类
类是多个类似事物组成的群体的统称。能够帮助我们快速理解和判断事物的性质
例如:
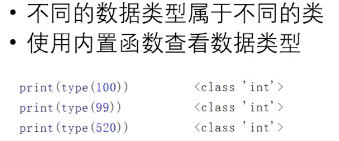
而对象是包含在类下面的具体实例,例如:

类的组成
包括类属性,实例方法,静态方法,类方法
下面将介绍一个模板,分别演示这四个模块:
class Student: # Student为类的名称由一个或者多个单词组成,每个单词的首字母要大写
,其余小写
native_place = 'place' # 直接写在类内部的变量称为类属性
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name = name # self.name称为实例属性,进行了一个赋
值操作,将局部变量name的值赋给实例属性
self.age = age
# 实例方法
def eat(self):
print('学生正在吃饭...')
# 静态方法
@staticmethod
def method(): # 静态方法中不允许写self
print('我使用了staticmethod进行修饰,所以我是静态方法')
# 类方法
@classmethod
def cm(cls): # cls即为class的意思
print('我是类方法,因为我使用了classmethod进行修饰')
类属性,类方法,静态方法的比较:

类方法的使用方式
使用类名进行调用
Student.cm()

静态方法的使用方式
使用类名直接调用
Student.method()

动态绑定属性和方法
动态绑定属性
Python是动态语言,在创建对象之后,可以动态地绑定属性和方法
class Student:
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
def eat(self):
print(self.name+'在吃饭')
stu1 = Student('张三',20)
stu2 = Student('李四',22)
stu2.gender = '女'
print(stu2.gender)
为stu2单独绑定gender属性,stu1和Student类中不含该属性

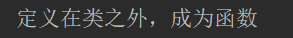
动态绑定方法
def show():
print('定义在类之外,成为函数')
stu1.show1 = show()
stu1.show1
小总结
