1.1数据可视化简述
数据可视化是借助图形化的手段将一组数据以图形的形式表示,并利用数据分析和开发工具发现其中未知信息的数据处理过程。
1.2常见的数据可视化方式
一、折线图
二、柱形图
三、条形图
四、堆积图
五、直方图
六、箱型图
七、饼图
八、散点图
九、气泡图
十、误差棒图
十一、雷达图
十二、统计地图
十三、3D图
2.1常见的数据可视化库
1.matplotlib
2.seaborn
3.ggplot
4.bokeh
5.pygal
6.pyecharts
3.1matplotlib概述
matplotlib是一个由约翰·亨特(John Hunter)等人员开发的、主要用于绘制2D图表的Python 库,它支持numpy、pandas 的数据结构,具有丰富的绘制图表、定制图表元素(图例、注释文本、表格等)或样式(如颜色、字体、线型等)的功能,可以帮助开发人员轻松获得高质量的图表。此外,matplotlib还可用于绘制一些3D图表。 matplotlib 实际上是一个面向对象的绘图库,它所绘制的图表元素均对应一个对象。但matplotlib 在设计之初仿照 MATLAB,它提供了一套与 MATLAB 命令类似的 API,方便熟悉MATLAB 的用户进行开发。matplotlib官网提供了了 种API :pyplot API、 object-oriented API、pylab API。
1. pyplot API
pyplot API是使用 pyplot 模块开发的接口,该接口的底层封裝了一系列与MATLAB 命令
同名的函数,使用这些函数可以像使用 MATLAB 命令一样快速地绘制图表。
2. object-oriented API
objec-oriented API 是面向对象的接口,该接口包含一系列对应图表元素的类,只有创建
这些类的对象并按照隶属关系组合到一起才能完成一次完整的绘图。
3. pylab API
pylab API 是使用 pylab模块开发的接口,它最初是为了模仿 MATLAB 的工作方式而设计
的,包括pyplot、numpy模块及一些其他附加功能,适用于 Python 交互环境中。
3.2安装matplotlib
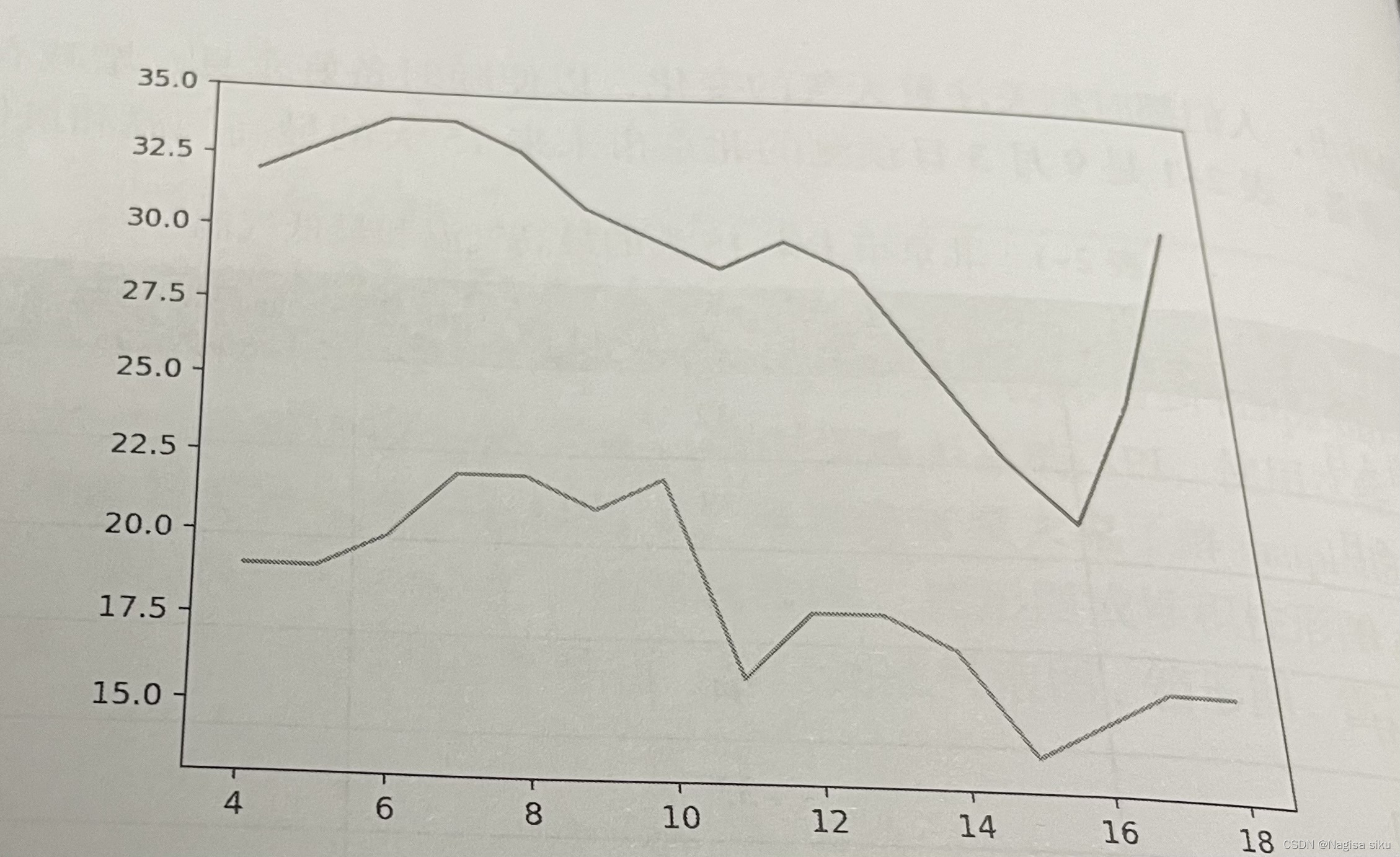
4.1绘制折线图
In [1]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
X = np arange (4, 19)
y_max = np.array([32,33,34,34,33,31,30,29,30,29,26,23,21,25,31])
y_min = np.array([19,19,20,22,22,21,22,16,18,18,17,14,15,16,16])
#绘制折线图
plt.plot (x, y_max)
plt.plot (x, y_min)
plt.show()
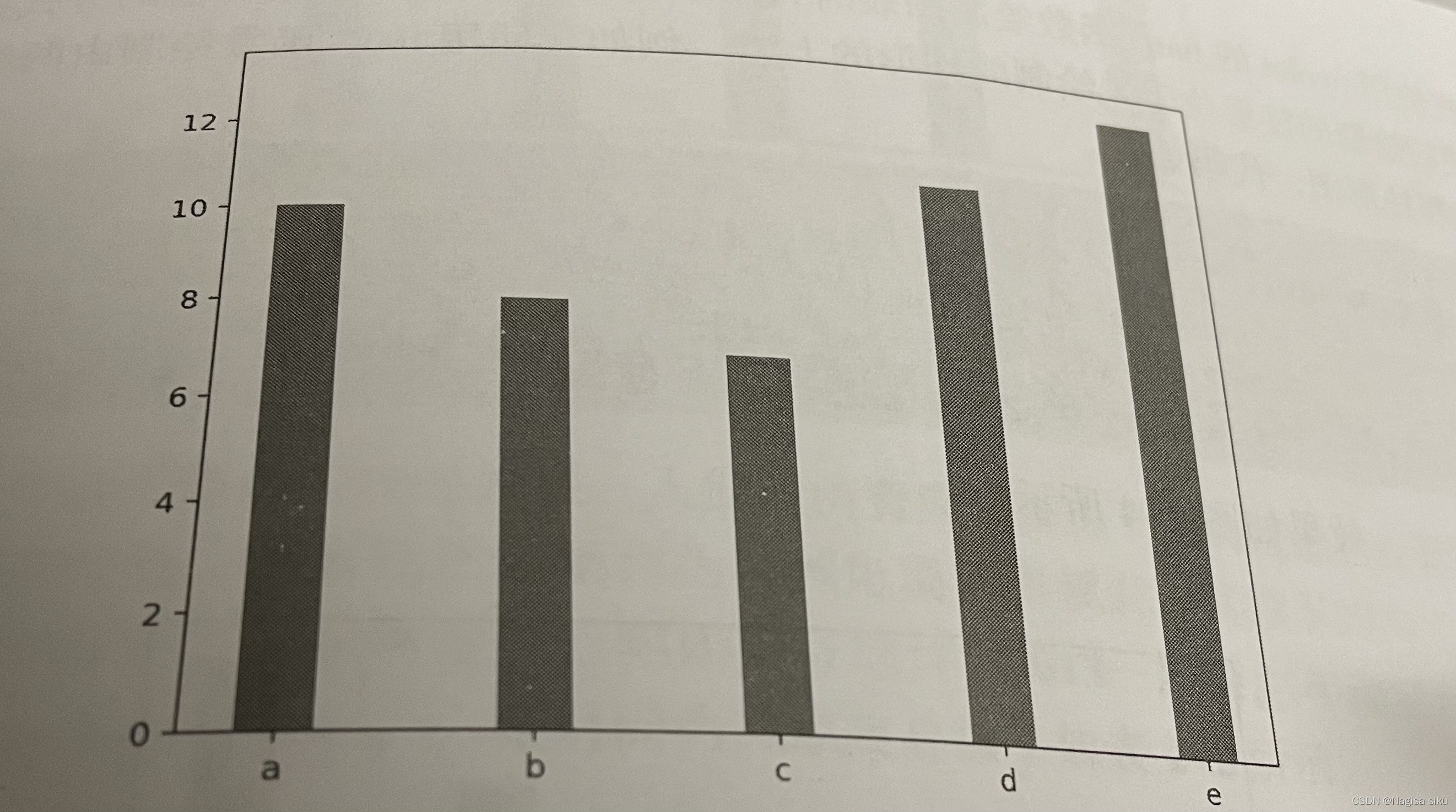
4.2绘制柱形图或堆积柱形图
In [2]:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
× = np.arange (5)
y1= np.array([10,8,7,11,13])
#柱形的宽度
bar_width = 0.3
# 绘制柱形图
plt.bar (x, y1, tick_label=['a', 'b', 'c','d','e'], width = bar_ width)
plt. show ()
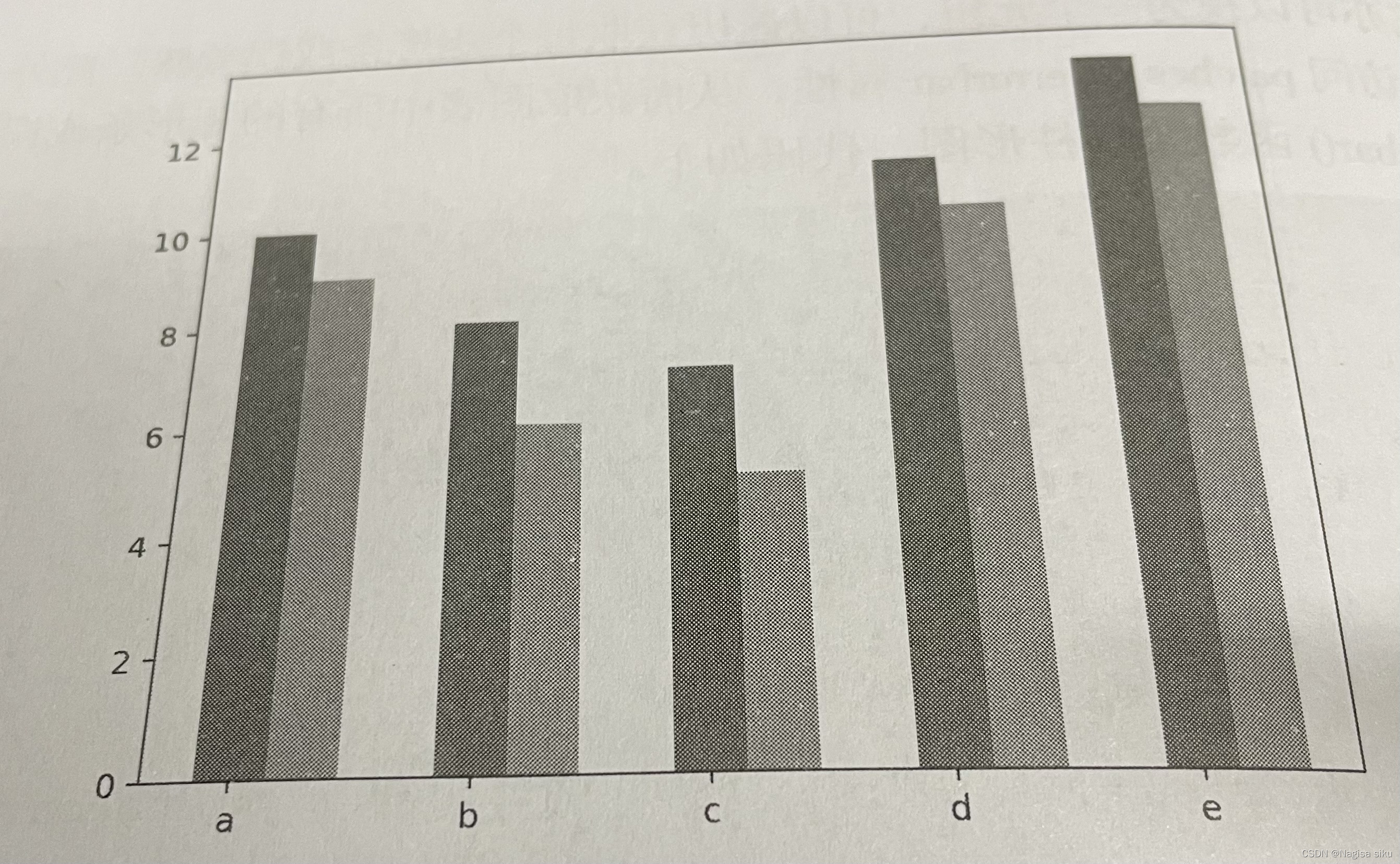
In [3]:
x = np.arange(5)
y1 = np.array([10,8,7,11,13])
y2 = np.array(19,6,5,10, 12])
# 柱形的宽度
bar_width =0.3
plt.bar (x, y1, tick_label=['a', 'b', 'c','d','e'], width = bar_ width)
plt.bar (x+bar_width, y2, width=bar_width)
plt. show ()
In [4]:
#绘制堆积柱形图
plt.bar (x, y1, tick_label=['a','b','c','d','e'], width = bar_ width)
plt.bar (x, y2, bottom=y1, width=bar_width)
plt.show ()
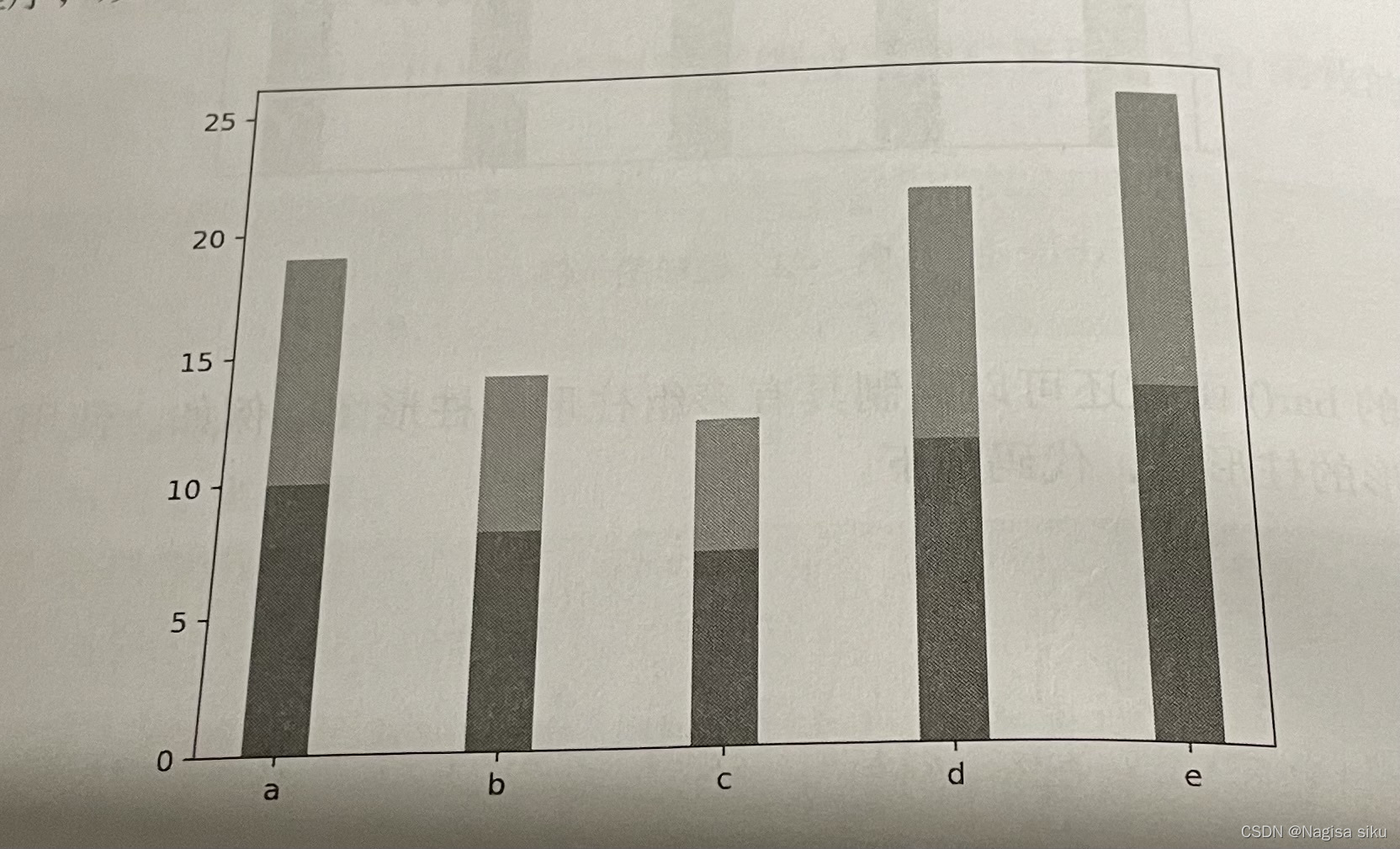
In [5]:
#偏差数据
error = [2,1,2.5,2,1.5]
#绘制带有误差棒的柱形图
plt.bar (x, y1, tick_label=['a','b','c','d','e'], width = bar_ width)
plt.bar (x, y1,bottom=y1, width=bar_width,yerr=error)
plt.show()
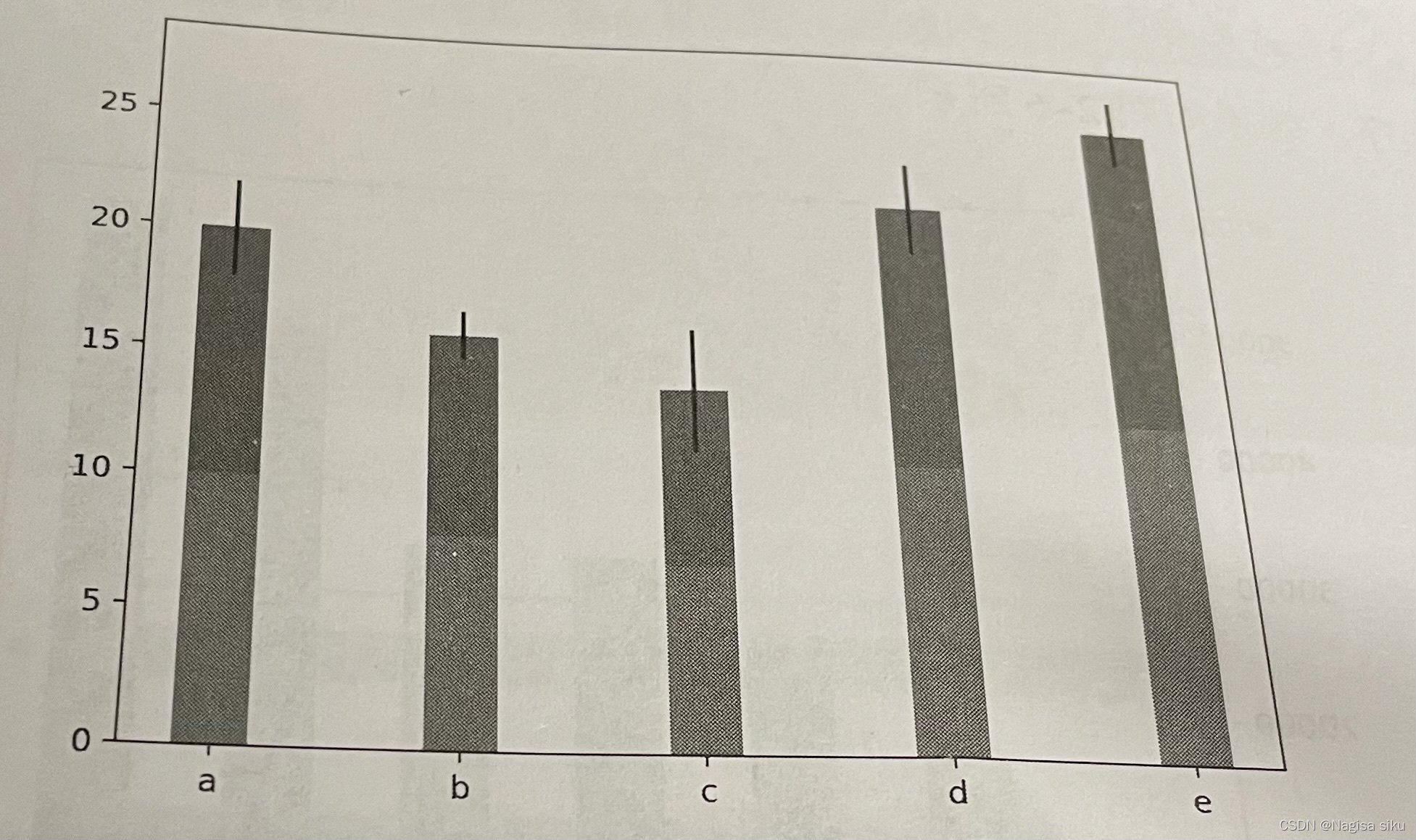
4.3绘制条形图或堆积条形图
In [7]:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
y = np.arange (5)
x1= np.array([10,8,7,11,13])
#条形的高度
bar_height = 0.3
绘制条形图
plt.barh(y, x1, tick_label=['a', 'b', 'c','d','e'], height = bar_ height)
plt. show ()
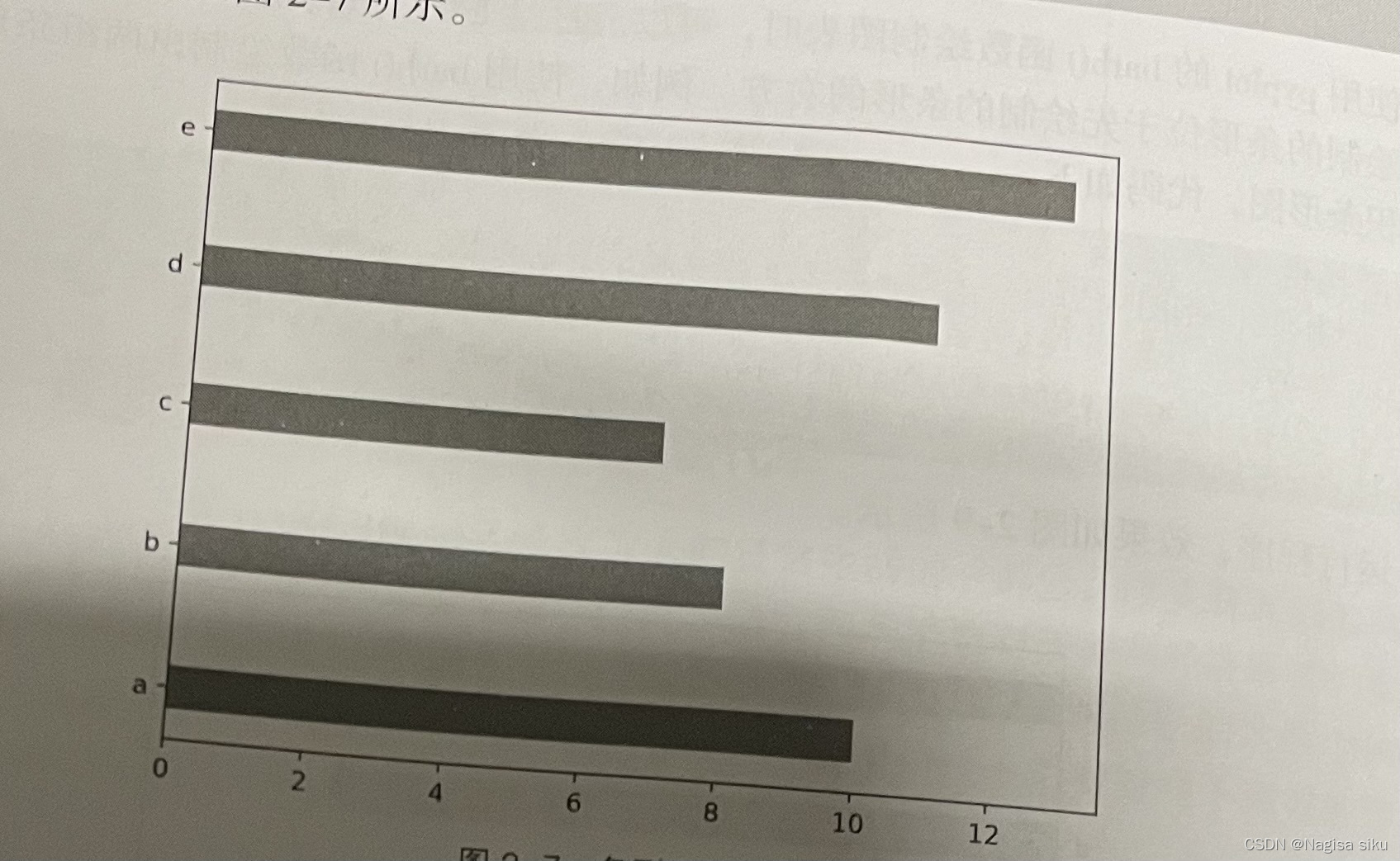
In [8]:
y = np.arange(5)
x1 = np.array([10,8,7,11,13])
x2 = np.array(19,6,5,10, 12])
条形的高度
bar_height =0.3
plt.barh (y, x1, tick_label=['a', 'b', 'c','d','e'], height = bar_ height)
plt.barh (y+bar_height, x2, height=bar_height)
plt. show ()
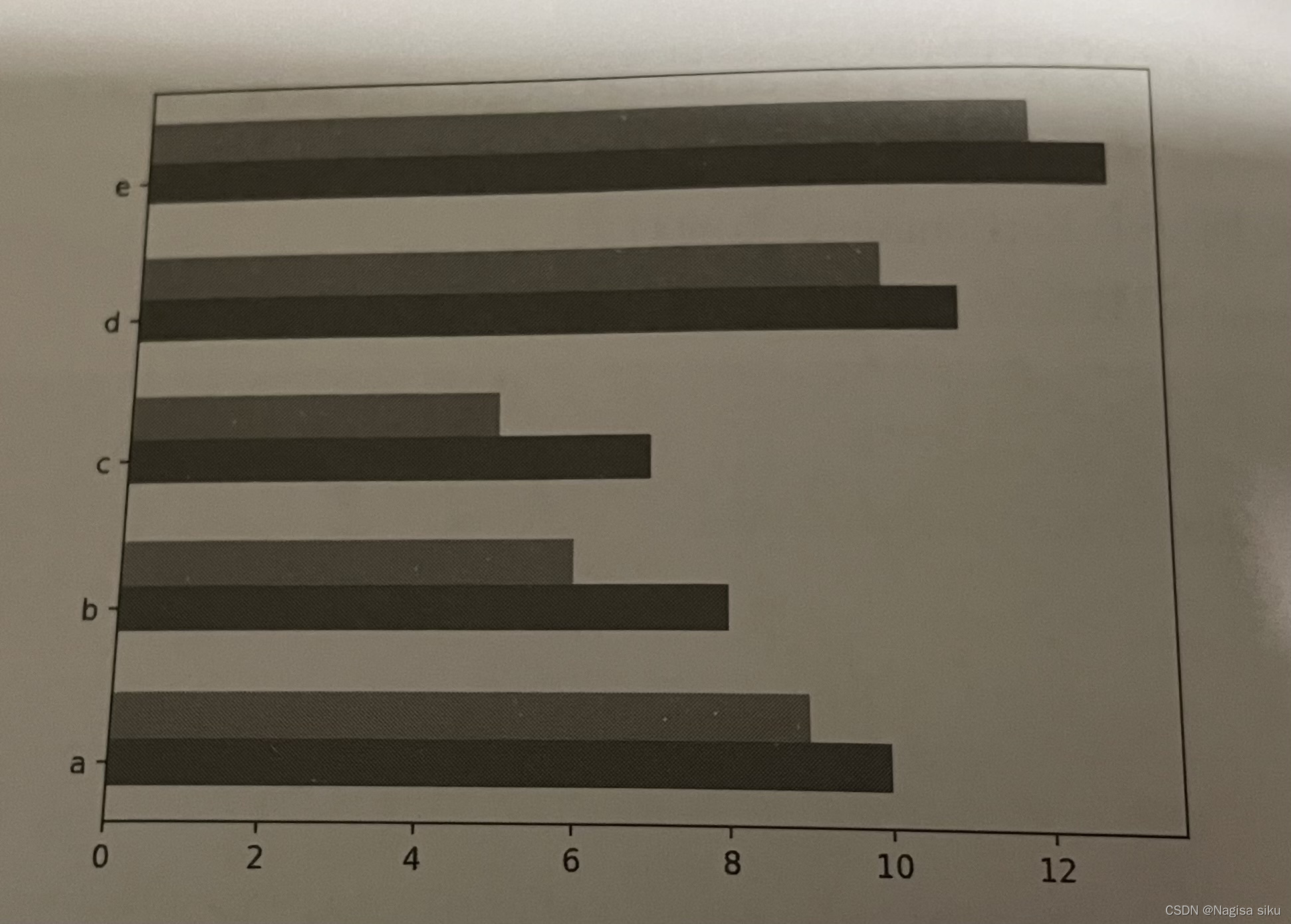
In [9]:
#绘制堆积条形图
plt.barh (y, x1, tick_label=['a','b','c','d','e'], height = bar_ height)
plt.barh (y, x2, left=x1, height = bar_ height)
plt.show ()

In [10]:
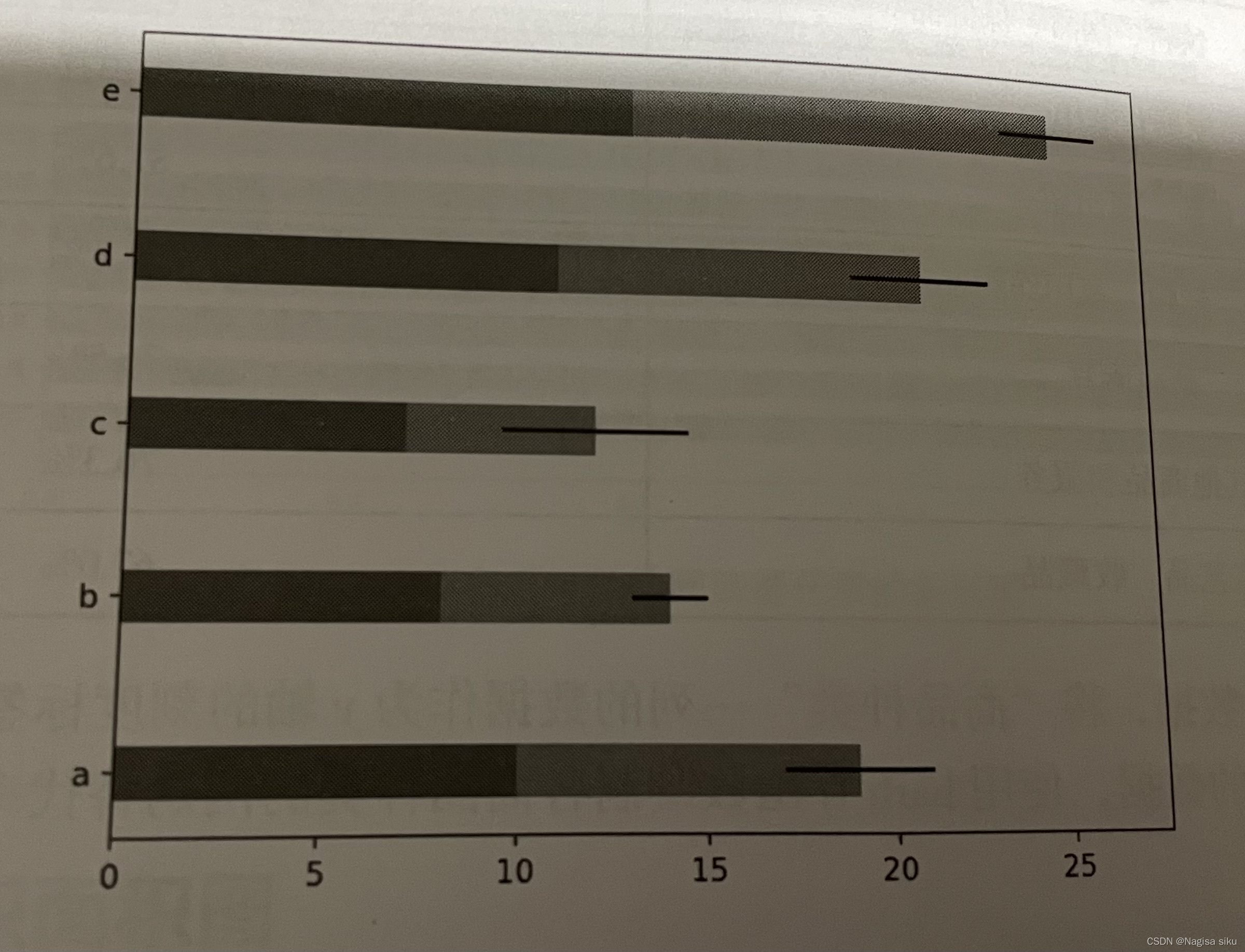
#偏差数据
error = [2,1,2.5,2,1.5]
#绘制带有误差棒的条形图
plt.barh (y, x1, tick_label=['a','b','c','d','e'], height = bar_ height)
plt.barh (y, x2, left=x1, height = bar_ height,xerr=error)
plt.show()