爬虫概述
爬虫:网络爬虫是一种按照一定的规则,自动地抓取万维网信息的程序或者脚本。其本质就是通过编写程序拟浏览器上网,抓取数据的过程。
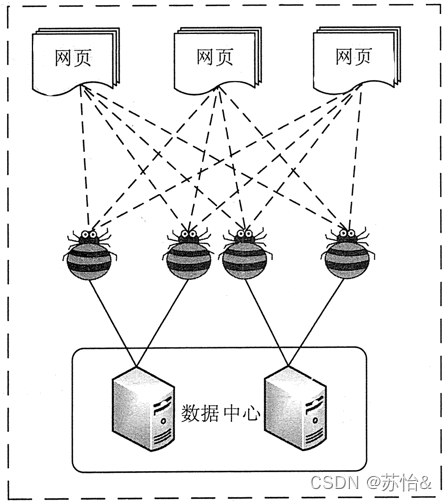
爬虫特点
- 在法律中都是不被禁止的;
- 具有违法风险;
- 爬虫是一个博弈的过程(反爬机制、反反爬策略)
- robots协议:规定了网站中哪些数据可以被爬取哪些数据不可以被爬取,属于一个君子协议。
爬虫分类
按照系统结构和实现技术,大致可以分为以下几种类型:
- 通用爬虫:通常抓取互联网整张页面数据;
- 聚焦爬虫:选择性地爬取与预定主题相关的网络爬虫;
- 增量式爬虫:监测网站中数据的更新情况,通常只抓取网站中最新更新的数据;
- 深层网络爬虫:通常通过关键字检索获取内容。
| 名称 | 场景 | 特点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 通用网络爬虫 | 门户站点搜索引擎、大型Web服务提供商采集数据 | 爬行范围和数量巨大、爬行页面顺序要求低、并行工作方式,爬取互联网上的所有数据 | 爬虫速度和存储空间要求高、刷新页面的时间长 |
| 聚焦网络爬虫 | 又称主题网络爬虫,只爬行特定的数据,商品比价 | 极大 节省了硬件和网络资源,页面更新快 | |
| 增量式网络爬虫 | 只抓取刚刚更新的数据 | 数据下载量少,及时更新已爬行的网页,减少时间可空间上的耗费、爬取到的都是最新页面 | 增加了爬行算法的复杂度和实现难度 |
| 深层网络爬虫 | 大部分内容不能通过静态链接获取,隐藏在搜索表单后,用户提交一些关键词才能获得 |
按实现方式,大致可以分为以下几种类型:
- 服务器渲染爬虫:在服务器直接把数据和html整合在一起,统一返回浏览器(在页面中可以看到数据)
- 客户端渲染爬虫:第一请求只返回html框架、第二次请求拿到数据,进行数据展示(在页面源码中,看不到数据)
http协议
超文本传输协议(http协议)是一个简单的请求-响应协议,它通常运行在TCP协议之上。它指定了客户端可能发送给服务器什么样的消息以及得到什么样的响应。
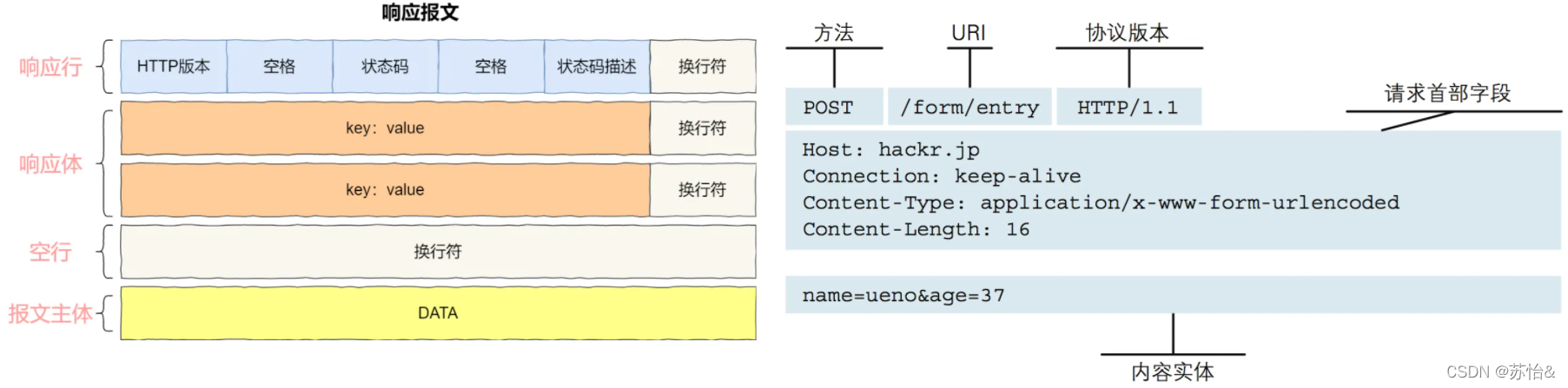
http请求
请求消息包括以下格式:请求行(request line)、请求头部(header)、空行和请求数据四个部分组成,常用的请求方式包括get请求和post请求。

get请求
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: www.baidu.com
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/51.0.2704.106 Safari/537.36
Connection: keep-alive
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, sdch
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8
post请求
POST / HTTP/1.1
Host: www.wrox.com
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; en-US; rv:1.7.6) Gecko/20050225 Firefox/1.0.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 40
Connection: Keep-Alive
name=Professional%20Ajax&publisher=Wiley开发中常用请求头属性
| 请求头属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Host | 服务器地址 |
| User-Agent | 请求载体的身份标识 |
| Connection | 请求完毕后,是断开连接还是保持连接 |
get和post区别
- get提交的数据会放在URL之后(以?分割),参数之间以&相连;post方法是把提交的数据放在HTTP包的Body中
- get提交的数据大小有限制(因为浏览器对URL的长度有限制);post提交的数据没有限制
- get提交数据,会带来安全问题;post相对安全
http响应
一般情况下,服务器接收并处理请求后会返回一个响应消息。HTTP响应由四个部分组成:状态行、消息报头、空行和响应正文
开发中常用响应头属性
| 响应头属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Content-Type | 服务器响应给客户端的数据类型 |
响应状态码
| 状态码 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 200 | 客户端请求成功 |
| 400 | 客户端请求有语法错误,不能被服务器所理解 |
| 401 | 请求未经授权,这个状态代码必须和WWW-Authenticate报头域一起使用 |
| 403 | 服务器收到请求,但是拒绝提供服务 |
| 404 | 请求资源不存在,或输入了错误的URL |
| 500 | 服务器发生不可预期的错误 |
| 503 | 服务器当前不能处理客户端的请求,一段时间后可能恢复正常 |
爬虫库/框架
请求库
| 模块/框架 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| urllib | urllib库用于操作网页 URL,并对网页的内容进行抓取处理。操作较为复杂,缺少实用的高级功能 |
| requests | 在urllib基础上进行封装,提供更加便捷的方法 |
| selenium | 自动化测试框架,解决requests无法执行javaScript代码的问题 |
解析库
| 模块/框架 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Beautiful Soup | 功能强大的html解析库,整合了一些常用爬虫功能。 |
| lxml | xpath解析库 |
爬虫框架
| 框架 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Scrapy | 强大的爬虫框架,可以满足绝大多数爬虫需求 |
requests库
requests概述
requests模块是一款基于网络请求的python三方库,具有功能强大,简单便捷,效率较高的特点。其功能在于模拟浏览器发请求。
requests模块安装
pip install requests -i https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple爬虫实现步骤
- 指定url
- 基于requests模块发送请求
- 获取服务器响应数据
- 持久化存储
第一个爬虫程序(抓取百度首页)
# 导入request模块
import requests
# 1、确定抓取网站网址
url = "https://www.baidu.com/"
# 2、通过requests模块发送请求
response = requests.get(url)
# 3、获取服务器响应
page_text = response.text
print(page_text)
# 4、持久化存储
with open("../files/baidu.html", mode="w", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
fp.write(page_text)常用属性/方法
请求属性/方法
| 属性/方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| requests.get(url,[params],[headers]) | get请求函数,实现get请求 |
| requests.post(url,[data],[headers]) | post请求函数,实现post请求 |
响应属性/方法
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| response.encoding | 编码方式 |
| response.text | Unicode型数据 |
| response.content | 字节型数据(二进制) |
| status_code | 状态码 |
| response.cookies | cookies值 |
| response.headers | 响应头信息 |
| response.request.headers | 请求头信息 |
| 方法 | 描述 |
| response.json() | 获取json数据 |
常用属性使用
import requests
# 1、确定抓取网站网址
url = "https://www.baidu.com/"
# 2、通过requests模块发送请求
response = requests.get(url)
response.encoding = 'utf-8'
# 3、获取服务器响应
print(response.text) # 响应文本
print(response.status_code) # 200
print(response.url) # https://www.baidu.com/
print(response.encoding) # utf-8
print(response.cookies) # <RequestsCookieJar[<Cookie BDORZ=27315 for .baidu.com/>]>
print(response.headers) # 响应头信息
print(response.headers.get("Content-Type"))
print(response.request.headers) # 请求头信息
print(response.request.headers.get("User-Agent"))requests实例
按请求方式的不同,requests抓取数据请求方式分为:get请求、post请求、异步请求、接口API请求等。
搜狗关键字查询(get)
# 导入request模块
import requests
# 1、确定抓取网站网址
url = "https://www.sogou.com/web?query=大数据"
header= {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.198 Safari/537.36"
}
# 2、通过responses模块发送请求
response = requests.get(url, headers=header)
response.encoding = "utf-8"
# 3、获取服务器响应
page_text = response.text
print(page_text)百度翻译(post | 异步)
import requests
# 1、确定抓取网站网址
url = "https://fanyi.baidu.com/sug"
data = {
"kw": "dog"
}
header = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.c0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.198 Safari/537.36"
}
# 2、通过responses模块发送请求
response = requests.get(url, data=data, headers=header)
response.encoding = "utf-8"
# 3、获取服务器响应
page_json = response.json()
print(page_json)API接口访问
| 接口名称 | 接口地址 |
|---|---|
| 免费API | http://api.wpbom.com/ |
| 木小果API | https://api.muxiaoguo.cn/ |
| 韩小韩API接口站 | https://api.vvhan.com/ |
| ALAPI | http://www.alapi.cn/ |
| Sky?API | https://api.6vzz.com/ |
import requests
url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts"
resp = requests.get(url)
print(resp.json()) # 接口通常返回json格式数据豆瓣电影信息抓取(异步数据)
import requests
url = "https://movie.douban.com/j/search_subjects"
header = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.198 Safari/537.36"
}
params = {
"type": "movie",
"tag": "热门",
"page_limit": "50",
"page_start": "0"
}
resp = requests.get(url, headers=header, params=params)
resp.encoding = "utf-8"
data = resp.json()
resp.close()
print(data)抓取豆瓣喜剧片前200条记录
import requests
import time
url = "https://movie.douban.com/j/chart/top_list"
header = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.198 Safari/537.36"
}
params = {
"type": "24",
"interval_id": "100:90",
"action": "",
"start": "0",
"limit": "20"
}
def download_douban(page_num):
movie_list = []
for i in range(page_num):
params['start'] = str(20 * i)
resp = requests.get(url, headers=header, params=params)
resp.encoding = "utf-8"
data = resp.json()
resp.close()
movie_list.extend(data)
print(f"第{i + 1}页下载完成!")
time.sleep(2)
return movie_list
info_list = download_douban(3)
print(info_list)
print(len(info_list))requests爬虫练习题
- 抓取搜狗主页(https://www.sogou.com/)
- 搜狗搜索关键词(搜索关键词由用户指定)
- 抓取纺专主页(https://www.cdtc.edu.cn/)
- 爬取【豆瓣电影分类排行榜 - 喜剧片】前200条记录信息(https://movie.douban.com/typerank?type_name=%E5%96%9C%E5%89%A7&type=24&interval_id=100:90&action=)
- 图片下载(http://img.netbian.com/file/2020/1028/c17345a23b00d07044d835c193d10a49.jpg)
数据解析
数据解析即从获取的html页面内容中获取指定标签属性或标签文本的过程。
| 解析方式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 正则式 | 存在难以构造、可读性差的问题,速度最快 |
| BeautifulSoup | 容易构造和理解,文档容错能力较强 |
| XPath | 通用性较强,效率与速率适中 |
正则式
分组命名
import re
str = """
<div class="info">
<h2>title1</h2>
<p>hello</p>
</div>
<div class="info">
<h2>title2</h2>
<p>world</p>
</div>
"""
# regex = '<div class="info">.*?<h2>(.*?)</h2>.*?<p>(.*?)</p>.*?</div>'
# result = re.findall(regex,str,re.S)
# print(result)
regex = '<div class="info">.*?<h2>(?P<title>.*?)</h2>.*?<p>(?P<content>.*?)</p>.*?</div>'
result2 =re.finditer(regex,str,re.S)
for obj in result2:
print(obj.group("title")) # 通过名字获取值
info_dict = obj.groupdict() # 根据?P<key> 将分组生成字典
print(info_dict.values(),type(info_dict.values())) # dict_values(['title1', 'hello']) <class 'dict_values'>若后期对获取的分组进行加工,使用finditer()更合适
获取指定内容
# 提取<div id="first"></div>中所用<h2>和<p>元素之间的内容
import re
str = """
<div id="first">
<div class="info">
<h2>title_first_1</h2>
<p>content_first_1</p>
</div>
<div class="info">
<h2>title_first_2</h2>
<p>content_first_2</p>
</div>
</div>
<div id="second">
<div class="info">
<h2>title_second_1</h2>
<p>content_second_1</p>
</div>
<div class="info">
<h2>title_second_2</h2>
<p>content_second_2</p>
</div>
</div>
"""
# 先找到重复部分
info = re.search('<div id="first">(.*)</div>.*?<div id="second">', str, re.S)
# 再对内容进行提取
result = re.findall('<div class="info">.*?<h2>(.*?)</h2>.*?<p>(.*?)</p>.*?</div>',info.group(),re.S)
print(result)采用正则式进行匹配时,先分析页面规律(找到重复部分),然后采用re模块进行数据提取
爬取豆瓣Top250
import requests
import re
import csv
url = "https://movie.douban.com/top250"
header = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.198 Safari/537.36"
}
params = {
"start": "0",
"filter": ""
}
resp = requests.get(url, headers=header, params=params)
resp.encoding = "utf-8"
page_text = resp.text
regex = '<li>.*?<div class="hd">.*?<span class="title">(?P<name>.*?)</span>.*?<br>.*?(?P<year>.*?) ' \
'.*?<span property="v:best" content="10.0"></span>.*?<span>(?P<person_num>.*?)人评价</span>'
# csv文件写入(newline=''处理windows下多出空行问题)
fp = open("../files/info.csv", mode="w", encoding="utf-8", newline='')
csvwriter = csv.writer(fp)
movie_iter = re.finditer(regex, page_text, re.S)
for movie in movie_iter:
# print(movie.group(1))
# print(movie.group(2).strip())
# print(movie.group(3))
dicts = movie.groupdict()
dicts['year'] = dicts['year'].strip()
# print(dicts.values())
csvwriter.writerow(dicts.values())
fp.close()抓取电影天堂中【迅雷电影资源】所列电影的下载地址
# https://dytt8.net/index2.htm
import requests
import re
url = "https://dytt8.net/index2.htm"
header = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.198 Safari/537.36"
}
params = {
}
resp = requests.get(url, headers=header, params=params)
resp.encoding = "gb2312"
page_text = resp.text
# 获取电影名和电影详情页地址
movie_list = []
movie_iter = re.finditer("最新电影下载</a>]<a href='(?P<address>.*?)'>(?P<name>.*?)</a><br/>", page_text, re.S)
for movie in movie_iter:
dicts = movie.groupdict()
dicts['address'] = "https://dytt8.net" + dicts['address']
movie_list.append(dicts)
# 到请求也获取下载地址
for obj in movie_list:
resp_son = requests.get(obj.get("address"), headers=header, params=params)
resp_son.encoding = "gb2312"
sonpage_text = resp_son.text
movie_link = re.search('◎简 介.*?<a target="_blank" href="(.*?)"><strong>',sonpage_text,re.S).group(1)
obj['address'] = movie_link
print(f"{obj.get('name')}下载完成")
print(movie_list)BeautifulSoup
概述
BeautifulSoup是一个从html字符串提取数据的工具。BeautifulSoup特点包括以下几个方面:
- API简单,功能强大
- 自动实现编码转换(自动将输入文档转为Unicode类型,将输出文档转为utf-8编码)
- 支持多种解析器(通常使用lxml解析器,若遇到一些无法使用lxml解析器解析的网站,使用html5lib解析器)
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python标准库 | soup = BeautifulSoup(page_text,“html.parser”) | pthon内置标准库;执行速度适中 | 容错能力较差 |
| lxml HTML解析器 | soup = BeautifulSoup(page_text,“lxml”) | 速度快;文档容错能力强 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| lxml XML解析器 | soup = BeautifulSoup(page_text,“xml”) | 速度快;唯一支持XML的解析器 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| html5lib | soup = BeautifulSoup(page_text,“html5lib”) | 容错性好;像浏览器一样解析html;不依赖外部扩展库; | 速度慢 |
BeautifulSoup安装
pip install bs4 -i https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple
#使用lxml解析器进行解析,需要安装lxml三方库
pip install lxml -i https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple
'''
若lxml库安装失败,提示需要C语言环境,只需要更新pip版本后再次安装即可
1、在pycharm终端将路径切换到Scripts目录
2、执行easy_install -U pip命令
3、重新安装lxml三方库:pip install lxml -i https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple
'''采用BeautifulSoup进行解析的流程如下图所示:

BeautifulSoup初始化
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup(markup,features) # markup:解析对象(html字符串或文件); features:解析器类型
# 字符串初始化(html_text通常为requests模块爬取的页面内容)
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_text,"lxml")
# 文件初始化
with open("index.html", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
soup = BeautifulSoup(fp, "lxml")选择器
选择器用来查找、定位元素,并获取数据。BeautifulSoup选择器分为节点选择器、方法选择器和CSS选择器。
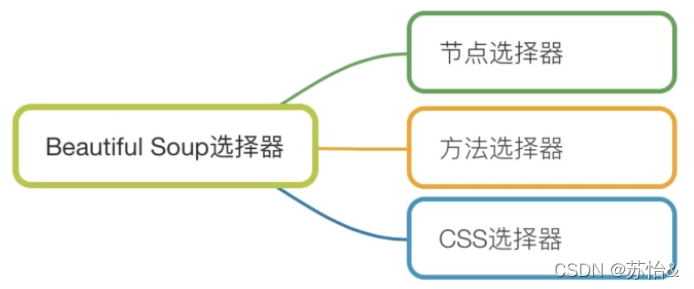
节点选择器是获取数据的基本方法,方法选择器和css选择器是查找、定位元素的常用方法。
节点选择器
通过元素节点间的关系进行元素选择与信息的提取。节点选择器利用Tag对象选择节点元素,对应html中的标签。
获取节点元素
节点选择器通过【soup.tag】获取节点元素
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>BeautifulSoup Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="intro"><em>This is em in p element</em></p>
<p class="mainInfo">There are three cats, their names are
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_white" class="cat" id="little_white">小白</a>,
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_red" class="cat" id="little_red">小红</a> and
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" class="cat" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>;
story over!
</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
# 获取title节点元素
print(soup.title) # <title>BeautifulSoup Test</title>
# 获取节点元素类型(节点选择器返回类型为Tag)
print(type(soup.title)) # <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
# 当html中存在多个相同节点时,仅返回第一个满足条件的节点
print(soup.a) # <a class="cat" href="http://baidu.com/little_white" id="little_white">小白</a>
# 获取嵌套子节点(每次返回都是Tag对象,可以级联选择)
print(soup.head.title) # <title>BeautifulSoup Test</title>关联节点选择
| 操作 | 返回类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| soup.tag.contents | <class ‘list’> | 返回元素直接子节点 |
| soup.tag.children | <class ‘list_iterator’> | 返回元素直接子节点 |
| soup.tag.descendants | <class ‘generator’> | 返回元素子孙节点 |
| soup.tag.parent | <class ‘bs4.element.Tag’> | 返回元素父节点 |
| soup.tag.parents | <class ‘generator’> | 返回元素祖先节点 |
| soup.tag.next_sibling | 根据情况返回标签、文本、None等 | 返回元素后面第一个兄弟节点 |
| soup.tag.next_siblings | <class ‘generator’> | 返回元素后面所有兄弟节点 |
| soup.tag.previous_sibling | 根据情况返回标签、文本、None等 | 返回元素前面第一个兄弟节点 |
| soup.tag.previous_siblings | <class ‘generator’> | 返回元素前面所有兄弟节点 |
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<html lang="en">
<head><title>BeautifulSoup Test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="mainInfo">There are three cats, their names are
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_white" class="cat" id="little_white">小白</a>,
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_red" class="cat" id="little_red">小红</a> and
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" class="cat" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>;
story over!
</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
# 以列表形式返回直接子节点(['There are three cats, their names are\n ', <a id="little_white">小白</a>, ',\n ', <a id="little_red">小红</a>, ' and\n ', <a id="little_blue">小蓝</a>, ';\n story over!\n '])
print(soup.p.contents)
# 以迭代器形式返回直接子节点
print(soup.p.children) # <list_iterator object at 0x0000027591E18130>
for obj in soup.p.children:
print(obj)
for i,obj in enumerate(soup.p.children):
print(i,obj)
# 以生成器形式返回子孙节点
print(soup.p.descendants)
for i,obj in enumerate(soup.p.descendants):
print(i,obj)
# 返回第一个a元素的父节点
print(soup.a.parent)
print(type(soup.a.parent)) # <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
# 返回第一个a元素的祖先节点
for i,obj in enumerate(soup.a.parents):
print(i,obj)
print(type(soup.a.parents)) # <class 'generator'>
# 返回第一个a元素前面的第一个兄弟节点
print(soup.a.previous_sibling) # There are three cats, their names are
# 返回第一个a元素的所有后续兄弟节点
for i,obj in enumerate(soup.a.next_siblings):
print(i,obj)CSS选择器
BeautifulSoup使用select()方法结合CSS选择器语法实现元素定位。
soup.select(css选择)标签选择器
<p>hello world<p>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
soup.select("p")id选择器
<p id="info">hello world<p>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
soup.select("#info")class选择器
<p class="font20">hello world<p>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
soup.select(".font20")子元素选择器
<div>
<span>div span</span>
<p>
<span>div p span</span>
<p>
</div>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
soup.select("div span")
soup.select("div > span")属性选择器
<p class="ele">info</p>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
soup.select("p[class='ele']")CSS选择器实例
html_str = """
<div class="wrap">
<div class="heading">
<h2>title information</h2>
</div>
<div class="content">
<ul class="list" id="list-main">
<li class="item">li1-1</li>
<li class="item">li1-2</li>
<li class="item">li1-3</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-follow">
<li class="item">li2-1</li>
<li class="item">li2-2</li>
<li class="item">li2-3</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
# 1、获取所有li元素
print(soup.select("li"))
# 2、获取第二个ul的li子节点
print(soup.select("#list-follow li"))
# 3、获取class='heading'的div
print(soup.select(".heading"))
# 4、获取<li class="item">li2-2</li> 可通过索引和选择器获取子元素
print(soup.select("#list-follow li")[1])
print(soup.select("#list-follow li:nth-of-type(2)"))select()返回类型
# 通过css选择器获取内容的步骤:
# 1、soup.select() 返回的结果是bs4.element.ResultSet
# 2、若想取到某一个元素的话,需要通过索引或切片进行选择(bs4.element.Tag)
# 3、只有bs4.element.Tag类型的对象才能获取文本或属性值
<ul class="list" id="list-main">
<li class="item">li1-1</li>
<li class="item">li1-2</li>
<li class="item">li1-3</li>
</ul>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
# soup.select()返回的是bs4.element.ResultSet,可以通过遍历实现数据获取
print(type(soup.select("li"))) # <class 'bs4.element.ResultSet'>
# 获取第二个li元素
print(soup.select("li")[1]) # <li class="item">li1-2</li>
print(type(soup.select("li")[1])) # <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>通过select()返回的结果为ResultSet,需要通过索引才可以获取Tag对象;只有Tage对象才可提取内容
CSS选择器获取属性
<p class="ele">info</p>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
print(soup.select("p")[0].attrs)CSS选择器获取文本
html_str = """
<main>
<div>
<p> main div p </p>
</div>
<p>main p</p>
</main>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
print(soup.select("p")[0].text)函数选择器
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| soup.find(name, attrs, recursive, text, **kwargs) | 获取第一个满足条件的元素 |
| soup.find_all(name, attrs, recursive, text, limit, **kwargs) | 获取所有满足条件的元素 |
find()
搜索并返回第一个满足条件的元素,返回形式为Tag对象。
- name属性(查找所有名字为name的节点<tag对象>)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<html lang="en">
<head><title>BeautifulSoup Test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="mainInfo">There are three cats, their names are
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_white" class="cat" id="little_white">小白</a>,
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_red" class="cat" id="little_red">小红</a> and
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" class="cat" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>;
story over!
</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
print(soup.find("title")) # <title>BeautifulSoup Test</title>
print(type(soup.find("title"))) # <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
# 当文本中存在多个元素时,返回第一个满足查询的元素
print(soup.find("a")) # <a class="cat" href="http://baidu.com/little_white" id="little_white">小白</a>- attrs属性(通过属性进行查询,属性以字典的形式提供)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<html lang="en">
<head><title>BeautifulSoup Test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="mainInfo">There are three cats, their names are
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_white" class="cat" id="little_white">小白</a>,
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_red" class="cat" id="little_red">小红</a> and
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" class="cat" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>;
story over!
</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
# {'href': 'http://baidu.com/little_white', 'class': ['cat'], 'id': 'little_white'}
print(soup.find("a", attrs={"id":"little_blue","class":"cat"})) - kwargs属性(通过属性进行查询,属性以属性=属性值的方式提供)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<html lang="en">
<head><title>BeautifulSoup Test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="mainInfo">There are three cats, their names are
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_white" class="cat" id="little_white">小白</a>,
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_red" class="cat" id="little_red">小红</a> and
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" class="cat" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>;
story over!
</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
print(soup.find("a", id="little_blue")) # <a class="cat" href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>
print(soup.find("a", id= "little_blue",class_="cat")) # 多属性书写方法采用dwargs方式时,当属性与python关键字冲突时,属性采用追加下划线的方式。如class -> class_
- text属性(通过文本查询)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<body>
<span>小白</span>
<p>
<a href="1.html">小白</a>
<a href="2.html">小红</a>
</p>
</body>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
print(soup.find(text="小白")) # 小白
print(soup.find("a", text="小白")) # <a href="1.html">小白</a>
print(soup.find(True, text="小白")) # <span>小白</span>(只返回第一个满足条件的对象)name属性为True表示在所有元素中进行查询
- recursive属性(设置是否搜索子孙节点,默认为True)
print(soup.find("a", recursive=False))find_all()
用于搜索当前节点下所有符合条件的节点,若未指定当前节点,就进行全文搜索
- name属性(查找所有名字为name的节点<tag对象>)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<html lang="en">
<head><title>BeautifulSoup Test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="mainInfo">There are three cats, their names are
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_white" class="cat" id="little_white">小白</a>,
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_red" class="cat" id="little_red">小红</a> and
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" class="cat" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>;
story over!
</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,'lxml')
# 1、name为字符串时是通过标签名查找
print(soup.find_all("a"))
print(type(soup.find_all("a"))) # <class 'bs4.element.ResultSet'>
# 2、name为列表时,表示与列表任意一项匹配,并以列表形式返回
print(soup.find_all(["a","head"]))
print(type(soup.find_all(["a","head"]))) # <class 'bs4.element.ResultSet'>
# 3、name为True时表示查询所有
print(soup.find_all(True))
print(type(soup.find_all(True))) # <class 'bs4.element.ResultSet'>
# 4、通过索引获取标签
a_list = soup.find_all("a")[1]
print(a_list)
# 5、通过切片获取标签
a_list2 = soup.find_all(("a"))[:2]
print(a_list2)- attrs属性(通过属性进行查询,属性以字典的形式提供)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<html lang="en">
<head><title>BeautifulSoup Test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="mainInfo">There are three cats, their names are
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_white" class="cat" id="little_white">小白</a>,
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_red" class="cat" id="little_red">小红</a> and
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" class="cat" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>;
story over!
</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all("a", attrs={"class": "cat"}))- kwargs属性(通过属性进行查询,属性以属性=属性值的方式提供)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<html lang="en">
<head><title>BeautifulSoup Test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="mainInfo">There are three cats, their names are
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_white" class="cat" id="little_white">小白</a>,
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_red" class="cat" id="little_red">小红</a> and
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" class="cat" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>;
story over!
</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all("a", id="little_white"))
print(soup.find_all("a", class_="cat"))
print(soup.find_all("a", id=True)) # 获取所有具有id属性的a标签采用dwargs方式时,当属性与python关键字冲突时,属性采用追加下划线的方式。如class -> class_
- text属性(通过文本查询)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<html lang="en">
<head><title>BeautifulSoup Test</title></head>
<body>
<span>小白</span>
<p class="mainInfo">There are three cats, their names are
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_white" class="cat" id="little_white">小白</a>,
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_red" class="cat" id="little_red">小红</a> and
<a href="http://baidu.com/little_blue" class="cat" id="little_blue">小蓝</a>;
story over!
</p>
</body>
</html>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(text="小白")) # ['小白', '小白']
print(soup.find_all(True, text="小白"))
print(soup.find_all("a", text="小白"))- limit属性(限制返回条数)
print(soup.find_all("a", limit=1))- recursive属性(设置是否搜索子孙节点,默认为True)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<body>
<div>
<a href="sina.com">百度</a>
<p>
<a href="sina.com">新浪</a>
<a href="aliyun.com">阿里</a>
</p>
</div>
</body>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
print(soup.find("div").find_all("a")) # [<a href="baidu.com">百度</a>, <a href="sina.com">新浪</a>, <a href="aliyun.com">阿里</a>]
print(soup.find("div").find_all("a",recursive=False)) # [<a href="baidu.com">百度</a>]提取信息
首先通过选择器获取Tag对象,然后采用表格中的属性提取相关信息
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| soup.tag.name | 获取元素名称 |
| soup.tag.attrs | 获取元素属性 |
| soup.tag.string | 获取元素文本 |
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<body>
<span>小白</span>
<p>
<a href="1.html" class="cat">Mary</a>
<a href="2.html" id="tar">Lucy</a>
</p>
</body>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
# 返回标签名字
print(soup.p.a.name) # a 通过节点选择器获取标签名
print(soup.select("p a")[0].name) # a 通过CSS选择器获取标签名
print(soup.find("a").name) # a 通关函数选择器获取标签名
# 返回标签属性
print(soup.p.a.attrs) # {'href': '1.html', 'class': ['cat']} 通过节点选择器获取标签属性
print(soup.select("p a")[0].attrs) # {'href': '1.html', 'class': ['cat']} 通过CSS选择器获取标签属性
print(soup.find("a").attrs) # {'href': '1.html', 'class': ['cat']} 通过函数选择器获取标签属性
# 返回标签文本
print(soup.p.a.string) # Mary 通过节点选择器获取标签属性
print(soup.select("p a")[0].string) # Mary} 通过CSS选择器获取标签属性
print(soup.find("a").string) # Mary 通过函数选择器获取标签属性返回class为一个列表,这是因为一个标签可以设置多个class取值
获取属性值
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| [attribute] | img[‘src’] |
| attrs[attribute] | img.attrs[‘src’] |
| get(attribute) | img.get(“src”) |
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<body>
<span>小白</span>
<p>
<a href="1.html" class="cat">Mary</a>
<a href="2.html" id="tar">Lucy</a>
</p>
</body>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str,"lxml")
a_list = soup.find_all("a")
# 方法1:通过属性获取
for obj in a_list:
print(obj['href'])
# 方法2:通过attrs[]方法获取
for obj in a_list:
print(obj.attrs['href'])
# 方法3:通过get()方法获取
for obj in a_list:
print(obj.get('href'))获取文本
| 属性/方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| string | 获取目标路径下第一个非标签字符串,返回字符串 |
| text | 获取目标路径下的子孙非标签字符串,返回字符串 |
| strings | 获取目标路径下所有的子孙非标签字符串,返回生成器 |
| stripped_strings | 获取目标路径下所有的子孙非标签字符串,会自动去掉空白字符串,返回生成器 |
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_str = '''
<body>
<span>百度</span>
<p>hello
<a href="sina.com" class="cat">新浪</a>
<a href="aliyun.com" id="tar">阿里</a>
</p>
</body>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_str, 'lxml')
# 当元素内包含多个子节点时,string无法判别返回哪个节点的文本,结果为None
print(soup.find("span").string) # 百度
print(soup.find("p").string) # None
# text返回所有子孙节点的文本
print(soup.find("span").text) # 百度
'''
hello
新浪
阿里
'''
print(soup.find("p").text)
# strings和stripped_strings都返回子孙节点的文本,stripped_strings会自动去除空白字符
for info in soup.find("p").strings:
print(info)
for info1 in soup.find("p").stripped_strings:
print(info1)练习
中国水果交易网(获取品种、产地、价格、日期信息) :https://www.guo68.com/market
图片下载:http://www.netbian.com/weimei/
Xpath
XPath 是一门在 XML 文档中查找信息的语言。XPath 使用路径表达式来选取 XML 文档中的节点或者节点集。这些路径表达式和我们在常规的电脑文件系统中看到的表达式非常相似。
依赖库安装
pip install bs4 -i https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple节点选取
| 表达式 | 描述 | 用法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodename | 选取此节点的所有子节点 | div | 选取div的所有子标签 |
| / | 从根节点选取 | //head/title | 选择head下的title标签 |
| // | 从全局节点中寻找节点,忽略位置 | //div | 选取html页面所有div标签 |
| . | 选取当前节点 | ./span | 选择当前节点下所有span标签 |
| … | 选取当前节点的父节点 | …/span | 父节点下所有span标签 |
| @ | 选取属性 | //div[@id] | 选择所有带id属性的div标签 |
'''
<main id="wrap">
<title>手机促销</title>
<div>
<title id='first'>华为nova7</title>
<strong class="low_price">2598</strong>
</div>
<div>
<title>OPPO Find X5</title>
<strong>6299</strong>
</div>
<div>
<title>Redmi 8100</title>
<strong class="low_price">2550</strong>
</div>
<p>gehehw</p>
</main>
'''
//div # 查找文档中的全部div标签
//div/title # 查找文档中的div下的所有title标签
//*[@id] # 查找所有具有id属性的标签
//div/strong[@class="low_price"] # 查找div下所有class="low_price"的strong标签
//main/title # 获取main标签下的title子标签 (<title>手机促销</title>)通过节点获取的是标签的内容
XPath路径
XPath路径分为绝对路径和相对路径
-
绝对路径:绝对路径从 HTML 根节点开始算,当页面较为复杂时,书写起来比较繁琐;
-
相对路径:相对路径从任意节点开始,通常会选取一个可以唯一定位到的元素开始写,可以增加查找的准确性。通常以"//"开头
# 绝对路径(按层级找到元素)
/html/body/div[2]/div/div/div/div/form/span/input
# 相对路径(选在id='nav-small'的div下所有p元素)
//div[@id='nav-small']/p谓语
谓语用来查找某个特定的节点或者包含某个指定的值的节点,谓语被嵌在方括号中。
| 表达式 | 用法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| tag[index] | //div/a[1] | 选择div下第一个a标签,需要从1开始 |
| tag[last()] | //div/a[last()] | 选择div下最有一个a标签 |
| tag[position()??] | //div/a[position()??] | 选择div下前两个a标签 |
| [tag>3] | //div[p>10]/p | 选择div下所有p元素,并且p元素取值大于10 |
谓语索引从1开始
'''
<main id="wrap">
<title>手机促销</title>
<div>
<title id='first'>华为nova7</title>
<strong class="low_price">2598</strong>
</div>
<div>
<title>OPPO Find X5</title>
<strong>6299</strong>
</div>
<div>
<title>Redmi 8100</title>
<strong class="low_price">2550</strong>
</div>
<p>gehehw</p>
</main>
'''
# 获取所有title元素
titles = html.xpath("//main//title")
titles2 = html.xpath("//title")
titles3 = html.xpath("//*[@id='wrap']//title")
# 获取<strong class="low_price">2550</strong>
//main/div[3]/strong
# 获取<strong>6299</strong>
# //main/div[strong>5000]取出的是div元素,[strong>5000]作为div的限定条件
//main/div[strong>5000]/strong谓语中的序号
'''
<main>
<p>游泳</p>
<p>爬山</p>
<p>跑步</p>
<main>
'''
//p # 获取所有p元素
//p[2] # 获取第二个p元素 (<p>爬山</p>)
'''
<main>
<div>
<p>拳击</p>
</div>
<div>
<p>游泳</p>
</div>
<main>
'''
//p # 获取所有p元素
//p[1] # 获取<p>拳击</p> <p>游泳</p>
str = '''
<main>
<div>
<p>拳击</p>
<p>游泳</p>
</div>
<main>
'''
//p # 获取所有p元素
//p[1] # 获取<p>拳击</p>XPath谓语是按层级关系返回,在实际开发中谨慎使用
通配符
| 通配符 | 描述 | 示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| * | 匹配任意元素节点 | //div[@id=“tar”]/* | 选择id="tar"的div标签下所有元素节点 |
| @* | 匹配任意属性节点 | //a[@*] | 选择所有拥有属性的a标签 |
//p/* # 选取p元素的所有子元素
//* # 选取文档中的所有元素
//a[@*] # 选取所有带有属性的a元素
//div[@id="tar"]/* # 选择id="tar"的div标签下的所有节点多路径选择
通过在路径表达式中使用“|”运算符,您可以选取若干个路径
//div/p | //div/a # 选取div元素的所有p和a元素
//p | //div # 选取文档中的所有p和div元素
//p[@id]/a | //div # 选取所有具有id属性p元素下的a元素,以及所有的div元素属性值/文本
| 表达式 | 描述 | 示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| text() | 获取文本 | //meta | //p | 获取所有的meta标签和p标签 |
| /@ | 获取属性值 | //a/@href | 获取a标签的href属性值 |
html_str = '''
<tr class="hobits">
<td id="hobit1">游泳</td>
<td id="hobit2">爬山</td>
<td id="hobit3">跑步</td>
<td id="hobit4">击剑</td>
<td id="hobit5">射击</td>
</tr>
'''
# 获取爬山
//td[@id="hobit2"]/text()
# 获取hobit3
//td[3]/@id内容解析
XPath不能直接解析字符串,要先将html文本转为html对象,然后再解析。
html字符串(requests获取的结果) -> html -> XPath解析
html字符串由requests库通过请求获取,html对象通过lxml库中的etree实现,内容提取由XPath实现
创建html对象
html对象可通过字符串和文件方式创建。
字符串创建html对象(常用)
html_str = '''
<tr class="hobits">
<td id="hobit1">游泳</td>
<td id="hobit2">爬山</td>
<td id="hobit3">跑步</td>
<td id="hobit4">击剑</td>
<td id="hobit5">射击</td>
</tr>
'''
from lxml import etree
# etree会将文本转为html结构,并补全必要的内容
html = etree.HTML(html_str)
print(html) # <Element html at 0x27724813980>
# html对象本身无法以文本形式打印,可通过下列方式获取文本内容
info = etree.tostring(html,encoding="utf-8").decode("utf-8")
print(info)文件创建html对象
# 采用该方法要求本地html文件完全遵循xml语法(例如标签必须封闭等)
from lxml import etree
# 根据实际情况更改文件路径
html = etree.parse("index.html")
print(html)
result = etree.tostring(html,encoding="utf-8").decode("utf-8")
print(result)将网页下载到本地,然后通过本地加载的方式进行解析,通常会报错。
通过指定解析器创建html对象
from lxml import etree
# 创建解析器
parser = etree.HTMLParser(encoding="utf-8")
# 为parse指定解析器
html = etree.parse("../files/index.html",parser=parser)
result = etree.tostring(html,encoding="utf-8").decode("utf-8")
print(result)通过指定解析器的方法可以修正本地html文件结构,确保解析正确。
通过XPath获取百度信息
import requests
from lxml import etree
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/86.0.4240.198 Safari/537.36"
}
resp = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
page_text = resp.text
# 方法1:通过拼接方式获取
# html = etree.HTML(page_text)
#
# info_list = html.xpath('//div[@id="s-top-left"]/a/text()')
# href_list = html.xpath('//div[@id="s-top-left"]/a/@href')
#
# reslut = []
# for info, href in zip(info_list, href_list):
# eg = {
# "info": info,
# "href": href
# }
# reslut.append(eg)
# print(reslut)
# 方法2:逐层获取
result_list = []
html = etree.HTML(page_text)
elements = html.xpath('//div[@id="s-top-left"]/a')
for aobj in elements:
info = aobj.xpath("./text()")[0]
href = aobj.xpath("./@href")[0]
eg = {
"info": info,
"href": href
}
result_list.append(eg)
print(result_list)xpath()函数返回的结果为列表,可以通过索引或切片的方式获取列表中的部分内容。
通常情况下使用XPath语法获取整体内容,然后通过索引或切片方式过滤需求内容,对于需求内容过滤要谨慎使用XPath谓语语法(谓语语法是按层次获取)
伪元素内容抓取
//span/following::text()[1] #获取::after伪元素多页内容抓取
# 爬取多记录时,过滤掉规则不同的页面
for url in page:
try:
#...
except:
continue练习
抓取微博热搜的标题和热度信息:https://s.weibo.com/top/summary
PyMySQL
概述
PyMySQL 是在 Python3.x 版本中用于连接 MySQL 服务器的一个库。
PyMySQL安装
pip install pymysql -i https://pypi.douban.com/simplePyMySQL操作流程
导入包 -> 创建连接对象 -> 获取游标对象 -> 执行sql语句 -> 【获取查询结果集(查询) | 将修改数据提交到数据库/回滚数据(增删改)】 -> 关闭资源(游标与连接)
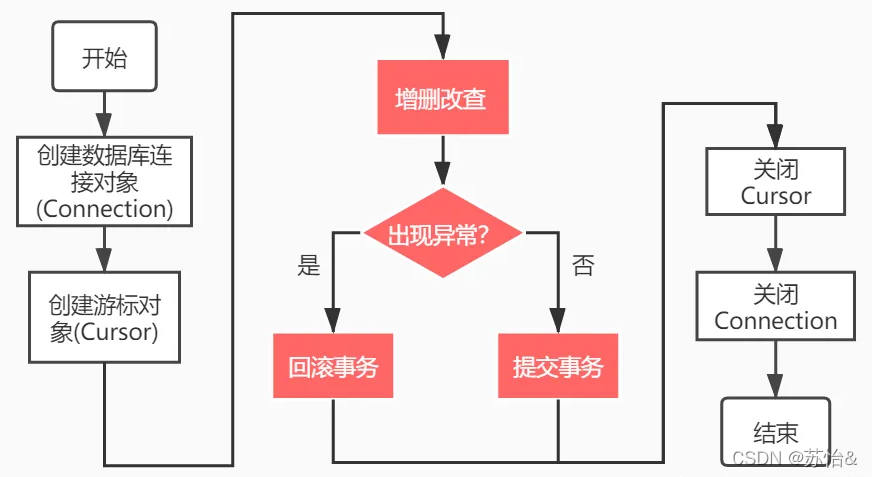
导入包
import pymysql创建连接对象
'''
host:指定服务器ip地址,本机为localhost
port:指定mysql端口号,默认3306
user:指定用户名
password:指定密码
database:指定数据库名
charset:指定字符集(注:utf8,不是utf-8)
'''
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()执行sql获取结果
'''
增删改查操作sql语句执行语法均相同
查询语句根据返回结果记录条数,使用fetchone()或者fetchall()
增刪改操作返回结果为更改记录条数
'''
# 获取查询结果
curosr.execute(sql)
obj = cursor.fetchone() # 获取单一结果(配合where语句)
obj_list = cursor.fetchall() # 获取满足查询条件的所有记录
# 获取增删改结果
row_count = cursor.execute(sql)关闭资源
# 关闭资源包括游标对象和连接对象
cursor.close()
conn.close()查询操作
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| fetchone() | 根据查询条件获取一条记录(通常配合where语句) |
| fetchall() | 获取满足条件的所有记录 |
| fetchmany(size) | 获取满足条件的前size条记录 |
获取单一记录
# 1、导入包
import pymysql
# 2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 4、准备sql
sql = f"select * from products where prod_id ='BR03'"
# 5、执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 6、获取结果
product_obj = cursor.fetchall()
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(product_obj)获取所有记录
# 1、导入包
import pymysql
# 2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 4、准备sql
sql = "select * from products"
# 5、执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 6、获取结果
stu_list = cursor.fetchall()
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
for obj in stu_list:
print(obj)获取部分记录
import pymysql
# 2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 4、准备sql
sql = f"select * from products"
# 5、执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 6、获取结果
product_list = cursor.fetchmany(3)
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
for obj in product_list:
print(obj)增加操作
# 1、导入包
import pymysql
# 2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 4、准备sql
sql = "insert into orders values ('20012',now(),'1000000001')"
# 5、执行sql语句
try:
row = cursor.execute(sql) # 6、获取结果
conn.commit() # 提交事务(若不提交新增不生效)
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback() # 操作失败要回滚
finally:
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(row)修改操作
# 1、导入包
import pymysql
# 2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 4、准备sql
sql = "update orders set cust_id = '1000000005' where order_num = '20012'"
# 5、执行sql语句
try:
row = cursor.execute(sql) # 6、获取结果
conn.commit() # 提交事务(若不提交新增不生效)
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback() # 操作失败要回滚
finally:
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(row)删除操作
# 1、导入包
import pymysql
# 2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 4、准备sql
sql = "delete from orders where order_num = '20012'"
# 5、执行sql语句
try:
row = cursor.execute(sql) # 6、获取结果
conn.commit() # 提交事务(若不提交新增不生效)
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback() # 操作失败要回滚
finally:
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(row)sql注入
用户提交带有恶意的数据与sql语句进行字符串拼接,从而影响了sql语句的语义,最终产生数据数据泄露的现象。
# 1、导入包
import pymysql
# 2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 4、准备sql(条件成立即可实现查询)
sql = "select * from orders where order_num = '20009' or '1==1' "
# 5、执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
info_list = cursor.fetchall()
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(info_list防止sql注入的方法
-
sql语句中使用%s占位,此处不是python字符串格式化操作。
-
将sql语句中的%s占位所需要的参数存在一个列表中,把参数列表传递给excute方法中的第二个参数
单一参数
# 1、导入包
import pymysql
# 2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 4、准备sql
sql = "select * from orders where order_num = %s"
# 5、执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql, "20009")
order_obj = cursor.fetchone()
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(order_obj)多参数
# 1、导入包
import pymysql
# 2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 4、准备sql
sql = "insert into orders values(%s,%s,%s)"
# 5、执行sql语句
try:
count = cursor.execute(sql, ("20010", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", time.localtime(time.time())), "1000000001"))
conn.commit() # 提交事务(若不提交新增不生效)
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback() # 操作失败要回滚
finally:
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(count)模板
查询模板
import pymysql
# 创建连接(根据实际情况为变量赋值)
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 准备sql(根据业务逻辑编写sql语句)
sql = "select * from products"
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 获取结果(根据需求在fetchone()、fetchall()和fetchmany(count)中选择一个进行查询操作)
product_obj = cursor.fetchone()
# product_list_all = cursor.fetchall()
# product_list_many = cursor.fetchmany(2)
# 关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
# 执行后续业务逻辑
for obj in product_list_all:
print(obj)若语句中存在where语句,需要采用%s进行变量占位,防止sql注入的产生
增删改模板
import pymysql
# 创建连接(根据实际情况为变量赋值)
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 准备sql(根据业务逻辑编写新增、修改或删除sql语句)
sql = "insert into orders values (%s,%s,%s)"
# sql = "update orders set cust_id = %s where order_num = %s"
# sql = "delete from orders where order_num = %s"
# 执行sql语句
try:
count = cursor.execute(sql, ("20010", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", time.localtime(time.time())), "1000000001"))
conn.commit() # 提交事务(若不提交新增不生效)
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback() # 操作失败要回滚
finally:
cursor.close() # 关闭资源
conn.close()
print(count)若语句中存在动态信息,需要采用%s进行变量占位,防止sql注入的产生
导入包
import pymysql
2、创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=“localhost”,
port=3306,
user=“root”,
password=“root”,
database=“test”,
charset=“utf8”
)
3、获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
4、准备sql
sql = “insert into orders values(%s,%s,%s)”
5、执行sql语句
try:
count = cursor.execute(sql, (“20010”, time.strftime(“%Y-%m-%d”, time.localtime(time.time())), “1000000001”))
conn.commit() # 提交事务(若不提交新增不生效)
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback() # 操作失败要回滚
finally:
# 7、关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
print(count)
### 模板
**查询模板**
```python
import pymysql
# 创建连接(根据实际情况为变量赋值)
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 3获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 准备sql(根据业务逻辑编写sql语句)
sql = "select * from products"
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
# 获取结果(根据需求在fetchone()、fetchall()和fetchmany(count)中选择一个进行查询操作)
product_obj = cursor.fetchone()
# product_list_all = cursor.fetchall()
# product_list_many = cursor.fetchmany(2)
# 关闭资源
cursor.close()
conn.close()
# 执行后续业务逻辑
for obj in product_list_all:
print(obj)
若语句中存在where语句,需要采用%s进行变量占位,防止sql注入的产生
增删改模板
import pymysql
# 创建连接(根据实际情况为变量赋值)
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="localhost",
port=3306,
user="root",
password="root",
database="test",
charset="utf8"
)
# 获取游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 准备sql(根据业务逻辑编写新增、修改或删除sql语句)
sql = "insert into orders values (%s,%s,%s)"
# sql = "update orders set cust_id = %s where order_num = %s"
# sql = "delete from orders where order_num = %s"
# 执行sql语句
try:
count = cursor.execute(sql, ("20010", time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", time.localtime(time.time())), "1000000001"))
conn.commit() # 提交事务(若不提交新增不生效)
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback() # 操作失败要回滚
finally:
cursor.close() # 关闭资源
conn.close()
print(count)若语句中存在动态信息,需要采用%s进行变量占位,防止sql注入的产生