1、IPythonde 的帮助和文档
1.1、用符号 ?获取文档
help(len)
Help on built-in function len in module builtins:
len(obj, /)
Return the number of items in a container.
len?

L = [1, 2, 3]
L.insert?

L?

def square(a):
"""返回参数的平方"""
return a ** 2
square?

1.2、通过符号 ??获取源代码
square??

len??

1.3、用 Tab 补全的方式探索模块
- 默认忽略私有方法和特殊方法
- 但是可以输入下划线来明确私有的属性或方法了列出
In [5]: L.<Tab>
append() count() insert() reverse()
clear() extend() pop() sort()
copy() index() remove()
In [5]: L.index
append() count() insert() reverse()
clear() extend() pop() sort()
copy() index() remove()
function(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807)
In [5]: L.c<Tab>
clear()
copy()
count()
In [5]: L._<Tab>
__add__ __delitem__ __format__()
__class__ __dir__() __ge__
__contains__ __doc__ __getattribute__ >
__delattr__ __eq__ __getitem__()
1.4、超越 Tab 自动补全:通配符匹配
- Tab 只能匹配末尾
- 如果要匹配其他,可以使用通配符 *
In [6]: *Warning?
BytesWarning
DeprecationWarning
FutureWarning
ImportWarning
PendingDeprecationWarning
ResourceWarning
RuntimeWarning
SyntaxWarning
UnicodeWarning
UserWarning
Warning
In [7]: str.*find*?
str.find
str.rfind
2、IPython shell中的快捷键
2.1、导航快捷键
| 快捷键 | 动作 |
|---|
Ctrl-a | 将光标移动到本行开始处 | Ctrl-e | 将光标移动到本行结尾处 | Ctrl-b or ← 箭头 | 将光标回退一个字符 | Ctrl-f or → 箭头 | 将光标前进一个字符 |
2.2、文本输入快捷键
| 快捷键 | 动作 |
|---|
| Backspace 键 | 删除前一个字符 | Ctrl-d | 删除后一个字符 | Ctrl-k | 从光标开始剪切至行尾 | Ctrl-u | 从行头剪切至光标 | Ctrl-y | Yank(即粘贴)之前剪切的文本 | Ctrl-t | Transpose(即交换)前两个字符 |
2.3、命令历史快捷键
| 快捷键 | 动作 |
|---|
Ctrl-p or ↑ 箭头 | 获取前一个历史命令 | Ctrl-n or ↓ 箭头 | 获取后一个历史命令 | Ctrl-r | 对历史命令的反向搜索 |
In [11]: def square(a):
...: """返回参数的平方"""
...: return a ** 2
...:
I-search backward: squ
2.4、其他快捷键
| 快捷键 | 动作 |
|---|
Ctrl-l | 清空终端屏幕显示内容 | Ctrl-c | 中断当前的Python命令 | Ctrl-d | 退出IPython会话 |
3、IPython魔法命令
- 行魔法命令:以 % 开头,作用于单行输入
- 单元魔法命令:以 %% 开头,作用于多行输入
3.1、粘贴代码块:%paste 和 %cpaste
- 用来解决一些由复制粘贴带来的代码格式问题
- %paste:粘贴并执行
- %cpaste:科安提示粘贴并执行多个代码块
In [11]: def donothing(x):
...: return x
...:
In [12]: def donothing(x):
...: ...: return x
...:
In [13]: %paste
def donothing(x):
...: return x
## -- End pasted text --
3.2、执行外部代码:%run
- 用于执行外部python文件
- 执行后,可使用文件内部函数
- 可以使用 %run? 来查看帮助文档
3.3、计算代码运行时间:%timeit
- 会自动多次执行命令,以获取更稳定的结果
- 可用于分析某个步骤执行耗时
%timeit L = [n ** 2 for n in range(1000)]
206 μs ± 1.63 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
%%timeit
L = []
for n in range(1000):
L.append(n ** 2)
237 μs ± 2.27 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
L = []
for n in range(5):
%timeit L.append(n ** 2)
218 ns ± 2.31 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
215 ns ± 1.84 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
211 ns ± 0.921 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
211 ns ± 1.45 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
213 ns ± 0.561 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
3.4、魔法函数的帮助:?、%magic 和 %lsmagic
- ?: 和其他方法一样,可获取说明文档
- %magic: 获取魔法函数的通用描述和一些示例
- %lsmagic:获取魔法函数列表
- 也可以自定义魔法函数
%timeit?

%magic

%lsmagic
Available line magics:
%alias %alias_magic %autoawait %autocall %automagic %autosave %bookmark %cat %cd %clear %colors %conda %config %connect_info %cp %debug %dhist %dirs %doctest_mode %ed %edit %env %gui %hist %history %killbgscripts %ldir %less %lf %lk %ll %load %load_ext %loadpy %logoff %logon %logstart %logstate %logstop %ls %lsmagic %lx %macro %magic %man %matplotlib %mkdir %more %mv %notebook %page %pastebin %pdb %pdef %pdoc %pfile %pinfo %pinfo2 %pip %popd %pprint %precision %prun %psearch %psource %pushd %pwd %pycat %pylab %qtconsole %quickref %recall %rehashx %reload_ext %rep %rerun %reset %reset_selective %rm %rmdir %run %save %sc %set_env %store %sx %system %tb %time %timeit %unalias %unload_ext %who %who_ls %whos %xdel %xmode
Available cell magics:
%%! %%HTML %%SVG %%bash %%capture %%debug %%file %%html %%javascript %%js %%latex %%markdown %%perl %%prun %%pypy %%python %%python2 %%python3 %%ruby %%script %%sh %%svg %%sx %%system %%time %%timeit %%writefile
Automagic is ON, % prefix IS NOT needed for line magics.
4、输入和输出历史
4.1、IPython的输入输出对象
import math
math.sin(2)
0.9092974268256817
math.cos(2)
-0.4161468365471424
print(In)
['', 'import math', 'math.sin(2)', 'math.cos(2)', 'print(In)']
Out
{2: 0.9092974268256817, 3: -0.4161468365471424}
- 请注意:不是所有的操作都有输出,例如:import,print 等,就不影响输出
- 原因 print 函数的返回值是 None,任何返回值是 None 的函数都不会记录在 Out 中的。
Out[2] ** 2 + Out[3] ** 2
1.0
4.2、下划线快捷键和以前的输出
- _ 代表倒数第一个输出
- __ 代表倒数第二个输出
- ___ 代表倒数第三个输出
- Out[ X ] 可简写成 _X
Out
{2: 0.9092974268256817, 3: -0.4161468365471424, 6: 1.0}
print(_)
1.0
print(__)
-0.4161468365471424
print(___)
0.9092974268256817
Out[2]
0.9092974268256817
_2
0.9092974268256817
4.3、禁止输出
- 当你希望一条命令不输出,或者不希望结果储存在 Out 中
- 在一行末尾加上一个分号 ;
import math
math.sin(2) + math.cos(2)
0.4931505902785393
math.sin(2) + math.cos(2);
Out
{2: 0.4931505902785393}
3 in Out
False
2 in Out
True
4.4、相关的魔法命令
- %history:查看历史命令
- %rerun:重新执行部分历史命令
- %save:将部分历史命令保存在一个文件中
%history
import math
math.sin(2) + math.cos(2)
math.sin(2) + math.cos(2);
Out
3 in Out
2 in Out
%history
%history -n 1-4
1: import math
2: math.sin(2) + math.cos(2)
3: math.sin(2) + math.cos(2);
4: Out
5、IPython 和 shell 命令
5.1、IPython中的shell命令
!echo "Hello Word"
Hello Word
!ls
01 第一章 IPython 超越Python.ipynb [31mmaster.zip[m[m
[34mPythonDataScienceHandbook-master[m[m
%ls
01 第一章 IPython 超越Python.ipynb
[34mPythonDataScienceHandbook-master[m[m/
[31mmaster.zip[m[m*
!pwd
/XXXX/学习笔记/20200304-Python数据科学
%pwd
'/XXXX/学习笔记/20200304-Python数据科学'
5.2、在shell中传入或传出值
- 魔法方法不能结果不能用于传递
- 参数传入给shell使用 {varname}
contents = !ls
print(contents)
['01 第一章 IPython 超越Python.ipynb', 'PythonDataScienceHandbook-master', 'master.zip']
contents_ = %ls
01 第一章 IPython 超越Python.ipynb
[34mPythonDataScienceHandbook-master[m[m/
[31mmaster.zip[m[m*
print(contents_)
None
directory = !pwd
print(directory)
['/XXXX/学习笔记/20200304-Python数据科学']
type(directory)
IPython.utils.text.SList
message = "Hello Word"
!echo {message}
Hello Word
5.3、与shell相关的魔法命令
- 经过一段时间的使用,你可能发现无法使用 !cd 来导航文件系统
!pwd
/XXXX/学习笔记/20200304-Python数据科学
!cd ..
!pwd
/XXXX/学习笔记/20200304-Python数据科学
- 原因是 Notebook 中的 shell 命令是一个临时的分支 shell 中执行的
- 如果你希望更改路径,可以使用 %cd 魔法命令
%cd ..
/XXXX/学习笔记
cd ..
/XXXX
- 这种方式被称之为 自动魔法 函数,可以通过 %automagic 魔法方法进行翻译
- 这类函数还有:
- %cat、%cp、%env、%ls、%man、%mkdir、%more、%mv、%pwd、%rm、%redir
6、错误和调试
6.1、控制异常:%xmode
- 控制 轨迹追溯 输出的样式
- 三种样式可选:
- Plain(更紧凑,信息更少)
- Context(默认)
- Verbose(提供一些额外的信息,包含任何被调用的函数参数)
def func1(a, b):
return a/b
def func2(x):
a = x
b = x - 1
return func1(a, b)
func2(1)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZeroDivisionError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-2-7cb498ea7ed1> in <module>
----> 1 func2(1)
<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36> in func2(x)
5 a = x
6 b = x - 1
----> 7 return func1(a, b)
<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36> in func1(a, b)
1 def func1(a, b):
----> 2 return a/b
3
4 def func2(x):
5 a = x
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
%xmode Plain
Exception reporting mode: Plain
func2(1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-5-7cb498ea7ed1>", line 1, in <module>
func2(1)
File "<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36>", line 7, in func2
return func1(a, b)
File "<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36>", line 2, in func1
return a/b
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
%xmode Verbose
Exception reporting mode: Verbose
func2(1)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ZeroDivisionError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-7-7cb498ea7ed1> in <module>
----> 1 func2(1)
global func2 = <function func2 at 0x111187950>
<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36> in func2(x=1)
5 a = x
6 b = x - 1
----> 7 return func1(a, b)
global func1 = <function func1 at 0x111187680>
a = 1
b = 0
<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36> in func1(a=1, b=0)
1 def func1(a, b):
----> 2 return a/b
a = 1
b = 0
3
4 def func2(x):
5 a = x
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
6.2、调试:当阅读轨迹追溯不足以解决问题时
- %debug 用于调试异常
- 当你希望在出现任何异常时都自动启动调试器,可以使用 %pdb 魔法函数来启动自动过程
%debug
> [0;32m<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36>[0m(2)[0;36mfunc1[0;34m()[0m
[0;32m 1 [0;31m[0;32mdef[0m [0mfunc1[0m[0;34m([0m[0ma[0m[0;34m,[0m [0mb[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m:[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m----> 2 [0;31m [0;32mreturn[0m [0ma[0m[0;34m/[0m[0mb[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 3 [0;31m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 4 [0;31m[0;32mdef[0m [0mfunc2[0m[0;34m([0m[0mx[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m:[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 5 [0;31m [0ma[0m [0;34m=[0m [0mx[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m
ipdb> print(a)
1
ipdb> print(b)
0
ipdb> quit
%debug
> [0;32m<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36>[0m(2)[0;36mfunc1[0;34m()[0m
[0;32m 1 [0;31m[0;32mdef[0m [0mfunc1[0m[0;34m([0m[0ma[0m[0;34m,[0m [0mb[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m:[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m----> 2 [0;31m [0;32mreturn[0m [0ma[0m[0;34m/[0m[0mb[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 3 [0;31m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 4 [0;31m[0;32mdef[0m [0mfunc2[0m[0;34m([0m[0mx[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m:[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 5 [0;31m [0ma[0m [0;34m=[0m [0mx[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m
ipdb> up
> [0;32m<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36>[0m(7)[0;36mfunc2[0;34m()[0m
[0;32m 3 [0;31m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 4 [0;31m[0;32mdef[0m [0mfunc2[0m[0;34m([0m[0mx[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m:[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 5 [0;31m [0ma[0m [0;34m=[0m [0mx[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 6 [0;31m [0mb[0m [0;34m=[0m [0mx[0m [0;34m-[0m [0;36m1[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m----> 7 [0;31m [0;32mreturn[0m [0mfunc1[0m[0;34m([0m[0ma[0m[0;34m,[0m [0mb[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m
ipdb> down
> [0;32m<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36>[0m(2)[0;36mfunc1[0;34m()[0m
[0;32m 1 [0;31m[0;32mdef[0m [0mfunc1[0m[0;34m([0m[0ma[0m[0;34m,[0m [0mb[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m:[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m----> 2 [0;31m [0;32mreturn[0m [0ma[0m[0;34m/[0m[0mb[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 3 [0;31m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 4 [0;31m[0;32mdef[0m [0mfunc2[0m[0;34m([0m[0mx[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m:[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 5 [0;31m [0ma[0m [0;34m=[0m [0mx[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m
ipdb> quit
- 当你希望在出现任何异常时都自动启动调试器,可以使用 %pdb 魔法函数来启动自动过程
%xmode Plain
%pdb on
func2(1)
Exception reporting mode: Plain
Automatic pdb calling has been turned ON
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<ipython-input-2-f80f6b5cecf3>", line 3, in <module>
func2(1)
File "<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36>", line 7, in func2
return func1(a, b)
File "<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36>", line 2, in func1
return a/b
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
> [0;32m<ipython-input-1-1643401e3e36>[0m(2)[0;36mfunc1[0;34m()[0m
[0;32m 1 [0;31m[0;32mdef[0m [0mfunc1[0m[0;34m([0m[0ma[0m[0;34m,[0m [0mb[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m:[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m----> 2 [0;31m [0;32mreturn[0m [0ma[0m[0;34m/[0m[0mb[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 3 [0;31m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 4 [0;31m[0;32mdef[0m [0mfunc2[0m[0;34m([0m[0mx[0m[0;34m)[0m[0;34m:[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m[0;32m 5 [0;31m [0ma[0m [0;34m=[0m [0mx[0m[0;34m[0m[0;34m[0m[0m
[0m
ipdb> print(b)
0
ipdb> quit
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|
list | 显示文件的当前路径 | h(elp) | 显示命令列表,或查询特定命令的帮助信息 | q(uit) | 退出调试器和程序 | c(ontinue) | 退出调试器,继续运行程序 | n(ext) | 调到程序下一步 | <enter> | 重复前一个命令 | p(rint) | 打印变量 | s(tep) | 步入子程序 | r(eturn) | 从子程序跳出 |
7、代码的分析和计时
- %time:对单个语句的执行时间计时
- %timeit:对单个语句的重复执行进行计时,以获取更高的精准度
- %prun:利用分析器运行代码
- %lprun:利用逐行分析器运行代码
- %memit:测量单个语句的内存使用
- %mprun:通过逐行的内存分析器运行代码
7.1、代码段计时:%timeit 和 %time
%timeit sum(range(100))
752 ns ± 3.06 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
%%timeit
total = 0
for i in range(1000):
for j in range(1000):
total += i * (-1) ** j
267 ms ± 3.86 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
import random
L = [random.random() for i in range(100000)]
%timeit L.sort()
447 μs ± 29.1 μs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
import random
L = [random.random() for i in range(100000)]
print("无序序列排序好耗时")
%time L.sort()
无序序列排序好耗时
CPU times: user 14.7 ms, sys: 340 μs, total: 15.1 ms
Wall time: 15.3 ms
print("有序序列排序好耗时")
%time L.sort()
有序序列排序好耗时
CPU times: user 1.04 ms, sys: 0 ns, total: 1.04 ms
Wall time: 1.04 ms
%%time
total = 0
for i in range(1000):
for j in range(1000):
total += i * (-1) ** j
CPU times: user 310 ms, sys: 3.11 ms, total: 314 ms
Wall time: 314 ms
7.2、分析整个脚本:%prun
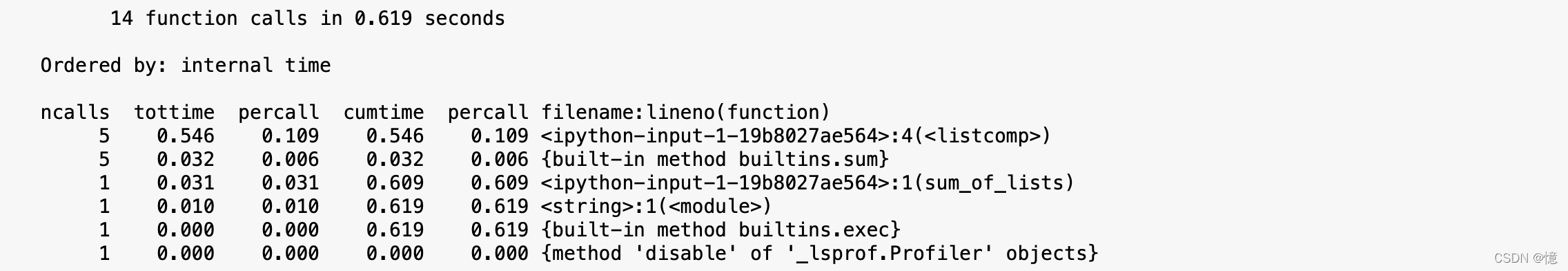
def sum_of_lists(N):
total = 0
for i in range(5):
L = [j^(j >> i) for j in range(N)]
total += sum(L)
return total
%prun sum_of_lists(1000000)
7.3、用 %lprun 进行逐行分析
- 需要安装:pip install line_profiler
- IPython 导入 line_profiler:%load_ext line_profiler
%load_ext line_profiler
%lprun -f sum_of_lists sum_of_lists(5000)
7.4、用 %memit 和 %mprun 进行内存分析
- 安装:pip install memory_profiler
- 引用:%load_ext memory_profiler
- %mprun:该函数仅仅对独立模块内部的函数有效
%load_ext memory_profiler
from mprun_demp import sum_of_lists
%memit sum_of_lists(1000000)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-2-104416b8696e> in <module>
----> 1 get_ipython().run_line_magic('memit', 'sum_of_lists(1000000)')
~/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py in run_line_magic(self, magic_name, line, _stack_depth)
2312 kwargs['local_ns'] = sys._getframe(stack_depth).f_locals
2313 with self.builtin_trap:
-> 2314 result = fn(*args, **kwargs)
2315 return result
2316
<~/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/decorator.py:decorator-gen-127> in memit(self, line, cell)
~/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/IPython/core/magic.py in <lambda>(f, *a, **k)
185 # but it's overkill for just that one bit of state.
186 def magic_deco(arg):
--> 187 call = lambda f, *a, **k: f(*a, **k)
188
189 if callable(arg):
~/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/memory_profiler.py in memit(self, line, cell)
1052 timeout=timeout, interval=interval,
1053 max_usage=True,
-> 1054 include_children=include_children)
1055 mem_usage.append(tmp)
1056
~/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/memory_profiler.py in memory_usage(proc, interval, timeout, timestamps, include_children, multiprocess, max_usage, retval, stream, backend, max_iterations)
341 # Therefore, the whole process hangs indefinitely. Here, we are ensuring that the process gets killed!
342 try:
--> 343 returned = f(*args, **kw)
344 parent_conn.send(0) # finish timing
345 ret = parent_conn.recv()
~/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/memory_profiler.py in _func_exec(stmt, ns)
825 # helper for magic_memit, just a function proxy for the exec
826 # statement
--> 827 exec(stmt, ns)
828
829
<string> in <module>
NameError: name 'sum_of_lists' is not defined
%mprun -f sum_of_lists sum_of_lists(1000000)
| 







