一、anaconda和Tensorflow是干啥的?
Anaconda是Python的一个发行版,里面内置了很多工具,因为做了优化免去了单独安装各个工具带来的不必要的麻烦。它是Python语言的免费增值开源发行版,可用于大规模数据处理、预测分析和科学计算,可以对python环境进行部署和管理。
Tensorflow是一个基于数据流编程的符号系统,被广泛应用于各类机器学习算法的编程实现,其前身是谷歌的神经网络算法库DistBelief。Tensorflow拥有多层级结构,可部署于各类服务器、PC终端和网页并支持GPU和TPU高性能数值计算,被广泛应用于谷歌内部的产品开发和各领域的科学研究。
二、在conda环境下安装tensorflow
使用pip安装tensorflow会遇到很多问题,建议在conda环境下安装会省去不少麻烦。
使用pip安装tensorflow,需要手动安装GPU支持的CUDA库和CuDNN库,而使用conda环境只需这条命令“conda install tensorflow-gpu”,就能自动安装相关的库。
在conda中安装tensorflow
1.首先在conda中创建虚拟环境
conda create tensorflow_env //表示创建一个名为tensorflow_env的虚拟环境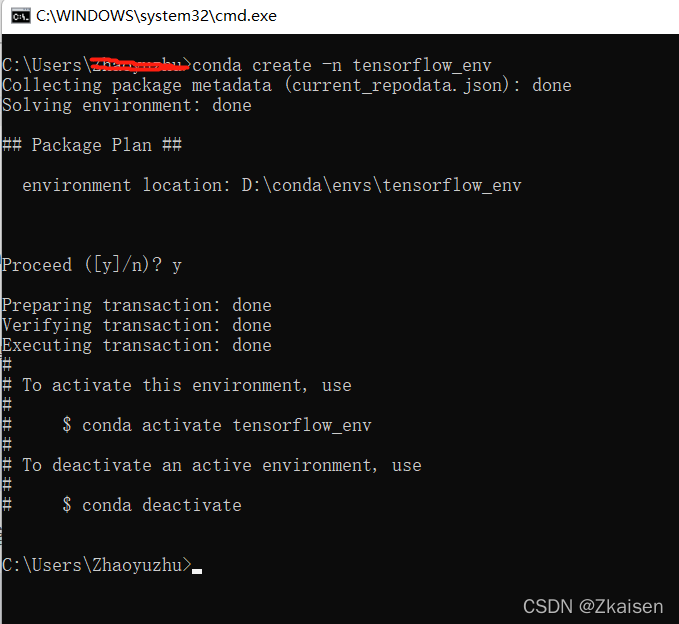 ?
?
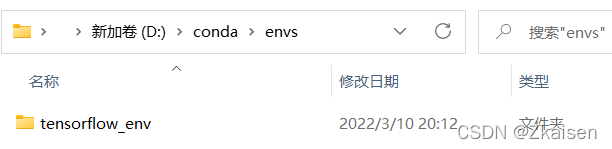
在你安装conda的env文件夹可以找到新创建的虚拟环境文件夹
 ?
?
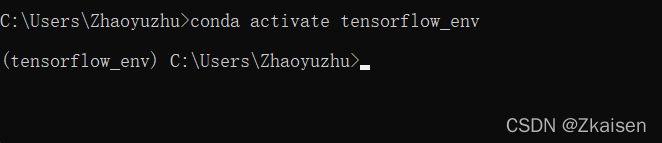
?2.激活虚拟环境:conda activate tensorflow_env
 ?
?
3.在虚拟环境中安装tensorflow
conda install tensorflow?4.创建指定 python 版本的环境
conda create --name your_env_name python=3.65.关闭某个激活环境
conda deactivate tensorflow_env6.删除某个虚拟环境
conda remove --name tensorflow --all三、reuters新闻分类项目实战
1.首先导入相关库文件
import keras
import numpy as np
from keras import models
from keras import layers
keras.__version__2.加载数据集
#加载reuters数据集
from keras.datasets import reuters
(train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels) = reuters.load_data(num_words=10000)
#num_words=10000 的意思是仅保留训练数据中前 10 000 个最常出现的单词
#train_data和test_data 这两个变量都是评论组成的列表,每条评论又是单词索引组成
#的列表(表示一系列单词)。 train_labels 和 test_labels 都是 0 和 1 组成的列表,其中 0
#代表负面(negative), 1 代表正面(positive)
3.将索引解码为新闻文本
#将索引解码为新闻文本
word_index = reuters.get_word_index()#获取索引
#print(word_index)
reverse_word_index = dict([(value, key) for (key, value) in word_index.items()])#保留的索引
#print(reverse_word_index)
#单纯好奇哪些索引保留了下来,用两个输出语句打印一下看看
# 注意,索引减去了3
# 因为0、1、2是为“padding”(填充)、“start of sequence”(序列开始)、“unknown”(未知词)分别保留的索引4.? 转化为二进制矩阵 one-hot编码
def vectorize_sequences(sequences, dimension=10000):
'''
把整数列表转为二进制矩阵 one-hot编码
'''
results = np.zeros((len(sequences), dimension))
for i, sequence in enumerate(sequences):
results[i, sequence] = 1.
return results
5.数据集向量化
# 将训练数据向量化
x_train = vectorize_sequences(train_data)
# 将测试数据向量化
x_test = vectorize_sequences(test_data)
def to_one_hot(labels, dimension=46):
results = np.zeros((len(labels), dimension))
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
results[i, label] = 1.
return results
# 将训练标签向量化
one_hot_train_labels = to_one_hot(train_labels)
# 将测试标签向量化
one_hot_test_labels = to_one_hot(test_labels)
from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categorical
one_hot_train_labels = to_categorical(train_labels)
one_hot_test_labels = to_categorical(test_labels)
6.构建网络
#构建网络
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='relu', input_shape=(10000,)))
model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(46, activation='softmax'))
7.编译模型
#编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
8.训练模型
#训练模型
history = model.fit(partial_x_train,
partial_y_train,
epochs=20,
batch_size=512,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val))
9.绘制损失及精确度图像
# 绘制训练损失与经验损失
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(loss) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
#绘制训练精度与训练精度
plt.clf() # clear figure
acc = history.history['acc']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
10.运行结果
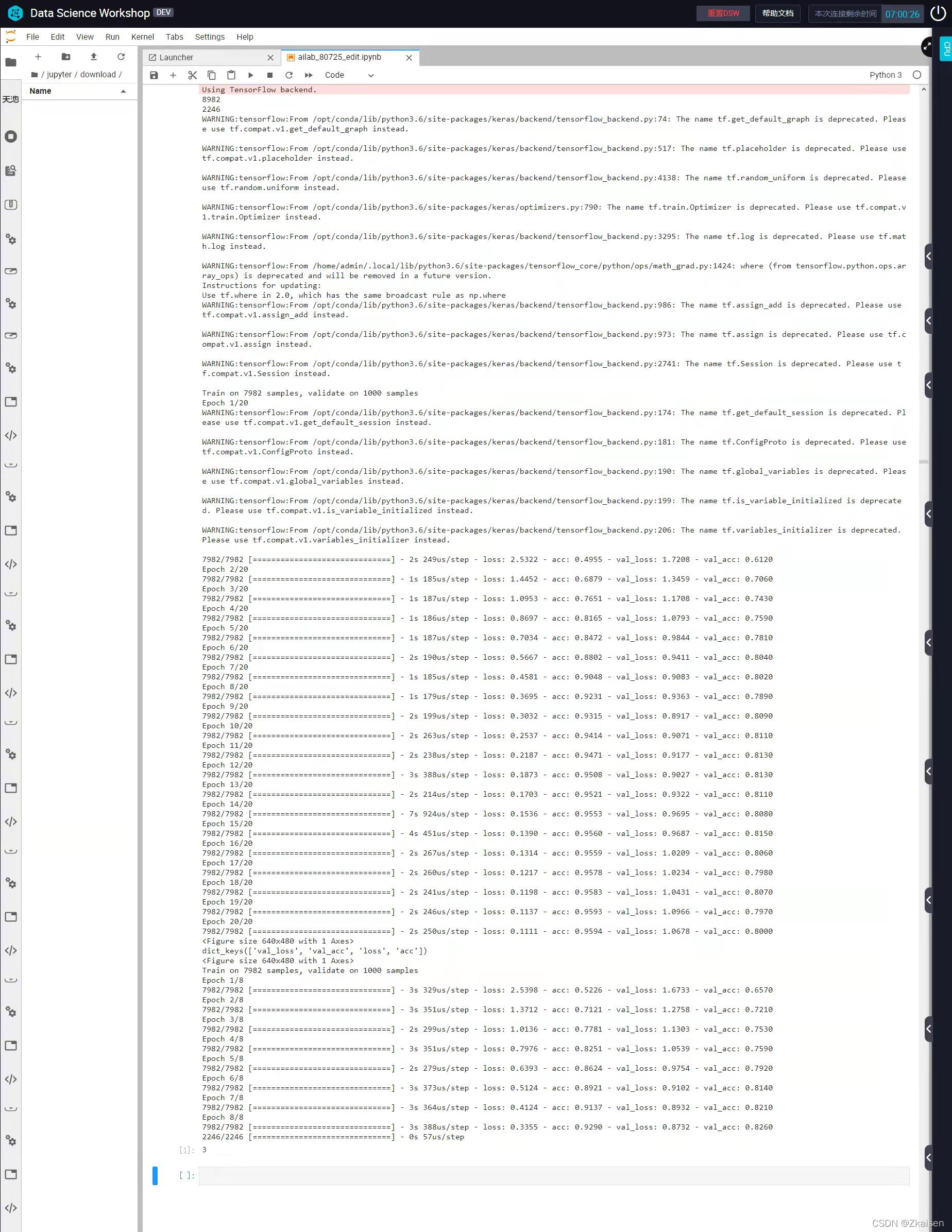 ?
?
11.误差图像与准确度图像
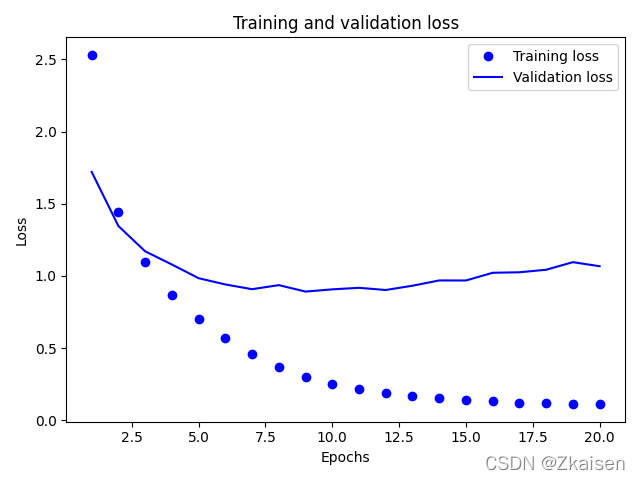 ?
?
?
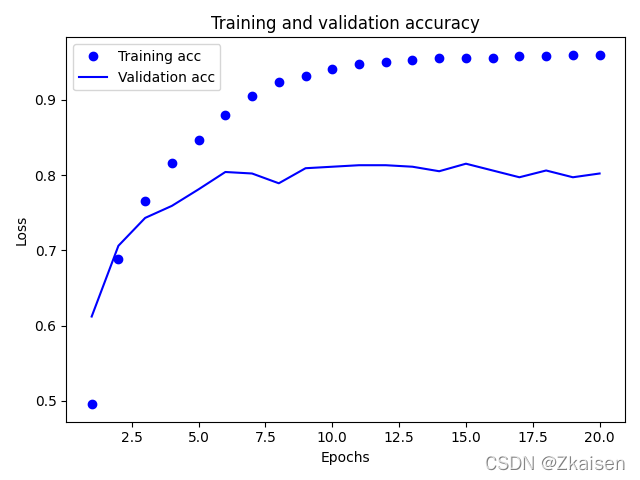 ?
?
?四、总结
1.training sets与validation sets,validation sets有何作用,
training sets是训练时用来调整权重使用的
validation sets不是用来调整权重用的,而是用作防止过拟合。也就是说当training sets随着训练次数增加,训练准确度也在增加,而经过validation sets计算后,若精度保持不变或精度没有增加反而减小了,说明发生了过拟合,应当停止训练。
2.为何validation loss总大于training loss,而validation accuracy总小于training accuracy?
查阅资料后,一般情况下validation loss>training loss,validation accuracy<training accuracy
有时也会有不同的情况:如
The validation loss < training loss and validation accuracy < training accuracy
This is a common thing with neural networks and different batch sizes. The training loss is the average of losses for the minibatch. Naturally for the first few batches you'll have a higher loss and as it goes through the data the loss gets smaller. Mean while the loss for the validation set is calculated against the entire dataset.
?关于validation sets的理解参考自以下两篇博客: