python编程快速上手(持续更新中…)
框架概念
框架和web服务器关系
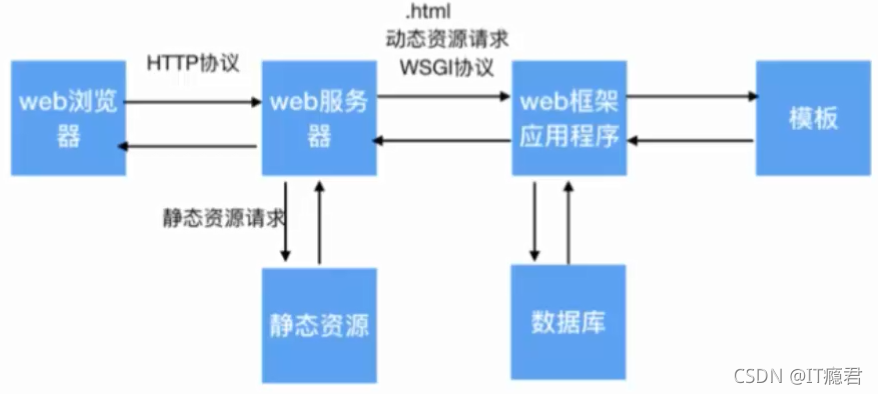
?静态资源:不是经常变化的资源、往往是固定不变的资源
?动态资源:经常变化的资源
?模板文件:提供了一个显示的模板,显示的内容不同,但是结构是一样的
?服务器的作用:
o1)接受客户端请求
o2)响应客户端请求
o3)调用应用框架获取
miniWeb框架构建基本构建
?思路:
o判断请求的资源路径是 是否是 .py 结尾
o如果 .py 结尾,——> 显示动态内容
o如果.html 结尾,——> 显示静态内容
?核心代码:
?核心代码:
# index.py
if file_path.endswith(".py"):
# 2. 让.py 显示的内容和.html显示的内容区别开开
response_body = "This is index Show! %s" % time.ctime()
# 调用 utils 模块的 create_http_response 函数,拼接响应协议
response_data = utils.create_http_response("200 OK", response_body.encode())
# index.html
else:
....
miniWeb框架构建-动态显示
?思路:
o首先必须是 .py 结尾的文件
o判断请求的资源路径,并且根据资源路径不同设置 不同的 response_body
o当请求的资源路径不存在,返回 404 错误
?核心代码:
# 3. 判断请求的资源路径,根据不同的路径显示不同的额内容
if file_path == "/index.py":
response_body = "This is index show!"
# 调用 utils 模块的 create_http_response 函数,拼接响应协议
response_data = utils.create_http_response("200 OK", response_body.encode())
elif file_path == "/center.py":
response_body = "This is center show!"
# 调用 utils 模块的 create_http_response 函数,拼接响应协议
response_data = utils.create_http_response("200 OK", response_body.encode())
elif file_path == "/gettime.py":
response_body = "helloworld! %s" % time.ctime()
# 调用 utils 模块的 create_http_response 函数,拼接响应协议
response_data = utils.create_http_response("200 OK", response_body.encode())
else:
response_body = "Sorry Page Not Found ! 404"
# 调用 utils 模块的 create_http_response 函数,拼接响应协议
response_data = utils.create_http_response("404 Not Found", response_body.encode())
路由列表(django)
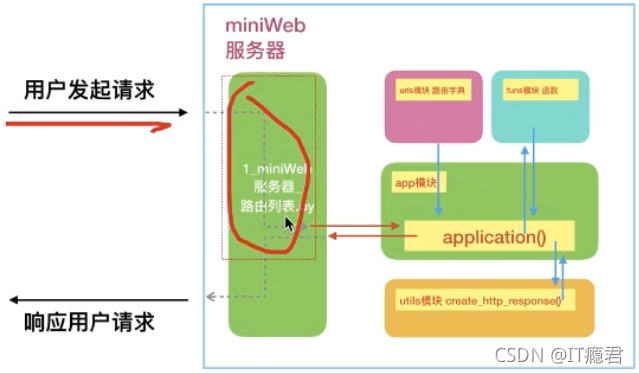
?实现步骤:
o创建 urls 模块,模块的作用提供一个路由字典
字典保存路径和函数的对应关系
o导入函数的模块 from application import funs
oroute_dict
定义路由字典
route_dict = {
'/index.py': funs.index,
'/center.py': funs.center,
'/gettime.py': funs.gettime
}
?创建 funs 模块, 提供了具体的功能对应的函数
定义路径对应的函数
import time
def index():
""" 处理 index.py 请求 """
return "This is index show!--funs"
def center():
""" 处理 index.py 请求 """
return "This is center show!"
def gettime():
""" 处理 index.py 请求 """
return "This is gettime show! %s " % time.ctime()
?修改app文件中 动态显示的判断部分
1.判断 路径 是否在 路由字典中 key in 字典
2.如果在字典中,根据key(请求路径) 取出 对应的函数的引用
3.执行函数,获取函数的返回值,然后赋值 给 response_body
if file_path in urls.route_dict:
# 根据key值,去urls.route_dict中,获取值(函数引用)
func = urls.route_dict[file_path]
# 根据路由字典,获取函数的引用,执行该函数,返回执行的结果,
# 保存到 response_body 变量中
response_body = func()
# 调用 utils 模块的 create_http_response 函数,拼接响应协议
response_data = utils.create_http_response("200 OK", response_body.encode())
else:
装饰器路由(flask)
使用装饰器工厂,实现装饰器路由
?修改urls模块
route_dict = { }
?修改funs模块
o导入 from application import urls
o创建装饰器工厂,并且把路径添加到字典中(创建路由字典)
def route(path):
# path 向装饰器内部传递的参数 path /index.py
# 装饰器
# 字典
# {"index.py":index函数引用}
def function_out(func): #func index函数的引用
# 2-----
urls.route_dict[path] = func
# print("装饰[%s]" % path)
# 装饰器内层函数
def function_in():
# 调用原函数并且执行
return func()
return function_in
return function_out
o装饰函数
@route("/center.py")
def center():
""" 处理 index.py 请求 """
return "This is center show!"
o在 app模块中导入 funs 模块
此时funs 模块中的函数被加载,加载的同时被装饰(就会向字典中添加路由信息)
模板替换
?思路
o拷贝资源(templates)到工程下
o修改 funs模块中的 index 和 center函数
o在函数中读取对应的文件
- List item
o使用正则替换网页中的内容 {%content%} —> helloworld!
o返回替换后的内容
with open("templates/index.html") as file:? content = file.read()
return content
数据库操作
数据加载
?创建并导入数据到数据库
o创建数据库 create database stock_db charset=utf8
o使用数据库 use stock_db
o导入数据库(先客户端登录)
o准备脚本文件
o导入脚本 source stock_db.sql
?修改index函数
o连接数据库,获取数据
?导入模块
?建立连接
?创建游标
?使用游标执行sql
?获取查询的结果
data_from_mysql = str(cur.fetchall())
?关闭资源
先关闭游标,在关闭连接
?替换为查询的数据
content = re.sub("{%content%}",data_from_mysql,content)
渲染页面
?思路:
o把查询的数据进行遍历,并且拼接html格式的文本
o表示一行 一列
o替换为拼接后的字符串
content = re.sub("{%content%}",data_from_myql,content)
o注意:
%s %s %s —> line # line 是一个元组
多表查询
?思路:
o关联查询
select i.code,i.short,i.chg,i.turnover,i.price,i.highs,f.note_info from info i, focus f where i.id = f.id
o把查询的数据进行遍历,并且拼接html格式的文本
o表示一行 一列
o替换为拼接后的字符串
content = re.sub("{%content%}",data_from_myql,content)
多进程版
?设置进程守护
p1.daemon = True
?启动进程
p1.start()
?关闭new_client_socket ,否则无法释放套接字
new_client_socket.close()