安装模块
pycwt这个库在官方文档中没有提供conda的安装方法,官网推荐使用pip进行安装pip install pycwt。
但是,conda也可以用如下方法安装,推荐conda安装
conda install -c conda-forge/label/gcc7 pycwt
官网例子
https://github.com/regeirk/pycwt
"""
In this example we will load the NINO3 sea surface temperature anomaly dataset
between 1871 and 1996. This and other sample data files are kindly provided by
C. Torrence and G. Compo at
<http://paos.colorado.edu/research/wavelets/software.html>.
"""
# We begin by importing the relevant libraries. Please make sure that PyCWT is
# properly installed in your system.
from __future__ import division
import numpy
from matplotlib import pyplot
import pycwt as wavelet
from pycwt.helpers import find
# Then, we load the dataset and define some data related parameters. In this
# case, the first 19 lines of the data file contain meta-data, that we ignore,
# since we set them manually (*i.e.* title, units).
url = 'http://paos.colorado.edu/research/wavelets/wave_idl/nino3sst.txt'
dat = numpy.genfromtxt(url, skip_header=19)
title = 'NINO3 Sea Surface Temperature'
label = 'NINO3 SST'
units = 'degC'
t0 = 1871.0
dt = 0.25 # In years
# We also create a time array in years.
N = dat.size
t = numpy.arange(0, N) * dt + t0
# We write the following code to detrend and normalize the input data by its
# standard deviation. Sometimes detrending is not necessary and simply
# removing the mean value is good enough. However, if your dataset has a well
# defined trend, such as the Mauna Loa CO\ :sub:`2` dataset available in the
# above mentioned website, it is strongly advised to perform detrending.
# Here, we fit a one-degree polynomial function and then subtract it from the
# original data.
p = numpy.polyfit(t - t0, dat, 1)
dat_notrend = dat - numpy.polyval(p, t - t0)
std = dat_notrend.std() # Standard deviation
var = std ** 2 # Variance
dat_norm = dat_notrend / std # Normalized dataset
# The next step is to define some parameters of our wavelet analysis. We
# select the mother wavelet, in this case the Morlet wavelet with
# :math:`\omega_0=6`.
mother = wavelet.Morlet(6)
s0 = 2 * dt # Starting scale, in this case 2 * 0.25 years = 6 months
dj = 1 / 12 # Twelve sub-octaves per octaves
J = 7 / dj # Seven powers of two with dj sub-octaves
alpha, _, _ = wavelet.ar1(dat) # Lag-1 autocorrelation for red noise
# The following routines perform the wavelet transform and inverse wavelet
# transform using the parameters defined above. Since we have normalized our
# input time-series, we multiply the inverse transform by the standard
# deviation.
wave, scales, freqs, coi, fft, fftfreqs = wavelet.cwt(dat_norm, dt, dj, s0, J,
mother)
iwave = wavelet.icwt(wave, scales, dt, dj, mother) * std
# We calculate the normalized wavelet and Fourier power spectra, as well as
# the Fourier equivalent periods for each wavelet scale.
power = (numpy.abs(wave)) ** 2
fft_power = numpy.abs(fft) ** 2
period = 1 / freqs
# We could stop at this point and plot our results. However we are also
# interested in the power spectra significance test. The power is significant
# where the ratio ``power / sig95 > 1``.
signif, fft_theor = wavelet.significance(1.0, dt, scales, 0, alpha,
significance_level=0.95,
wavelet=mother)
sig95 = numpy.ones([1, N]) * signif[:, None]
sig95 = power / sig95
# Then, we calculate the global wavelet spectrum and determine its
# significance level.
glbl_power = power.mean(axis=1)
dof = N - scales # Correction for padding at edges
glbl_signif, tmp = wavelet.significance(var, dt, scales, 1, alpha,
significance_level=0.95, dof=dof,
wavelet=mother)
# We also calculate the scale average between 2 years and 8 years, and its
# significance level.
sel = find((period >= 2) & (period < 8))
Cdelta = mother.cdelta
scale_avg = (scales * numpy.ones((N, 1))).transpose()
scale_avg = power / scale_avg # As in Torrence and Compo (1998) equation 24
scale_avg = var * dj * dt / Cdelta * scale_avg[sel, :].sum(axis=0)
scale_avg_signif, tmp = wavelet.significance(var, dt, scales, 2, alpha,
significance_level=0.95,
dof=[scales[sel[0]],
scales[sel[-1]]],
wavelet=mother)
# Finally, we plot our results in four different subplots containing the
# (i) original series anomaly and the inverse wavelet transform; (ii) the
# wavelet power spectrum (iii) the global wavelet and Fourier spectra ; and
# (iv) the range averaged wavelet spectrum. In all sub-plots the significance
# levels are either included as dotted lines or as filled contour lines.
# Prepare the figure
pyplot.close('all')
pyplot.ioff()
figprops = dict(figsize=(11, 8), dpi=72)
fig = pyplot.figure(**figprops)
# First sub-plot, the original time series anomaly and inverse wavelet
# transform.
ax = pyplot.axes([0.1, 0.75, 0.65, 0.2])
ax.plot(t, iwave, '-', linewidth=1, color=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
ax.plot(t, dat, 'k', linewidth=1.5)
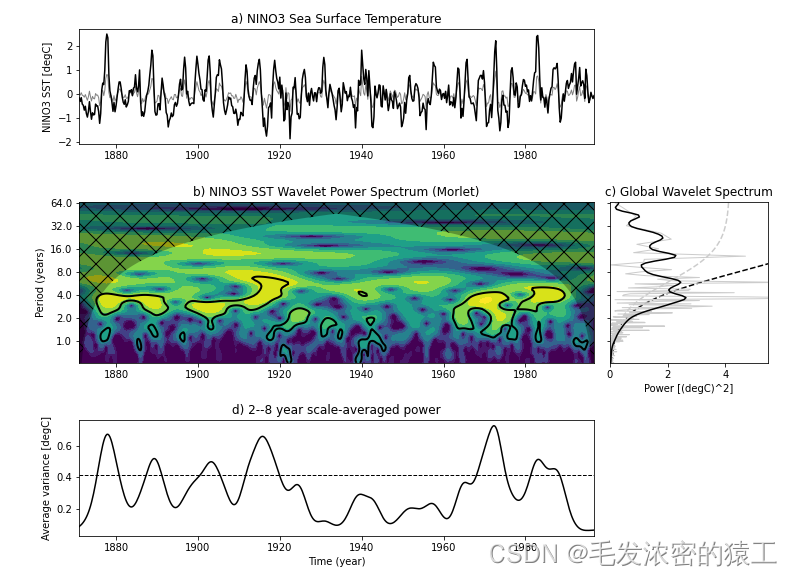
ax.set_title('a) {}'.format(title))
ax.set_ylabel(r'{} [{}]'.format(label, units))
# Second sub-plot, the normalized wavelet power spectrum and significance
# level contour lines and cone of influece hatched area. Note that period
# scale is logarithmic.
bx = pyplot.axes([0.1, 0.37, 0.65, 0.28], sharex=ax)
levels = [0.0625, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16]
bx.contourf(t, numpy.log2(period), numpy.log2(power), numpy.log2(levels),
extend='both', cmap=pyplot.cm.viridis)
extent = [t.min(), t.max(), 0, max(period)]
bx.contour(t, numpy.log2(period), sig95, [-99, 1], colors='k', linewidths=2,
extent=extent)
bx.fill(numpy.concatenate([t, t[-1:] + dt, t[-1:] + dt,
t[:1] - dt, t[:1] - dt]),
numpy.concatenate([numpy.log2(coi), [1e-9], numpy.log2(period[-1:]),
numpy.log2(period[-1:]), [1e-9]]),
'k', alpha=0.3, hatch='x')
bx.set_title('b) {} Wavelet Power Spectrum ({})'.format(label, mother.name))
bx.set_ylabel('Period (years)')
#
Yticks = 2 ** numpy.arange(numpy.ceil(numpy.log2(period.min())),
numpy.ceil(numpy.log2(period.max())))
bx.set_yticks(numpy.log2(Yticks))
bx.set_yticklabels(Yticks)
# Third sub-plot, the global wavelet and Fourier power spectra and theoretical
# noise spectra. Note that period scale is logarithmic.
cx = pyplot.axes([0.77, 0.37, 0.2, 0.28], sharey=bx)
cx.plot(glbl_signif, numpy.log2(period), 'k--')
cx.plot(var * fft_theor, numpy.log2(period), '--', color='#cccccc')
cx.plot(var * fft_power, numpy.log2(1./fftfreqs), '-', color='#cccccc',
linewidth=1.)
cx.plot(var * glbl_power, numpy.log2(period), 'k-', linewidth=1.5)
cx.set_title('c) Global Wavelet Spectrum')
cx.set_xlabel(r'Power [({})^2]'.format(units))
cx.set_xlim([0, glbl_power.max() + var])
cx.set_ylim(numpy.log2([period.min(), period.max()]))
cx.set_yticks(numpy.log2(Yticks))
cx.set_yticklabels(Yticks)
pyplot.setp(cx.get_yticklabels(), visible=False)
# Fourth sub-plot, the scale averaged wavelet spectrum.
dx = pyplot.axes([0.1, 0.07, 0.65, 0.2], sharex=ax)
dx.axhline(scale_avg_signif, color='k', linestyle='--', linewidth=1.)
dx.plot(t, scale_avg, 'k-', linewidth=1.5)
dx.set_title('d) {}--{} year scale-averaged power'.format(2, 8))
dx.set_xlabel('Time (year)')
dx.set_ylabel(r'Average variance [{}]'.format(units))
ax.set_xlim([t.min(), t.max()])
pyplot.show()