绝对布局
每个程序都是以像素为单位区分元素的位置,衡量元素的大小。所以我们完全可以使用绝对定位搞定每个元素和窗口的位置。但是这也有局限性:
- 元素不会随着我们更改窗口的位置和大小而变化。
- 不能适用于不同的平台和不同分辨率的显示器
- 更改应用字体大小会破坏布局
- 如果我们决定重构这个应用,需要全部计算一下每个元素的位置和大小
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget,QLabel,QApplication
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
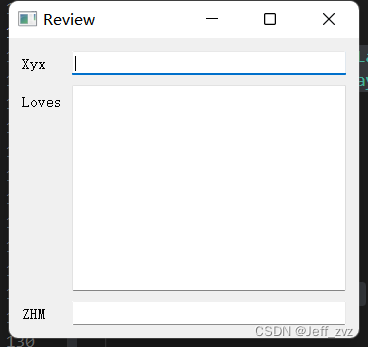
lb1 =QLabel('ZHM',self)
lb1.move(15,15)
lb2 = QLabel('XYX',self)
lb2.move(35,35)
lb3 =QLabel('Love Forever',self)
lb3.move(55,55)
self.setGeometry(300,300,250,250)
self.setWindowTitle('Absolute layout')
self.show()
if __name__=='__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
说明:
QLabel()创建布局标签
效果:
盒布局
使用盒布局能让程序具有更强的适应性。这个才是布局一个应用的更合适的方式。QHBoxLayout和QVBoxLayout是基本的布局类,分别是水平布局和垂直布局
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QPushButton,
QHBoxLayout, QVBoxLayout, QApplication)
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
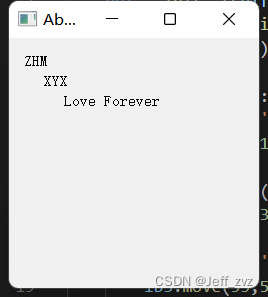
okbutton = QPushButton('OK',self)
cancelbutton =QPushButton('CANCEL',self)
hbox = QHBoxLayout()
hbox.addStretch(1) #增加弹性
hbox.addWidget(okbutton)
hbox.addWidget(cancelbutton)
vbox = QVBoxLayout()
vbox.addStretch(1)
vbox.addLayout(hbox)
self.setLayout(vbox)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Buttons')
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
说明:
hbox = QHBoxLayout()创建hbox对象hbox.addStretch(1)增加弹性空间,就是在两个控件间增加弹性。- 添加控件到hbox,他会将按钮都挤到窗口右边
vbox.addLayout(hbox)把水平布局放到垂直布局里
效果:
栅格布局
将窗口分为行和列
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QGridLayout,
QPushButton, QApplication)
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
grid = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(grid)
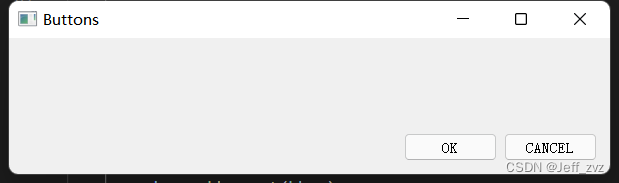
names = ['X', 'Y', '', 'X',
'I', 'LOVE', 'YOU', 'AND',
'I', 'WILL', 'MARRY', 'YOU',
'1', '2', '3', '-',
'0', '.', '=', '+']
positions = [(i,j) for i in range(5) for j in range(4)]
for position, name in zip(positions, names):
if name == '':
continue
button = QPushButton(name)
grid.addWidget(button, *position)
self.move(300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('GRID')
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
说明:
grid = QGridLayout()创建栅格布局对象self.setLayout(grid)窗口布局设置为栅格布局names为按钮内容positions为按钮位置,栅格位置zip函数将positions和names一一对应,组成元组。*为解运算符grid.addWidget(button, *position)将控件添加到(row,col)
效果:
栅格布局跨行跨列
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QLabel,QApplication,
QTextEdit,QLineEdit,QGridLayout,QWidget)
class Example(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
XYX = QLabel('Xyx')
LOVES =QLabel('Loves')
ZHM = QLabel('ZHM')
LOVESe = QTextEdit()
XYXe = QLineEdit()
ZHMe = QLineEdit()
grid = QGridLayout()
grid.setSpacing(10) #设置行距
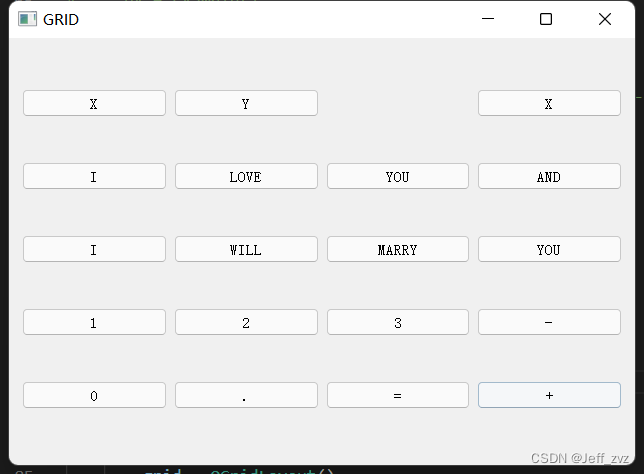
grid.addWidget(XYX,1,0)
grid.addWidget(XYXe,1,1)
grid.addWidget(LOVES,2,0)
grid.addWidget(LOVESe,2,1,5,1) #跨5行1列
grid.addWidget(ZHM,8,0)
grid.addWidget(ZHMe,8,1)
self.setLayout(grid)
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 300)
self.setWindowTitle('Review')
self.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
说明
grid.setSpacing(10)为各元素的行距grid.addWidget(LOVESe,2,1,5,1)从2行1列,跨到7行1列
效果: