本文主要是以语义分割模型为例进行后处理操作以及图像可视化。
0.TensorBoard可视化效果
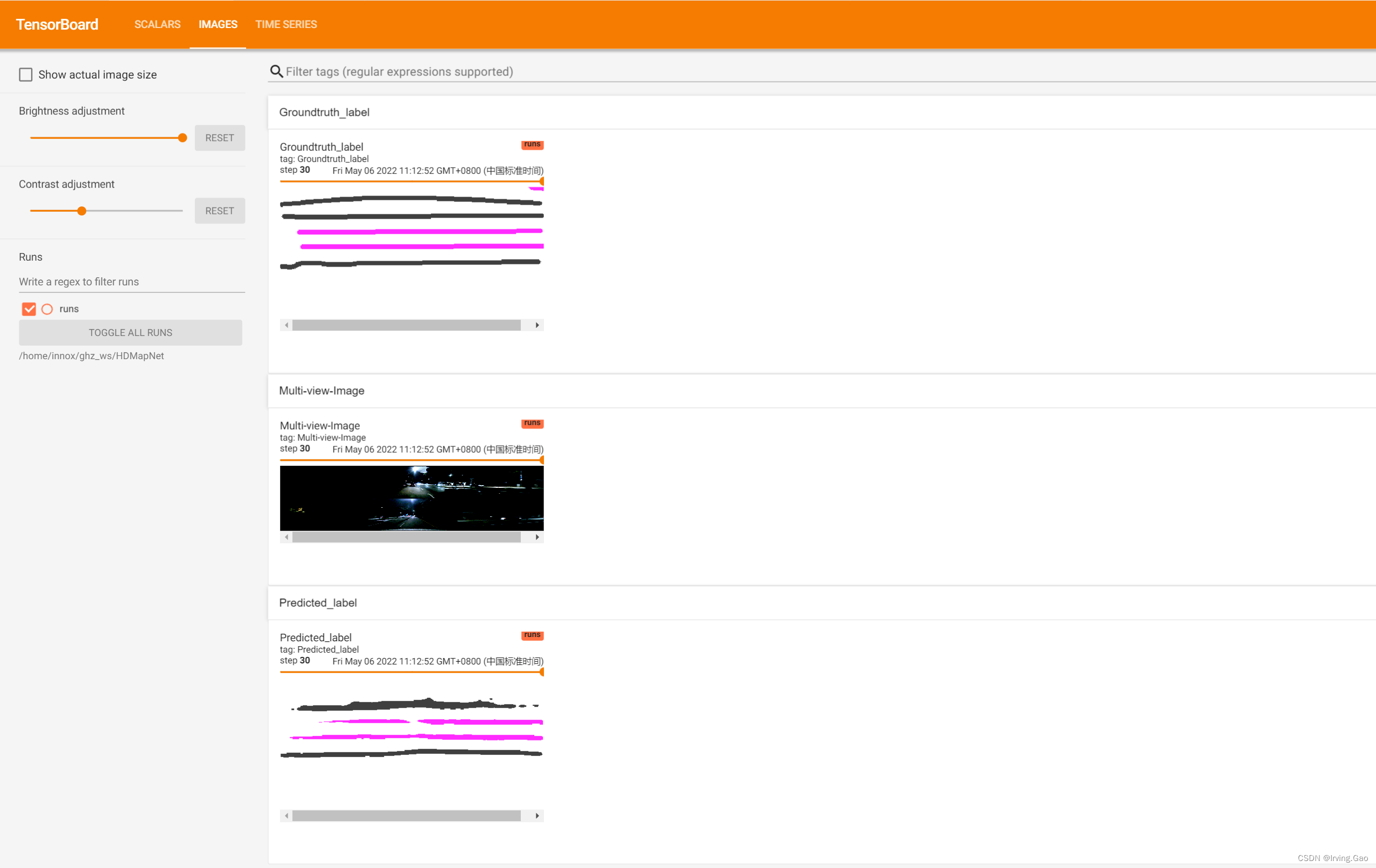
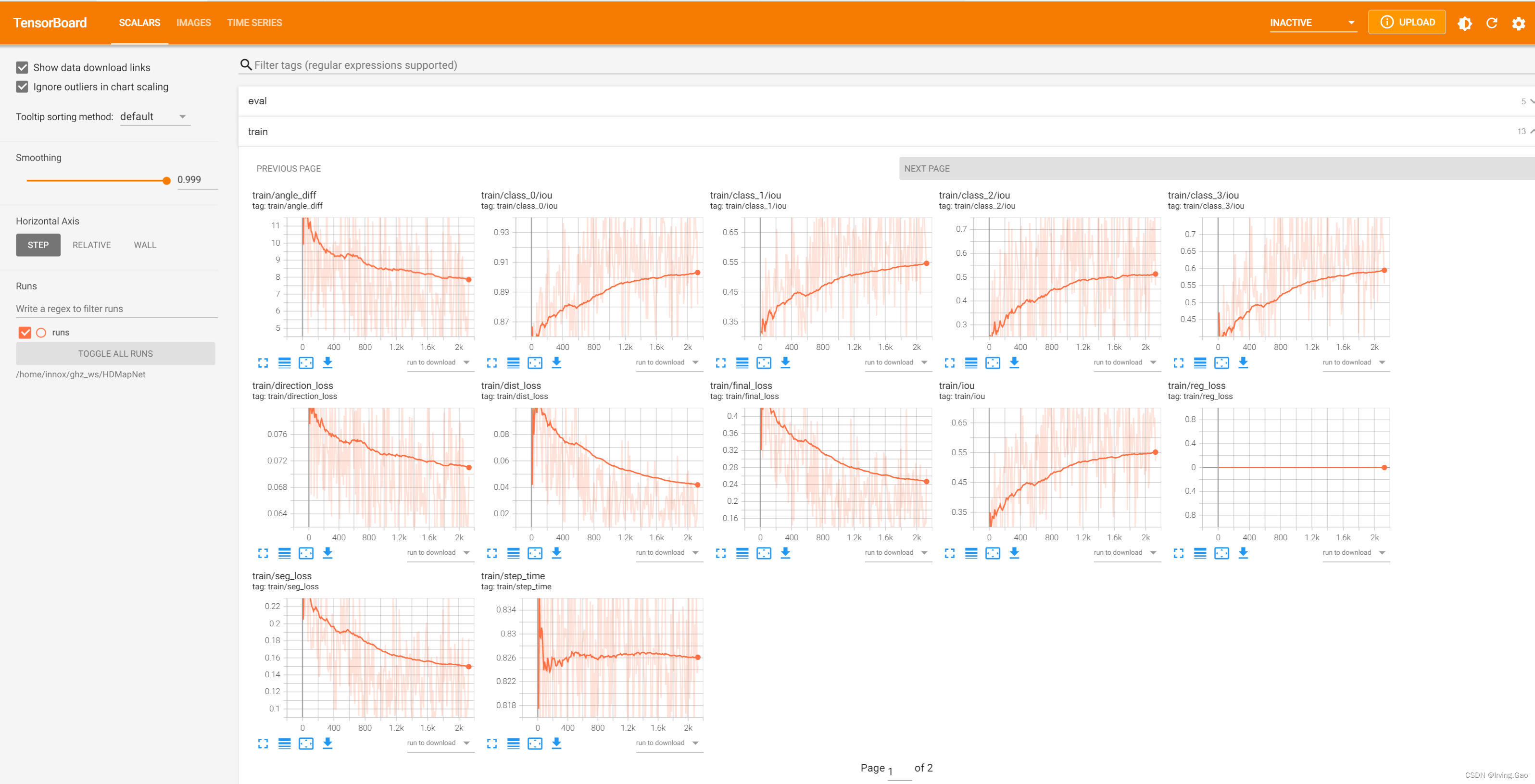
1. TensorBoard可视化配置
(1)TensorBoard初始化
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
writer = SummaryWriter(logdir=args.logdir)
(2)数值可视化
- 使用
writer.add_scalar()函数:
def add_scalar(
self,
tag: str,
scalar_value: Union[float, numpy_compatible],
global_step: Optional[int] = None,
walltime: Optional[float] = None,
display_name: Optional[str] = "",
summary_description: Optional[str] = ""):
"""Add scalar data to summary.
Args:
tag: Data identifier
scalar_value: Value to save, if string is passed, it will be treated
as caffe blob name.
global_step: Global step value to record
walltime: Optional override default walltime (time.time()) of event
display_name: The title of the plot. If empty string is passed,
`tag` will be used.
summary_description: The comprehensive text that will showed
by clicking the information icon on TensorBoard.
"""
在训练过程中,直接加入即可:
writer.add_scalar('train/step_time', batch_time, global_step)
(3)图像可视化
- 使用
writer.add_image()和torchvision.utils.make_grid()函数实现:torchvision.utils.make_grid()用来将Tensor或者是图像列表转换为一个可以直接被writer.add_image()使用的图像;writer.add_image()将torchvision.utils.make_grid()合成的图像进行可视化操作。
def make_grid(
tensor: Union[torch.Tensor, List[torch.Tensor]],
nrow: int = 8,
padding: int = 2,
normalize: bool = False,
value_range: Optional[Tuple[int, int]] = None,
scale_each: bool = False,
pad_value: int = 0,
**kwargs
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""Make a grid of images.
Args:
tensor (Tensor or list): 4D mini-batch Tensor of shape (B x C x H x W)
or a list of images all of the same size.
nrow (int, optional): Number of images displayed in each row of the grid.
The final grid size is ``(B / nrow, nrow)``. Default: ``8``.
padding (int, optional): amount of padding. Default: ``2``.
normalize (bool, optional): If True, shift the image to the range (0, 1),
by the min and max values specified by :attr:`range`. Default: ``False``.
value_range (tuple, optional): tuple (min, max) where min and max are numbers,
then these numbers are used to normalize the image. By default, min and max
are computed from the tensor.
scale_each (bool, optional): If ``True``, scale each image in the batch of
images separately rather than the (min, max) over all images. Default: ``False``.
pad_value (float, optional): Value for the padded pixels. Default: ``0``.
"""
def add_image(
self,
tag: str,
img_tensor: numpy_compatible,
global_step: Optional[int] = None,
walltime: Optional[float] = None,
dataformats: Optional[str] = 'CHW'):
"""Add image data to summary.
Note that this requires the ``pillow`` package.
Args:
tag: Data identifier
img_tensor: An `uint8` or `float` Tensor of shape `
[channel, height, width]` where `channel` is 1, 3, or 4.
The elements in img_tensor can either have values
in [0, 1] (float32) or [0, 255] (uint8).
Users are responsible to scale the data in the correct range/type.
global_step: Global step value to record
walltime: Optional override default walltime (time.time()) of event.
dataformats: This parameter specifies the meaning of each dimension of the input tensor.
Shape:
img_tensor: Default is :math:`(3, H, W)`. You can use ``torchvision.utils.make_grid()`` to
convert a batch of tensor into 3xHxW format or use ``add_images()`` and let us do the job.
Tensor with :math:`(1, H, W)`, :math:`(H, W)`, :math:`(H, W, 3)` is also suitible as long as
corresponding ``dataformats`` argument is passed. e.g. CHW, HWC, HW.
"""
一般用法如下:
#
post_img = imgs.cpu()[0]
# get softmax output from model
semantic = torch.max(semantic, 1)[1].detach().cpu().numpy()
# post process
post_predict_img = decode_seg_map_sequence(semantic)[0]
semantic_gt = torch.max(semantic_gt, 1)[1].detach().cpu().numpy()
post_gt_img = decode_seg_map_sequence(semantic_gt)[0]
# make grids and add images
grid_image = make_grid(, 3, normalize=True)
writer.add_image('Image', grid_image, counter)
grid_image = make_grid([post_predict_img], 3, normalize=True, value_range=(0, 1))
writer.add_image('Predicted_label', grid_image, counter)
grid_image = make_grid([post_gt_img], 3, normalize=True, value_range=(0, 1))
writer.add_image('Groundtruth_label', grid_image, counter)
后处理
label_colors = np.array([
[255, 255, 255], # 白色
[128, 64, 128],
[244, 35, 232],
[70, 70, 70],
[102, 102, 156],
[190, 153, 153],
])
def decode_segmap(mask):
r = mask.copy()
g = mask.copy()
b = mask.copy()
rgb = np.ones((mask.shape[0], mask.shape[1], 3)) # 创建一个全白矩阵(保证没类别的地方都是白色,方便查看效果)
for idx, color in enumerate(label_colors):
r[r == idx] = color[0]
g[g == idx] = color[1]
b[b == idx] = color[2]
rgb[:, :, 0] = r / 255.0
rgb[:, :, 1] = g / 255.0
rgb[:, :, 2] = b / 255.0
return rgb.astype(np.float)
def post_process(semantic):
'''
imgs (list): [B, C, W, H]
semantic_res (list): [B, N, W, H]
'''
B, W, H = semantic.shape
# 遍历第一维(batch size)
mask_images = np.zeros(shape=(B,W, H,3))
for i in range(semantic.shape[0]):
mask_images[i] = decode_segmap(semantic[i]) # 将mask合成为rgb图
return mask_images
def decode_seg_map_sequence(semantic):
'''
Args:
semantic (Tensor): [B,N,W,H]
semantic_gt (Tensor): [B,N,W,H]
Return:
- semantic (Tensor): [B,3,W,H]
'''
masks = post_process(semantic)
semantic = torch.from_numpy(np.array(masks).transpose([0, 3, 1, 2]))
return semantic
