Gaussian Processes to Speed up Hybrid Monte Carlo for Expensive Bayesian Integrals
高斯过程加速HMC
文章目录
代码路径:D:\pycharm\projects\GPHMC\gphmc-master
实例程序:example_2d.py
1.导入相关的库
1.1 普通库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
1.2 专属库(点击查看具体内容)
from gphmc.gaussian_process_regression.gaussian_process.covariance import (
SquaredExponential
)
from gphmc.gaussian_process_regression.gaussian_process.gp import (
GaussianProcess
)
from gphmc.gaussian_process_regression.gaussian_process.optimizer import (
SECovLikelihoodOptimizer
)
from gphmc.gaussian_process_regression.gaussian_process.util import (
get_logger
)
from gphmc.gphmc import GPHMCSampler
2.函数定义
2.1 势能函数
- π ( θ ∣ x ) ∝ exp ? ( U ( θ ∣ x ) ) \pi(\theta|x)∝\exp(U(\theta|x)) π(θ∣x)∝exp(U(θ∣x))
- 势能: U ( θ ∣ x ) = ? log ? π ( θ ∣ x ) U(\theta|x)=-\log \pi(\theta|x) U(θ∣x)=?logπ(θ∣x)
- 势能->energy-> U ( θ ∣ x ) U(\theta|x) U(θ∣x)
- 目标分布: π ( θ ∣ x ) \pi(\theta|x) π(θ∣x) -> probability
#噪声
FUZZ = 1e-300
# 势能:potentials energy
def potential_energy(x):
"""Density to estimate
:param x: input parameter
:return: value of the density at (x, y)
"""
probability = np.exp(-8*(x[0]**2/2+x[1]**2-1)**2) + FUZZ
energy = -np.log(probability)
return energy
2.2 观测数据获取
- 观测输入: X = { x 1 , . . . , x n } X=\{x_1,...,x_n\} X={x1?,...,xn?} x k = ( i , j ) , k ∈ [ 1 , n ] x_k=(i,j),k∈[1,n] xk?=(i,j),k∈[1,n]
- 观测输出: Y = { y 1 , . . . , y n } Y=\{y_1,...,y_n\} Y={y1?,...,yn?}
def get_observations(xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax, n):
"""Get a list of random observation
:param xmin: minimum x value where to plot the density
:param xmax: maximum x value where to plot the density
:param ymin: minimum y value where to plot the density
:param ymax: maximum y value where to plot the density
:param n: number of observation
:return: two lists of the same length. One list of the observation points,
and one list of the evaluation of the density at the observation points
"""
list_observations = []
list_y = []
for _ in range(n):
i = np.random.uniform(low=xmin, high=xmax)
j = np.random.uniform(low=ymin, high=ymax)
list_observations.append((i, j))
list_y.append(potential_energy((i, j)))
return list_observations, list_y
2.3 绘制概率密度函数
def plot_density(n=50):
"""Plot the density
:param n: number of point on each axis to estimate the density on.
The density will be estimated on a regular n x n grid n the [-2, 2, -2, 2]
space.
"""
list_x = np.linspace(-2, 2, n)
coords = np.meshgrid(list_x, list_x, indexing='ij')
density_value = np.exp(-potential_energy([coords[0], coords[1]]))
plt.imshow(
density_value, cmap='viridis',
extent=[-2, 2, -2, 2], vmin=0.0, vmax=1.0, aspect='equal'
)
plt.title('Real Density')
plt.savefig('figures/density.png', dpi=100, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
2.4 GP绘制函数
def plot_gp(current_cov_param, list_obs, list_y, n=50):
"""Plot the Gaussian process estimation of the density
:param current_cov_param: tuple with the 3 parameters of the exponential
covariance matrix
:param list_obs: list of 2-tuple corresponding to the point observed
:param list_y: list of scalar corresponding to the density value at the
observed points
:param n: number of point on each axis to estimate the density on.
The density will be estimated on a regular n x n grid n the [-2, 2, -2, 2]
space.
"""
cov = SquaredExponential(current_cov_param[0], current_cov_param[1:])
gp = GaussianProcess(cov, list_observations=list_obs,list_y=list_y, noise=1e-3)
gp.covariance_matrix()
list_x = np.linspace(-2, 2, n)
current_estimation = np.zeros((n, n))
current_estimation_flat = [
(i, j, gp.mean([(xi, yj)])[0])
for (i, xi) in enumerate(list_x)
for (j, yj) in enumerate(list_x)
]
for coord_value in current_estimation_flat:
current_estimation[coord_value[:2]] = np.exp(-coord_value[2])
plt.imshow(current_estimation, cmap='viridis', vmin=0, vmax=1,
extent=[-2, 2, -2, 2], aspect='equal')
idx_x = np.array([abs(x[0]) <= 1.8 for x in gp.list_observations])
idx_y = np.array([abs(x[1]) <= 1.8 for x in gp.list_observations])
idx = idx_x & idx_y
x = np.array([-x[0] for x in gp.list_observations])
y = np.array([x[1] for x in gp.list_observations])
z = np.array([np.exp(-y) for y in gp.list_y])
plt.scatter(
y[idx], x[idx], c=z[idx], cmap='viridis', s=100, vmin=0, vmax=1
)
plt.xlim(-2, 2)
plt.ylim(-2, 2)
plt.title('Gaussian process after exploration')
plt.savefig('figures/estimation.png', dpi=100, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
2.5 绘制样本
def plot_samples(samples):
"""Plot the final samples
:param samples: list of tuple corresponding to the samples of the GPHMC
"""
x = [-sample[0] for sample in samples]
y = [sample[1] for sample in samples]
plt.imshow(np.ones((50, 50)), cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=1,
extent=[-2, 2, -2, 2], aspect='equal')
plt.scatter(y, x, s=100, c='red')
plt.xlim(-2, 2)
plt.ylim(-2, 2)
plt.title('Final samples')
plt.savefig('figures/sample.png', dpi=100, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
3.主函数
- 绘制概率密度函数
np.random.seed(0)
plot_density()
- 获取(50个)观测数据
logger = get_logger()
logger.info('Get initial observations')
list_obs, list_y = get_observations(xmin=-2, xmax=2, ymin=-2, ymax=2, n=50)
- 定义采样器
logger.info('Instantiate the sampler')
sampler = GPHMCSampler(
covariance_class=SquaredExponential, target_function=potential_energy,
likelihood_optimizer_class=SECovLikelihoodOptimizer,
list_obs=list_obs, list_y=list_y, noise=1e-3, dimension=2, n_explo=50,
init_cov_param=np.array([1, 1, 1])
)
- 探索阶段
logger.info('Exploration phase')
sampler.exploration(
epsilon=0.1, length=400, momentum_std=1.0, gp_update_rate=10
)
plot_gp(sampler.current_cov_param, sampler.list_obs, sampler.list_y)
- 采样阶段
logger.info('Sampling phase')
samples = []
sample_generator = sampler.sample(
epsilon=0.01, length=200, momentum_std=1.0
)
for _ in tqdm(range(500)):
samples.append(next(sample_generator))
plot_samples(samples)
4.输出
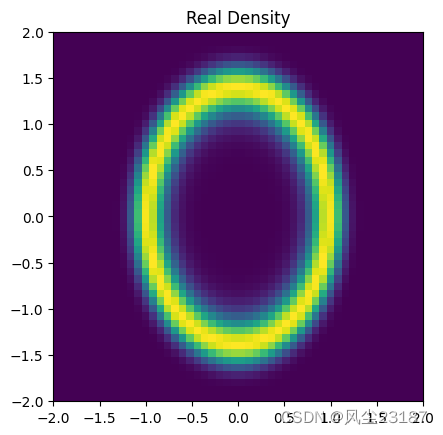
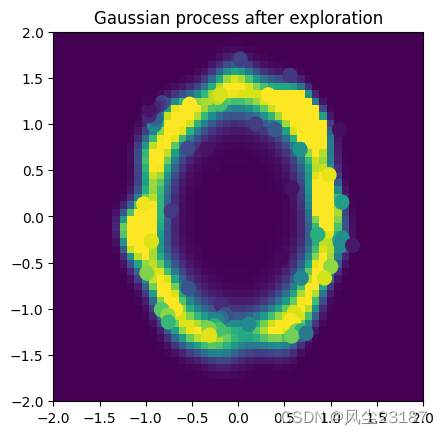
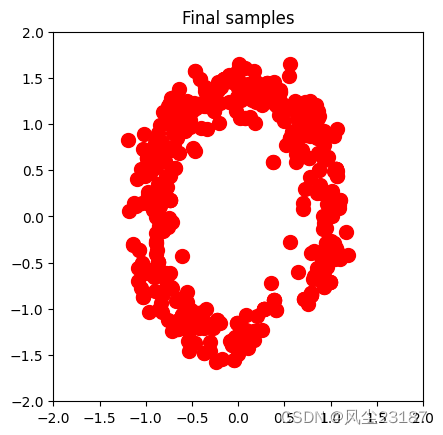
附录1 核函数类
核函数
SquaredExponential:
w
0
exp
?
(
?
0.5
(
x
?
y
)
2
/
w
1
2
)
w_0\exp (-0.5(x-y)^2/w^2_1)
w0?exp(?0.5(x?y)2/w12?)
"""Covariance"""
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod
import numpy as np
class Covariance(object, metaclass=ABCMeta):
"""Base class for the covariance function"""
def __call__(self, x, y):
return self.compute(x, y)
@abstractmethod
def compute(self, x, y):
"""Evaluate the covariance function"""
raise NotImplementedError
@abstractmethod
def compute_pd(self, x, y, **kwargs):
"""Evaluate the partial derivative of the covariance function"""
raise NotImplementedError
@abstractmethod
def compute_pdpd(self, x, y, **kwargs):
"""Second order partial derivative of the covariance function"""
raise NotImplementedError
class SquaredExponential(Covariance):
"""Squared exponential covariance function"""
def __init__(self, w0, w1):
"""Init
:param w0: variance parameter
:param w1: correlation parameter
"""
assert isinstance(w1, np.ndarray)
# We take the absolute value to make sure the parameters are positive
# (this is a lay way to enforce constraint during optimization)
self.w0 = abs(w0)
self.w1 = abs(w1)
def compute(self, x, y):
"""Evaluate the covariance function
:param x: first parameter
:param y: secon parameter
:return: covariance between x and y
"""
assert len(x) == len(y)
assert len(x) == len(self.w1)
x_array = np.array(x)
y_array = np.array(y)
euclidean_norm = np.linalg.norm(
x_array / self.w1 - y_array / self.w1
) ** 2
return self.w0 * np.exp(-euclidean_norm / 2)
def compute_pd(self, x, y, i):
"""Evaluate the partial derivative of the covariance function
The partial derivative is evaluated between x and y at x_i
where x = [x_0, x_1, ...., x_n]
:param x: first parameter
:param y: second parameter
:param i: dimension of x where the partial derivative is evaluated
:return: partial derivative of the covariance between x and y
"""
return self.compute(x, y) * (-(x[i] - y[i]) / (self.w1[i]**2))
def compute_pdpd(self, x, y, i, j):
"""Second order partial derivative of the covariance function
The partial derivative is evaluated between x and y at x_i and y_j
where x = [x_0, x_1, ...., x_n], and y = [y_0, y_1, ...., y_n]
:param x: first parameter
:param y: second parameter
:param i: dimension of x where the partial derivative is evaluated
:param j: dimension of y where the partial derivative is evaluated
:return: second order partial derivative between x and y
"""
result = (
self.compute_pd(x, y, i=i) * (x[j] - y[j]) / self.w1[j] ** 2
)
if i == j:
result += self.compute(x, y) / self.w1[i] ** 2
return result
附录2 高斯过程类
高斯过程
"""Gaussian process"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from functools import partial
from .covariance import Covariance
FUZZ = 1e-20
class NotTestedFeature(Exception):
"""Raised when using a feature that is not tested"""
pass
class GaussianProcess:
"""Gaussian process"""
def __init__(self, covariance: Covariance, noise=1e-7,
list_observations=None, list_y=None):
"""Init
:param covariance: instance of a covariance class
:param noise: noise
:param list_observations: list of observation
:param list_y: list of evaluation of the function to interpolate
"""
self.covariance = covariance
self.list_observations = list_observations if list_observations else []
self.list_y = list_y if list_y else []
self.n_observation = len(self.list_observations)
self.cov_matrix = np.zeros((0, 0))
self.noise = noise
self._sigma_inv_times_centered_y = None
self._mean_y = None
@staticmethod
def _center_data(list_y):
"""Center the list
:param list_y: input list
:return: tuple with the centered list and the empirical mean
"""
assert isinstance(list_y, list)
mean = np.mean(list_y)
centered_list_y = list_y - mean
return centered_list_y, mean
def _compute_covariance_matrix(self, list_obs_1, list_obs_2):
"""Compute the covariance matrix between two lists of observations
:param list_obs_1: first list of observation
:param list_obs_2: second list of observation
:return: covariance matrix between the elements of list_obs_1 and
list_obs_2
"""
assert isinstance(list_obs_1, list)
assert isinstance(list_obs_2, list)
cov_matrix = np.zeros((len(list_obs_1), len(list_obs_2)))
cov_matrix_flat = [
(i, j, self.covariance(xi, yj))
for (i, xi) in enumerate(list_obs_1)
for (j, yj) in enumerate(list_obs_2)
]
for coord_value in cov_matrix_flat:
cov_matrix[coord_value[:2]] = coord_value[2]
return cov_matrix
def _compute_covariance_matrix_pd(self, list_obs_1, list_obs_2, pd_dim):
"""Compute the partial derivative of the covariance matrix"""
assert isinstance(list_obs_1, list)
assert isinstance(list_obs_2, list)
fction = partial(self.covariance.compute_pd, i=pd_dim)
cov_matrix = np.zeros((len(list_obs_1), len(list_obs_2)))
cov_matrix_flat = [
(i, j, fction(xi, yj))
for (i, xi) in enumerate(list_obs_1)
for (j, yj) in enumerate(list_obs_2)
]
for coord_value in cov_matrix_flat:
cov_matrix[coord_value[:2]] = coord_value[2]
return cov_matrix
def _gp_up_to_date(self):
"""Assert the Gaussian process is up to date"""
n = len(self.list_observations)
assert n == len(self.list_y)
assert self.cov_matrix.shape[0] == n
def _order_observations(self):
"""Order the observation
Can be useful to stabilize the covariance matrix
"""
list_observations_y = zip(self.list_observations, self.list_y)
list_observations_y = sorted(
list_observations_y,
key=lambda obs_y: np.linalg.norm(np.array(obs_y[0]))
)
self.list_observations = [obs for obs, y in list_observations_y]
self.list_y = [y for obs, y in list_observations_y]
def _solve_linear_system(self):
"""Solve the linear system to compute _sigma_inv_times_centered_y"""
# Solve the linear system
centered_list_y, mean = self._center_data(self.list_y)
y = np.linalg.solve(self.cov_matrix, centered_list_y)
# Assert the resolution of the linear system went well
assert np.allclose(np.array(centered_list_y), self.cov_matrix @ y)
return y, mean
def _update_mean_and_sigma_inv_times_centered_y(self):
"""Update the empirical mean of list_y and solve the linear system
For improved speed, the solution of _sigma_inv_times_centered_y is
part of the class state. This is where it is update if it has not
been computed before, or if new observation has been added
"""
if self._sigma_inv_times_centered_y is not None:
update_condition = (
len(self._sigma_inv_times_centered_y) != len(self.list_y)
)
else:
update_condition = self._mean_y is None
if update_condition:
y, mean = self._solve_linear_system()
self._sigma_inv_times_centered_y = y
self._mean_y = mean
def add_observation(self, x, y):
"""Add an observation
:param x: parameter where the function to interpolate is evaluated
:param y: value of the interpolated function
"""
self.list_observations.append(x)
self.list_y.append(y)
self.n_observation += 1
def covariance_matrix(self):
"""Compute the covariance matrix of the Gaussian process
:return: covariance matrix between the observation of the Gaussian
process
"""
self._order_observations()
self.cov_matrix = self._compute_covariance_matrix(
self.list_observations, self.list_observations)
self.cov_matrix += np.diag(np.array([self.noise] * self.n_observation))
return self.cov_matrix
def likelihood(self):
"""Likelihood of the Gaussian process
:return: log likelihood of the Gaussian process
"""
# assert the Gaussian process is up to date
self._gp_up_to_date()
noise_penalization_term = -1 / 2 * np.log(
np.linalg.det(self.cov_matrix))
y = np.linalg.solve(self.cov_matrix, self.list_y)
y = np.array(self.list_y) @ y
data_fidelity_term = -1 / 2 * y
nbr_obs_term = - self.n_observation * np.log(2 * np.pi)
likelihood = (
noise_penalization_term + data_fidelity_term + nbr_obs_term
)
return likelihood
def mean(self, x, derivative=False, i=None):
"""Compute the conditional mean of the Gaussian process
Knowing the observations, compute the value of the mean of the Gaussian
process at x
:param x: parameter where to evaluate the mean of the Gaussian process
:param derivative: boolean, whether or not to compute the derivative
of sigma
:param i: dimension along which to compute the derivative if True
:return: interpolated value at x which is the mean of the Gaussian
process (i.e. mean of the posterior probability of the Gaussian
process knowing the observations)
"""
assert isinstance(x, list)
assert len(x) > 0
assert isinstance(x[0], tuple)
if derivative:
assert 0 <= i < len(x[0])
cov_function = partial(
self._compute_covariance_matrix_pd, pd_dim=i
)
else:
cov_function = self._compute_covariance_matrix
# assert the Gaussian process is up to date
self._gp_up_to_date()
# Compute the correlation between the parameter x and the observation
current_cov = cov_function(x, self.list_observations)
self._update_mean_and_sigma_inv_times_centered_y()
mean = 0 if derivative else self._mean_y
return mean + current_cov @ self._sigma_inv_times_centered_y
def sample_generator(self, x):
"""Sample a Gaussian process on x
:param x: parameter where to sample_generator the Gaussian process
:return: a sample_generator from the Gaussian process
"""
assert isinstance(x, list)
assert len(x) > 0
assert isinstance(x[0], tuple)
mean = self.mean(x)
sigma = self.sigma(x)
# 获取特征值和特征向量
d, u = np.linalg.eig(sigma)
assert np.allclose(u@np.diag(d)@u.T, sigma)
d = np.real(d)
d[d < FUZZ] = FUZZ
d_sqrt = np.sqrt(d)
while True:
sample = np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1, size=len(x))
sample = mean + u@np.diag(d_sqrt)@sample
yield sample
def sigma(self, x, derivative=False, i=None):
"""Compute the conditional variance of the Gaussian process
Knowing the observations, compute the value of the variance of the
Gaussian process at x
:param x: parameter where to evaluate the mean of the Gaussian process
:param derivative: boolean, whether or not to compute the derivative
of sigma
:param i: dimension along which to compute the derivative if True
:return: variance of the Gaussian process at x (i.e. mean of the
posterior probability of the Gaussian process knowing the
observations)
"""
assert isinstance(x, list)
assert len(x) > 0
assert isinstance(x[0], tuple)
if derivative:
if len(x) > 1:
error_msg = 'Derivatives of the variance'
error_msg += ' has not been tested for a vector input'
raise NotTestedFeature(error_msg)
assert 0 <= i < len(x[0])
cov_function = partial(
self._compute_covariance_matrix_pd, pd_dim=i
)
else:
cov_function = self._compute_covariance_matrix
# assert the Gaussian process is up to date
self._gp_up_to_date()
current_sigma = cov_function(x, x)
# Compute the correlation between the parameter x and the observation
current_cov = self._compute_covariance_matrix(
x, self.list_observations
)
# Solve the linear system
y = np.linalg.solve(self.cov_matrix, current_cov.T)
# Assert the resolution of the linear system went well
assert np.allclose(current_cov.T, self.cov_matrix @ y)
if derivative:
current_cov_pd = self._compute_covariance_matrix_pd(
x, self.list_observations, pd_dim=i
)
# Solve the linear system
y_2 = np.linalg.solve(self.cov_matrix, current_cov_pd.T)
# Assert the resolution of the linear system went well
assert np.allclose(current_cov_pd.T, self.cov_matrix @ y_2)
second_term = -current_cov @ y_2 - current_cov_pd @ y
else:
second_term = - current_cov @ y
return current_sigma + second_term
class GaussianProcess1d(GaussianProcess):
"""1D Gaussian process"""
def _estimate_gp(self, list_x):
"""Estimate the mean and variance of the Gaussian process
:param list_x: points where to do the estimation
:return: tuple with the mean and variance estimated at the points
in list_x
"""
assert isinstance(list_x, list)
mean = self.mean(list_x)
sigma = np.squeeze(
np.array([self.sigma([x]) for x in list_x])
)
return mean, sigma
def plot(self, list_x, ymin, ymax, n_samples=3, confidence_band=True):
"""Plotting utility
:param list_x: list of point where to evaluate the interpolation
:param ymin: minimum y axis value for the plot
:param ymax: maximum y axis value for the plot
:param n_samples: number of samples from the Gaussian process to plot
:param confidence_band: boolean, whether or not to plot the confidence
band
"""
assert isinstance(list_x, list)
mean, sigma = self._estimate_gp(list_x)
sample_generator = self.sample_generator(list_x)
for _ in range(n_samples):
plt.plot(
list_x, next(sample_generator), color='black', linewidth='1'
)
if confidence_band:
plt.plot(list_x, mean + 2*np.sqrt(sigma), color='pink',
linewidth='2')
plt.plot(list_x, mean - 2*np.sqrt(sigma), color='pink',
linewidth='2')
plt.plot(list_x, mean, color='b', linewidth='3')
plt.scatter(
self.list_observations, self.list_y, s=50, facecolors='red',
zorder=3
)
plt.axis([list_x[0][0], list_x[-1][0], ymin, ymax])
class GaussianProcess2d(GaussianProcess):
"""2D Gaussian process"""
@staticmethod
def _get_estimation(function, derivative, index, list_x, list_y):
n = len(list_x)
current_estimation = np.zeros((n, n))
current_estimation_flat = [
(i, j, function([(xi, yj)], derivative=derivative, i=index)[0])
for (i, xi) in enumerate(list_x)
for (j, yj) in enumerate(list_y)
]
for coord_value in current_estimation_flat:
current_estimation[coord_value[:2]] = coord_value[2]
return current_estimation
def _estimate_gp(self, list_x, list_y):
"""Estimate the Gaussian process mean and variance
:param list_x: list of point on the first dimension where to evaluate
the interpolation
:param list_y: list of point on the second dimension where to evaluate
the interpolation
:return: two arrays of size (len(list_x), len(list_y)) with the
estimation of the mean and variance of the Gaussian process
"""
assert isinstance(list_x, list)
assert isinstance(list_y, list)
assert len(list_x) == len(list_y)
# Dictionary with key the name of the estimation, and value a list with
# [{function_used_to_estimate}, {derivative}, {i},
# {sigma_derivation_function}], where derivative and i are parameters
# of function_used_to_estimate, and sigma_derivation_function is the
# function to apply to get the standard deviation
def sqrt(x, x_der):
"""Derivative of sqrt(x)"""
return np.sqrt(x)
def sqrt_der(x, x_der):
"""Derivative of sqrt(x)"""
return x_der/(2*x + FUZZ)
params = {
'mean': [self.mean, False, None, None],
'mean_x': [self.mean, True, 0, None],
'mean_y': [self.mean, True, 1, None],
'std': [self.sigma, False, None, sqrt],
'std_x': [self.sigma, True, 0, sqrt_der],
'std_y': [self.sigma, True, 1, sqrt_der],
}
result = {}
for param_key in np.sort(list(params.keys())):
param = params[param_key]
current_estimation = self._get_estimation(
param[0], param[1], param[2], list_x, list_y
)
result[param_key] = current_estimation
if params[param_key][3]:
result[param_key] = params[param_key][3](
result['std'], current_estimation
)
return result
def _plot_data(self, fig, ax, *, img, x, y, xmin, xmax, ymin,
ymax, title):
"""Plotting utility"""
vmin = np.min(img)
vmax = np.max(img)
im = ax.imshow(
img, cmap='viridis', extent=[xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax],
interpolation='none', vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax
)
c = fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax, shrink=.5)
c.ax.tick_params(labelsize=5)
ax.scatter(y, x, c=self.list_y, cmap='viridis', s=10,
vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax)
ax.set_axis_off()
ax.set_title(title, fontsize=8)
def plot(self, list_x, list_y):
"""Plotting utility
:param list_x: list of point on the first dimension where to evaluate
the interpolation
:param list_y: list of point on the second dimension where to evaluate
the interpolation
"""
assert isinstance(list_x, list)
assert isinstance(list_y, list)
assert len(list_x) == len(list_y)
result = self._estimate_gp(list_x, list_y)
x = [-x[0] for x in self.list_observations]
y = [x[1] for x in self.list_observations]
fig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 3)
ordered_plot = np.sort(list(result.keys()))
for result_key, ax in zip(ordered_plot, axs.ravel()):
self._plot_data(
fig, ax,
img=result[result_key], x=x, y=y,
xmin=list_x[0], xmax=list_x[-1],
ymin=list_y[0], ymax=list_y[-1],
title=result_key
)
# Plot the empirical standard deviation
full_list_tuple = [(x, y) for x in list_x for y in list_y]
sample_generator = self.sample_generator(full_list_tuple)
samples = []
for i in range(50):
current_sample = next(sample_generator)
current_sample = np.reshape(
current_sample, (len(list_x), len(list_y))
)
samples.append(current_sample)
samples = np.array(samples)
std_empirical = np.std(samples, axis=0)
self._plot_data(
fig, axs[2, 0],
img=std_empirical, x=x, y=y,
xmin=list_x[0], xmax=list_x[-1],
ymin=list_y[0], ymax=list_y[-1],
title='Empirical std'
)
axs[2, 1].set_axis_off()
axs[2, 2].set_axis_off()
附录3 优化器类
优化器
"""Likelihood optimizer"""
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod
from scipy.optimize import minimize
from .gp import GaussianProcess
from .covariance import Covariance
class LikelihoodOptimizer(object, metaclass=ABCMeta):
"""Likelihood optimizer"""
def __init__(self, covariance_class, list_observations, list_y,
initial_guess=None, noise=1e-7):
"""Init
:param covariance_class: class of the covariance
:param list_observations: list of observations
:param list_y: list of evaluation of the function to interpolate
:param initial_guess: initial guess for the optimization
:param noise: noise
"""
self.covariance_class = covariance_class
self.list_observations = list_observations
self.list_y = list_y
self.initial_guess = initial_guess
self.noise = noise
def _get_current_likelihood(self, covariance_param):
"""Compute likelihood
:param covariance_param: parameters used to instantiate the covariance
:return: likelihood of the current Gaussian process
"""
gp = self.instanciate_gp(covariance_param)
gp.covariance_matrix()
return gp.likelihood()
@abstractmethod
def _instantiate_covariance(self, covariance_param):
"""Instantiate the covariance class with covariance_param"""
raise NotImplementedError
def instanciate_gp(self, covariance_param):
"""Instantiate the Gaussian process
:param covariance_param: parameters used to instantiate the covariance
:return: Gaussian process instance
"""
cov = self._instantiate_covariance(covariance_param)
assert isinstance(cov, Covariance)
gp = GaussianProcess(
cov, list_observations=self.list_observations,
list_y=self.list_y, noise=self.noise
)
return gp
def maximum_likelihood(self, method='COBYLA', maxiter=1000, disp=True):
"""Maximize the likelihood
:param method: string, method to use for optimization
:param maxiter: int, maximum number of iterations
:param disp: boolean, whether or not to display the results
:return: results of the optimization
"""
# Define the function which is optimized: we minimize the negative log
# likelihood
def likelihood_optimization_func(param):
return -self._get_current_likelihood(param)
res = minimize(likelihood_optimization_func, self.initial_guess,
method=method,
options={'disp': disp, 'maxiter': maxiter})
self.initial_guess = res.x
return res
class SECovLikelihoodOptimizer(LikelihoodOptimizer):
"""Likelihood optimizer for the squared exponential covariance"""
def _instantiate_covariance(self, covariance_param):
"""Instantiate the covariance
:param covariance_param: parameters used to instantiate the covariance
:return: Covariance instance
"""
return self.covariance_class(covariance_param[0], covariance_param[1:])
附录4 gpHMC采样器
采样器
"""GPHMC"""
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
from tqdm import tqdm
from .gaussian_process_regression.gaussian_process.covariance import Covariance
from .gaussian_process_regression.gaussian_process.optimizer import (
LikelihoodOptimizer
)
class NoExplorationError(Exception):
"""Raised when the exploration stage has been skipped"""
pass
class GPHMCSampler:
def __init__(self, dimension, covariance_class: Covariance, n_explo,
likelihood_optimizer_class: LikelihoodOptimizer, list_obs,
list_y, init_cov_param, noise, target_function):
"""Init
:param dimension: int, the dimension of the parameter space
:param covariance_class: the class of the covariance matrix
:param n_explo: the number of exploratory space to refine the Gaussian
process
:param likelihood_optimizer_class: the class of the likelihood
optimizer
:param list_obs: the initial list of observation
:param list_y: the initial list of target function evaluation
:param init_cov_param: the initial parameters of the covariance
function
:param noise: the noise
:param target_function: the target function to be sampled (i.e. the
negative log likelihood of the density probability of interest)
"""
self.dimension = dimension
self.n_explo = n_explo
self._list_obs = deepcopy(list_obs)
self._list_y = deepcopy(list_y)
self.current_cov_param = init_cov_param.copy()
self.target_function = target_function
self.init_y = None
self.init_obs = None
self.gp = None
# Note that we make use of the fact that the lists are passed by
# reference here. We instantiate the likelihood_optimizer_class
# with _list_y and _list_obs which will be updated as observations are
# added
self.likelihood_optimizer = likelihood_optimizer_class(
covariance_class, self._list_obs, self._list_y,
initial_guess=init_cov_param, noise=noise
)
self._assert_dimension()
def _assert_dimension(self):
"""Assert that the input list have the correct length"""
assert len(self._list_y) == len(self._list_obs)
for obs, y in zip(self._list_obs, self._list_y):
assert len(obs) == self.dimension
def _fit_covariance_parameters(self, maxiter=1000, disp=True):
"""Fit the parameters of the covariance function"""
res = self.likelihood_optimizer.maximum_likelihood(
maxiter=maxiter, disp=disp
)
self.current_cov_param = res.x
def _potential_energy_grad(self, obs, type):
"""Compute the gradient of the potential energy
The potential energy is approximated with a Gaussian process. In the
sampling phase, it is the mean of the Gaussian process. In the
exploration phase, it is the mean minus the standard deviation.
:param obs: array of dimension self.dimension
:param type: 'sampling' or 'exploration'
:return: the gradient of the potential energy and the standard
deviation of the Gaussian process at obs
"""
assert len(obs) == self.dimension
assert type in ['sampling', 'exploration']
potential_energy_grad = np.squeeze(np.array([
self.gp.mean([tuple(obs)], derivative=True, i=i)
for i in range(self.dimension)
]))
sigma = np.squeeze(self.gp.sigma([tuple(obs)]))
std = np.sqrt(sigma)
# During the exploratory phase, the potential energy is the sum of the
# normal potential energy with the opposite of the standard deviation
# to explore space of high uncertainty
if type == 'exploration':
std_grad = np.squeeze(np.array([
self.gp.sigma([tuple(obs)], derivative=True, i=i)
for i in range(self.dimension)
]))
std_grad /= 2*std
potential_energy_grad -= std_grad
return potential_energy_grad, std
def _hamiltonian_dynamics(self, type='sampling', epsilon=0.1, length=100,
std_thr=3, momentum_std=1.0):
"""Hamiltonian dynamics using the leapfrog numerical scheme
The momentum is drawn from a normal distribution
:param type: 'sampling' or 'exploration'
:param epsilon: time step of the Hamiltonian dynamics
:param length: length of the Hamiltonian dynamics
:param std_thr: threshold on the standard deviation when to stop the
dynamics
:param momentum_std: standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution
the momentum is drawn from
:return: dictionary with keys 'dynamics_end_obs' the point at the end
of the dynamics, 'momentum_1' the momentum at the beginning of the
dynamics, 'momentum_2' the momentum at the end of the dynamics, and
'momentum_std' the standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution the
momentum is drawn from
"""
assert type in ['sampling', 'exploration']
obs = deepcopy(self.init_obs)
momentum_start = np.random.randn(self.dimension)*momentum_std
momentum = momentum_start.copy()
# Half step for the momentum
pot_energy_grad, std = self._potential_energy_grad(obs, type=type)
momentum -= pot_energy_grad*epsilon/2
# Run the Hamiltonian dynamics
for idx in range(length):
obs += momentum*epsilon/momentum_std**2
# For the last step, skip the momentum full update
if idx < length-1:
pot_energy_grad, std = (
self._potential_energy_grad(obs, type=type)
)
momentum -= pot_energy_grad*epsilon
# If the standard deviation is greater than std_thr, stop the
# dynamics
if type == 'exploration' and std > std_thr:
break
if type == 'sampling':
energy_pot = self.gp.mean([tuple(obs)])
# Half step for the momentum
pot_energy_grad, std = self._potential_energy_grad(obs, type=type)
momentum -= pot_energy_grad*epsilon/2
result = {
'dynamics_end_obs': tuple(obs),
'momentum_1': momentum_start,
'momentum_2': momentum,
'momentum_std': momentum_std
}
return result
def _update_current_sample(self, type, epsilon=0.1, length=100,
momentum_std=1.0):
"""Update the current state of the sampler with Hamiltonian dynamics
Run the Hamiltonian dynamics with the proposed parameters and
update the init_obs and init_y of the sampler with a
Metropolis-Hastings acceptance criteria
:param type: 'sampling' or 'exploration'
:param epsilon: time step of the Hamiltonian dynamics
:param length: length of the Hamiltonian dynamics
:param momentum_std: standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution
the momentum is drawn from
"""
assert type in ['sampling', 'exploration']
dynamics_output = self._hamiltonian_dynamics(
type=type, epsilon=epsilon, length=length,
momentum_std=momentum_std
)
y_end = self.add_observation(dynamics_output['dynamics_end_obs'])
self.init_obs, self.init_y = (
self._metropolis_hastings_acceptance_criteria(
dynamics_output, y_end
)
)
def _metropolis_hastings_acceptance_criteria(self, dynamics_output, y_2):
"""Metropolis-Hastings acceptance criteria
:param dynamics_output: Output of the hamiltonian dynamics: Dictionary
with keys 'dynamics_end_obs' the point at the end of the dynamics,
'momentum_1' the momentum at the beginning of the dynamics,
'momentum_2' the momentum at the end of the dynamics, and
'momentum_std' the standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution the
momentum is drawn from
:param y_2: value of the target function at the end of the dynamics
:return: tuple with the accepted observation and target function
evaluation
"""
kin_energy_1 = self.kinetic_energy(
dynamics_output['momentum_1'], dynamics_output['momentum_std']
)
kin_energy_2 = self.kinetic_energy(
dynamics_output['momentum_2'], dynamics_output['momentum_std']
)
metropolis_hastings_ratio = (
np.exp(self.init_y - y_2 + kin_energy_1 - kin_energy_2)
)
random_nbr = np.random.rand(1)[0]
if random_nbr < metropolis_hastings_ratio:
return dynamics_output['dynamics_end_obs'], y_2
else:
return self.init_obs, self.init_y
def add_observation(self, obs):
"""Add observation & target function evaluation
:param obs: tupple with size dimension
:return: evaluation of the target function at obs
"""
assert len(obs) == self.dimension
self._list_obs.append(tuple(obs))
y_end = self.target_function(obs)
self._list_y.append(y_end)
return y_end
def define_gp(self, maxiter=1000, disp=True):
"""Instantiate the Gaussian process with the best covariance param"""
self._fit_covariance_parameters(maxiter=maxiter, disp=disp)
self.gp = self.likelihood_optimizer.instanciate_gp(
self.current_cov_param
)
self.gp.covariance_matrix()
def exploration(self, epsilon=0.1, length=100, gp_update_rate=4,
momentum_std=1.0):
"""Exploration phase
The new observations and target function evaluations are added to
_list_obs and _list_y
:param epsilon: time step of the Hamiltonian dynamics
:param length: length of the Hamiltonian dynamics
:param gp_update_rate: int, rate at wich the Gaussian process
covariance parameters are updated
:param momentum_std: standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution
the momentum is drawn from
"""
self.define_gp(disp=False)
self.init_y = np.min(self._list_y)
self.init_obs = self._list_obs[np.argmin(self._list_y)]
for idx in tqdm(range(self.n_explo)):
self._update_current_sample(
'exploration', epsilon=epsilon, length=length,
momentum_std=momentum_std
)
if idx % gp_update_rate == 0:
self.define_gp(disp=False)
@staticmethod
def kinetic_energy(momentum, std):
"""Kinetic energy
:param momentum: fictitious momentum
:param std: standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution the
momentum is drawn from
:return: kinetic energy corresponding to the momentum
"""
energy = np.sum(np.power(momentum/std, 2))/2
return energy
@property
def list_y(self):
"""List of target function evaluation"""
return deepcopy(self._list_y)
@property
def list_obs(self):
"""List of observation where the target function has been evaluated"""
return deepcopy(self._list_obs)
def sample(self, epsilon=0.1, length=100, momentum_std=1.0):
"""Sampling phase
This is a generator which will generate new samples according to the
state of the sampler and the input parameters. The new observations and
target function evaluations will be added to _list_obs and _list_y
:param epsilon: time step of the Hamiltonian dynamics
:param length: length of the Hamiltonian dynamics
:param momentum_std: standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution
the momentum is drawn from
"""
if not (self.init_obs and self.init_y and self.gp):
raise NoExplorationError
self.init_y = np.min(self._list_y)
self.init_obs = self._list_obs[np.argmin(self._list_y)]
while True:
self._update_current_sample(
'sampling', epsilon=epsilon, length=length,
momentum_std=momentum_std
)
yield self.init_obs