目录
前言
????????初学者者工具编写!
????????仅用学习使用,不做其他任何用途!
一、基于字典的目录资源破解工具编写
1.工具原理
????????同目录扫描工具类似;
2.工具思路
如下:
????????1)命令行工具参数获取
????????2)字典读取
????????3)多线程访问
????????4)状态码判断输出结果
????????5)结果分析
二、工具初始化
1.Banner信息函数
????????'''''''''
????????def banner()
????????用于介绍工具和名称
????????'''''''''
# Banner信息函数
def banner():
print('*'*50)
print('*'*2+' '*16+'DirBrute v1.0'+' '*17+'*'*2)
print('*' * 50)2.使用方法信息函数
'''''''''
1)def usage():
2)使用方法
url:-u
thread:-t
dictionary:-d
'''''''''
# Usage信息
def usage():
print("This is the tool's usage")
print('python 基于字典的目录资源破解工具编写.py -u url -t thread -d dictionary.txt')三、命令行工具参数获得
1.模块介绍
'''''''''
1)sys:sys.argv[n]获取python命令执行的数据
2)getopt:python自带的解析命令行参数模块
'''''''''
2.参数获得
'''''''''
opts,args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:],'u:t:d:')
'''''''''
opts,args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:],'u:t:d:')
print(opts) # [('-u', 'www.baidu.com'), ('-t', '5'), ('-d', '.\\pass.txt')]
print(args) # []3. 封装start函数(参数获得内容)
def start():
if(len(sys.argv) == 7):
# This is ture length
opts, args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:], 'u:t:d:')
for k,v in opts:
if k == '-u':
url = v
elif k == '-t':
thread = v
elif k == '-d':
dic = v
# print('url:'+url)
# print('thread:'+thread)
# print('dictionary:'+dic)
multi_scan(url,thread,dic)
else:
print('Error Argument')
sys.exit()四、字典文件读取
1.python字典文件读取
'''''''''
1)with open(filename,mode) as f
2)f.readlines()
'''''''''
with open(dic,'r') as f:
dic_list = f.readlines()
# print(dic_list)
# print(len(dic_list)) # 162.多线程思路
'''''''''
1)一个线程读取固定数目的字典文件内容
2)制作多线程使用的字典列表(存储是以列表的格式)
'''''''''
# 第二部,确定读取的行数
# len(dic_list)/thread
if len(dic_list) % int(thread) == 0:
thread_read_line_num = len(dic_list) / int(thread)
else:
thread_read_line_num = math.ceil(len(dic_list) / int(thread)) # math.ceil向上取整,结果为4;若不加这个math.ceil,结果为3.2,不现实;
# print(thread_read_line_num)
# 第三步制作一个线程读取的字典列表 [[t1],[t2],[t3],[t4]]
i = 0
temp_list = [ ]
for line in dic_list:
i += 1
if i % thread_read_line_num == 0:
temp_list.append(line.strip())
result_list.append(temp_list)
temp_list = []
else:
temp_list.append(line.strip())
# print(result_list)3.扫描函数
def scan(url,dic):
# 实现扫描功能
for line in dic:
r = requests.get(url+'/'+line)
if r.status_code == 200:
print(r.url+' : '+str(r.status_code))五、多线程访问
'''''''''
1.python多线程
threading.Thread(target=,args=())
start()
# 线程扫描
for i in result_list:
thread_list.append(threading.Thread(target=scan,args=(url,i)))
for t in thread_list:
t.start()六、完整代码如下
# coding=utf8
# @time:2022/5/7 9:47
# Author 浩宇
# 需要使用到的python模块
import sys,getopt,math,threading,requests
# ---------------------------------------------------------------
# python 基于字典的目录资源破解工具编写.py -u url -t thread -d dictionary.txt
# ---------------------------------------------------------------
# Banner信息函数
def banner():
print('*'*50)
print('*'*2+' '*16+'DirBrute v1.0'+' '*17+'*'*2)
print('*' * 50)
# Usage信息
def usage():
print("This is the tool's usage")
print('python 基于字典的目录资源破解工具编写.py -u url -t thread -d dictionary.txt')
# opts,args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:],'u:t:d:')
# print(opts) # [('-u', 'www.baidu.com'), ('-t', '5'), ('-d', '.\\pass.txt')]
# print(args) # []
# 封装start函数(参数获得内容)
def start():
if(len(sys.argv) == 7):
# This is ture length
opts, args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:], 'u:t:d:')
for k,v in opts:
if k == '-u':
url = v
elif k == '-t':
thread = v
elif k == '-d':
dic = v
# print('url:'+url)
# print('thread:'+thread)
# print('dictionary:'+dic)
multi_scan(url,thread,dic)
else:
print('Error Argument')
sys.exit()
# 多线程
def multi_scan(url,thread,dic):
result_list = []
thread_list = []
# 第一步读取字典文件
with open(dic,'r') as f:
dic_list = f.readlines()
# print(dic_list)
# print(len(dic_list)) # 16
# 第二部,确定读取的行数
# len(dic_list)/thread
if len(dic_list) % int(thread) == 0:
thread_read_line_num = len(dic_list) / int(thread)
else:
thread_read_line_num = math.ceil(len(dic_list) / int(thread)) # math.ceil向上取整,结果为4;若不加这个math.ceil,结果为3.2,不现实;
# print(thread_read_line_num)
# 第三步制作一个线程读取的字典列表 [[t1],[t2],[t3],[t4]]
i = 0
temp_list = [ ]
for line in dic_list:
i += 1
if i % thread_read_line_num == 0:
temp_list.append(line.strip())
result_list.append(temp_list)
temp_list = []
else:
temp_list.append(line.strip())
# print(result_list)
# 线程扫描
for i in result_list:
thread_list.append(threading.Thread(target=scan,args=(url,i)))
for t in thread_list:
t.start()
def scan(url,dic):
# 实现扫描功能
for line in dic:
r = requests.get(url+'/'+line)
if r.status_code == 200:
print(r.url+' : '+str(r.status_code))
banner()
usage()
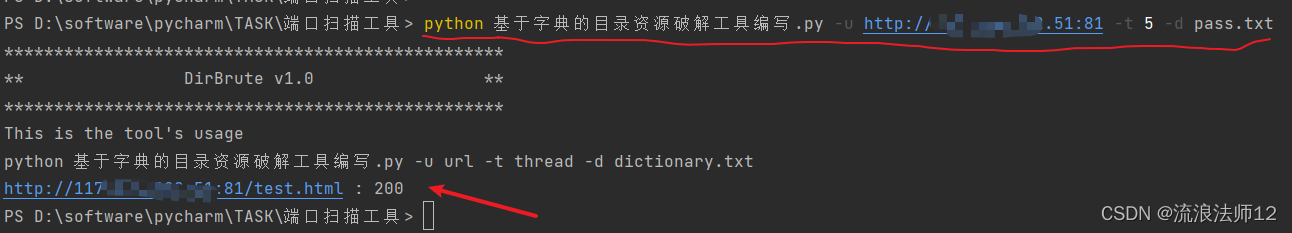
start()效果展示:
更多安全分享,请关注【安全info】微信公众号!
