的, "left"左边, "center中央", "right右边", "fill填充", "justify两端对齐",
"center中心 连续不断的Continuous连续的", "distributed" 分布
# vertical /?v??rt?kl/,垂直方向对齐方式:"top顶端", "center", "bottom底部", "justify两端对齐", "distributed" 分布
# text_rotation,旋转角度。
# wrap_text,是否自动换行。
cell = sheet.cell(1, 1)
cell.alignment = Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='distributed', text_rotation=45,wrap_text=True)
print("p2.xlsx")
# 5.边框
# side的style有如下:dashDot','dashDotDot', 'dashed','dotted','double','hair', 'medium', 'mediumDashDot', 'mediumDashDotDot','mediumDashed', 'slantDashDot', 'thick', 'thin'
【'medium中等', 'mediumDashDot中等点画线', 'mediumDashDotDot中等划点点线',
'mediumDashed中等虚线', 'slantDashDot斜电话线', 'thick厚的', 'thin薄的细的'】
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Alignment, Border, Side, Font, PatternFill, GradientFill
wb = load_workbook('p1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.worksheets[0]
cell = sheet.cell(9, 2)
# 可以和对齐方式搭配使用
# cell.alignment = Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='center', text_rotation=0, wrap_text=True)
cell.border = Border(
top=Side(style="thin", color="FFB6C1"),
bottom=Side(style="dashed", color="FFB6C1"),
left=Side(style="dashed", color="FFB6C1"),
right=Side(style="dashed", color="9932CC"),
diagonal=Side(style="thin", color="483D8B"), # 对角线
diagonalUp=True, # 左下 ~ 右上
diagonalDown=True # 左上 ~ 右下
)
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 6.字体
cell = sheet.cell(5, 1)
cell.font = Font(name="微软雅黑", size=45, color="ff0000", underline="single") # underline下划线
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 7.背景色
cell = sheet.cell(5, 3)
cell.fill = PatternFill("solid", fgColor="99ccff")
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 8.渐变背景色
cell = sheet.cell(5, 5)
cell.fill = GradientFill("linear", stop=("FFFFFF", "99ccff", "000000")) 、
# stop左边是 "FFFFFF"颜色,中间是 "99ccff"颜色,右边是 "000000"颜色,可以指定多个颜色
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 9.宽高(索引从1开始)
sheet.row_dimensions[1].height = 50 # 设置高度找到行,1号设置高度为50
sheet.column_dimensions["E"].width = 100 # 设置宽度找到列,E列设置宽度为100
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 10.合并单元格
sheet.merge_cells("B2:D8") # 合并单元格B2到D8
方式二:
# 分别代表起始位置和结束位置
sheet.merge_cells(start_row=15, start_column=3, end_row=18, end_column=8)
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 解除合并单元格,两种方式都支持这么写
sheet.unmerge_cells("B2:D8")
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 11.写入公式
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('p2.xlsx')
sheet = wb.worksheets[3]
sheet["D1"] = "合计"
sheet["D2"] = "=B2*C2"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 也支持Excel内部公司,直接写入即可
sheet = wb.worksheets[3]
sheet["D3"] = "=SUM(B3,C3)"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
#12. 删除
# idx,要删除的索引位置
# amount,从索引位置开始要删除的个数(默认为1)
sheet.delete_rows(idx=1, amount=20)
sheet.delete_cols(idx=3, amount=2)
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 13.插入
sheet.insert_rows(idx=5, amount=10)
sheet.insert_rows(idx=3, amount=2)
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 14.循环写内容
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Alignment, Border, Side, Font, PatternFill, GradientFill
wb = load_workbook('p2.xlsx') #打开Excel
sheet = wb["Sheet2"]
cell_range = sheet['A1:C2']
for row in cell_range:
for cell in row:
cell.value = "OOO"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 方式二
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=5, min_col=1, max_col=7, max_row=10):
for cell in row:
cell.value = "oo"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 15.移动
# 将H2:J10 范围的数据,向右移动15个位置,向上移动一个位置
sheet = wb["Sheet3"]
sheet.move_range("H2:J10", rows=1, cols=15) # 选择指定区域,以及移动坐标,且数据会移动走。垂直方向:负值表示向下移动,正值表示向上移动。水平方向:负值表示向左移动,正值表示向右移动。
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 自动翻译公式
sheet = wb.worksheets[3]
sheet["D1"] = "合计"
sheet["D2"] = "=B2*C2"
sheet["D3"] = "=SUM(B3,C3)"
sheet.move_range("B1:D3",cols=10, translate=True) # 自动翻译公式
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 16.打印区域
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Alignment, Border, Side, Font, PatternFill, GradientFill
wb = load_workbook('p2.xlsx')
sheet = wb.worksheets[0]
sheet.print_area = "A1:D200"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
# 17.打印时,每个页面的固定表头
# 打印页面滚动时可以看到表头是固定的
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Alignment, Border, Side, Font, PatternFill, GradientFill
wb = load_workbook('p2.xlsx')
sheet = wb.worksheets[0]
sheet.print_title_cols = "A:D"
sheet.print_title_rows = "1:1"
wb.save("p2.xlsx")
6.压缩文件
基于python内置的 shutil 模块可以实现对压缩文件的操作
import shutil
# 1.压缩文件
# base_naeme : 压缩后的压缩包文件
# format, 压缩的格式,例如:"zip", "tar", "gztar", "bztar", or "xztar".
# root_dir: 要压缩的文件夹路径
shutil.make_archive(base_name=r'datafile',format='zip',root_dir=r'files')
#注释:
root_dir=r'files':要压缩的文件
base_name=r'datafile':压缩后的文件要放置的路径
format='zip':压缩成什么包
# 2.解压缩文件
# filename,要解压的压缩包文件
# extract_dir,解压的路径
# format,压缩文件格式
shutil.unpack_archive(filename=r'datafile.zip', extract_dir=r'xxxxxx/xo', format='zip')
# 注释:
filename=r'datafile.zip':要直接压的压缩包
extract_dir=r'xxxxxx/xo':解压到哪个路径,目录不存在,会自动创建,并且支持多级创建
format='zip':指定要解压的压缩包是什么格式
7.路径相关
7.1 转义
windows路径使用的是\,linux路径使用的是/。
特别的,在windows系统中如果有这样的一个路径 D:\nxxx\txxx\x1,程序会报错。因为在路径中存在特殊符 \n(换行符)和\t(制表符),Python解释器无法自动区分。
所以,在windows中编写路径时,一般有两种方式:
- 加转义符,例如:
"D:\\nxxx\\txxx\\x1" - 路径前加r,例如:
r"D:\\nxxx\\txxx\\x1"
7.2程序当前路径
项目中如果使用了相对路径,那么一定要注意当前所在的位置
例如:在/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/路径下编写 demo.py文件
with open("a1.txt", mode='w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write("你好呀")
用以下两种方式去运行:
-
方式1,文件会创建在
/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/目录下。cd /Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/ python demo.py -
方式2,文件会创建在
/Users/peiqi目录下。cd /Users/peiqi python /Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/demo.py
import os
"""
# 1.获取当前运行的py脚本所在路径
abs = os.path.abspath(__file__)
# __file__代指的就是当前运行的.py文件
# os.path.abspath() 功能是获取绝对路径
print(abs) # 打印当前脚本路径:
# C:\Users\dw\Desktop\python笔记\模块二\代码\day09\项目路径写法.py
path = os.path.dirname(abs) # 获取abs文件的上一级目录
print(path) # C:\Users\dw\Desktop\python笔记\模块二\代码\day09
base_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
print(base_dir) # C:\Users\dw\Desktop\python笔记\模块二\代码\day09
"""
# 拼接实现绝对路径,这样就不用担心路径引起的错误了
base_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
file_path = base_dir + r"\files\info.txt"
print(file_path)
#输出:C:\Users\dw\Desktop\python笔记\模块二\代码\day09\files\info.txt
# 因为window系统是\,所以上面的方式不完美,不能兼容,使用os.path.join()
base_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
file_path = os.path.join(base_dir, 'files', 'info.txt')
print(file_path)
#输出:C:\Users\dw\Desktop\python笔记\模块二\代码\day09\files\info.txt
import os
base_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
file_path = base_dir + "\info.txt"
print(file_path)
# # C:\Users\dw\Desktop\python笔记\模块二\代码\day09\files\info.txt
if os.path.exists(file_path):
file_object = open(file_path, mode='r', encoding='utf-8')
data = file_object.read()
file_object.close()
print(data)
else:
print("文件不存在")
7.3 文件和路径相关
import shutil
import os
# 1. 获取当前脚本绝对路径
"""
abs_path = os.path.abspath(__file__)
print(abs_path)
"""
# 2. 获取指定目录的上级目录
"""
base_path = os.path.dirname( os.path.dirname(路径) )
print(base_path)
"""
# 3. 路径拼接,支持多路径拼接
"""
p1 = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx')
print(p1)
p2 = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx', 'oo', 'a1.png')
print(p2)
"""
# 4. 判断路径是否存在
"""
exists = os.path.exists(p1)
print(exists)
"""
# 5. 创建文件夹,支持递归创建
"""
os.makedirs(路径)
"""
"""
path = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx', 'oo', 'uuuu')
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
"""
# 6. 是否是文件夹
"""
file_path = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx', 'oo', 'uuuu.png')
is_dir = os.path.isdir(file_path)
print(is_dir) # False
folder_path = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx', 'oo', 'uuuu')
is_dir = os.path.isdir(folder_path)
print(is_dir) # True
"""
# 7. 删除文件或文件夹
"""
os.remove("文件路径")
"""
"""
path = os.path.join(base_path, 'xx')
shutil.rmtree(path)
"""
# 8. 拷贝文件夹
"""
shutil.copytree("/Users/peiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files")
/Users/peiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/:源文件夹
/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files:目标文件夹
"""
# 9.拷贝文件
# 目标文件加/表示放入到此目录
shutil.copy("/Users/peiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/WX20201123-112406@2x.png","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/")
# 不加/表示将图片复制且重命名为x.png
shutil.copy("/Users/peiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/WX20201123-112406@2x.png","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/x.png")
# 先写源文件,再写目标文件
# 10.文件或文件夹重命名
# 重命名
shutil.move("/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/x.png","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/xxxx.png")
# 移动
shutil.move("/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/images")
# "/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files":源路径
# "/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/images":目标路径
总结
-
文件相对路径,在使用相对路径时可能会执行程序的目录不同,导致路径出问题。所以,如若使用相对路径请务必清楚当前运行程序所在目录。
-
文件绝对路径(推荐),不要将文件路径写死,而是基于 os 模块中的相关功能自动化获取绝对路径,以方便项目移动到其他文件或电脑上。
import os base_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__)) file_path = os.path.join(base_dir, 'files', 'info.txt') -
路径转义
- 手动写路径,需要在路径中添加 “r” 或 “\” 来进行处理
- 基于os.path.join拼接,内部自动处理,不需要手动处理
-
内置函数,内置模块,第三方模块的区别?
-
下载第三方模块
pip install 模块名称 -
基于文件的读写,打开模式,上下文管理
-
其他格式:CSV,ini,xml,excel格式的处理(无需记忆,做好笔记即可)
h, ‘xx’, ‘oo’, ‘a1.png’)
print(p2)
“”"
4. 判断路径是否存在
“”"
exists = os.path.exists(p1)
print(exists)
“”"
5. 创建文件夹,支持递归创建
“”"
os.makedirs(路径)
“”"
“”"
path = os.path.join(base_path, ‘xx’, ‘oo’, ‘uuuu’)
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
“”"
6. 是否是文件夹
“”"
file_path = os.path.join(base_path, ‘xx’, ‘oo’, ‘uuuu.png’)
is_dir = os.path.isdir(file_path)
print(is_dir) # False
folder_path = os.path.join(base_path, ‘xx’, ‘oo’, ‘uuuu’)
is_dir = os.path.isdir(folder_path)
print(is_dir) # True
“”"
7. 删除文件或文件夹
“”"
os.remove(“文件路径”)
“”"
“”"
path = os.path.join(base_path, ‘xx’)
shutil.rmtree(path)
“”"
8. 拷贝文件夹
“”"
shutil.copytree("/Users/peiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files")
/Users/peiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/:源文件夹
/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files:目标文件夹
“”"
9.拷贝文件
目标文件加/表示放入到此目录
shutil.copy("/Users/peiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/WX20201123-112406@2x.png","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/")
不加/表示将图片复制且重命名为x.png
shutil.copy("/Users/peiqi/Desktop/图/csdn/WX20201123-112406@2x.png","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/x.png")
先写源文件,再写目标文件
10.文件或文件夹重命名
重命名
shutil.move("/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/x.png","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/xxxx.png")
移动
shutil.move("/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files","/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/images")
“/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/files”:源路径
“/Users/peiqi/PycharmProjects/CodeRepository/images”:目标路径
## 总结
1. 文件相对路径,在使用相对路径时可能会执行程序的目录不同,导致路径出问题。所以,如若使用相对路径请务必清楚当前运行程序所在目录。
2. 文件绝对路径(推荐),不要将文件路径写死,而是基于 os 模块中的相关功能自动化获取绝对路径,以方便项目移动到其他文件或电脑上。
```python
import os
base_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__))
file_path = os.path.join(base_dir, 'files', 'info.txt')
-
路径转义
- 手动写路径,需要在路径中添加 “r” 或 “\” 来进行处理
- 基于os.path.join拼接,内部自动处理,不需要手动处理
-
内置函数,内置模块,第三方模块的区别?
-
下载第三方模块
pip install 模块名称 -
基于文件的读写,打开模式,上下文管理
-
其他格式:CSV,ini,xml,excel格式的处理(无需记忆,做好笔记即可)