URL 分发器
视图:
视图一般都是写在app的views.py中,并且视图的第一个参数永远都是request(一个HttpRequest)对象。这个对象存储了请求过来的所有信息,包括携带的参数以及一些头部信息等,在视图张,一般是完成逻辑相关的操作。比如这个请求是添加一篇博客,那么可以通过request来接受到这些数据,然后存储到数据库中,最后再把执行的结果返回给浏览器。视图函数的返回结果必须是HttpResponse对象或者子类的对象。
pycharm 打开一个新创建的view_func_demo项目
cmd 创建一个app
workon first
cd C:\Users\henan\Desktop\codes\view_func_demo>
python manage.py startupapp book # 创建一个app
pycharm app 为book的视图文件中创建一个视图函数
from django.http import HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
def book(request):
return HttpResponse('图书首页')

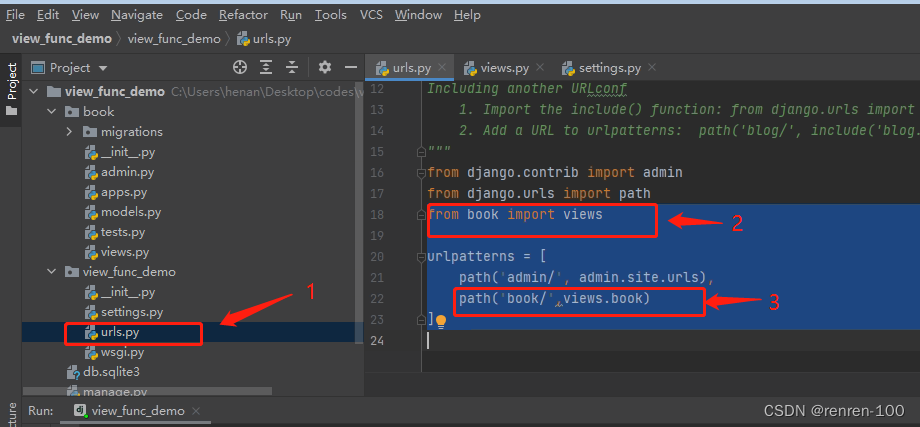
再在项目的视图文件中添加app的视图函数与url 的映射:
from book import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('book/',views.book)
]
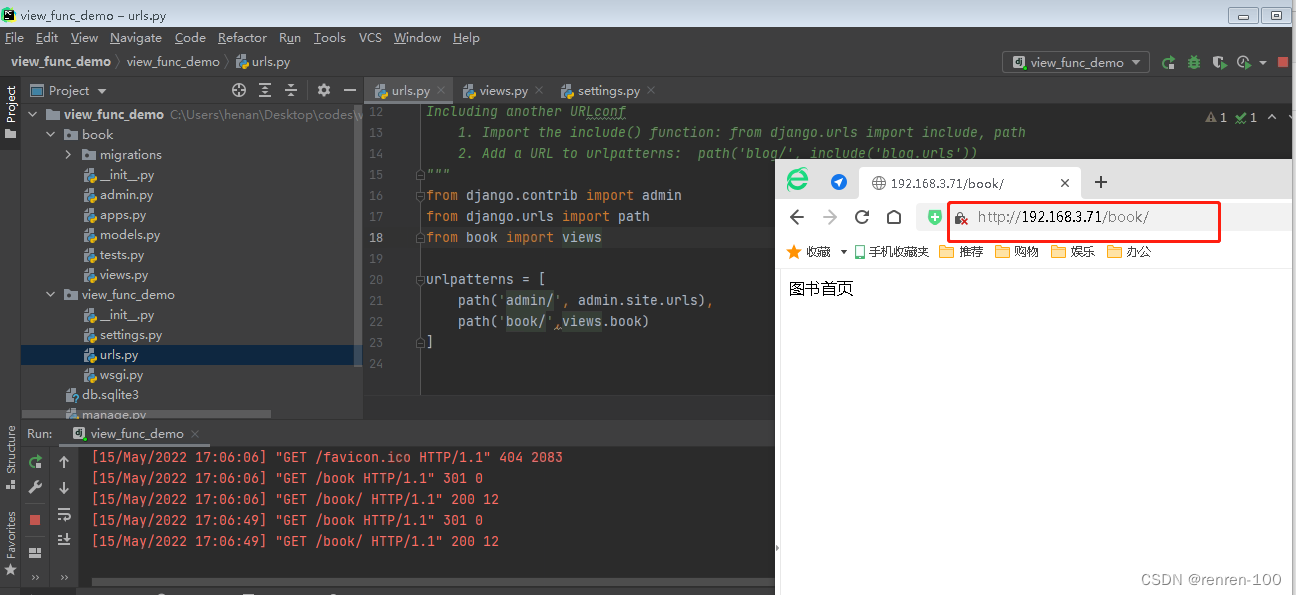
最后点击运行就可以获得如下效果
视图函数:
- 1,视图函数的第一个参数必须是request, 这个参数绝对不能少。
- 2,视图函数的返回值必须是 jdango.httpresponse.httpResponseBase 的子类的对象
url 映射:
1,为什么会去urls.py 文件中寻找映射呢?
是因为在’settings.py ’ 文件中配置了’ROOT_URLCONF’为’urls.py’, 所以django会去urls.py 中寻找。
2, 在urls.py 中我们所有的映射,都因该放在’urlpatterns’ 这个变量中。
3, 所有的映射不是随便写的,而是使用’path’函数或者是’re_path’ 函数进行包装的。
第十二节完
第十三课时
url中传递参数给视图函数
有的时候,url 中包含有一些参数需要动态调整。比如简书某篇文章的详情页面的url, https://www.jianshu.com/p/b295bec5f55c 中 最后的b295bec5f55c就是这篇文章的id,那么简书的文章详情页面的url 就可以写成这样https://www.jianshu.com/p/, 其中id就是文章的id , 那么如何在django中实现这种需求呢,这个时候可以在path 函数中,使用尖括号的形式来定义一个参数。比如现在想要获取一本书籍的详细信息,就可以在url 中指定这个参数。示例代码如下:
# 定义的带参数的视图函数
from django.http import HttpResponse
def book_detail(request,book_id,category_id):
# 可以从数据库中根据book_id 提取这个图书的信息。
text = "您获取的图书id是:%s, 图书分类: %s " %(book_id,category_id)
return HttpResponse(text)`

url 映射
from django.http import HttpResponse
from book import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('',index),
path('book/',views.book),
path('book/detail/<book_id>/<category_id>/',views.book_detail) #跟上面定义的视图函数的url映射
]

最终的效果:

采用查询字符串的方式
#定义视图函数
def author_detail(request):
author_id = request.GET.get('id')
text = '作者的id是:%s' % author_id
return HttpResponse(text)

关联到url 中:
from django.http import HttpResponse
from book import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('',index),
path('book/',views.book),
path('book/detail/<book_id>/<category_id>/',views.book_detail),
path('book/author/',views.author_detail) # 用于关联查询字符串的视图函数的url
]

url 传入参数:
1,采用在url 中使用变量的方式:在path的第一个参数中,使用’<参数名>'的方式可以传递参数。然后在视图函数中也要写一个参数,视图函数中的参数必须和url 中的参数名称保持一致,不然就找不到这个参数,另外,url 中可以传递多个参数。
2, 采用查询字符串的方式: 在url 中,不需要单独的匹配查询字符串的部分。只需要在视图函数中使用’request.GET.get(‘参数名称’)'的方式来获取,示例代码如上
url 在传参的时候可以指定参数的类型:
from django.http import HttpResponse
from book import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('',index),
path('book/',views.book),
path('book/detail/<book_id>/<category_id>/',views.book_detail),
path('book/author/',views.author_detail),
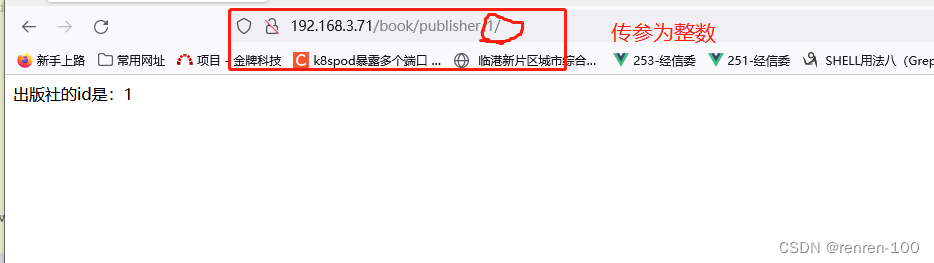
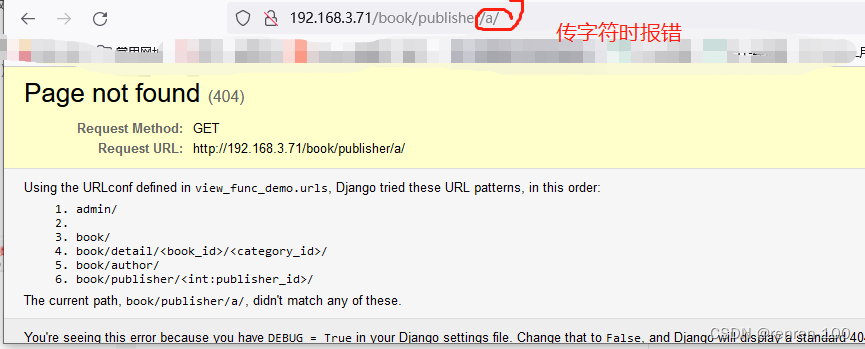
path('book/publisher/<int:publisher_id>/',views.publisher_detail)
] # 定义传入参数为整数
第十四课时待续
