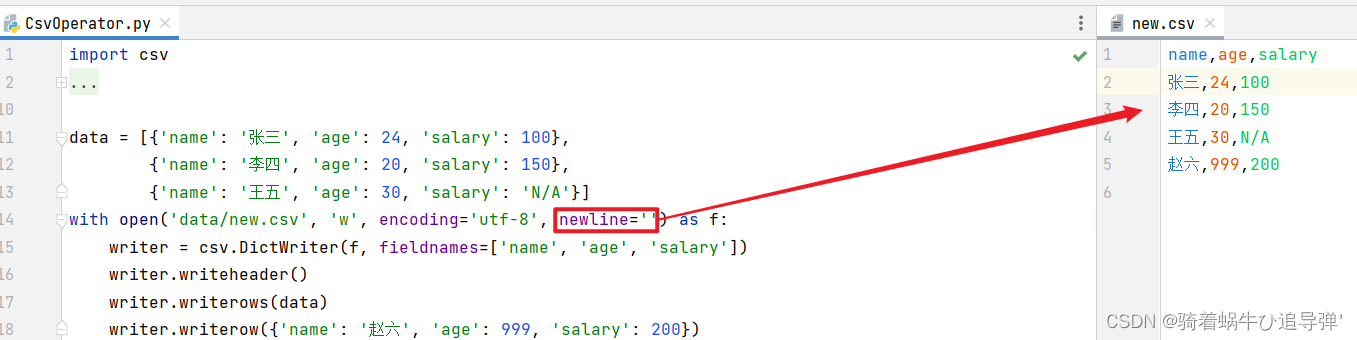
通过 python 写数据到 csv 文件的时候,遇到如下图所示的问题,写出来的文件会隔一行:
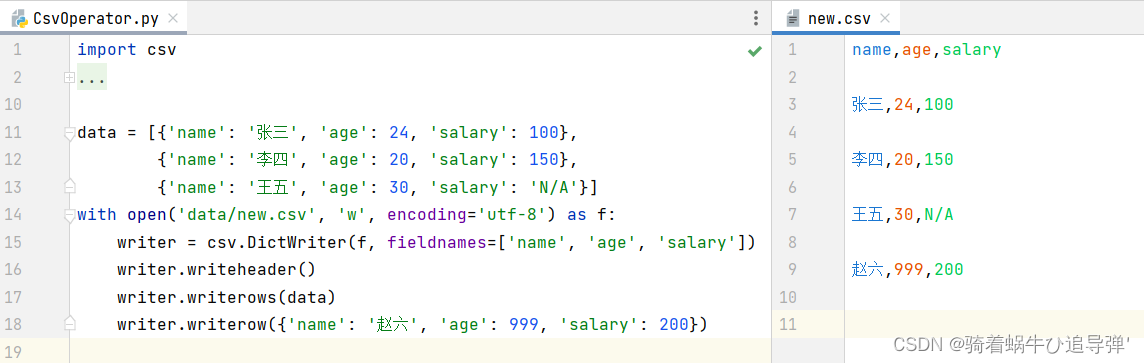
代码如下:
import csv
# 构建数据集
data = [{'name': '张三', 'age': 24, 'salary': 100},
{'name': '李四', 'age': 20, 'salary': 150},
{'name': '王五', 'age': 30, 'salary': 'N/A'}]
with open('data/new.csv', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=['name', 'age', 'salary'])
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerows(data)
writer.writerow({'name': '赵六', 'age': 999, 'salary': 200})
查看了一下 open() 的源码,发现参数 newline:
newline controls how universal newlines works (it only applies to text mode).
It can be None, '', '\n', '\r', and '\r\n'. It works as follows:
* On input, if newline is None, universal newlines mode is
enabled. Lines in the input can end in '\n', '\r', or '\r\n', and
these are translated into '\n' before being returned to the
caller. If it is '', universal newline mode is enabled, but line
endings are returned to the caller untranslated. If it has any of
the other legal values, input lines are only terminated by the given
string, and the line ending is returned to the caller untranslated.
* On output, if newline is None, any '\n' characters written are
translated to the system default line separator, os.linesep. If
newline is '' or '\n', no translation takes place. If newline is any
of the other legal values, any '\n' characters written are translated
to the given string.
在输入时,如果换行符为无,则启用通用换行符模式。输入中的行可以以 '\n'、'\r' 或 '\r\n' 结尾,这些行在返回给调用者之前会被翻译成 '\n'。如果是 ‘’,则启用通用换行模式,但行尾返回给调用者未翻译。如果它具有任何其他合法值,则输入行仅由给定字符串终止,并且行结束符未翻译地返回给调用者。
在输出时,如果换行符为 None,则写入的任何 '\n' 字符都将转换为系统默认行分隔符 os.linesep。如果换行符是 '' 或 '\n',则不进行翻译。如果换行符是任何其他合法值,则写入的任何 '\n' 字符都将转换为给定的字符串。
os.linesep 是用来分割文件的每一行(即文件结束符),由于在不同操作系统下文件结束符不一定相同,所以 os.linesep 是跨平台的文件描述符,比如在 Windows平台上是 '\r\n',在Linux平台上则是 '\n'。但是以 open 默认的文本模式读写时,'\n'会被自动转换成'\r\n'。所以本来是要写入结束符'\r\n',结果由于python自动把'\n'替换成'\r\n'导致写入的是'\r\n\n',最终导致多了一个空行。
所以只要设定参数 newline=‘’ 就可以了: