seaborn随笔
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# 自定义函数的方式观察matplotlib的作图风格
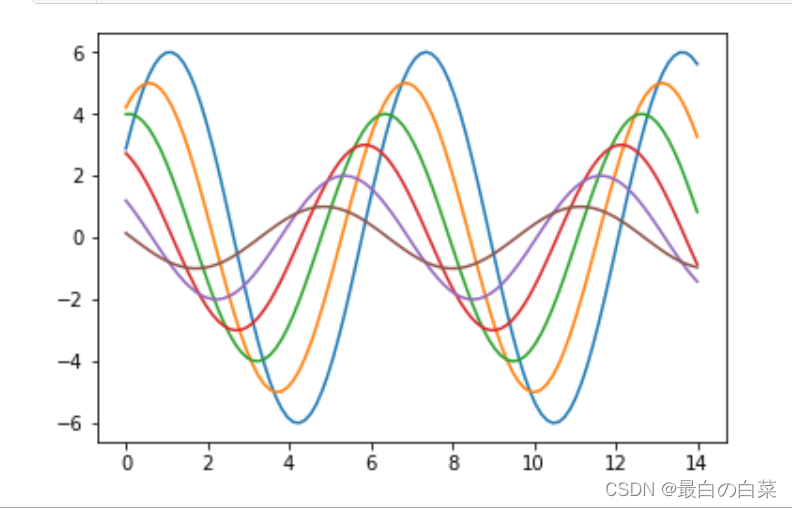
def sinplot(flip=1):
# 在0-14的区间上取100个点
x = np.linspace(0,14,100)
for i in range(1,7):
plt.plot(x,np.sin(x+i*.5)*(7-i)*flip)
sinplot()
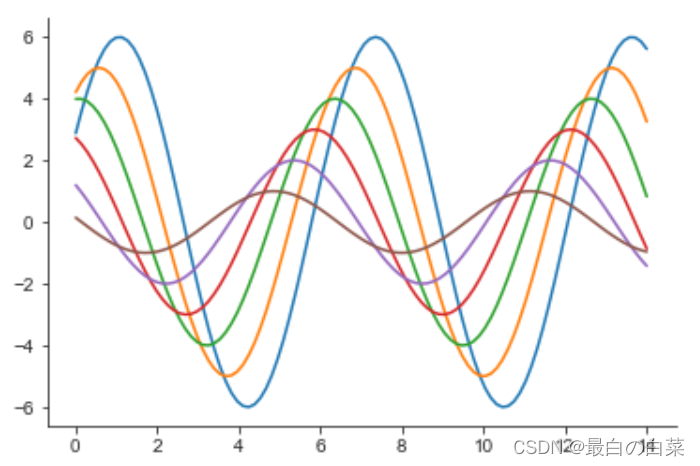
# 使用seaborn的默认设置
sns.set()
sinplot()
'''
5种主题风格,darkgrid,whitegird,dark,white,ticks
'''

# sns.set_style("whitegrid")
# sns.set_style("dark")
# sns.set_style("white")
sns.set_style("ticks")
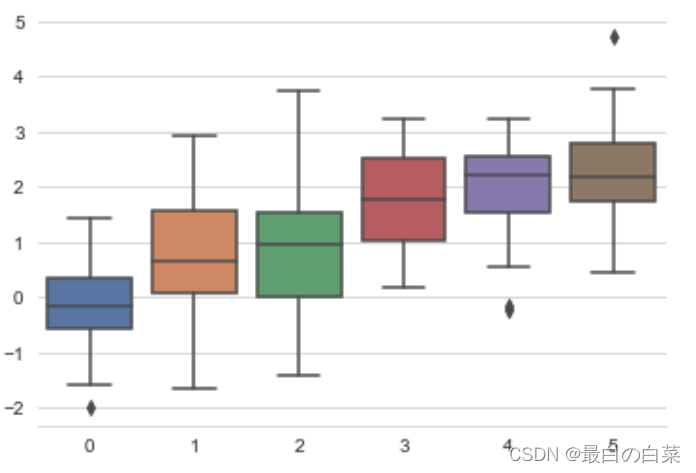
data = np.random.normal(size=(20,6)) + np.arange(6) / 2
sns.boxplot(data=data)

sinplot()
# 去掉最上面和右面的刻度线
sns.despine()
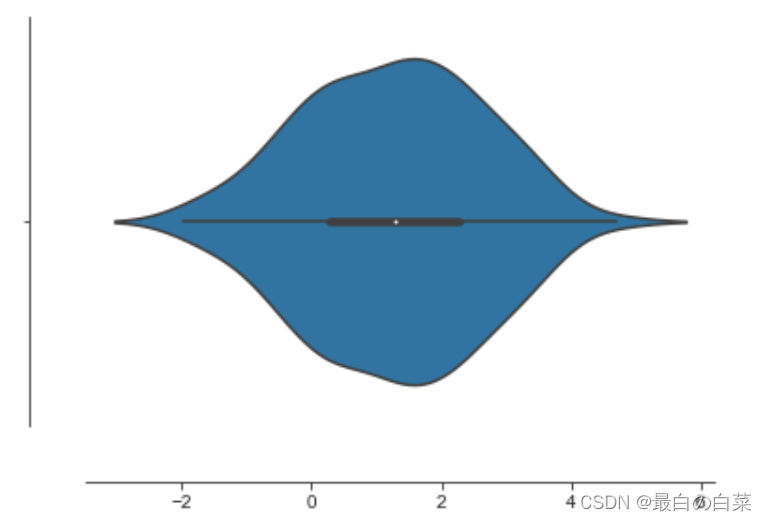
sns.violinplot(data)
# offset=10设置图形与轴线的距离
sns.despine(offset=30)
sns.set_style("whitegrid")
sns.boxplot(data=data,palette="deep")
# 指定哪个轴的竖线被隐藏
sns.despine(left=True)
# 用with打开style风格
with sns.axes_style("darkgrid"):
plt.subplot(211)
sinplot()
plt.subplot(212)
sinplot(-1)

# 用seaborn的默认值
sns.set()
# 设置画图域的大小和线条大小
sns.set_context("paper")
plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
sinplot()

sns.set_context("talk")
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sinplot()

sns.set_context("poster")
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sinplot()
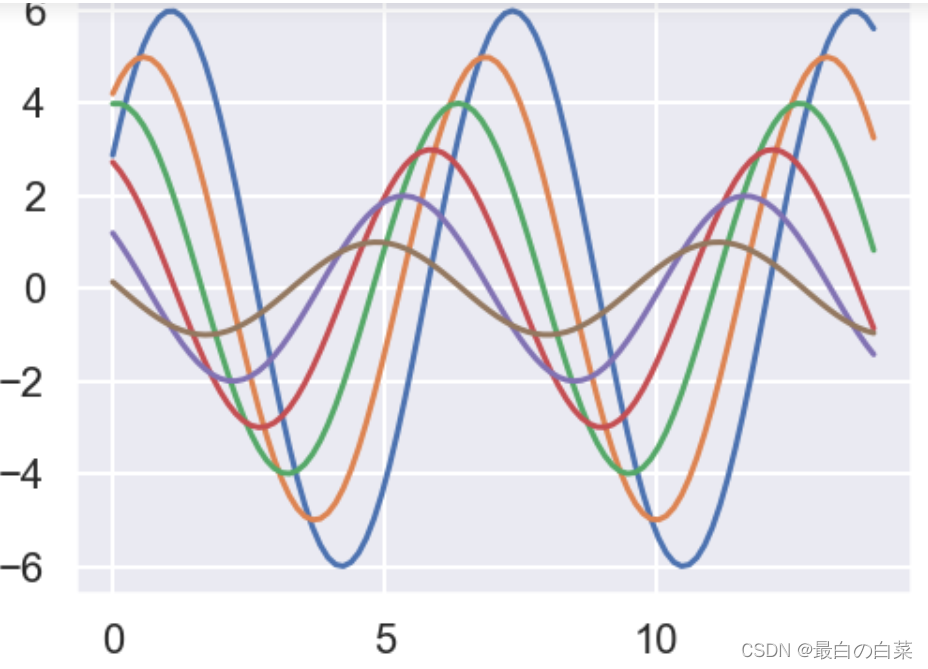
# font_scale字体的风格,lines.linewidth指定线条的粗细
sns.set_context("notebook", font_scale=2.5, rc={"lines.linewidth": 3.5})
sinplot()

调色板:
颜色很重要
color_palette()能传入任何Matplotlib所支持的颜色
color_palette()不写参数则默认颜色
set_palette()设置所有图的颜色
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
sns.set(rc={"figure.figsize": (6, 6)})
# 分类色板:默认的颜色循环主题
current_palette = sns.color_palette()
sns.palplot(current_palette)

圆形画板
当你有六个以上的分类要区分时,最简单的方法就是在一个圆形的颜色空间中画出均匀间隔的颜色(这样的色调会保持亮度和饱和度不变)。这是大多数的当他们需要使用比当前默认颜色循环中设置的颜色更多时的默认方案。
最常用的方法是使用hls的颜色空间,这是RGB值的一个简单转换。
# 需要几个颜色,后面的数字就可以写成几
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("hls",8))

# 想要将上述的八种颜色放入数据当中
data = np.random.normal(size=(20, 8)) + np.arange(8) / 2
sns.boxplot(data=data,palette=sns.color_palette("hls", 8))

hls_palette()函数来控制颜色的亮度和饱和
l-亮度 lightness
s-饱和 saturation
# 8,l=.5,s=.9 八种颜色,调节亮度和饱和度
sns.palplot(sns.hls_palette(8,l=.5,s=.9))

# Paired调出的颜色是一对一对的,两个颜色是相近,浅深之分
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("Paired",10))

使用xkcd颜色来命名颜色
xkcd包含了一套众包努力的针对随机RGB色的命名。产生了954个可以随时通过xdcd_rgb字典中调用的命名颜色。
# 用数组指定一些点,然后lw=3指的是线宽,指定固定颜色可以用xkcd
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], sns.xkcd_rgb["pale red"], lw=3)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 2], sns.xkcd_rgb["medium green"], lw=3)
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 3], sns.xkcd_rgb["denim blue"], lw=3)

colors = ["windows blue", "amber", "greyish", "faded green", "dusty purple"]
sns.palplot(sns.xkcd_palette(colors))

连续色板
色彩随数据变换,比如数据越来越重要则颜色越来越深
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("Blues"))

# 如果想要翻转渐变,可以在面板名称中添加一个_r后缀
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("BuGn_r"))

cubehelix_palette()调色板
色调线性变换,即当前的亮度和饱和度线性变换
sns.palplot(sns.color_palette("cubehelix", 8))

# 指定颜色的分布情况
# start指定颜色区间,观察色彩变换
sns.palplot(sns.cubehelix_palette(8, start=.5, rot=-.75))

sns.palplot(sns.cubehelix_palette(8, start=.75, rot=-.150))

light_palette() 和dark_palette()调用定制连续调色板
# 其实也就是指定颜色深浅变换 light_palette从浅到深
sns.palplot(sns.light_palette("green"))
# 反转
sns.palplot(sns.light_palette("navy", reverse=True))

# dark_palette从深到浅
sns.palplot(sns.dark_palette("purple"))

x, y = np.random.multivariate_normal([0, 0], [[1, -.5], [-.5, 1]], size=300).T
pal = sns.dark_palette("green", as_cmap=True)
sns.kdeplot(x, y, cmap=pal);
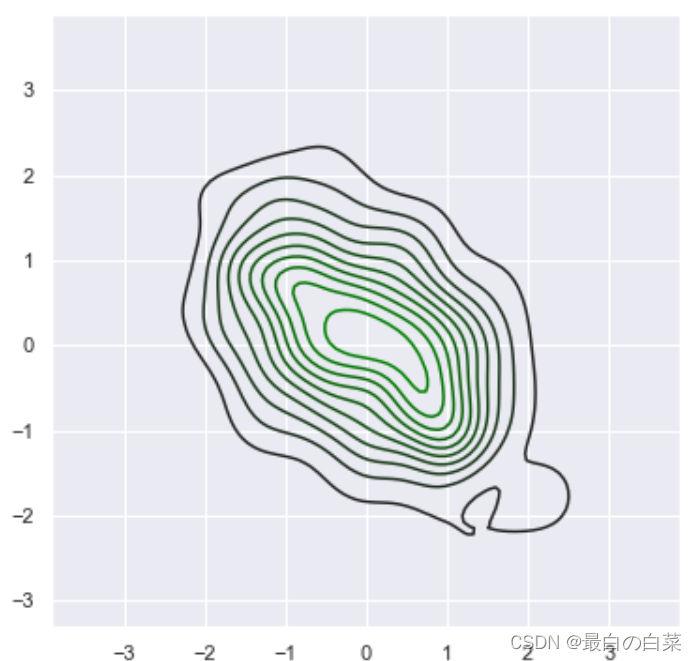
# 如果对颜色空间熟悉,可以指定空间husl,然后指定它的值(210, 90, 60),大部分都是用默认值就行
sns.palplot(sns.light_palette((210, 90, 60), input="husl"))

%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from scipy import stats, integrate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(color_codes=True)
np.random.seed(sum(map(ord, "distributions")))
# 做直方图
x = np.random.normal(size=100)
# kde这个属性就是看是否做密度估计
sns.distplot(x,kde=False)
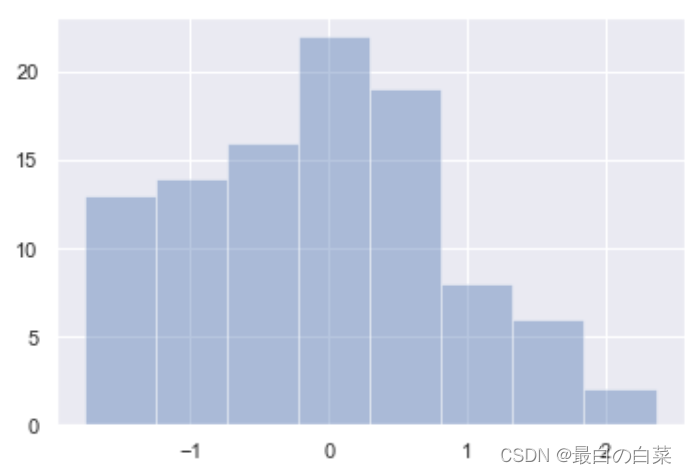
# 指定几等份,将数据切分成20个小块
sns.distplot(x,bins=20,kde=False)

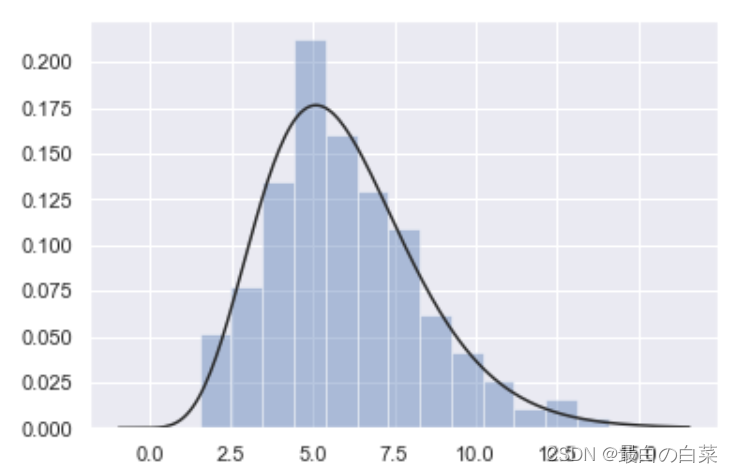
# 数据分布情况
x = np.random.gamma(6, size=200)
# fit指的是当前的统计指标
sns.distplot(x, kde=False, fit=stats.gamma)
# 根据均值和协方差生成数据
mean, cov = [0, 1], [(1, .5), (.5, 1)]
# 生成200个数据
data = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 200)
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=["x", "y"])
df
# 观测两个变量之间的分布关系最好用散点图
sns.jointplot(x="x",y="y",data=df)

# 想观察哪个区域分布的数据多,如果点比较多,观察就会很费劲,全是蓝色点
# hex图可以帮助解决上述问题
x, y = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 1000).T
with sns.axes_style("white"):
sns.jointplot(x=x, y=y, kind="hex", color="k")

# 如果有四个特征,想观察两两特征之间的关系
# iris是一种花的数据集,但是直接写会报错,需要下载数据集到seaborn-data文件夹里面
# github上下载地址:https://github.com/mwaskom/seaborn-data,将所有文件拖进电脑中seaborn-data的空文件夹里即可。
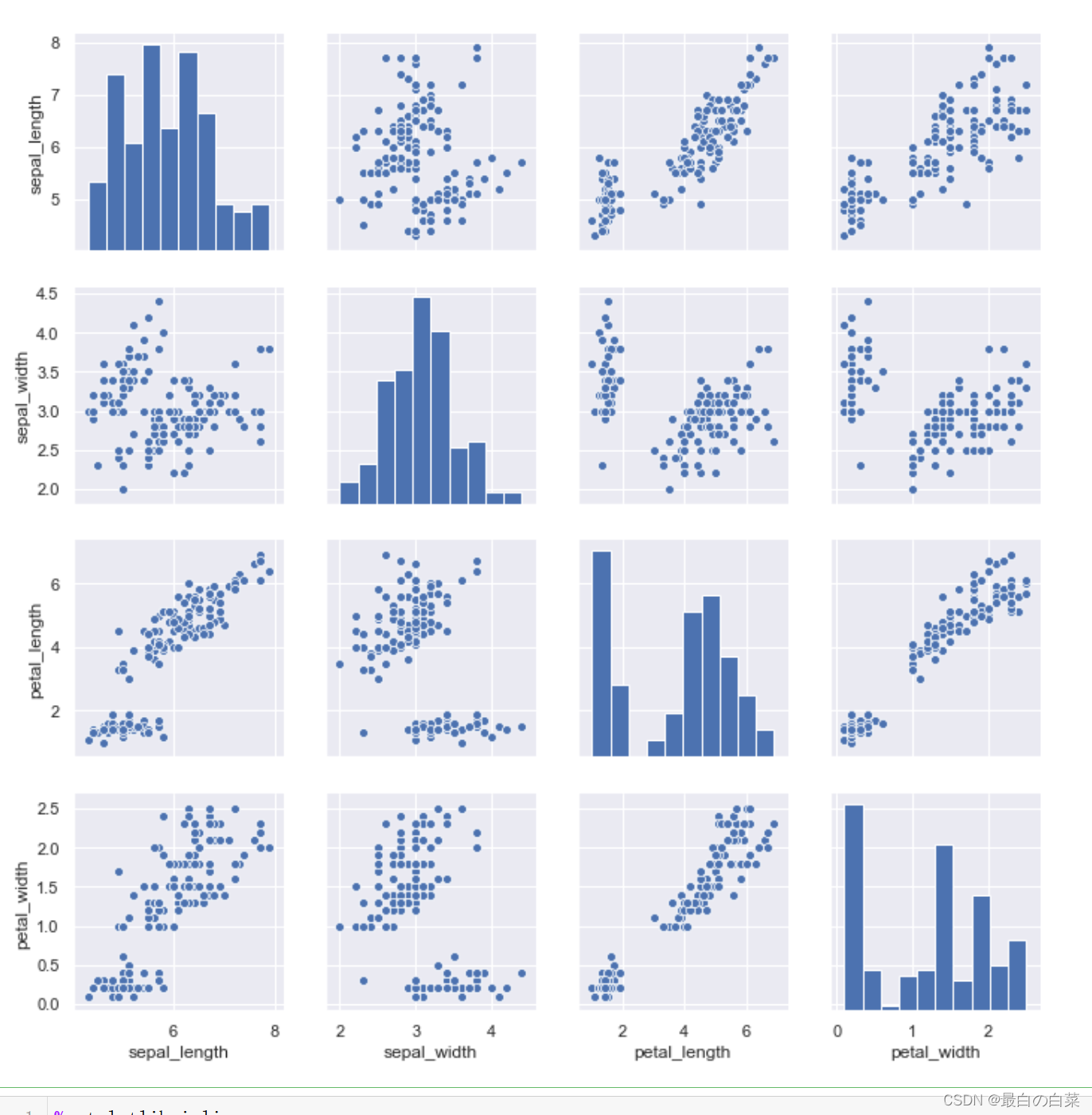
iris =sns.load_dataset("iris")
sns.pairplot(iris)
# 分析:对角线上的图就是直方图,因为自变量和因变量都是自己,其它位置都是散点图
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(color_codes=True)
np.random.seed(sum(map(ord,"regression")))
tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
tips.head()
# regplot()和lmplot()都可以绘制回归关系,推荐regplot()
sns.regplot(x="total_bill",y="tip",data=tips)

sns.lmplot(x="total_bill", y="tip", data=tips);

sns.regplot(data=tips,x="size",y="tip")

# 上面的点都在一条直线上,不符合数据的随机性,x_jitter指定浮动范围,可以让回归模型更准确
sns.regplot(x="size", y="tip", data=tips, x_jitter=.05)

sns.set(style="whitegrid", color_codes=True)
np.random.seed(sum(map(ord, "categorical")))
titanic = sns.load_dataset("titanic")
tips = sns.load_dataset("tips")
iris = sns.load_dataset("iris")
# 重叠是很常见的现象,但是重叠影响我观察数据的量了
sns.stripplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips);

sns.stripplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, jitter=True)

# jitter使数据不太均匀,swarmplot让数据更加均匀分布
sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips)

# hue="sex"以这个属性为标准
sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="sex",data=tips)
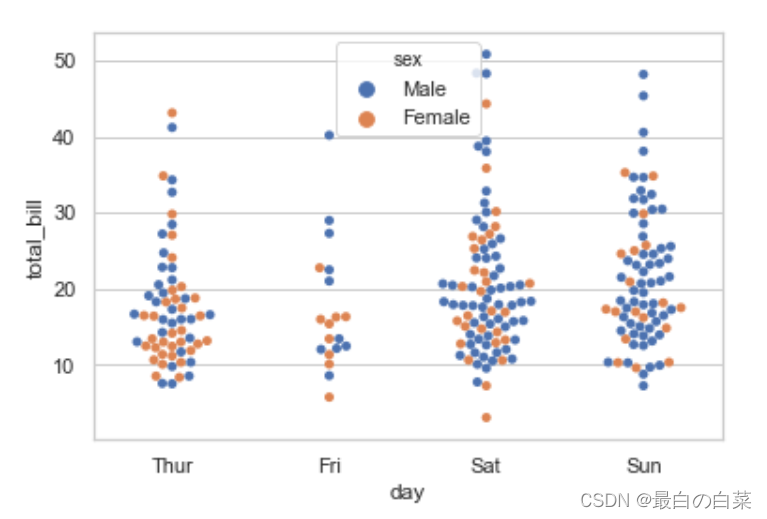
# 坐标颠倒
sns.swarmplot(x="total_bill", y="day", hue="time", data=tips);

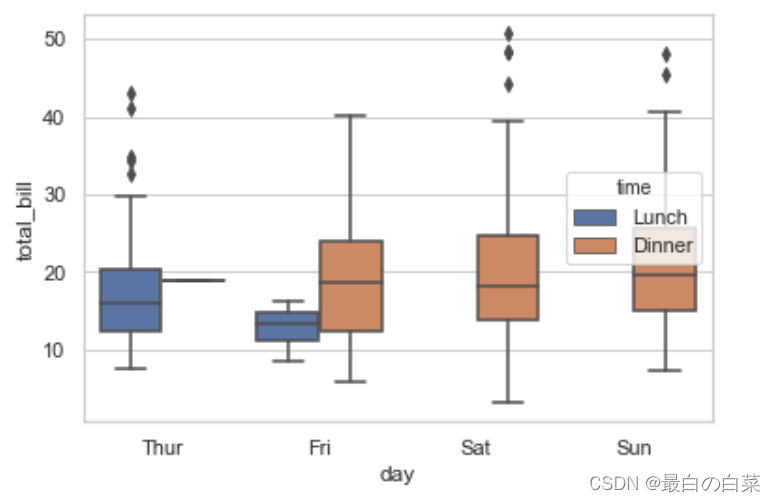
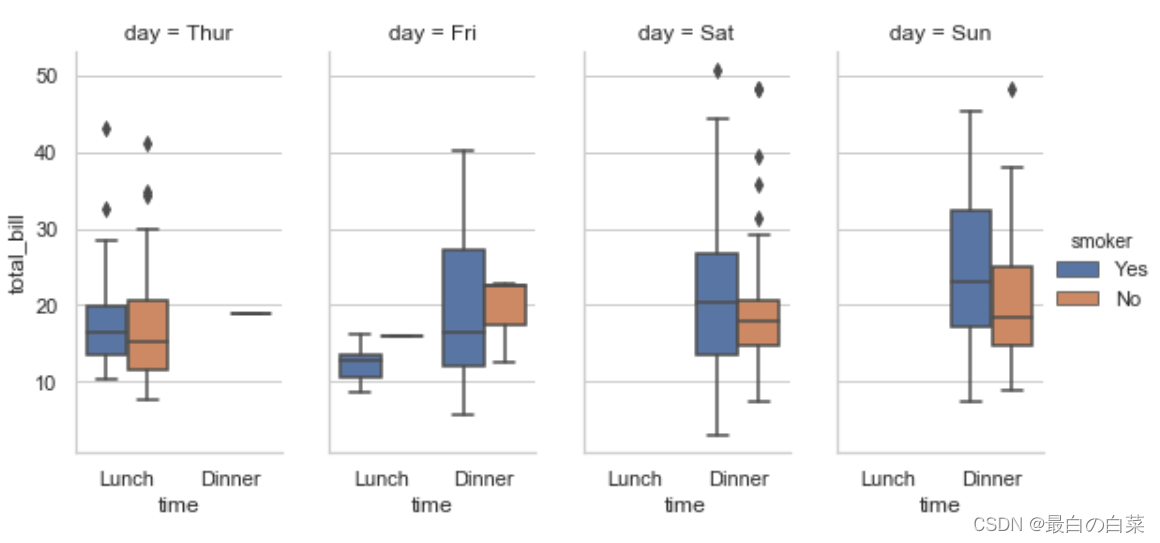
盒图
IQR即统计学概念四分位距,第一/四分位与第三/四分位之间的距离
Q3第三/四分位,Q1第一/四分位
N = 1.5IQR 如果一个值>Q3+N或 < Q1-N,则为离群点
sns.boxplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="time", data=tips);
# 这个菱形就是离群点
# violinplot小提琴图
sns.violinplot(x="total_bill", y="day", hue="time", data=tips);
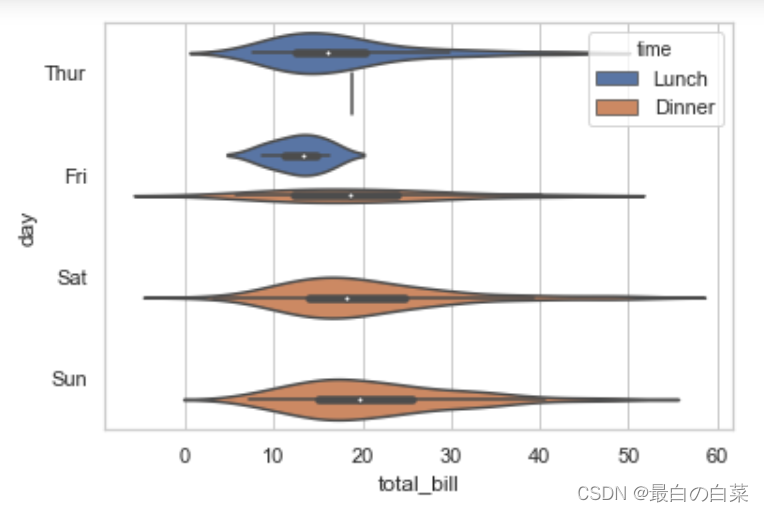
# 上面那个把属性分开了,不方便观察,split=True 指定左右各表示一种属性,更加方便
sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="sex", data=tips, split=True);

sns.violinplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, inner=None)
# alpha值指的是透明度
sns.swarmplot(x="day", y="total_bill", data=tips, color="w", alpha=.5)

# 显示值的集中趋势可以用条形图 hue="class"指的是看class指标
sns.barplot(x="sex", y="survived", hue="class", data=titanic);

# 点图可以更好的描述变化差异
sns.pointplot(x="sex", y="survived", hue="class", data=titanic);

# palette设置颜色;markers指的是设置点的样式,三角圆形;linestyles是线形,虚线实线
sns.pointplot(x="class", y="survived", hue="sex", data=titanic,
palette={"male": "g", "female": "m"},
markers=["^", "o"], linestyles=["-", "--"]);

# 想横着画盒图,orient
sns.boxplot(data=iris,orient="h");

# 多层面板分类图
# 不指定,默认是折线图
sns.factorplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="smoker", data=tips)

# 指定为条形图
sns.factorplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="smoker", data=tips, kind="bar")

# 树状图
sns.factorplot(x="day", y="total_bill", hue="smoker",
col="time", data=tips, kind="swarm")
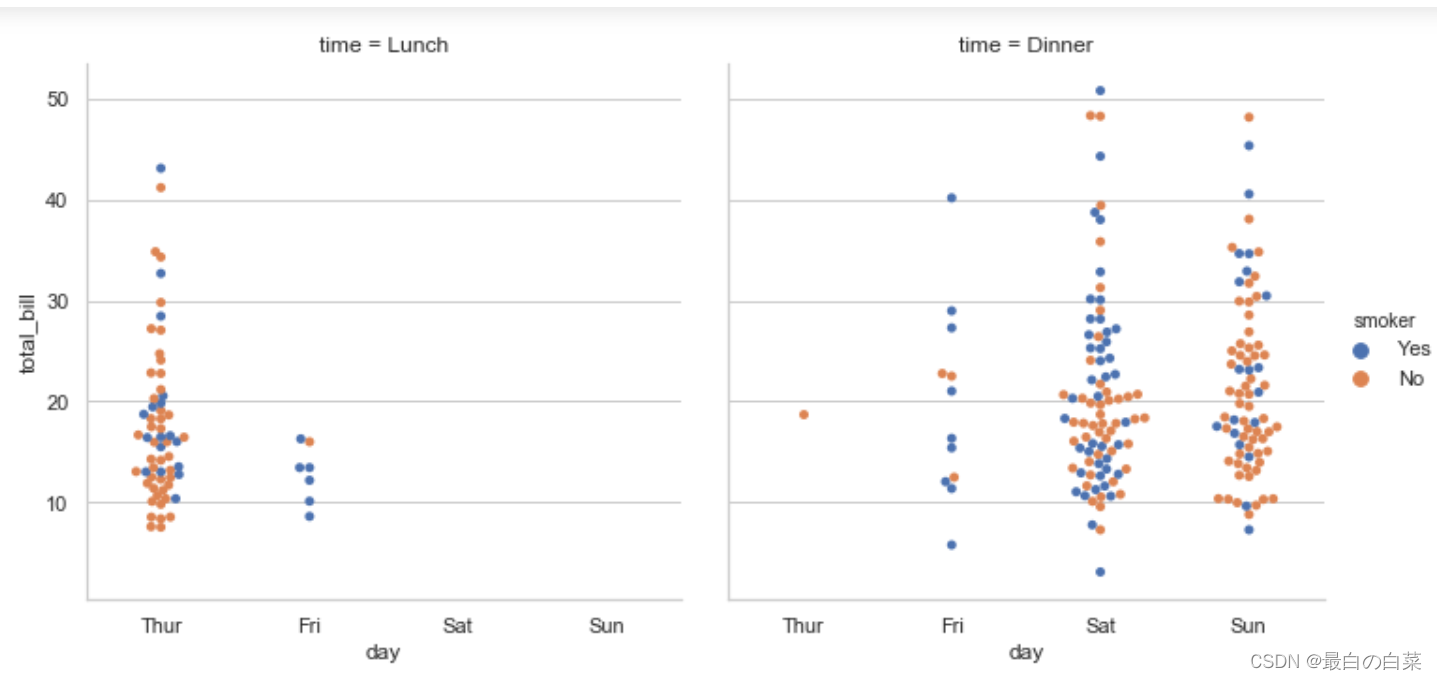
# 盒图 aspect是长宽比;size是大小
sns.factorplot(x="time", y="total_bill", hue="smoker",
col="day", data=tips, kind="box", size=4, aspect=.5)
seaborn.factorplot(x=None, y=None, hue=None, data=None, row=None, col=None, col_wrap=None, estimator=, ci=95, n_boot=1000, units=None, order=None, hue_order=None, row_order=None, col_order=None, kind=‘point’, size=4, aspect=1, orient=None, color=None, palette=None, legend=True, legend_out=True, sharex=True, sharey=True, margin_titles=False, facet_kws=None, **kwargs)
Parameters:
x,y,hue 数据集变量 变量名
date 数据集 数据集名
row,col 更多分类变量进行平铺显示 变量名
col_wrap 每行的最高平铺数 整数
estimator 在每个分类中进行矢量到标量的映射 矢量
ci 置信区间 浮点数或None
n_boot 计算置信区间时使用的引导迭代次数 整数
units 采样单元的标识符,用于执行多级引导和重复测量设计 数据变量或向量数据
order, hue_order 对应排序列表 字符串列表
row_order, col_order 对应排序列表 字符串列表
kind : 可选:point 默认, bar 柱形图, count 频次, box 箱体, violin 提琴, strip 散点,swarm 分散点 size 每个面的高度(英寸) 标量 aspect 纵横比 标量 orient 方向 "v"/"h" color 颜色 matplotlib颜色 palette 调色板 seaborn颜色色板或字典 legend hue的信息面板 True/False legend_out 是否扩展图形,并将信息框绘制在中心右边 True/False share{x,y} 共享轴线 True/False
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
from scipy import stats
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sns.set(style="ticks")
np.random.seed(sum(map(ord, "axis_grids")))
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips,col="time")
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="time")
# 将指定的图形放入map中 条形图
g.map(plt.hist, "tip");

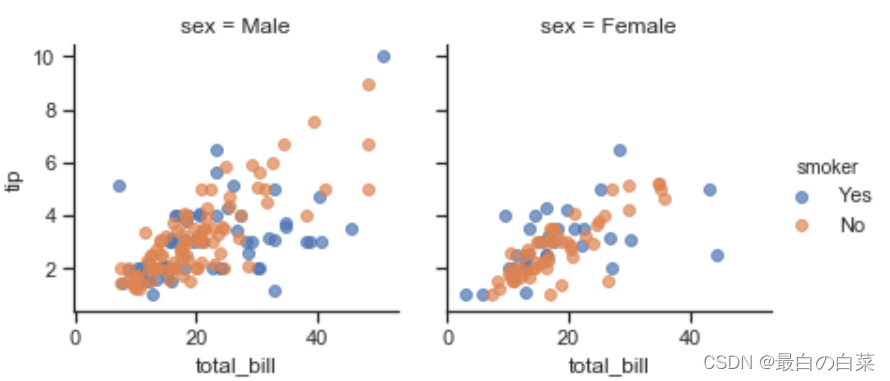
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="sex", hue="smoker")
# 散点图;alpha透明度,越小越透明
g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", alpha=.7)
# 指定smoker右边的说明项,说明yes和no分别代表什么颜色
g.add_legend();
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, row="smoker", col="time", margin_titles=True)
# color 的数值越大越透明;fit_reg指的是回归线
g.map(sns.regplot, "size", "total_bill", color=".1", fit_reg=False, x_jitter=.1);

# 设置长宽比和大小
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col="day", size=4, aspect=.5)
g.map(sns.barplot, "sex", "total_bill");

from pandas import Categorical
ordered_days = tips.day.value_counts().index
print (ordered_days)
ordered_days = Categorical(['Thur', 'Fri', 'Sat', 'Sun'])
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, row="day", row_order=ordered_days,
size=1.7, aspect=4,)
g.map(sns.boxplot, "total_bill");

from pandas import Categorical
ordered_days = tips.day.value_counts().index
print (ordered_days)
# 改变顺序
ordered_days = Categorical(['Thur', 'Fri', 'Sat', 'Sun'])
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, row="day", row_order=ordered_days,
size=1.7, aspect=4,)
g.map(sns.boxplot, "total_bill");

pal = dict(Lunch="seagreen", Dinner="gray")
# palette调色板
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, hue="time", palette=pal, size=5)
# s表示圆圈的大小
g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", s=50, alpha=.7, linewidth=.5, edgecolor="white")
g.add_legend();

# marker图形的形状
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, hue="sex", palette="Set1", size=5, hue_kws={"marker": ["^", "v"]})
g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", s=100, linewidth=.5, edgecolor="white")
g.add_legend();

with sns.axes_style("white"):
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, row="sex", col="smoker", margin_titles=True, size=2.5)
g.map(plt.scatter, "total_bill", "tip", color="#334488", edgecolor="white", lw=.5);
g.set_axis_labels("Total bill (US Dollars)", "Tip");
# xticks是设置X轴的刻度取值
g.set(xticks=[10, 30, 50], yticks=[2, 6, 10]);
# wspace设置子图的宽间隔
g.fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=.52, hspace=.02);
# 调节整体偏移
#g.fig.subplots_adjust(left = 0.125,right = 0.5,bottom = 0.1,top = 0.9, wspace=.02, hspace=.02)

iris = sns.load_dataset("iris")
# 两两变量之间
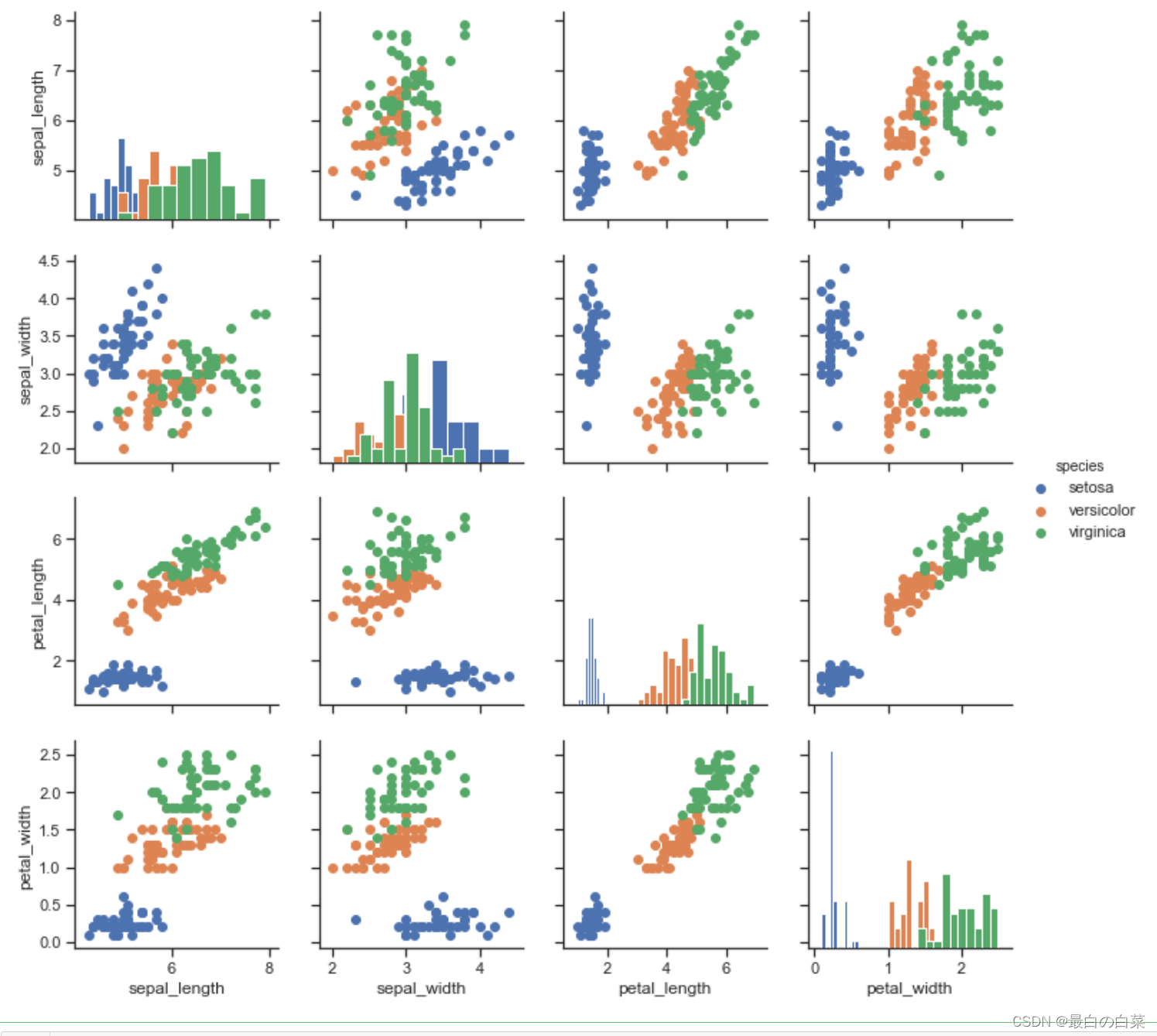
g = sns.PairGrid(iris)
g.map(plt.scatter);

g = sns.PairGrid(iris)
# 指定对角线和非对角线应该画什么图形
g.map_diag(plt.hist)
g.map_offdiag(plt.scatter);
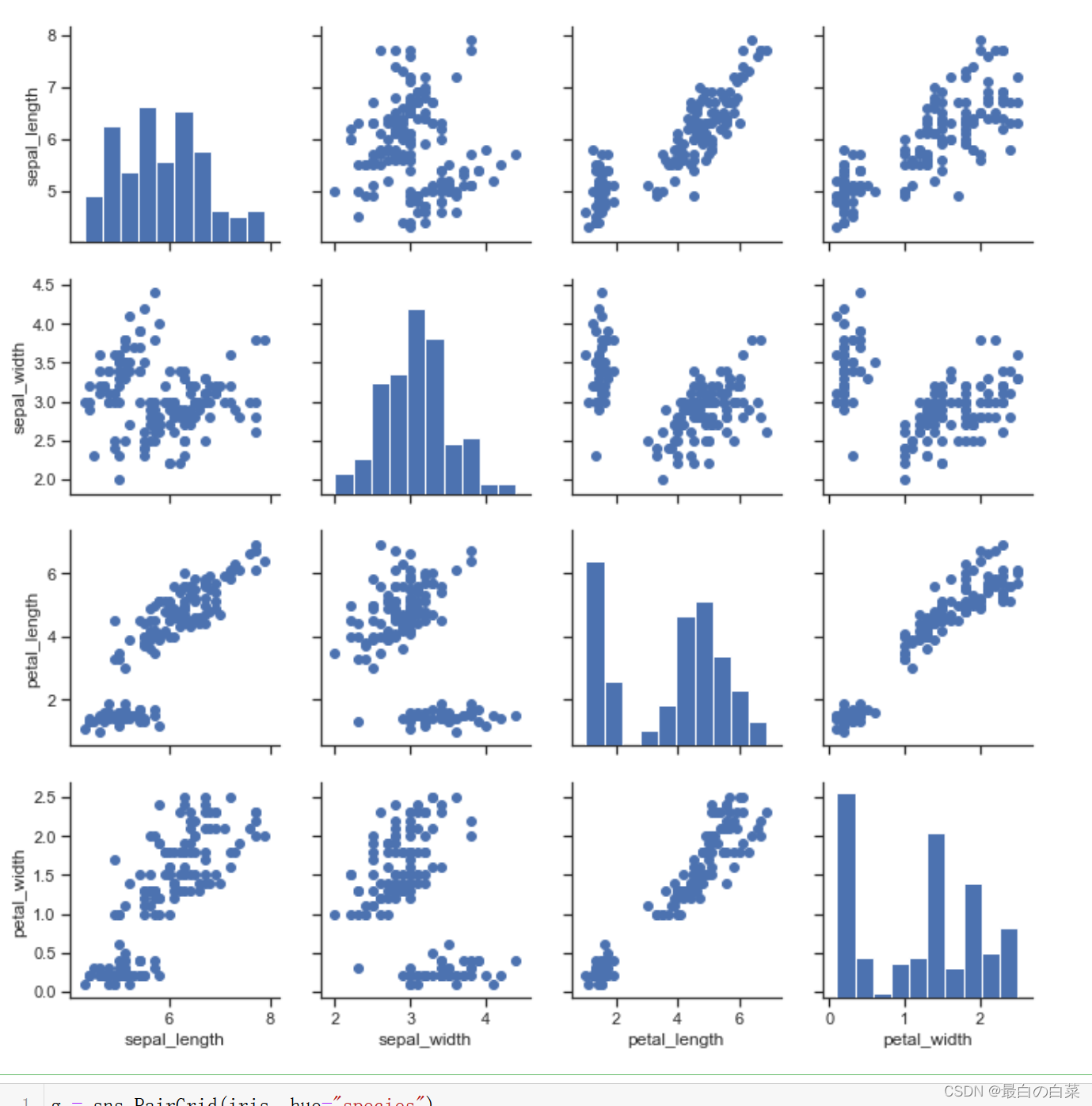
g = sns.PairGrid(iris, hue="species")
g.map_diag(plt.hist)
g.map_offdiag(plt.scatter)
g.add_legend();
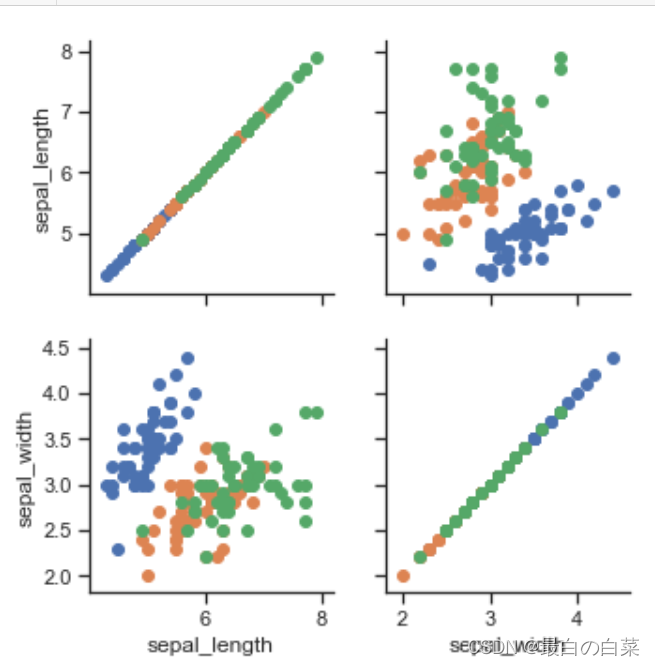
# 不想画四个特征,可以用vars指定特征
g = sns.PairGrid(iris, vars=["sepal_length", "sepal_width"], hue="species")
g.map(plt.scatter);
g = sns.PairGrid(tips, hue="size", palette="GnBu_d")
g.map(plt.scatter, s=50, edgecolor="white")
g.add_legend();

# 热度图绘制,把变化的趋势用颜色表示出来
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np;
np.random.seed(0)
import seaborn as sns;
sns.set()
uniform_data = np.random.rand(3, 3)
print (uniform_data)
heatmap = sns.heatmap(uniform_data)

# vmin指的是调色板最小的取值,vmax最大,超出最大值就都是最大值那个颜色,最小值同理
ax = sns.heatmap(uniform_data, vmin=0.2, vmax=0.5)
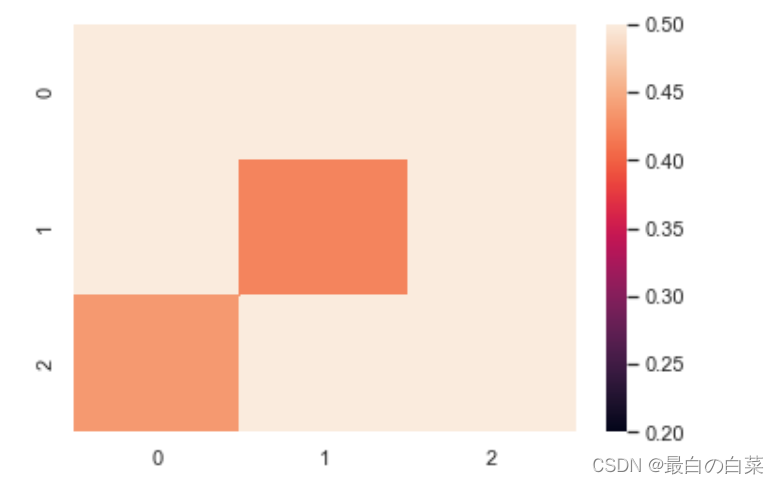
normal_data = np.random.randn(3, 3)
print (normal_data)
# center=0就是以0为中心画这个数据
ax = sns.heatmap(normal_data, center=0)

flights = sns.load_dataset("flights")
flights.head()
flights = flights.pivot("month", "year", "passengers")
print (flights)
ax = sns.heatmap(flights)

# 把实际的值放入图中,fmt设置文字的格式,不加就会乱
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, annot=True,fmt="d")

# 设置格子之间的间距,使图像更加清晰
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, linewidths=.5)

# 指定自己的调色板
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, cmap="YlGnBu")

# 将右边的颜色条隐藏
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, cbar=False)
