1.文件的打开和关闭
1.1 文件的打开
操作文件的整体过程:
- 打开或新建立一个文件
- 读/写数据
- 关闭文件
在python中,使用open方法打开文件:
open(文件名,访问模式)
#“文件名”必须要填写
#“访问模式”是可选的
注意:
如果使用open函数打开文件时,如果没有注明访问模式,则默认为只读?,此时必须保证文件是存在的,否则会报异常。
异常信息:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<input>", line 1, in <module>
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'test.txt'
1.2 文件的模式
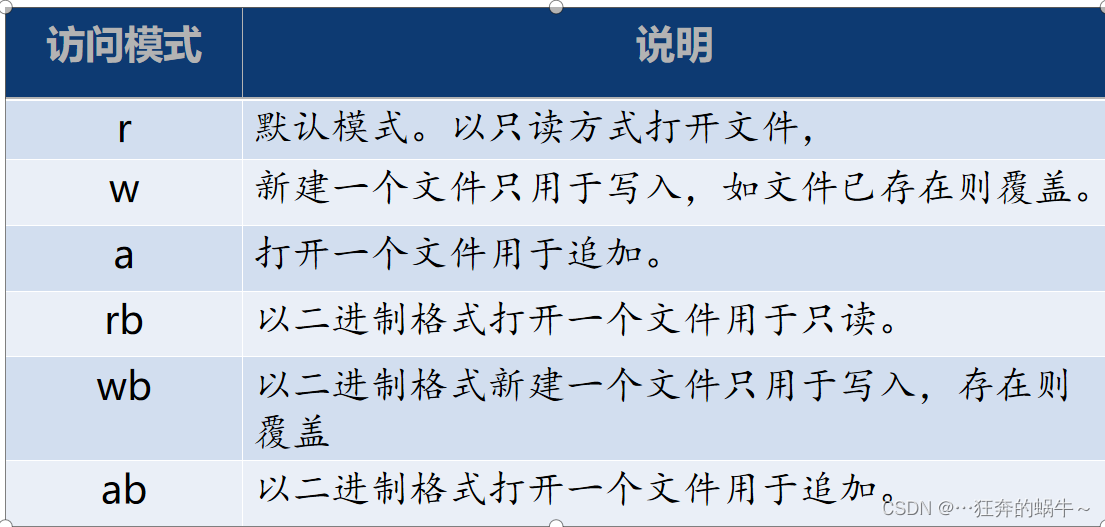

1.3 文件的关闭
凡是打开的文件,切记要使用close方法关闭文件。
例:
# 新建一个文件,文件名为:test.txt
f = open('itheima.txt', 'w')
# 关闭这个文件
f.close()

如果文件不和当前运行的python文件在同一个路径下,需要使用相对路径和绝对路径,这时使用的是左斜杠/,或者右斜杠转义\,而不是右斜杠\。
f = open('C:/Users/dell/Desktop/test.txt')
f = open('../test/test.txt')
2 文件的读写
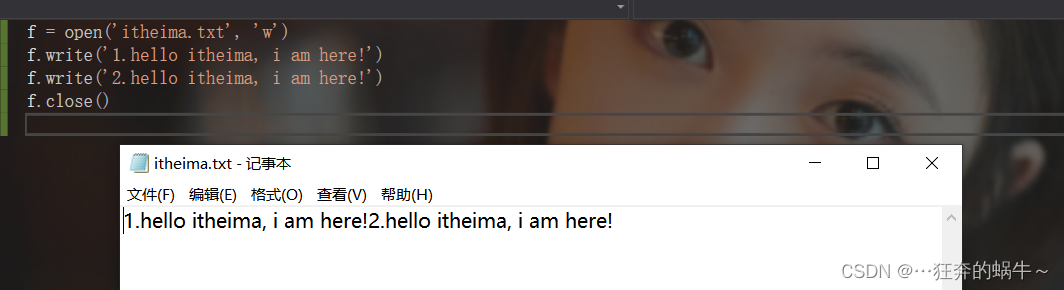
2.1 写文件
向文件写数据,需要使用write方法来完成,在操作某个文件时,每调用一次write方法,写入的数据就会追加到文件末尾。
f = open('itheima.txt', 'w')
f.write('1.hello itheima, i am here!')
f.write('2.hello itheima, i am here!')
f.close()
2.2 文件的读写

2.3 读文件
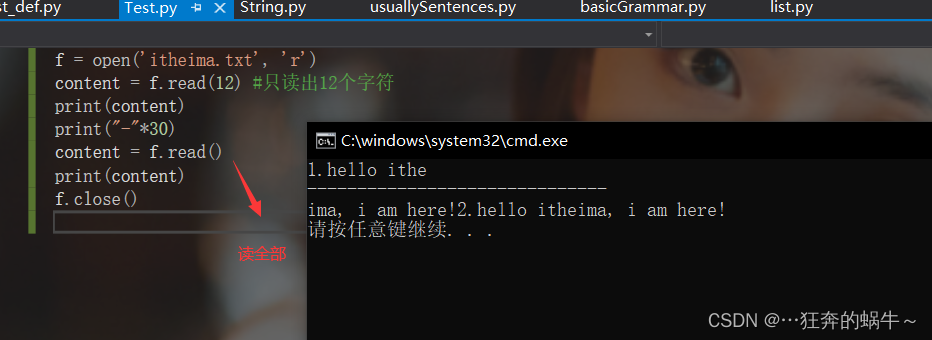
方式1:使用read方法读取文件
f = open('itheima.txt', 'r')
content = f.read(12) #只读出12个字符
print(content)
print("-"*30)
content = f.read()
print(content)
f.close()
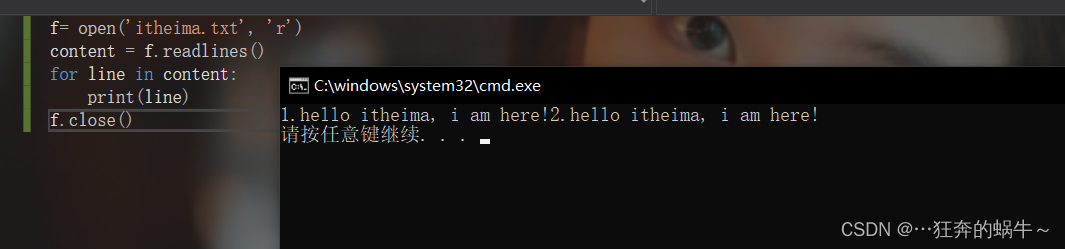
方式2:使用readlines方法读取文件
f= open('itheima.txt', 'r')
content = f.readlines()
for line in content:
print(line)
f.close()
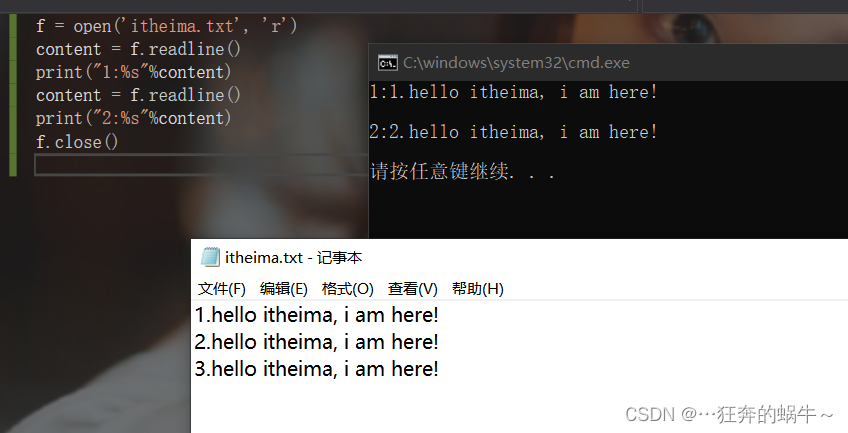
方式3:使用readline方法一行一行读数据
f = open('itheima.txt', 'r')
content = f.readline()
print("1:%s"%content)
content = f.readline()
print("2:%s"%content)
f.close()

2.4 文件的定位读写
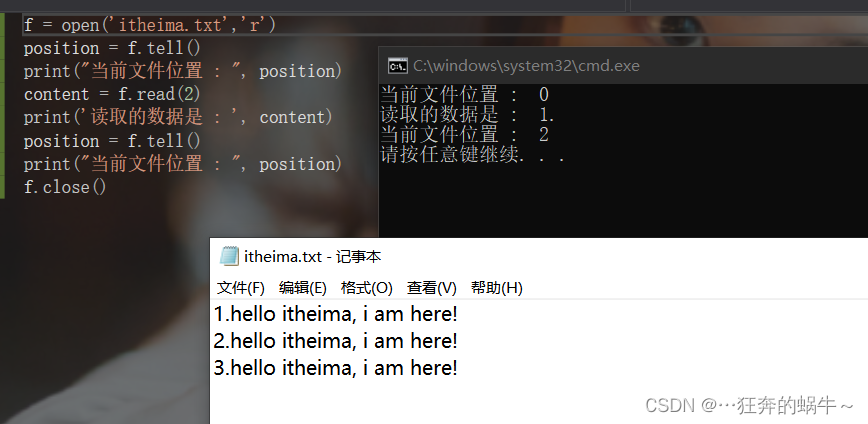
方式1:使用tell方法来获取文件当前的读写位置
f = open('itheima.txt','r')
position = f.tell()
print("当前文件位置 : ", position)
content = f.read(2)
print('读取的数据是 : ', content)
position = f.tell()
print("当前文件位置 : ", position)
f.close()
方式2:使用seek方法来移动文件当前的读写位置
seek(offset, from)方法包含两个参数:
- offset:表示偏移量,也就是代表需要移动偏移的字节数
- from:表示方向,可以指定从哪个位置开始偏移
0:表示文件开头(默认值)
1:表示当前位置
2:表示文件末尾
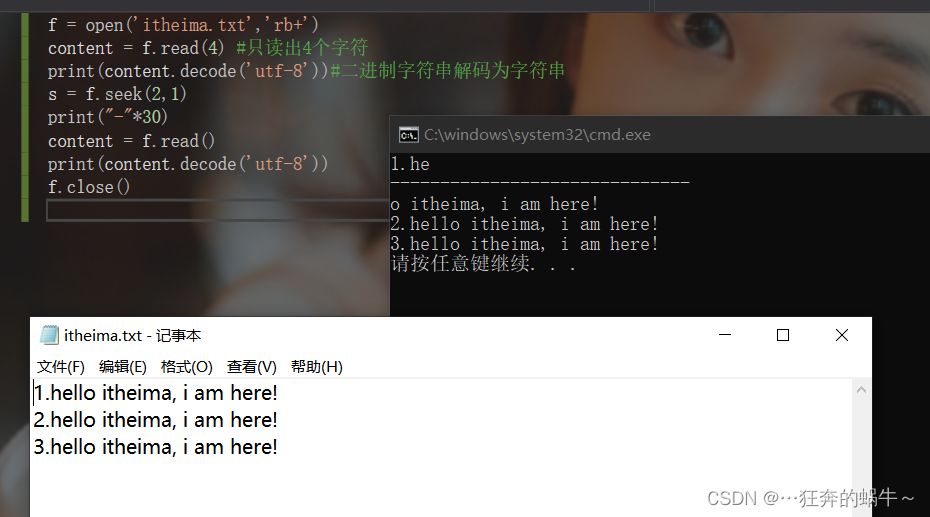
seek使用实例(无中文情况):
f = open('itheima.txt','rb+')
content = f.read(4) #只读出4个字符
print(content.decode('utf-8'))#二进制字符串解码为字符串
s = f.seek(2,1)
print("-"*30)
content = f.read()
print(content.decode('utf-8'))
f.close()
seek使用实例(有中文情况):

3. 文件的重命名和删除
3.1 文件的重命名
os模块中的rename()方法可以完成文件或者文件夹的重命名。新的文件名也要有路径
#rename(需要修改的文件名, 新的文件名)
import os
os.rename('./test','./t1')
3.2 文件的删除
os模块中的remove()方法可以完成文件的删除操作。
#remove(待删除的文件名)
import os
os.remove('./t1/t1.txt')
4 文件的相关操作
- 创建文件夹
- os模块的mkdir方法用来创建文件夹,示例如下:
import os
os.mkdir("张三")
- 获取当前目录
- os模块的getcwd方法用来获取当前的目录
示例如下: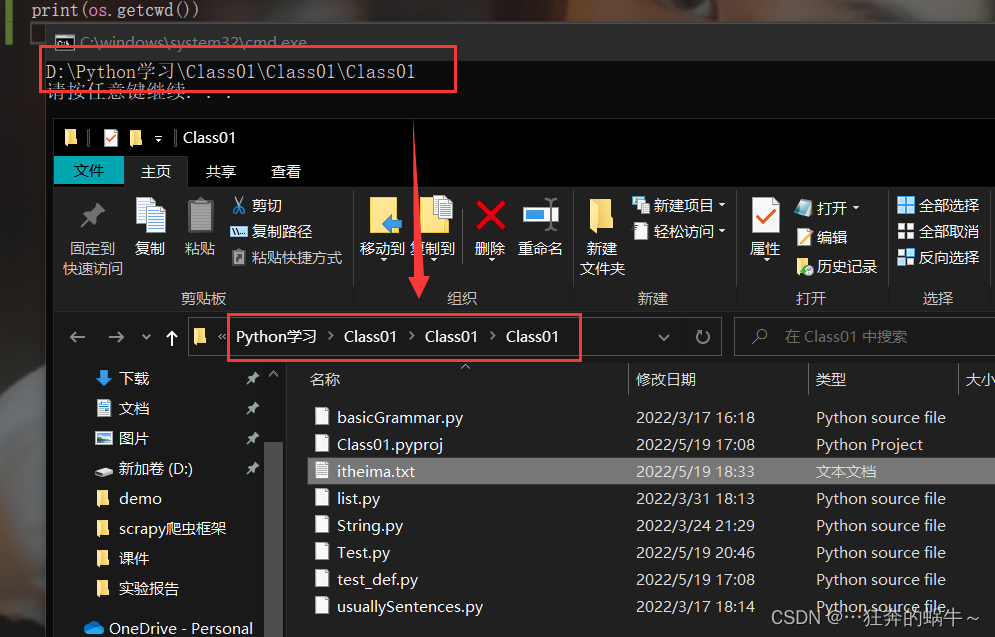
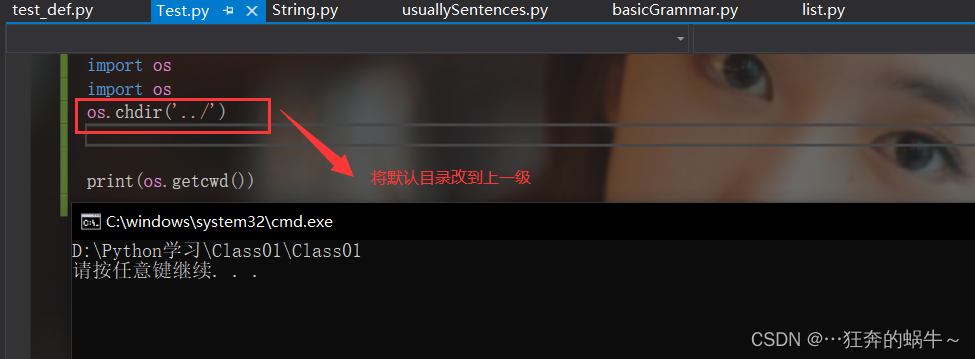
3. 改变默认目录
os模块的chdir方法用来改变默认目录,示例如下:
import os
os.chdir('../')
print(os.getcwd())
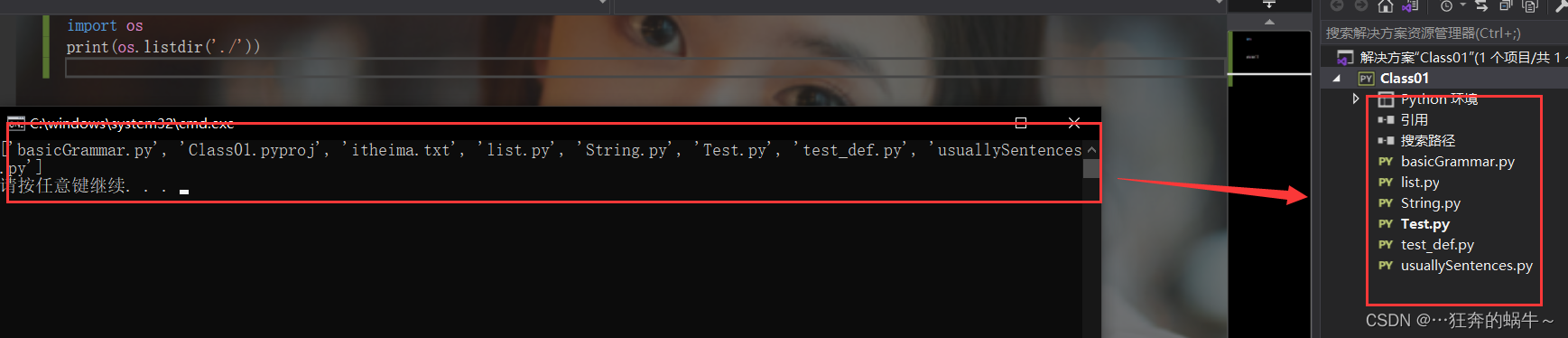
4.获取目录列表
os模块的listdir方法用于获取目录列表,示例如下:
import os
print(os.listdir('./'))
5.删除文件夹
os模块的rmdir方法用于删除文件夹,示例如下:
import os
os.rmdir('t1')
5.序列化与反序列化
序列化:让对象持久化保存到硬盘中
with open('student.pickle', 'wb+') as f:
pickle.dump(self.studentList,f)
反序列化:让硬盘中文件读取到内存中成为对象
try:
with open('student.pickle', 'rb') as f:
self.studentList = pickle.load(f)
print('读取成功')
except:
print('载入文件出错')
