Python字符串格式化
字符串格式化用来把整数、实数等对象转化为特定格式的字符串
1.?% 格式字符
% 格式字符:% 之前的字符串为格式字符串,之后的部分为需要格式化的内容。
例如:
name = "cspsy"
job = "student"
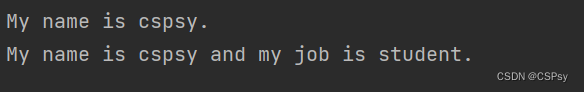
print("My name is %s." % name)
# 如果有多个需要进行格式化的内容,需要使用 () 将其包裹。
print("My name is %s and my job is %s." % (name, job))
1.1)常见的格式字符

2.?format()
format(): .format() 之前的字符串为格式字符串,里面的部分的内容为需要格式化的内容。
格式串中的 {} 的内容与 format() 里面的内容相对应。
format() 方法进行格式化:
- 可以使用位置进行格式化
- 可以使用自定义的参数名字进行格式化
- 支持序列解包来进行格式化
2.1)使用位置
- 不写位置下标,则格式字符串内的花括号带的下标默认从 0 开始递增排列
name = "cspsy"
job = "student"
print("My name is {} and my job is {}.".format(name, job))

- 书写位置下标,输出括号内指定位置下标的内容(括号内下标从 0 开始递增排列)
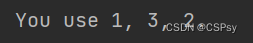
one, two, three = 1, 2, 3
print("You use {0}, {2}, {1}.".format(one, two, three))
2.2)使用自定义的参数名字
- 可以在格式字符串的
{}内使用自定义的参数名字,与待格式化的内容对应。
例如:
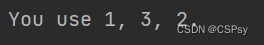
one, two, three = 1, 2, 3
print("You use {o}, {thr}, {tw}.".format(o=one, tw=two, thr=three))
2.3)使用序列解包
将解包后的名字,key 值放在格式化字符串内。
例如:
number = {'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3}
print("You use {one}, {three}, {two}.".format(**number))

2.4)格式风格
- 数字
进制转换
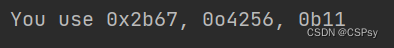
one, two, three = 11111, 2222, 3
print("You use {0:#x}, {1:#o}, {2:#b}".format(one, two, three))
保留小数点
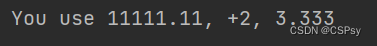
使用 :.xf,x 为想要保留的小数点个数,如果 : 后面带有 +,则会保留符号输出。
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
print("You use {0:.2f}, {1:+.0f}, {2:.3f}".format(one, two, three))
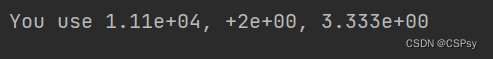
科学计数法
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
print("You use {0:.2e}, {1:+.0e}, {2:.3e}".format(one, two, three))
百分比形式
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
print("You use {0:.0%}, {1:.2%}, {2:.3%}".format(one, two, three))

以逗号分隔
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
print("You use {0:,}, {1:,}, {2:,}".format(one, two, three))

- 对齐方式
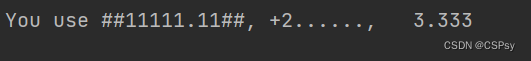
使用 :cxn 来进行,n 为最小长度,c 为长度不够时,填充的字符(不写则为空格)
x 为对齐方式:其中,^:居中,<:左对齐,>:右对齐
例如:
one, two, three = 11111.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333333
print("You use {0:#^12.2f}, {1:.<+8.0f}, {2:>7.3f}".format(one, two, three))
3.?map
可以通过内置 map() 函数来进行格式化字符串输出:
formatter = "You use {0}".format
for num in map(formatter, range(1, 6)):
print(num)
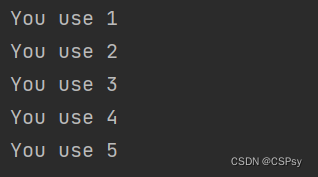
这个例子写法与下面等价:
formatter = "You use {0}".format
for num in range(1, 6):
print(formatter(num))
4.?f-字符串
从 Python 3.6.x 开始支持一种新的字符串格式化方式,官方叫做 Formatted String Literals,简称 f-字符串,在字符串前加字母 f,在 {} 里填写表达式。
使用如下:
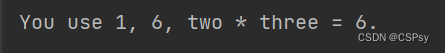
one, two, three = 11, 222, 3333
print(f'You use {one}, {two * three}.')
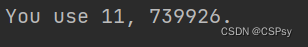
Python 3.8 之后,还可以 {xxx=},将 xxx=输出出来且输出它对应的值:
one, two, three = 1, 2, 3
print(f'You use {one}, {two * three}, {two * three = }.')